A reduced level of basophils is called basopenia, but this is a conditional laboratory concept. The concentration of cells is extremely low, and therefore they may simply not be detected in a blood test.
Basophils are called white blood cells. This is a group of granulocytic leukocytes responsible for hypersensitivity reactions. It is through basophils that the body is protected from allergens, toxins and poisons. Due to them, local and systemic manifestations of allergic reactions develop.
What it is
Basophils are a type of leukocyte (white blood cell).
Produced in the bone marrow and present in small quantities in the body. The proportion of basophils from the total number of leukocytes in an adult healthy person is only 0.5-1%. This relatively small presence in the blood is enough for basophils to perform their functions. These include:
- Maintenance of allergic reactions. They migrate to allergic foci, where they release the contents of their granules (histamine, heparin), which ensures the maintenance of the allergic reaction1.
- Protection from foreign agents. Basophils are part of the innate immune system. They are activated upon contact with foreign agents. In particular, this is indicated for parasites.
- Sources of cytokines. Basophils secrete interleukins 3 and 4. In turn, the latter enhance the activity of other immune cells during infectious and inflammatory reactions.
- Improved blood flow. Basophils contain heparin, a blood thinner. During inflammatory processes, this allows immune cells to freely enter the site of inflammation.
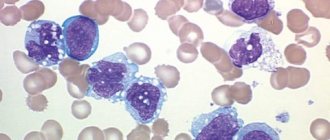
Figure 1. Spatial model of the basophil. Image: Blausen.com staff (2014). "Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014". WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436 (CC BY 3.0)
conclusions
Basophils are protective blood cells, indicators of allergies, inflammatory and oncological processes. In a healthy person, no more than 1% of white blood cells should be detected among all leukocytes and no less than 0.1 * 10⁹/l. If the number of cells is less, they speak of basopenia. The condition rarely indicates a serious illness, but this option should not be ruled out.
The level of basophils increases in allergic, inflammatory reactions, as well as in oncohematological diseases. Despite the insignificant content of cells in the blood, it is necessary to pay attention to their values so as not to miss serious pathologies. Read more about basophilia in the article: “Elevated basophils - what it is and its causes in adults and children. Is the condition dangerous?
If according to the results of the OAC there are other abnormalities, you need to consult a doctor for help.
Blood test for basophils
Basophils are determined as part of a clinical blood test. In medical documents, the indicator is referred to as “basophils”, “BA%”, “BA” or “BASO”.
Typically, basophils are expressed as a percentage of the total number of remaining white blood cells (BA%). Their absolute number can also be indicated (BA - the number of cells per liter of blood). This is 0.01-0.065x109/l., which is approximately 0.5-1% of the total number of white blood cells.
Cell counting is performed in a special device - a hematology analyzer. This is also done manually. A blood smear is taken, stained with special dyes, after which the basophils are counted under a microscope.
Basophil activation testing is carried out as part of an allergy test. It is possible to find out which allergens the basophils are activated to in order to identify the specific allergen that causes adverse symptoms.
Preparing for analysis
A general blood test requires proper preparation. Before the study, it is important to adhere to the following rules:
- Blood must be donated on an empty stomach. Otherwise, nutrients (entered into the blood) may interfere with the correct determination of the blood formula.
- You should refrain from smoking for several hours before donating blood.
- It is advisable to abstain from alcohol 2-3 days before the planned analysis.
- The day before donating blood, avoid physical and emotional stress.
- The day before you should refrain from taking medications (if possible). If you cannot refuse the medication, you should notify your doctor.
Basophils and estrogens
It has been established that drugs containing estrogen increase the number of basophils. Therefore, if you are taking such drugs, tell your doctor. When deciphering the analysis for basophil content, the specialist will make an adjustment for this.
Norms of basophils in the blood
The normal level of basophils in the blood (BASO) changes in children under 2 years of age.
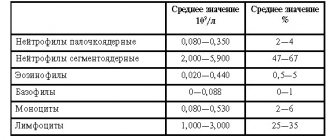
In adults (men and women), the norm is 0.5-1% (Table 1). Table 1. Norm of basophils (BASO) in the blood by age and gender
| Newborns | Up to 1 month | One year old children | Children under 2 years old | Adults (men, women) | |
| Basophil level (BASO) | 0,75% | 0,5% | 0,6% | 0,7% | 0,5-1% |
Causes of elevated basophils
A high level of basophils is called basophilia. This condition can be dictated by both pathological and physiological reasons. Let's take a closer look at them.
Physiological causes of increased basophils:
- Menstruation and ovulation, when there is a high level of female sex hormones in the blood. As mentioned above, estrogens increase the level of basophils.
- The recovery period after an infection (basophil levels may be elevated for several days or weeks).
- When exposed to small doses of radiation. Often, an increased number of basophils is observed among radiologists or laboratory technicians.
- After taking contraceptives containing estrogen.
Pathological causes of high basophil content:
- allergic reactions²;
- bone marrow diseases³;
- thyroid deficiency (hypothyroidism);
- inflammatory diseases;
- ulcerative colitis;
- autoimmune diseases (eg rheumatoid arthritis4);
- asthma;
- infectious pathologies (viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic).
Basophilia in children can be caused by other reasons, including:
- poisoning;
- parasites (worms);
- insect bites;
- anemia (iron deficiency, hemolytic);
- allergy;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- sinusitis;
- blood diseases;
- endocrine diseases (usually thyroid diseases);
- gastrointestinal pathologies.
Basophils are counted both manually and under a microscope. Photo: gstockstudio / freepik.com
Causes of low basophils
A decreased level of basophils is called basopenia. This condition is not dangerous to health. It can occur, for example, when basophils migrate from the blood to inflammatory foci. If the basophil has released its granules, then it is already considered inactive. Such cells are not taken into account when counting. For doctors, “empty” basophils serve as an additional diagnostic criterion, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory reaction.
Common causes of a pathological decrease in basophils include:
- Hyperthyroidism is an overactive thyroid gland.
- Urticaria is an allergic disease that manifests itself as a skin rash.
- Lupus is an autoimmune pathology in which foci of inflammation form in the joints, skin, heart and brain.
- Taking corticosteroid drugs. If you are taking such medications, please notify your doctor so that the results can be corrected.
- Depression. The mechanism of the decrease in basophils in depression is unknown, but the fact itself has been established.
- Smoking – contributes to a slight decrease in the level of basophils5. After giving up the bad habit, basophils rise again to normal levels.
Smoking reduces basophil levels. Photo: freepik.com
In what diseases are basophils reduced?
A deficiency of corpuscles is determined much less frequently than their excess (basophilia). The reasons for the increased number of basophils are allergic reactions, inflammatory processes, and cancer (see “Elevated basophils” for more details). Basopenia in adults can be accompanied by:
- acute immune responses to the invasion of toxins, infections, parasites, allergens, cell death, or directed against one’s own body;
- chronic exposure to stress;
- physical exhaustion (with long-term and severe illnesses, malnutrition, acute deficiency of vitamins and minerals);
- pathologies of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
- treatment with hormonal drugs;
- diseases of the nervous system.
The basophil count drops to a critical level (up to complete absence) with agranulocytosis. This condition is accompanied by a decrease in the number of all granulocyte bodies (segmented neutrophils and eosinophils also decrease).
Agranulocytosis may be of myelotoxic origin (due to damage or malignant degeneration of bone marrow cells). It is caused by radiation, treatment with cytostatics, and some antibiotics (from the penicillin group, Gentamicin, Rifampicin). Immune agranulocytosis can develop against the background of thyroiditis, malaria, polio, influenza, collagen diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma).
During pregnancy
In women, basophils may be absent in a blood test during pregnancy. Most often this is caused by anemia (B12- or B9-deficiency). A temporary decrease sometimes occurs during ovulation, however, this is an irregular phenomenon. In some cases, a slight increase in cell levels is noted. If the CBC shows a normal content of blood cells, except for basophils, one can suspect a natural decrease in their concentration against the background of an increase in the volume of circulating blood.
In children
Basopenia in a child is most often caused by a past infection or severe allergy, which leads to a redistribution of cells in the body. It is also encountered by almost all small patients who undergo chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Since these methods inhibit cell division, a decrease in all groups of leukocytes is observed simultaneously.
Useful information: Nitrites in urine - causes, treatment. What to do with nitrituria and is the condition dangerous?
Approximately 1 person in 100 thousand suffers from Cushing's syndrome. It has been proven that pathology occurs 5 times more often in women than in men. It is diagnosed from 20 to 45 years of age, but there are cases among children. Cushing's disease is caused by hyperplastic degeneration of the pituitary lobes and leads to excessive synthesis of adrenal hormones. The pathology is accompanied by manifestations of hypercortisolism. In childhood, they provoke retardation in mental and physical development, and subsequently lead to disruptions in the functioning of all organs and systems, and severe metabolic disorders.
How to reduce or increase basophils
The physiological causes of basophilia are short-lived and disappear after discontinuation of the factor that increases basophils. Thus, the abolition of hormonal contraceptives and avoidance of radiation bring basophils back to normal in a short time.
As for pathological basophilia, BASO levels can be normalized by starting treatment for the underlying disease. This includes antiallergic therapy, deworming (elimination of worms), treatment of inflammatory diseases and blood diseases.
To reduce the level of basophils in basophilia, it is also recommended to saturate the body with a sufficient amount of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) and iron. These components are found in meat, offal, eggs, fish and dairy products. In some cases, the doctor prescribes preparative vitamin and mineral complexes with iron and B12.
How to get rid of basopenia
A physiological decrease in protective blood cells (after an illness, for example) does not require drug intervention. Cell parameters return to normal as the body recovers. To monitor the process, it is worth stopping blood tests 1–2 weeks after complete recovery.
If lymphocytes and basophils are low in a pregnant woman, you should not take measures on your own. Immunodeficiency can be caused by hormonal changes, which are aimed at preserving the life of the fetus in the womb. The doctor may prescribe vitamin and mineral complexes to the woman and advise her to rationalize her diet.
When the objective reasons for the decrease in basophil concentration cannot be established (no diseases have been identified, other blood elements are normal), the patient is recommended to optimize the daily routine, diversify the menu, get enough rest and spend more time in the fresh air.
If basopenia accompanies some pathology, treatment is aimed specifically at the disease, and not at abnormalities in the CBC. Autoimmune diseases are treated with hormonal agents, bone marrow lesions are treated with chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and sometimes bone marrow transplantation is used. If the disorders are caused by medications, you will need to adjust the dose or discontinue the offending drugs. In case of severe immunodeficiency, the patient will need to be hospitalized and placed in an aseptic box.