What does a fluorography image show?
If you want to know what fluorography is and why it is needed, you should familiarize yourself with the information that will become known as a result of the diagnosis. As a rule, fluorography is used to examine the chest organs, and is more often used to diagnose tuberculosis or neoplasms. It allows you to detect a lot of deviations, while the doctor has the opportunity to assess the condition of the chest structures, and he can prescribe treatment tactics adequate to the disease. You can familiarize yourself with the pathologies that such diagnostics can identify below.
Changes in lung tissue
If you don’t know what fluorography shows, it’s worth finding out that the image will show abnormalities in the lungs. Foci of tissue damage, their location, size and outline. The changes can be sclerotic in nature, when the normal tissue of an organ is replaced by connective tissue, or fibrous, when compactions and scars form on the connective tissue.
The overall picture allows the doctor to make a diagnosis or prescribe additional tests, for example, to determine the nature of the tumor in the lungs.
Inflammatory processes in the lungs
If you don’t know what fluorography is, what it shows and what diseases it will help identify, you should know that any inflammatory processes will be visible on the film. They appear as darker areas, and the darker they will be the more severe the inflammatory process. The procedure will detect:
- inflammation of the lungs, which is called “pneumonia”;
- tuberculosis;
- abscesses;
- etc.
Using fluorographic examination, the disease can be detected at a very early stage.
What not to do before fluorography
There are no obvious restrictions before conducting a fluorographic examination. The result of the study can only be affected by non-compliance with the specialist’s instructions during the imaging.
Many people mistakenly believe that there are a number of restrictions before fluorography:
- Foods and medications - before certain types of examinations, it is not recommended to eat foods that increase gas formation, blood sugar or pressure, but this prohibition does not apply to fluorography, since this will not affect the condition of the respiratory tract and lungs. There are also no restrictions on the use of medications before diagnosis.
- Playing sports - physical exercise, exercise, morning jogging or visiting a fitness club will not distort the final picture of fluorography. Playing sports does not affect the functioning of the lungs and respiratory tract, so you can not neglect exercises on the day of FLG.
- Smoking – it is impossible to determine who smokes based on fluorography results. Smoking does not in any way affect the accurate diagnosis, so the common myth that you should not smoke before fluorography is wrong.
Pulmonary tuberculosis
Preparation for fluorography is most often necessary for those whose doctors suspect tuberculosis. However, it is recommended to undergo diagnostics even without the direct instructions of a doctor if you begin to be bothered by shortness of breath, a cough that does not go away for a long time, as well as constant weakness.
Often, for preventive purposes, doctors resort to prescribing fluorography to all family members of a woman who has learned about pregnancy and registers with a public clinic at her place of residence. This is necessary in order to be sure that there is no threat to the life and health of the expectant mother, as well as her child.
Types of fluorography
To this day, there are two types of FLG left:
- Film. The study is carried out using outdated equipment, the radiation dose is higher than with conventional radiography, and the information content is low due to the small size of the film.
- Digital. A modern minimally invasive method in which the radiation dose is significantly reduced thanks to computer data processing.
Modern equipment takes pictures not only in a direct classical projection, but also in a lateral one. The angle allows us to examine the lesions that are covered by the bony framework of the chest (sternum, ribs), as well as the shadow of the heart.
Preparation and performance of fluorography
If you have not encountered fluorography of the lungs before, or do not know how often such a procedure can be done, it is worth knowing that it does not require preparation. All you need to do is make an appointment and visit the doctor at the appointed time. The patient enters the office, undresses to the waist and removes all metal accessories and jewelry that may affect the quality of the image. Doctors often ask the patient to hold the chain in his teeth so as not to unfasten or remove it. After this, you need to go into the machine’s booth and follow the doctor’s instructions. You will need to take a special position and hold your breath for a few seconds at the doctor’s signal. If everything is in order and no pathologies are found, an appropriate certificate will be issued. This is often enough to get a job or obtain a driver's license.
How does a CT scan differ from an X-ray of the lungs?
The fluorography method was patented in the 1940s. The first images were printed on film containing silver. The research was expensive and was not as widespread and widespread as it is today. However, in the middle of the 20th century, fluorography of the chest organs proved to be excellent in the diagnosis of tuberculosis, oncological tumors, and bone fractures. When images began to be displayed on a screen instead of film and digital fluorography appeared, the method became more accessible, images became more convenient to store, and it became possible to enlarge them and adjust the quality.
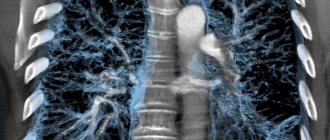
CT scanning was not invented and patented until the 1970s, but it revolutionized modern medical diagnostics and scientists Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack were awarded the Nobel Prize for their discovery. The novelty consisted of a fundamentally important and new opportunity to study internal organs, bones and the vascular bed “in volume”, that is, on slice images in three projections. Computer processing made it possible to combine multiple images obtained as a result of scanning the body with dynamically rotating sensitive sensors into a detailed and detailed 3D model.
Computed tomography (CT) differs from x-rays in a number of ways:
1. Result of lung examination. A fluorogram is a planar two-dimensional image in a frontal projection. Digitization of the image allows you to enlarge the image, but the information content of lung fluorography is lower due to an incomplete two-dimensional view and possible artifacts (distortions). Inaccuracies are possible due to the overlapping of shadows of organs on some areas of tissue. The result of a CT scan of the lungs is recorded on a DVD, which stores many cross-sectional scans (up to 1 mm thick) of the chest in three projections: horizontal, frontal, sagittal, as well as a 3D model of the respiratory tract, skeleton and vascular bed (if the study was carried out with contrast).
2. Technique. Both fluorography and CT of the lungs are performed quickly (1-3 minutes) and do not require preliminary preparation. An exception is a CT scan of the lungs with contrast - such an examination takes 10-15 minutes; there are recommendations that should be followed before the examination. Modern multislice tomographs (in particular, our Siemens somatom go.now device) scan the chest in dynamics - the patient moves on the tomograph table to the gantry (ring-shaped frame), and sensitive sensors located in several rows move in a spiral and take pictures. To obtain a fluorographic image, the patient needs to press his chest against the screen and hold his breath.
3. Image clarity. The clarity of chest CT images is improved. Make the picture more contrast, better examine the vessels and soft tissues, possibly by intravenous administration of an iodine-containing drug (CT scan with contrast). Thanks to the special technique of the X-Ray procedure, the rays obtained during tomography have a higher penetrating power.
4. Radiation dose. Radiation exposure during fluorography is minimal - 0.05–0.5 mSv. CT scan of the lungs shows 2–2.9 mSv. This is a harmless radiation exposure. It is believed that it is safe to do up to 5 CT scans within a year.
5. Availability. The cost of computed tomography is higher, and not all medical institutions have special equipment. Meanwhile, fluorography is suitable for annual preventive screening (if there are no special indications for CT) and various medical commissions.
How often can fluorography be done?
To find out the answer to the question of how often fluorography can be done, it is worth paying attention to the fact that such a procedure can be carried out for preventive purposes. Especially when it comes to digital fluorography, it allows you to reduce the radiation dose to the body by 5-10 times. However, this study is still associated with X-ray radiation, which is why it is often impossible to undergo such diagnostics. The recommended number of tests per year for prevention purposes is 1. If tuberculosis has been detected, the number of procedures per year is doubled, that is, fluorography needs to be done once every six months. In this case, the radiation dose is not exceeded, which will avoid negative consequences for the body.
Stereotypes and differences from radiography
Regardless of where the procedure took place, it is important to pay attention to what is written in the direction issued by the attending doctor. If it says that it is required to undergo fluorography, there is no need to go against the instructions. Most people far from medicine believe that a classic x-ray will better show the condition of the lungs. But in reality, ignoring the advice of a specialist will result in the body receiving an unreasonably high dose of radiation.
In addition to the difference in the percentage of radiation, the differences between two similar testing formats also lie in the resolution of the image. Fluorography has a reduced radioactive load, but you will have to pay for taking care of your own body with a “photograph” of lower quality.
This is where the temptation arises to get high-quality results straight away. But in fact, the average quality of an X-ray photograph is quite sufficient to establish a possible pathology even at an early stage of the development of the disease. Because of this, doctors recommend following the instructions, and if you suspect any anomaly, look for where to undergo a traditional x-ray of the chest organs.
People are often interested in the question of how much radiation the patient will receive if he agrees to undergo the procedure. It is believed that one round of conventional radiophotography is equivalent to the dosage that the body receives in ten days in the natural environment.
But here you should definitely take into account how health monitoring is done. If film devices were used, then the one-time load is from 0.2 to 0.25 mSv. The older the device, the higher the chances of getting unnecessary radiation, which could be avoided if you went to an office with a modern analogue.
According to the results of a scientific experiment, digital equipment has approximately 4 times less load. At the same time, traditional X-rays demonstrate a load one and a half times higher than even the oldest fluorograph.
It follows from this that the question: can radiography be used instead of radio photography can be answered in the affirmative. But for a preventive examination of the lungs, a fluorogram is suitable.
Contraindications for the study
If you familiarize yourself with how fluorography occurs, what this type of research is and what it is based on, it will become clear that this procedure is not so harmless. Therefore, there are a number of restrictions on its passage.
Age up to 15 years
It will not be possible to find out what fluorography is or how such a procedure is done if the patient is under 15 years of age. This is due to the fact that the effect of X-ray radiation on a child’s body is much stronger than on an adult. In this regard, a doctor can prescribe fluorography only as a last resort, when there is a threat to life.
Severe respiratory failure
Respiratory failure is a serious contraindication to fluorography. The thing is that radiation can have a negative effect on the human body and worsen an already bad condition. It is best to opt for a more gentle diagnostic method, for example MRI. Fluorography is safer than x-rays, but it is still extremely undesirable in such a situation.
Pregnancy
If you are thinking about how to undergo a fluorography procedure if you are pregnant, there is only one answer - nothing. Pregnancy is an absolute contraindication, since X-rays can affect the body of both the expectant mother and the baby. The child is at much greater risk; the harm can be so significant that it can lead to the loss of the fetus.
We can talk about how to prepare for a fluorography procedure during pregnancy only when there is a threat to life. In this case, the doctor can determine whether there are other research methods, and, if there is no other way out, try to reschedule fluorography to the third trimester. In later stages, x-ray examination is less dangerous, since all the vital systems of the child have already been formed.
How to undergo fluorography correctly

Gulzhan Konurshina, the chief specialist of the screening program monitoring department of the Department for the Prevention of Noncommunicable Diseases of the National Center for Public Health of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan (hereinafter referred to as the DPNIZ NCPH), spoke about how to properly undergo fluorography and why it is needed, zakon.kz reports.
Chest fluorography is a preventive and diagnostic method of x-ray examination of the chest cavity and lungs. Chest fluorography is a screening test for cancer, tuberculosis and occupational lung diseases, she said.
How many times a year should you undergo fluorography?
According to the specialist, fluorography is performed for diagnostic purposes once a year for all adults and adolescents from 15 years of age. However, there are groups of people for whom this examination is carried out more often (2 times a year):
• People working in “harmful industries” (steel, mining, rubber, asbestos, polypropylene, and chemical plants); • People working with children (teachers, educators); • Medical workers in maternity hospitals, tuberculosis dispensaries, infectious diseases departments and perinatal centers; • Patients with chronic pathologies (asthma, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and so on).
Who is fluorography contraindicated, what cases are an exception? Any x-ray examination before the age of 14 years is contraindicated.
Fluorography is suitable for almost every person, with the exception of only 2 cases: • persons under 15 years of age; • pregnant women, especially in the first trimester.
Fluorography is carried out in the first days after childbirth to identify tuberculosis in a woman. After the procedure, it is recommended to express a portion of milk, after which you can continue to feed the baby.
How to prepare for fluorography and the procedure for carrying it out Gulzhan Konurshina noted that fluorography does not require special preparation and is carried out at any time.
Basic principles of the study: • Before conducting the study, you should stop smoking for several hours - this will allow you to get a clearer and clearer picture. • Before starting the procedure, you should expose your upper body, remove all metal objects (chains, necklaces, pendants, crosses, etc.) before the procedure, and also remove cosmetics containing even the smallest metal particles from your face and body. • Women are required to remove their bra or lower it at the waist so that the clasp is not visible; • For patients with long hair, it is recommended to pin it up so that it does not fall on the shoulders and do not interfere with the image. • The study is carried out only in an upright position, so it is not prescribed for bedridden patients. • During fluorography, you should strictly follow all the recommendations of the radiologist. The picture is taken while inhaling as deeply as possible - during this period the lungs open well, which allows you to get a more complete picture. • During the study, X-rays pass through the body from behind and fall on a cassette with ultra-sensitive film to form a pattern, which is subject to further study and research.
Why do fluorography
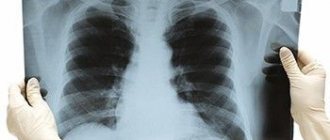
A fluorogram may be normal - in a healthy person who has not previously suffered from any lung diseases. The normal fluorography is transparent lung fields without any shadows.
There is a pathological fluorogram - when changes are detected that indicate a previous or existing disease: • various benign and malignant tumors; • focus of inflammation; • fibrous formation; • pulmonary tuberculosis; • foreign bodies; • necrosis of tissues of internal organs; • abscesses.
Of course, fluorography of the lungs will not provide the most accurate information about the pathology, but it allows timely diagnosis of changes in the lung tissues, the appearance of fluid and neoplasms. Until now, the procedure is the most popular in the preventive diagnosis of the lungs.
Fluorography and X-ray - what's the difference?
The basis of these studies is X-ray radiation. If fluorography is used as screening, then x-ray is a more in-depth technique, which is prescribed according to indications.
If fluorography is performed exclusively in a standing position, then x-rays are performed in any position and even in severe condition of the patient, as well as at home.
When fluorography of the lungs, the images are less clear than radiographic ones, therefore the information content and dose of the second study are higher. Read more about the difference between methods in this article.
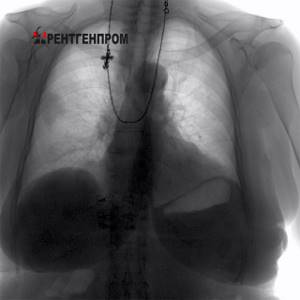
Radiography
An important aspect is also the cost of diagnostics: the price of radiography is approximately 2 times higher than FLG.
How to prepare for fluorography and the procedure for conducting it
Gulzhan Konurshina noted that fluorography does not require special preparation and is carried out at any time.
Basic principles of the study: • Before conducting the study, you should stop smoking for several hours - this will allow you to get a clearer and clearer picture. • Before starting the procedure, you should expose your upper body, remove all metal objects (chains, necklaces, pendants, crosses, etc.) before the procedure, and also remove cosmetics containing even the smallest metal particles from your face and body. • Women are required to remove their bra or lower it at the waist so that the clasp is not visible; • For patients with long hair, it is recommended to pin it up so that it does not fall on the shoulders and do not interfere with the image. • The study is carried out only in an upright position, so it is not prescribed for bedridden patients. • During fluorography, you should strictly follow all the recommendations of the radiologist. The picture is taken while inhaling as deeply as possible - during this period the lungs open well, which allows you to get a more complete picture. • During the study, X-rays pass through the body from behind and fall on a cassette with ultra-sensitive film to form a pattern, which is subject to further study and research.
Where are diagnostics done?
Fluorography and x-rays of the lungs are carried out in any medical institution. The test can also be done in a private diagnostic center, where the patient receives the result in hand and gives it to the doctor who sent it for an x-ray.
Digital fluorography for lung pathologies is a necessary study that identifies such dangerous diseases as tuberculosis, pneumonia and malignant neoplasms. X-rays are used not only for diagnostics. For example, they can treat retinoblastoma, a malignant pathology of the organs of vision. When conducting a digital examination, the radiation dose is minimal, which means that the diagnosis will not harm the patient’s health.
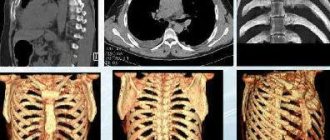
What does the study show and what diseases does the study reveal?
What diseases does fluorography reveal?
Depending on the radiological signs, the doctor assumes that the patient has the following pathologies:
| Symptoms that can be seen on fluorography | Main pathologies |
| Strengthening the pulmonary pattern | Inflammatory lung diseases. Obstruction of the bronchopulmonary system. Hypertension of the pulmonary circulation in congenital and acquired diseases of the cardiovascular system. Enlarged heart. Compaction of the aorta. |
| Ring shadows | Open forms of tuberculosis are cavities. Lung abscesses or cysts with fluid contents. |
| Darkening in the lungs | Inflammation (focal pneumonia). Oncological focus. Metastases of cancer of other organs to the lungs. Tuberculoma. |
| Violation of the structure of the pulmonary roots | Infectious process of lung tissue (both nonspecific with pneumonia, bronchitis, and with specific damage to tuberculosis, Pneumocystis pneumonia). Chronic obstructive disease of the lung tissue. Lymphogranulomatosis and other lesions of lymphoid tissue. |
| Calcifications (focal shadows, bone density) | Long-term infection with tuberculosis. |
| Diffuse small shadows in the form of a “snow storm” | Diffuse form of tuberculosis or Pneumocystis pneumonia in association with HIV infection. |
| Changes in the sinuses (disappearance of the angle, presence of fluid level in it) | The presence of pathological pleural effusion or adhesive pleurisy. |
| Fibrosis | The result of chronic pulmonary pathology. |
| Adhesions (seals in the area of contact of the parenchyma and pleura) | Indicate previous pleurisy, pleuropneumonia. |
| Pleuroapical layers (thickening of areas of the pleural layer) | Chronic long-term pulmonary tuberculosis, relapse of the disease. |
| Emphysema | COPD Bronchial asthma. |
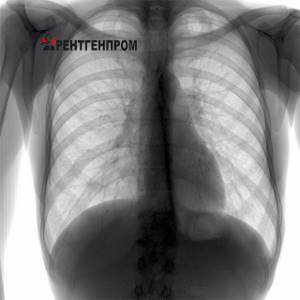
Compaction syndrome. Infiltrate. Cancer.
When to do research
Indications for the study, in addition to the annual screening examination, are:
- prolonged unmotivated fever (temperature stays up to 37.5˚C);
- persistent cough;
- chest pain;
- hemoptysis;
- shortness of breath attacks;
- rapid loss of body weight for no apparent reason.
For the listed symptoms, the doctor prescribes an x-ray of the lungs .
Low to medium density lesion. Tuberculosis. Sometimes the study is required for a preventive examination twice a year. The following categories of people need in-depth diagnostics:
- workers of tuberculosis dispensaries, infectious diseases departments, sanatoriums, maternity hospitals;
- HIV patients;
- people with diabetes;
- presence of tuberculosis in the family;
- radiation, hormonal and/or cytostatic therapy;
- cancer patients.
The study is necessary, since in this category of people the risk of infection with the tuberculosis bacillus or the spread of metastatic lesions to the lungs increases. This approach will allow us to identify foci of pathology in the early stages, prevent the spread of infection and begin therapy in a timely manner.
Does food affect results?
As can be seen from the contraindications, they also do not indicate that the procedure is prohibited on a full stomach. Therefore, no diet is required. Before fluorography, it is not forbidden to consume food and water. The method is based on tissue permeability, so food has no effect on the results.
In addition, in the photographs, shadows from different organs overlap each other. As a result, some of them are not identified. For example, the esophagus is located behind the mediastinum. For this reason, it (and even more so its contents) is not displayed at all in the pictures.
The stomach is located under the diaphragm, is not visualized during scanning and does not interfere with the examination when diagnosing the chest. Many studies are carried out using contrast solutions.
In this case, it is necessary to first follow a diet or fast for several hours before the procedure. Since fluorography is not done with contrast, there is no need to change your usual diet or diet.
What will an x-ray show?
An X-ray of the lungs helps visualize the organs located in the chest. In the image you can visualize both soft structures and dense ones, but the rays will give different shades. Diagnostics makes it possible to look at the heart, bronchi, lungs, lymph nodes and trachea. The description of these organs is enough to suspect abnormalities in one of them.
Tuberculosis
As for lung pathologies diagnosed by x-ray, these include:
- sarcoidosis;
- pneumonia;
- pleurisy;
- emphysema;
- oncology;
- swelling of the lungs;
- asthma;
- pulmonary tuberculosis.
X-ray copes with many diagnostic tasks successfully. Therefore, when sending for an x-ray, you should not worry about radiation exposure - it is much more important to see damage to organs.
Indications for chest x-ray
- Cough, shortness of breath, chest pain.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Suspicion of inflammatory and non-inflammatory lung diseases (pneumonia, tuberculosis, tumors).
- Suspicion of the presence of fluid in the pleural cavity.
- Suspicion of diseases of the hematopoietic organs.
- Pulmonary embolism.
- Diseases of the spine and joints.
- Injuries to soft tissues and skeletal bones, fractures, dislocations.
- Contraindications to chest x-ray.
- There are no absolute contraindications.
- Relative contraindications – pregnancy.