Despite the fact that humanity learned about cholesterol back in the 18th century, people began to actively talk about it in the late 90s. With the advent of the joke that lard is pure cholesterol from a slaughtered animal, we began to associate this term with something bad or a direct threat to our health. Today, we often hear “I have high cholesterol” or “I need to get my cholesterol checked.” Let's try to figure out what cholesterol is and whether we should be afraid of it.
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance that we need to:
- Creation of healthy cells (red blood cell membranes, liver cell membranes, brain (gray and white matter)
- Normal digestion (cholesterol is needed for the production of cholic or bile acids, which break down fat and fat-soluble vitamins (for example vitamin D)
- Synthesis of hormones (testosterone, estrogen, progesterone and even cortisol)
- Vitamin D synthesis
- The work of the immune, reproductive, nervous systems and generally normal functioning of the body.
Where does cholesterol come from?
Sources of cholesterol are partly the foods we consume (about 20% of the total amount of cholesterol in the body). But the main percentage of the substance is synthesized in the liver, which is responsible for producing 80% of endogenous cholesterol. Other sites of synthesis, but to a much lesser extent, are the adrenal cortex, testes, ovaries and intestines.
The liver synthesizes cholesterol for export to other cells and also helps remove excess cholesterol from the body. This is achieved by converting cholesterol into bile salts and transporting it into bile, from which it is ultimately excreted. In addition, the liver synthesizes most of the essential lipoproteins needed to transport cholesterol throughout the body. Since cholesterol is transported through the blood, but having a fat-like structure, it does not dissolve in it, but attaches to proteins that act as its carriers. The combination of proteins and cholesterol is called lipoproteins.
Complexes with this research
Cola and chips Analysis of metabolic disorders caused by unbalanced diet RUB 3,020 Composition
Preventive check-up Universal annual preventive screening RUB 11,960 Composition
Pregnancy planning. Clinical indicators 6,630 R Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Liver and pancreas RUB 3,050
- Entry into IVF RUB 23,020
- Expanded hospital complex 7,700 RUR
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 9,620 RUR
- Female infertility RUB 16,210
High-density lipoproteins (HDL) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL) or “bad” and “good cholesterol”
There are several important types of lipoproteins responsible for the movement of cholesterol. The main ones are:
- Low-density lipoproteins ( LDL ), which move cholesterol from the liver to other cells in the body. They are often called " bad cholesterol" . They carry cholesterol particles throughout the body and can accumulate on the walls of damaged blood vessels, making them less elastic and narrowed.
- High-density lipoprotein ( HDL ) or " good" cholesterol , which absorbs excess cholesterol in the body and transports it to the liver for excretion in bile. These lipoproteins are highly soluble and do not tend to precipitate cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels (that is, they do not contribute to the formation of atherogenic plaques).
Often, when people talk about high cholesterol, they mean elevated levels of low- and very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). When LDL increase, your risk of heart disease increases.
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" | High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol or good cholesterol | Very low density lipoprotein cholesterol (pre-beta lipoproteins), triglycerides |
|
|
|
Controlling your bad cholesterol levels is an important part of reducing your risk of heart disease, heart attack or stroke.
When cholesterol levels rise, fatty deposits can develop in the blood vessels. Over time, these deposits grow, making it difficult for enough blood to pass through the arteries. Sometimes these deposits can suddenly break away and form a clot that causes a heart attack or stroke by traveling through the bloodstream to the heart or brain.
What is the atherogenic coefficient?
Many people are interested in what is the atherogenic coefficient in a biochemical blood test? The atherogenic coefficient is usually called the proportional ratio of good and general x-rays. This indicator is the most accurate reflection of the state of lipid metabolism in the body, as well as an assessment of the likelihood of atherosclerosis and other ailments. To calculate the atherogenic index, you need to subtract the HDL cholesterol value from the total cholesterol value, and then divide this difference by the HDL cholesterol level.
The norm for women and the norm for men of this indicator is as follows:
- 2-2.8 – young people under 30 years old;
- 3-3.5 is the norm for people over 30 years of age who do not have signs of atherosclerosis ;
- from 4 – an indicator typical for people suffering from coronary artery disease .
If the atherogenic coefficient is below normal, then this is not a cause for concern. On the contrary, if the coefficient is reduced, then the person’s risk of atherosclerosis is low.
It is important to pay attention to the patient's condition if the atherogenicity coefficient is increased. A specialist will tell you what it is and how to act in this case. If a patient’s atherogenic coefficient is increased, the reasons for this are due to the fact that bad cholesterol is increased in the body. What to do in such a situation? First of all, you need to contact a qualified doctor who will adequately assess the atherogenic index. What this means can only be clearly assessed and explained by a specialist.
Atherogenicity is the main criterion for monitoring how effective hypercholesterolemia . One should strive to ensure that lipoprotein levels are restored. At the same time, it is important to ensure not only a decrease in total cholesterol, but also an increase in high-density lipoproteins. Therefore, decoding the lipid spectrum of the blood provides that β-lipoproteins, the norm for which is different in women and men, as already noted, are necessarily taken into account when assessing the patient’s condition.
Heredity or inherited high cholesterol
High cholesterol can often run in families and can only be diagnosed through laboratory tests as a result of a heart attack or stroke. Tell your doctor right away if anyone in your family has had these conditions, especially at a young age, and consider getting tested.
Familial hypercholesterolemia is an inherited disorder that causes atypically high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). With this disease, the liver is not able to utilize the natural supply of cholesterol, which is constantly being produced. As a result, cholesterol becomes dangerously overabundant, which dramatically increases the risk of atherosclerotic plaque deposits and the development of coronary heart disease (lack of oxygen reaching the heart due to vasoconstriction). Imagine faulty waste disposal through a garbage chute. Every night you have to throw out new trash and spoiled food, but previous waste has already clogged the pipes. As you may have guessed, this will soon lead to disaster. If your liver doesn't filter and process LDL cholesterol properly, it's not much different from improperly disposing of garbage. The vessels suffer the most due to the deposits of cholesterol plaques; they narrow and have less elasticity.
Possible complications
Cholesterol can be both bad and good. Is low blood cholesterol good or bad? What does the pathology threaten and is it dangerous? Hypocholesterolemia poses a danger to human health. In addition to the fact that cancerous tumors may begin to develop, low cholesterol can cause:
Cholesterol test interpretation
- development of vascular fragility and circulatory disorders in the brain, which often leads to internal hemorrhages;
- disruption of the functioning of serotonin receptors, which provokes the occurrence of depression or attacks of aggression, in which the patient is unable to control his behavior;
- development of a syndrome of increased intestinal permeability, as a result of which accumulations of toxins are not eliminated from the body, but penetrate into the bloodstream and have a negative impact on the functioning of internal organs and systems;
- vitamin D deficiency in the body, which increases the risk of osteoporosis;
- low production of sex hormones, increasing the risk of infertility;
- impaired digestion of fats, which entails a risk of developing obesity.
Hypocholesterolemia is a dangerous disease that can provoke the development of various ailments. That is why it is important to take a blood test at the first symptoms and seek help from a doctor who will create an individual method of therapy that will allow you to overcome the unpleasant disease.
No ads 2
Symptoms of High Cholesterol
Sometimes cholesterol is deposited on the surface of the skin (in the form of plaques on the skin of the face, lower eyelids, limbs and torso, but the most dangerous deposits of cholesterol are inside our body, which are not visible. Often, high levels of low-density cholesterol in the body have no symptoms. And in In most cases, the disease remains undetected in time, which can lead to a heart attack, myocardial infarction, stroke at an early age, as well as problems with atherosclerosis.
Symptoms
It is impossible to determine hypocholesterolemia by external manifestations. To determine cholesterol levels, the patient must take a biochemical blood test performed on an empty stomach. In cases where you cannot visit the hospital for some reason, you should pay attention to your own well-being.
Symptoms such as lack of appetite for a long time, decreased sensitivity, systematic weakness, fatigue, and the presence of fatty loose stools can signal low cholesterol.
Enlarged lymph nodes, rapid mood swings, and decreased sexual activity appear. The listed symptoms may indicate hypocholesterolemia, so it is important to urgently consult a doctor and get tested!
Cholesterol and lipid profile tests
Lipid profile measures:
- total cholesterol;
- cholesterol associated with HDL ( high-density lipoprotein or alpha lipoprotein ), which can reduce or inhibit the increase in “bad” cholesterol in the blood);
- olesterol of very low density lipoproteins (pre-beta lipoproteins which are the main transport form of triglycerides . They are classified as highly atherogenic lipoproteins involved in the mechanism of formation of atherosclerotic plaques;
- olesterol carried by LDL particles ( low -density lipoproteins, beta lipoproteins ), that is, bad cholesterol, which contributes to vascular disease);
You can take these basic indicators separately or order a more extensive lipid profile analysis using the 112 lipid complex or 113 extended lipid complex , which include additional studies
- Triglyceride levels;
- Atherogenic index;
- Presence of Apolipoprotein – A 1, Apolipoprotein – B;
- Lipoprotein (a) - additional factors in the development of atherosclerosis;
Norms
Below is a table with cholesterol standards for males and females.
| Age category | Normal cholesterol levels in women | Normal cholesterol levels in men |
| 0-5 years | 2,91-5,19 | 2,95-5,25 |
| 5-10 years | 2,27-5,31 | 3,13-5,25 |
| 10-15 years | 3,22-5,21 | 3,09-5,23 |
| 15-20 years | 3,09-5,18 | 2,93-5,10 |
| 20-25 years | 3,16-5,59 | 3,16-5,59 |
| 25-30 years | 3,32-5,75 | 3,44-6,32 |
| 30-35 years | 3,37-6,58 | 3,57-6,58 |
| 35-40 years | 3,64-6,27 | 3,78-6,99 |
| 40-45 years | 3,81-6,53 | 3,91-6,94 |
| 45-50 years | 3,95-6,87 | 4,09-7,15 |
| 50-55 years | 4,20-7,08 | 4,09-7,17 |
| 55-60 years | 4,46-7,77 | 4,04-7,15 |
| 60-65 years | 4,46-7,69 | 4,12-7,15 |
| 65-70 years | 4,42-7,85 | 4,09-7,10 |
| 70-90 years | 4,49-7,25 | 3,73-7,86 |
As you age, cholesterol levels begin to rise. However, in males after 70 years of age, cholesterol in the blood may decrease sharply, which is considered a normal condition. Experts also note that women are much less likely than men to deposit “bad” cholesterol on the vascular walls due to the protective effect of female sex hormones.
What could be the causes of low blood cholesterol in women? Cholesterol levels may rise sharply during pregnancy, which is explained by hormonal changes. In addition, the pathological condition can cause a number of diseases.
No ads 3
Hypothyroidism is often the cause of hypocholesterolemia. Thyroid hormones take an active part in the process of regulating the level of cholesterol concentration in the circulatory system. In cases where the gland begins to produce a large amount of hormones, this means that the cholesterol level decreases sharply.
The indicator of the organic compound contained in the cell membranes (cholesterol) of an adult or adolescent is also influenced by the season. Mostly small fluctuations in the indicator occur in the winter months. Also, the results of a biochemical blood test can be affected by the phase of the menstrual cycle and the ethnic characteristics of the patient.
Biochemistry results are available after 12-20 hours
When is it recommended to get tested for cholesterol?
Young people without risk factors for cardiovascular disease are usually tested once between the ages of 17 and 19. Repeat testing for adults without risk factors for heart disease is usually done every five years.
The American Heart Association recommends cholesterol testing every 4 to 6 years for people age 20 and older.
Patients taking medications for high cholesterol, such as statins, should have their cholesterol levels checked as directed by their doctor or 4 to 12 weeks after the first dose and then every 3 to 12 months thereafter. It is recommended to test your cholesterol levels at least once every five years if a person has a total cholesterol level of 5.2 mmol or there are prerequisites for the development of cardiovascular diseases and stroke. Additional causes of possible heart disease include diabetes, high blood pressure or use of antihypertensive medications), low HDL levels, a family history of coronary artery disease (CHD) and hypercholesterolemia, and cigarette smoking.
Cholesterol: good, bad, total
The fact that if cholesterol levels are higher than normal is harmful, they talk very often and actively. Therefore, many people are under the impression that the lower the cholesterol, the better. But in order for all systems in the body to function normally, this substance is very important. It is important that a person’s cholesterol remains normal throughout his life.
It is customary to distinguish between so-called bad and good cholesterol. Low cholesterol (bad) is the one that settles on the walls inside the blood vessels and forms plaques. It has low or very low density and combines with special types of protein - apoproteins . As a result, VLDL fat-protein complexes . It is when the LDL level increases that a dangerous health condition occurs.
VLDL – what is it? The norm of this indicator and all the necessary information can be obtained from a specialist.
Now the LDL norm in men and the LDL norm in women after 50 years of age and at a younger age are determined by conducting cholesterol tests and are expressed by different laboratory methods, the units of determination are mg/dL or mmol/L. You need to understand when determining LDL that this is a value that should be analyzed by a specialist and appropriate treatment prescribed if LDL cholesterol is elevated. What this means depends on the metrics. Thus, in healthy people, this indicator is considered normal at a level below 4 mmol/l (160 mg/dl).
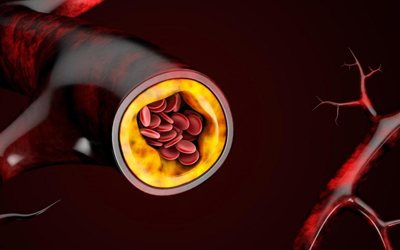
Cholesterol plaques in arteries
If a blood test shows that cholesterol is high, you should ask your doctor what to do. As a rule, if the value of such cholesterol is elevated, this means that the patient will be prescribed a diet, or this condition should be treated with medications.
The question of whether you should take cholesterol pills is controversial. It is important to note that statins do not eliminate the causes of high cholesterol. We are talking about diabetes , low mobility and obesity . Statins only suppress the production of this substance in the body, but at the same time they provoke numerous side effects. Sometimes cardiologists say that the use of statins is more dangerous for the body than elevated cholesterol levels.
- In people suffering from coronary artery , angina pectoris , or those who have had a stroke or myocardial infarction , cholesterol levels should be below 2.5 mmol/l or 100 mg/dl.
- Those who do not suffer from heart disease, but have more than two risk factors, need to maintain blood pressure at 3.3 mmol/l or below 130 mg/dl.
Bad cholesterol is counteracted by so-called good cholesterol, HDL cholesterol. What is high-density lipoprotein cholesterol? It is an essential substance for the body, as it collects bad cholesterol from the walls of blood vessels, after which it promotes its removal to the liver, where it is destroyed. Many people are interested: if HDL is lowered, what does this mean? It should be borne in mind that this condition is dangerous, since atherosclerosis develops not only against the background of increased low-density cholesterol, but also if LDL cholesterol is reduced. If HDL cholesterol is elevated, what does this mean, you need to ask a specialist.
That is why the most undesirable option in adults is when the level of bad x-x is increased and the level of good x-x is decreased. According to statistics, approximately 60% of mature people have this combination of indicators. And the earlier such indicators can be determined and treatment carried out correctly, the lower the risk of developing dangerous diseases.
Good cholesterol, unlike bad cholesterol, is produced only by the body, so it will not be possible to increase its level by consuming certain foods.
The normal level of good cholesterol in women is slightly higher than normal HDL cholesterol in men. The most important recommendation on how to increase its level in the blood is the following: it is necessary to practice physical activity, during which its production increases. Even if you do ordinary exercises at home every day, this will help not only increase HDL, but also reduce levels of bad cholesterol, which comes into the body from food.

Differences between good and bad cholesterol
If a person has eaten food that contains very high cholesterol, to activate its removal it is necessary to ensure the active work of muscles of all groups.
Thus, those who want the LDL and HDL levels to be restored need to:
- move more (especially for those who have suffered a heart attack or stroke);
- exercise moderately;
- practice intense physical activity (in the absence of contraindications).
You can also increase the level of good x-n by taking a small dose of alcohol. However, in no case should it be more than one glass of dry wine per day.
It is important to take into account that excessive load threatens to suppress the synthesis of xenon.
To correctly decipher a blood test, you should take into account the level of cholesterol in a person’s blood. There is a table of cholesterol norms for women by age, from which, if necessary, you can find out what the cholesterol norm is for women after 50 years of age, and what the norm is considered to be for women at a young age. Accordingly, the patient can independently determine whether her cholesterol is high or low and consult a doctor who will help find out the reasons for low or high cholesterol levels. It is the doctor who determines what treatment and diet should be.
- The normal level of cholesterol in the blood for women and men based on HDL, if the condition of the heart and blood vessels is normal, is above 1 mmol/l or 39 mg/dl.
- In people with coronary artery disease who have had a stroke or heart attack, the indicator should be 1-1.5 mmol/l or 40-60 mg/dl.
The analysis process also determines the norm of total cholesterol in women and men, that is, how good and bad cholesterol correlate. Total cholesterol in the blood should be no more than 5.2 mmol/l or 200 mg/dl.
If the norm in young men is even slightly exceeded, then this must be considered a pathology. There is also a table of cholesterol norms in men by age, which can easily be used to determine the cholesterol norm in men and its indicators at different ages. From the corresponding table you can find out what norm of hdl-cholesterol is considered optimal
However, in order to determine whether the level in men and women is actually normal for this indicator, first of all, you need to do a blood test, which makes it possible to find out the content of total h-chloride, as well as the content of other indicators - low or high sugar and etc.
After all, even if the norm of total cholesterol is noticeably exceeded, it is impossible to determine the symptoms or special signs of such a condition. That is, a person does not even realize that the norm has been exceeded, and his blood vessels are clogged or narrowed, until he begins to notice that he has pain in the heart , or until a stroke or heart attack .
Therefore, it is important even for a healthy person of any age to get tested and monitor whether the permissible cholesterol level is exceeded. Also, each person should prevent an increase in these indicators in order to avoid the development of atherosclerosis and other serious ailments in the future.
Risk factors for having high cholesterol include:
- Eating an unbalanced diet, consuming saturated fat found in animal products and trans fat found in some cookies, sauces, crackers and even popcorn, red meat, and full-fat dairy products can increase cholesterol levels;
- Obesity. Having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher increases your risk of high cholesterol;
- Lack of exercise. Exercise helps raise HDL, or “good” cholesterol;
- Smoking. Smoking cigarettes damages the walls of blood vessels, making them more prone to the accumulation of fatty deposits. Smoking can also lower your HDL or “good” cholesterol levels;
- Elderly age. As chemical processes change with age, the risk of high cholesterol increases. For example, as we age, the liver becomes less able to remove LDL cholesterol;
- Diabetes. High blood sugar increases levels of dangerous cholesterol called very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and decreases HDL cholesterol. High blood sugar also damages the lining of the arteries, which promotes the deposition of cholesterol in damaged areas;
- High blood pressure. This is a signal of problems with the cardiovascular system that occur with high cholesterol levels;
- Diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract contribute to disruption of cholesterol metabolism;
- Endocrine diseases also affect cholesterol synthesis.
General information
Cholesterol is the substance from which atherosclerotic plaques are formed in the human body. They are the cause of the manifestation of atherosclerosis , which is a very dangerous disease.
What cholesterol is can be judged by the meaning of this word, which is translated from Greek as “hard bile.”
A substance belonging to the class of lipids comes from food. However, in this way, only a small part of cholesterol enters the body - approximately 20% a person receives mainly from animal products. The remaining, more significant part of this substance (approximately 80%) is produced in the human liver.
This substance in the body is the most important building element for cells; it is involved in metabolic processes, as it is included in cell membranes. Also, it is important for the production of sex hormones: estrogens , testosterone , and cortisol .
In the human body, pure cholesterol is present only in small quantities, being part of lipoproteins. These compounds can be low density (called bad LDL cholesterol ) or high density (called good HDL cholesterol ).
What should be the normal level of cholesterol in the blood, as well as good and bad cholesterol - what it is, you can find out from this article.
Complications of high cholesterol
- Development of atherosclerosis. High cholesterol levels can cause a dangerous buildup of cholesterol and other deposits on the walls of your arteries (atherosclerosis). These deposits (plaques) can reduce blood flow through the arteries;
- Angina pectoris (coronary heart disease). If the arteries that supply the heart with blood (coronary arteries) are affected, chest pain (angina) or other symptoms of coronary heart disease may occur;
- Heart attack. If cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels rupture, a blood clot (thrombus) can form at the site of damage. The clot blocks the flow of blood, blocking the vessel downstream. If blood flow in part of an organ stops, tissue necrosis (death) occurs, which is observed, for example, during myocardial infarction;
- Stroke. Like a heart attack, a stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks blood flow to part of the brain.
Prevention
To help prevent high cholesterol, you can:
- Be regularly examined in Deal's laboratory;
- Follow a diet low in salt and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains;
- Limit the amount of animal fats and use vegetable fats in moderation;
- Maintain a healthy weight;
- Quit smoking and reduce alcohol consumption;
- Do physical exercise for at least 30 minutes a day;
- Control the level of stress you are exposed to;
Reduced cholesterol levels
Decreased is also a problem. Since cholesterol is an important component of cell membranes, a precursor to hormones, bile acids and other components that are important in a living organism, reducing its amount has negative consequences
- It turns out that people with low cholesterol are more likely to have symptoms of depression and anxiety;
- There are studies that show a possible link between low cholesterol levels and the risk of cancer;
- Cholesterol is necessary for the normal synthesis of sex hormones, pregnancy and a normal menstrual cycle. Low cholesterol may be associated with a risk of premature birth or having a low birth weight baby;
The external symptoms of hypocholesterolemia may manifest differently in each person, but laboratory diagnostics can help determine their cause.
When can you suspect low cholesterol or hypocholesterolemia?
- With regular malnutrition, strict diets;
- In the presence of diseases with reduced liver function (including cirrhosis, hepatitis);
- Inflammatory bowel diseases or protein-losing enteropathies;
- For hyperthyroidism or hypoadrenocorticism (Addison's disease). Reduced amounts of glucocorticoids may reduce intestinal absorption of cholesterol;
- If you are exposed to chronic stress;
- For hyperthyroidism or an overactive thyroid gland;
- Adrenal insufficiency;
- With malabsorption (insufficient absorption of nutrients from the intestines), for example, with celiac disease;
- For leukemia.
Who needs to control cholesterol levels?
If a person is healthy, he does not show negative symptoms, he does not need to think about the condition of the blood vessels or check whether the level of h-phen in the body is normal. That is why patients are often not even aware of the increased level of this substance at first.
This indicator should be measured especially carefully and regularly for those who suffer from hypertension or have problems with the heart and blood vessels. In addition, indications for regular tests have the following categories:
- people who smoke;
- those who suffer from hypertension ;
- overweight people;
- patients suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- those who prefer a sedentary life;
- women after menopause ;
- men after reaching 40 years of age;
- aged people.
Those who need a blood test for cholesterol should ask appropriate professionals about how to take a cholesterol test. The blood formula, including cholesterol content, is determined by a biochemical blood test . How to donate blood for cholesterol? This analysis is carried out in any clinic; for this, approximately 5 ml of blood is taken from the ulnar vein. Those who are interested in how to donate blood correctly should note that before these indicators are determined, the patient should not eat for half a day. Also, in the period before blood donation, you should not engage in intense physical activity.
There is also a special test for use at home. These are disposable test strips that are easy to use. The portable analyzer is used by people with diabetes and lipid metabolism disorders.