General information
Eosinophilia is diagnosed in a patient if a laboratory analysis reveals an absolute or relative increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood.
Eosinophilia is defined if the number of eosinophils in the peripheral blood exceeds 500/μl. This condition is a marker of pathological changes in the body; it is characteristic of a very large number of diseases. Very often, a similar phenomenon is observed with a parasitic infection, as well as with allergic manifestations. Hypereosinophilic syndrome is a condition in which there is eosinophilia in the peripheral blood and there is damage or dysfunction of organ systems. Hypereosinophilic syndrome is characterized by eosinophilia in people without parasitic, allergic manifestations, or other causes of eosinophilia.
This article will discuss why eosinophilia occurs and what to do if such a condition has been diagnosed.
Decreased eosinophil levels
If the analysis showed a reduction in eosinophils to a level below 1%, we are talking about problems with the production of new cells. The condition itself goes away if it is caused by a massive movement of leukocytes to the site of infection, however, a prolonged lack of defenders may indicate the body’s inability to replenish their supply. Diseases and environmental factors lead to this:
- stress, lack of sleep, physical fatigue - their constant impact weakens the body;
- injuries, including from burns and operations, radiation during tumor therapy;
- shock from excessive concentration of toxins released by microorganisms, poisoning with heavy metal salts;
- taking corticosteroids;
- serious bacterial infections such as typhoid fever;
- inflammation of the peritoneum, appendicitis, blood poisoning;
- bone marrow damage;
- anemia due to lack of vitamin B12.
For infections, once eosinophils return to normal, one can judge the effectiveness of the chosen drug. Eosinophils may be reduced in a woman during pregnancy and the first two weeks after childbirth; the latter turn out to be serious stress for the body. Eosinopenia in such cases is considered normal, just like its development after surgery or from taking certain medications.
Pathogenesis
Eosinophils are cells in body tissues. Eosinophilia (increased eosinophils) is characterized as an immune response. But the degree of peripheral blood eosinophilia does not always accurately predict the risk of organ damage. If the number of eosinophils is high, there is not always damage to the target organ, and if their number is low, then damage cannot be ruled out. Although eosinophilia occurs in many diseases and infections, the function of eosinophils is not completely known. Cytokines that stimulate the production of eosinophils are produced mainly by lymphocytes . Their products may cause certain infections or allergic reactions.
In parasitic infections, eosinophilia manifests itself due to stimulation by T helper cells. As a rule, such a response is observed after infiltration of the parasite into tissue and contact with an immunological effector cell. The T helper response produces interleukin 4 (IL-4), which in turn stimulates the production of IgE and an increase in the number of eosinophils. IL-5 is also produced, which stimulates the active production of eosinophils, their exit from the bone marrow and activation.
A decrease in blood eosinophils can occur under the influence of viral and bacterial infections, fever .
The target organs of eosinophils are the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and skin. But when the number of these cells is elevated, damage to the heart and nervous systems can also occur.
Eosinophils
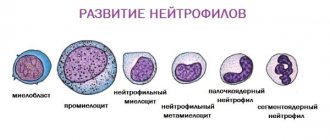
When talking about this condition, it is important to understand what eosinophils in a blood test. This is a type of white blood cell , part of the human immune system. They develop from the same cells as monocytes-macrophages, neutrophils and basophils. The following functions of eosinophils are noted: protection against the effects of intracellular bacteria, protection against parasitic infections, modulation of immediate hypersensitivity reactions. Speaking about what these cells are “responsible for,” it should be noted that they are especially important for protection against parasitic infections.
Eosinophils modulate immediate hypersensitivity reactions by breaking down or inactivating mediators that release histamine , leukotrienes , lysophospholipids , and heparin . Eosinophils live in the bloodstream for 6-12 hours, most of them are found in body tissues.
Normal eosinophil count
The normal percentage of eosinophils in the blood is no more than 5%. However, whether eosinophils are elevated is not determined solely by the percentage of these cells. This is a relative number, and it varies depending on the number of leukocytes, relative percentages of lymphocytes, neutrophils and other indicators.
The designation in the blood test is EOS (eosinophils). The content of these cells in the blood does not depend on gender or age. Therefore, those who are looking for a table of the norm of eosinophils in the blood of women by age should take into account that in both women and men, in percentage terms, the norm is 1-5% of eosinophils from the total number of leukocytes. If we convert the percentages into absolute numbers, then the normal rate is 120-350 eosinophils per milliliter of blood. If the percentage of eosinophils in the blood is increased or is much lower than normal, we are talking about the development of pathological processes in the body.
If we are talking about determining these indicators in a child under 5 years old, then it may be 1-2% higher. The normal absolute value of this indicator for children is 0.07–0.65 x 10^9/ml. But to understand what this means - eosinophils are higher than normal, it is necessary to take both indicators into account. So, if only their relative content increases, this may be due to a decrease in the proportion of other components of the leukocyte formula. Absolute indicators will be normal.
If both indicators exceed the norm, this is evidence of a true increase in the level of eosinophils in the blood.
If eosinophils are low or eosinophils are 0, this may indicate a severe purulent infection or heavy metal poisoning. In this case, what this means will be shown by further research.
Unlike the norms in an adult, in a child under 5 years of age, eosinophils of 1-6% are normal. In a child under 2 years of age, the norm is eosinophils of 1-7%. Higher results already indicate the presence of certain deviations. If the analysis shows eosinophils of 8% in an adult or a child, this already indicates a deviation from the norm. If 10% eosinophils are detected in a child or adult, we are talking about moderate eosinophilia.
However, when processing assays with elevated eosinophils, it is also important to consider diurnal fluctuations. So, in the morning and evening this figure increases.
Structure and activity of eosinophils
Eosinophils are slightly larger in size than neutrophils, reaching 12-14 microns. Their core consists of 2-3 parts, the cytoplasm is dotted with orange-pink inclusions. Color is related to the exposure of blood cells to the dye during study; this type of leukocyte absorbs eosin. Most of their functions are protective.
- Participation in the allergic process. Inflammation and increased blood supply during allergies are caused by histamine and other substances that are released by basophils that encounter an enemy. Attracted by the signal, eosinophils move to the site of inflammation and enter into a fight. At the same time, they can both inactivate histamine and heparin and release them, which allows regulating the process.
- Phagocytosis is the absorption of bacteria and foreign particles. Eosinophils play the role of microphages: they can only capture small cells, and in general, phagocytosis is not their main job.
- Fight against parasites. By activating the receptors, eosinophils cause the cells surrounding the worm to be destroyed. Thus, they block the invader and attract more aggressive participants in the immune system. The granules of the representatives of leukocytes themselves contain a protein that is harmful to helminth larvae and peroxidase that is aggressive towards them.
- Preventing antigens from entering blood vessels.
Half of the mature eosinophils settle in the tissues within an hour. Cells do not live long in the blood, about 3-8 hours. Outside the vascular bed, they can exist for up to 12 days.
Basophils are a type of granulocytes, which, in turn, are representatives of white blood cells. An increase in their number in a woman’s blood is often associated with allergies and inflammatory processes, although physiological reasons also play a large role in this. Read more in the article: “reasons for increased basophils in adults.”

Classification
Depending on the severity of the process, peripheral blood eosinophilia is divided into the following types:
- light (indicator 500-1500 eoz/microliter);
- medium (1500-5000 eoz/microliter);
- severe (more than 5000 eoz/microliter).
Depending on the causes of the pathology:
- Primary - clonal proliferation of eosinophils that occurs in hematological pathologies. A similar phenomenon is typical for leukemia and myeloproliferative diseases.
- Secondary – provoked by a number of non-hematological disorders.
- Idiopathic - the causes of this phenomenon are still unknown.
- Hypereosinophilia is a condition when the number of eosinophils is more than 1500 eose/microliter.
Causes of eosinophilia
The reasons for the increase in eosinophils in adults and children may be associated with a number of diseases and manifestations. In particular, eosinophilia occurs in the following diseases:
- Bronchial asthma , allergic rhinitis - the causes of eosinophilia in children are often associated with allergic manifestations. A variety of allergic reactions cause an increase in eosinophils. Eosinophilic pneumonia is a condition in which eosinophilic infiltration of the lung manifests itself. Develops as the body's response to the influence of an allergen. Some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are also of an allergic nature - eosinophilic esophagitis, eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders. With such manifestations, eosinophilia is also noted.
- Myeloproliferative disorders, neolastic processes - in this case, severe eosinophilia is noted (indicator ≥100,000 eose/microliter). This is observed in acute and chronic eosinophilic leukemia , cellular lymphoma , acute lymphoblastic leukemia, tumor processes, etc. Chronic myeloid leukemia is characterized by an increased number of eosinophils and basophils (eosinophilic-basophilic association).
- Parasitic infections - sometimes if a person has elevated eosinophils in the blood, this means that a parasite infection has occurred. Often the cause of an increase in eosinophils is infection with helminths . A number of parasites are distributed only in certain geographical areas. The cause of this phenomenon may be: strongyloidiasis , toxocariasis , nematodosis , trichinosis , etc. Sometimes it is difficult to answer the question of why eosinophils increase, since these infectious processes are asymptomatic.
- Non-helminthic parasites and other infections - the reasons for the increase in eosinophils in the blood of a child and an adult can be associated with infection with protozoan parasites, scabies mites, and fungal infections.
- Infectious diseases - as Dr. Komarovsky and other pediatricians confirm, eosinophilia is possible in infectious diseases. These are scarlet fever , chickenpox , measles , tuberculosis and other lung diseases. The treatment regimen for such diseases may include Polyoxidonium and other immunostimulants. However, with many bacterial and viral infections, the number of acidophilic granulocytes may decrease. There is no evidence of a connection between eosinophilia and toxoplasma , tuberculosis, bartonellosis , or streptococcal infection .
- Retroviral infections - HIV.
- Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) may occur with certain medications. This reaction is potentially life-threatening.
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Adrenal insufficiency , especially in acute form.
- Connective tissue diseases - eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyvasculitis, Wegener's granulomatosis, rheumatoid arthritis , systemic lupus erythematosus , etc.
- Other diseases are dermatitis herpetiformis , irritation of the mucous membranes, sarcoidosis , transplant rejection.
Norms of eosinophils in the blood
When deciphering the analysis, the patient’s age is taken into account, since these factors affect the content of eosinophils in the blood.
Table 1. Norm of eosinophils by age
| Children under 5 years old | Children 5 – 14 years old | Adults |
| 0,5 – 7% | 1 – 5% | 0,5 – 5% |
It should also be taken into account that in women in the first days of menstruation there is a slight excess of the norm in the content of eosinophils, while after ovulation their number may be slightly below the norm.
In absolute terms, the norm for adults is 0.15-0.450X10.0⁹ per liter of blood plasma. Exceeding the normal percentage of leukocytes is called eosinophilia. There are three stages of eosinophilia:
1. Light (no more than 10% of the total number of leukocytes).
2. Average (up to 15%).
3. Heavy (over 15%).
Symptoms
If eosinophils are elevated in an adult or child, the symptoms of this condition are caused by a disease that has led to the fact that the eosinophil level has been disrupted.
- If the causes of eosinophilia are associated with allergic and skin diseases, the patient is bothered by itching, redness, and dry skin. Wetting, the appearance of ulcers and blisters, and detachment of the epidermis are also possible.
- If eosinophils in the blood of an adult are elevated due to autoimmune and reactive diseases, anemia , increased body temperature, weight loss, pulmonary fibrosis , enlarged spleen and liver, joint pain, heart failure, and inflammation of the veins may occur.
- In the case of helminthic infestations, the lymph nodes become enlarged and painful, the spleen and liver are also enlarged, and signs of general intoxication are noted - nausea, headaches, myalgia, weakness.
- With pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilic syndrome, a whole range of manifestations is observed. The condition is characterized by peripheral blood eosinophilia. Eosinophilic pneumonia is characterized by fever, cough, night sweats , weight loss, shortness of breath , and pleural pain. The condition can be either acute or chronic. In the acute process, respiratory failure develops, which requires artificial ventilation.
- With an eosinophilic reaction to drugs, various syndromes are likely to occur. This may be cholestatic jaundice , serum sickness , interstitial nephritis , immunoblastic lymphadenopathy , etc. Reaction to drugs in eosinophilia and systemic symptoms are rare. In this case, a rash , atypical lymphocytosis , lymphadenopathy , etc. may be observed.
How to reduce the number of eosinophils in the blood
Eosinophilia is not an independent nosological entity, but only a consequence of a particular disease. Therefore, it cannot be treated in isolation - first of all, it is important to eliminate the cause of its occurrence, that is, the disease that caused the change in the leukocyte formula.
Possible treatment options:
- Desensitizing therapy. For allergies, antihistamines are used to reduce hypersensitivity reactions. Some of them may cause mild drowsiness (for example, chloropyramine), but newer generation drugs such as cetirizine, levocetirizine, desloratadine and rupatadine do not have this side effect and have a mild anti-inflammatory effect.
- Antibacterial therapy - for infectious diseases, antibiotics are prescribed (amoxicillin, ceftriaxone, azithromycin, erythromycin, etc.). The choice of antibacterial drug depends on the pathogen and its sensitivity to a specific group of antibiotics.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy. An increase in the level of leukocytes (including eosinophils) is observed during inflammatory processes. When they are severe, glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone) are used.
- Chemotherapy. This treatment method is aimed at eliminating malignant tumors. For this purpose, cytostatics and antimetabolites are used.
- Hormonal therapy. For multisystem diseases accompanied by immunodeficiency (for example, Jobe's syndrome), the use of steroid drugs and interferon gamma is indicated. Treatment is supplemented with antibiotics, calcineurin inhibitors, H1-histamine blockers, and antifungal drugs.
- Antihelminthic therapy. To combat helminthic infestations, drugs such as albendazole, levamisole, bephenia hydroxynaphthoate, piperazine, tetrachlorethylene, and mebendazole are prescribed. The choice of medication depends on the type of parasite and the stage of infestation. Additionally, antibiotics, enterosorbents, enzymes, probiotics, and glucocorticoids are prescribed.
Additionally, the following measures can be taken:
- Normalize your lifestyle. It is important to avoid frequent drinking of alcohol and give up cigarettes (or at least significantly limit the number of them).
- Avoid chronic intoxication. In people working in hazardous industries or living in environmentally unfavorable regions, the number of eosinophils in the blood increases as a result of constant chemical intoxication.
- Maintain a healthy diet. You should not overuse spicy, smoked, canned and fatty foods. To increase the level of eosinophils, you should limit the amount of meat, poultry and fish in your diet (consume mainly low-fat varieties). The menu should include yogurt, cheeses, vegetables, fruits, beans, bran and whole grain bread.

Giving up bad habits will help normalize the level of eosinophils. Photo: vgstockstudio / freepik.com
Tests and diagnostics
Since there is a very large list of reasons why a person’s number of eosinophils increases, during the diagnostic process the doctor needs to study the medical history in detail and conduct an examination of the patient. First of all, the doctor conducts a survey and analyzes the likelihood of the most common causes - allergic reactions, neoplastic complications, infectious diseases. The specialist must find out what medications the person took and whether he had systemic symptoms.
A blood test for eosinophils is performed as part of a general blood test. A biochemical blood test is performed to more accurately determine the condition of the body.
If necessary, eosinophilic cationic protein is determined - a non-invasive marker of eosinophilic inflammation in allergic diseases and other conditions. Speaking about what eosinophil cationic protein shows, it should be noted that the ECP content is directly proportional to the number of eosinophils.
Another indicator, eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), allows you to determine the severity of eosinophilic inflammation.
If eosinophilia is confirmed, additional studies are performed:
- A nasal swab for eosinophils (rhinocytogram) is carried out to exclude the allergic nature of the disease. It is advisable to perform a nasal swab if allergic rhinitis is suspected.
- Examination of stool for the presence of worm eggs and parasites. A repeat test may be required, as well as testing for other parasites.
- Other tests - to find out the cause of the condition, they examine the heart, skin, nervous and respiratory systems. A urine test, chest x-ray, liver function tests, etc. may be required.
Indications for analysis
A complete blood test with a count of eosinophils is prescribed for most people who visit the clinic. The range of indications is very wide, but in modern clinical practice, the initial eosinophil count is most often used as a biomarker to assess the effectiveness of drugs prescribed to patients with bronchial asthma. In this regard, the absolute number of eosinophils is of greatest value to the physician.
Eosinophils belong to microphages. This means that they can only absorb small foreign particles.
The study is relevant when confirming a preliminary diagnosis, checking the effectiveness of the prescribed therapeutic course, assessing the state of a person’s health during medical examinations or medical examinations. The doctor also prescribes a general blood test in the postoperative period. In addition, counting eosinophils is important when the development of infectious, oncological and autoimmune diseases is suspected.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is possible to practice auxiliary treatment with folk remedies only if the disease is diagnosed and the doctor has approved the use of such methods.
For allergies, decoctions and infusions of herbs are used - both for external and internal treatment. The affected areas are treated with decoctions of string, celandine, calendula, chamomile, and bay leaves. A decoction of fresh nettle is taken internally, as well as an infusion of a mixture of rose hips, St. John's wort, dandelion root, corn silk, and centaury. They are mixed in equal proportions and 2 tbsp. l. pour 250 ml of boiling water into the mixture. An infusion of young viburnum shoots is also used internally.
For ascariasis and enterobiasis, consumption of garlic, onions, pumpkin seeds, and walnuts is effective. A decoction of pomegranate peels is effective, for the preparation of which 5 g of dry crushed peels are poured into 150 ml of boiling water. After half an hour, drink the entire portion. This medication is taken for three days.
Other methods are used depending on the disease.
In children
The norm of eosinophils in children, depending on their age, is 0.07-0.65 x 10^9/ml. If a blood test determines that a child’s eosinophils are elevated, the reasons may be associated with a number of diseases and conditions:
- parasitic infections, helminthiasis;
- autoimmune diseases;
- allergic manifestations;
- asthma;
- granulomatous processes;
- taking medications;
- lymphogranulomatosis , malignant formations (the level of eosinophils is several thousand times higher than normal, a basophilic-eosinophilic association is possible).
However, eosinophilia in children can occur due to a variety of reasons, so when interpreting the tests, it is important to take into account the general health of the child.
In an infant, this condition may be associated with a reaction to medications, the consequences of an intrauterine infection, allergies, or eosinophilic colitis. In infants, this condition can also be a consequence of lactose intolerance.
Place among blood cells
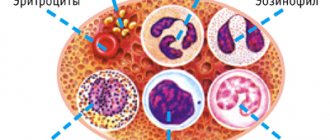
Leukocytes are the body's natural protectors. Their structure and ability to absorb different dyes during microscopy allowed researchers to divide cells into groups, and the functions of each of these groups may be special. Granular leukocytes include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils; They are united by segmentation of the nucleus and granules in the cytoplasm. Lymphocytes and monocytes are considered nongranular. All white blood cells try to be the first to meet any invader, so the body intensively replenishes their number during infections, allergies or parasite invasions. Eosinophils are no exception.
Diet
Hypoallergenic diet
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 21-40 days
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1300-1400 rubles. in Week
Nutrition for this condition depends on the diagnosed disease. When it comes to allergic reactions, it is important to exclude all foods that can trigger allergic reactions. In general, nutrition should be nutritious, varied and consist as much as possible of healthy foods.