Women dreaming of pregnancy often resort to early ultrasound. A delay in menstruation gives them hope, and to reinforce it, they ask the doctor to conduct additional diagnostics. A referral for an ultrasound examination is issued from the 7th week of pregnancy. What is visible on an ultrasound, what factors can affect the accuracy of the result?
How does pregnancy develop in the first weeks after conception?
After the fusion of the sperm with the female reproductive cell, the resulting zygote moves towards the uterus. After 24 hours, the fragmentation process begins, leading to the formation of a blastocyst consisting of approximately 100 cells on the 5th day. On the 8th day, the blastocyst penetrates the uterine endometrium.
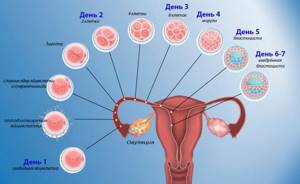
The fetal tissues begin to produce human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), and the formation of the fertilized egg begins. 14 days after ovulation, when menstruation should begin, there is no discharge - their delay indicates pregnancy (see also: what kind of discharge can there be in early pregnancy before menstruation is delayed?).
At what stage and at what level of hCG is the fertilized egg visible during an ultrasound?
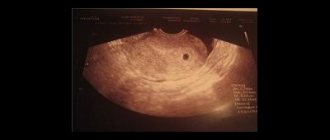
During an ultrasound, the fertilized egg is detected as a small black dot. A blurry white spot is clearly visible in it - an embryo. The study is carried out transvaginally. The fertilized egg is an anechoic (not reflecting ultrasonic waves) formation of a round or oval shape. The microscopic size of the embryo at the very beginning of its development does not make it possible to see it using ultrasound. In the early stages, a sonologist detects pregnancy and determines its duration by detecting the fertilized egg and measuring it.
When is the egg visualized well? In the first weeks, the fertilized egg grows by about 1 mm per day: at 4 weeks its diameter is 3 mm, at 5 weeks – 6 mm. Until 8–10 weeks of pregnancy, its duration is determined by the diameter of the fetal egg, then by the coccygeal-parietal size (CPR) of the fetus.
The doctor will be able to see the fertilized egg and embryo no earlier than the 5th obstetric week. A convincing sign of pregnancy is the hCG level detected through a blood test from 1500 to 5000 IU/l. As a rule, if the test result is normal, you can go for an ultrasound - the doctor will be able to see the fertilized egg.
When does ultrasound determine the presence of an embryo in the fertilized egg and what does it look like?
If conception occurred in a woman with a regular menstrual cycle, the diagnostician will detect the embryo at 6–7 weeks. By this time, the size of the fertilized egg increases to 7 mm. In addition, during the ultrasound, the fetal heartbeat is heard. On the monitor, the embryo looks like the letter “C”. Towards the end of the 8th week of pregnancy, clearly visible outlines of the head, legs and arms appear. From next week, the embryo is already considered a fetus.
If during the examination the doctor does not detect a fertilized egg in the uterus, and all tests indicate pregnancy, you can undergo a second examination 6-7 days after the first one. In a situation where the fertilized egg is visible but the embryo is not identified, the procedure can be repeated after 2 weeks. Listening to a heartbeat outside the uterine wall suggests an ectopic pregnancy.
Modern diagnostic methods
From the first days of delayed menstruation, especially if the pregnancy is desired, a woman has a desire to confirm or refute her assumptions. And in this regard, the question arises about which method to choose and after how many days of delay you can get a reliable result.
The main methods for diagnosing pregnancy are:
- pregnancy test
- determination of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood
- ultrasound diagnostics.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages.
A pregnancy test is based on determining the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin in the urine. Modern tests make it possible to determine the presence of pregnancy already on the first day of missed menstruation. The method is convenient, easy to implement, and accessible. However, there is a risk of error (albeit small), diagnosis is possible only after the appearance of a delay in menstruation, and does not exclude the development of an ectopic pregnancy. As a rule, this method is used first, and then, based on its results, other methods are carried out.
Determination of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood is the only method for diagnosing pregnancy even before the onset of delayed menstruation, 6-7 days after conception. The method is highly accurate, but, like the test, does not exclude the possibility of developing an ectopic pregnancy. The method is not “ready-to-hand”; to get tested you need to go to a antenatal clinic or medical center, the result is ready on the same day or every other day.
Ultrasound examination is often used by women as a starting method for determining pregnancy. And they are very upset when they get a negative result, especially in cases where there is a pregnancy.
Ultrasound is a reliable method of determining not only the presence of pregnancy, but also determining its duration, location and development of the unborn child. However, the information content of the method depends on the period of the study. Therefore, there is a need to choose the right day for an ultrasound, as well as its method.
Why is the embryo not visualized at 6–7 weeks?
The woman saw two lines on the test, was delighted, came for an ultrasound, but the doctor did not find an embryo. Why is the embryo not visualized during a positive pregnancy test during an ultrasound? Possible reasons:
- The gestational age was incorrectly calculated. The embryo becomes clearly visible at 6–7 weeks.
- The examination was carried out using outdated equipment, or the doctor is not sufficiently qualified.
- The study was carried out by the transabdominal route, which increases the error of the result.
- A spontaneous miscarriage occurred, which the woman mistook for normal menstruation. The hCG concentration did not have time to decrease by the time of the examination, and ultrasound gives a negative result.
If the doctor said during an ultrasound examination that there is no embryo, the woman should not worry too much. Erroneous detection of anembryony (absence of an embryo) may be due to various factors. An argument in favor of successful conception is an increase in hCG levels over time and the absence of bleeding and other signs of early miscarriage. To get the final result, you need to undergo an ultrasound again after 7-14 days.
Difference between obstetric and actual gestational age
The gestational age can be obstetric or embryonic. Obstetrical is counted from the 1st day of the last menstruation; in the second case, the count is from the day of conception, which is taken as the day of ovulation. As a rule, the obstetric period is 14 days longer than the embryonic period.
When performing an ultrasound, the obstetric period is taken into account. During the procedure, the doctor correlates the identified indicators of embryo development with the obstetric period. The accuracy of the final result depends on the gestational age:
- when examining a pregnant woman up to the 12th week, the permissible deviation is 1–2 days;
- within 12–28 weeks – 1 week;
- after the 28th week the permissible error increases.
All subsequent examinations and tests are carried out taking into account the obstetric period. Its duration is 280 days, or 40 weeks. In practice, the difference from the embryonic gestational age of 2 weeks may vary for individual reasons. According to statistics, in 20% of pregnant women it is less than two weeks, in 45% it can reach 3 weeks, and in 15% it can exceed 3.
External factors: quality of equipment and qualifications of the doctor
Misdiagnosis during ultrasound occurs in rare cases. If the doctor does not detect the embryo, it is necessary to re-examine a week later or undergo the procedure using other equipment. It is possible that the specialist conducting the ultrasound examination does not have sufficient qualifications. It is advisable to clarify information about the equipment and specialist before the ultrasound.
Absence of embryo
The absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg can be caused by various reasons:
- acute viral or bacterial infection in a woman in the first weeks of pregnancy;
- chromosomal and anatomical defects of the embryo;
- blood clotting disorder in a pregnant woman.

There are no pronounced physiological signs of the absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg. Even a gynecologist examining a woman cannot detect anembryonia. Only an ultrasound diagnostic specialist can reliably determine the pathology, and then at least 5-6 obstetric weeks (1-2 weeks after a missed period).
On the monitor screen, an empty fertilized egg is visualized as a black spot of irregular shape, usually smaller in size than it should be according to the stage of pregnancy. Sometimes a specialist sees a normal round-shaped fertilized egg, but there is no yolk sac in it. In the first weeks of pregnancy, an ultrasound examination has low information content, so it is recommended to undergo the first ultrasound at 10–12 weeks - at this time the fetus is already clearly visible.
Ultrasound method for determining pregnancy
The transabdominal method is the most common diagnostic method in gynecology and obstetrics. The study is carried out through the anterior abdominal wall using a convex sensor. To conduct the study, a good filling of the bladder is necessary. The method has low information content in diagnosing pregnancy in the early stages and will show pregnancy within a few weeks.
A transabdominal examination can be done when the expected pregnancy is about 5 weeks (the period is counted from the first day of the last menstruation) . In women whose subcutaneous fat layer is significantly pronounced, diagnosis is possible even at a later date. This is due to the large distance to the area under study and, accordingly, the impossibility of a detailed study of the uterus and its cavity.
To diagnose pregnancy, the transabdominal ultrasound method is used extremely rarely. It can be done when the size of the embryo is more than 0.5-0.7 cm. Transabdominal examination is carried out as a screening test in the second and third trimester.
Transvaginal ultrasound is performed using a special transvaginal sensor. No special preliminary preparation is required before the procedure . This method is more effective for diagnosing pregnancy and allows it to be diagnosed at an earlier stage. This is due to the closer location of the sensor to the structures being studied.
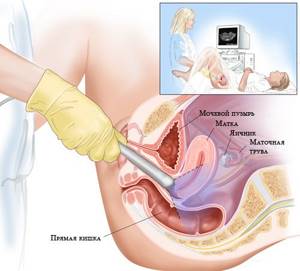
Transvaginal ultrasound
Using transvaginal ultrasound, pregnancy can be diagnosed within 4-5 days after a missed period. And when conducting research using modern expert-class equipment with high resolution, diagnosis is possible within 1-2 days after the delay appears.
It should be noted that the information presented on what day pregnancy can be determined is relevant for women with a regular menstrual cycle with an average duration of 28-30 days.
To accurately determine when to go for an ultrasound, it is recommended to first test for human chorionic gonadotropin. Depending on the level of hCG in the blood, you can find out whether an ultrasound will show pregnancy or not.
- If the hCG level is less than 2000 units, then there is no point in going for an ultrasound, since the chances of visualizing pregnancy are extremely low.
- If the hCG level is 2000-2500 units, pregnancy can be determined by transvaginal examination.
- If the level of human chorionic gonadotropin is more than 7500 U, pregnancy can be diagnosed by transabdominal examination.
What to do if the ultrasound did not detect an embryo?
If the absence of an embryo was detected at 5–7 obstetric weeks, the woman should have her blood tested within 1–2 weeks to monitor hCG levels. Its steady growth in accordance with normal indicators will be evidence of a developing pregnancy. Stopping growth and decreasing the level of human chorionic gonadotropin is a signal that the embryo has died. After 1-2 weeks you need to undergo a repeat ultrasound.
When the absence of an embryo is confirmed by laboratory tests and the results of a repeat ultrasound, a decision is made to terminate the pregnancy. A medical abortion is performed, the method depends on the gestational age. If it is 5–12 weeks, vacuum aspiration is performed.
Anembryonia is not evidence of a woman’s inability to carry a pregnancy to term. Women who receive this diagnosis are interested in how long it will take to plan a pregnancy again. It depends on the reason for which anembryonia occurred. If this happened due to an infectious disease, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment, and then a full examination to prevent a recurrence of the situation.
In any case, it is necessary to give the body time to fully recover. You should plan to conceive no earlier than six months after the previous attempt.
Dead fertilized egg
The saddest pathology of pregnancy development can be a dead fertilized egg at any stage of development. The causes of its death can be various diseases of the fetus, as well as elements of the fetal egg (placenta, membrane, umbilical cord), as well as a violation of oxygen metabolism in the embryo (fetus). The embryo may die due to insufficient yolk blood circulation for its nutrition, which results in oxygen deficiency, which leads to anomalies, as well as due to various infectious diseases of the fetus during intrauterine development.
The phenomenon of a dead fertilized egg is caused by the following diseases of a pregnant woman:
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- anemia;
- hypertension;
- severe kidney disease;
- infantilism;
- hormonal imbalance;
- high body temperature due to illness.
To prevent miscarriage, women at risk due to a history of these pathologies must be intensively monitored and, if necessary, hospitalized.
The main role in the death of the fetal egg belongs to hypoxia, which arose as a result of disruption of the uteroplacental-fetal circulation. In cases where a dead fertilized egg remains in the uterus, it becomes susceptible to maceration, mummification and petrification.