During pregnancy, any woman needs to undergo 3 scheduled ultrasounds, plus additional ones on the recommendation of an obstetrician-gynecologist. When is the last ultrasound scan done? The duration of the study may vary. According to the law, the third screening (comprehensive study) must be completed at 30-34 weeks, and a planned ultrasound earlier - at 30-32 weeks. But the third scan is not always the last: sometimes the doctor prescribes another procedure just before the birth.
Why is the last ultrasound needed?
The main task of ultrasound during pregnancy 30-34 weeks is to determine the readiness of mother and baby for childbirth and determine the tactics for childbirth.
As with previous ultrasounds, one of the main functions of the analysis is to identify the presence/absence of serious developmental defects in the child. Most pathologies are shown by the second ultrasound, but some abnormalities can only be seen in the third trimester. These include renal hydronephrosis (fluid accumulation in children's kidneys), megaureter (enlargement of the ureter).
If pathology is detected, the final scan will decide whether the baby needs surgery immediately after birth or if there is a possibility of delay. Surgery can be postponed if the anomaly does not threaten the baby’s life. If a defect is diagnosed that is incompatible with life, the doctor may recommend artificial birth (up to the 40th week).
Preparation and carrying out the procedure
Preparing for your final prenatal ultrasound is similar to previous ultrasound scans. Before the study, it is forbidden to eat food that causes excessive gas formation in the intestines.
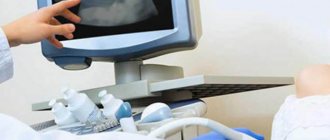
First, the pregnant woman exposes her belly. The sonologist applies a special gel to it, which better conducts ultrasonic waves and allows the sensor to move freely. The image of the uterus and fetus is transmitted to an ultrasound machine.
Before the ultrasound, it is recommended to take disposable absorbent diapers and napkins to wipe off the gel after the procedure.
In addition, see how the procedure works:
Objectives of the last ultrasound
Regardless of which week of the third trimester the last ultrasound is performed, its tasks are the same. In the last stages of pregnancy, ultrasound is designed to evaluate:
- Fetoplacental and uteroplacental blood flow (deviations may indicate developmental delay);
- The size of the baby, their correspondence to the gestational age;
- Localization of the placenta and the degree of its maturity;
- Position of the baby in the uterus (cephalic, pelvic or transverse).
The last two points directly influence the choice of birth tactics - natural or cesarean section. At the same time, the position of the baby in the uterus is not always the determining factor. When scanning is done at 33 weeks or earlier, there is still a risk that the baby will turn over.
Where to get a 3D ultrasound in Moscow
Such an examination must be carried out in a specialized clinic with modern, high-quality and serviceable equipment. We invite you to undergo a 3D ultrasound during pregnancy inexpensively in. We have installed a new device of the latest generation, decoding is carried out by top-class specialists, which eliminates any errors. If necessary, after a 3D ultrasound, you can consult an experienced geneticist and undergo additional examinations.
To make an appointment with a doctor, please call the numbers provided or leave a request on the website below.
What does the last ultrasound determine?
The last ultrasound during pregnancy is always done using the transabdominal method (through the outer wall of the abdomen). First, the doctor assesses the number of fetuses and their location, then the anatomical structures of the fetus, and clarifies the condition of the placenta and amniotic (amniotic) fluid.
During the last ultrasound you can determine:
- number of fruits and their position;
- difference in the size of the embryos (if twins or triplets are expected);
- some child developmental defects;
- changes in the cerebral cortex in the fetus;
- infection of the embryo due to diseases that the mother suffered during 9 months of gestation;
- position, structure and thickness of the placenta;
- distance from the edge of the placenta to the internal os of the cervix;
- the amount of amniotic fluid, its color and purity (heterogeneous composition may indicate fetal hypoxia).
Ultrasound in pregnant women
28.07.2021
ultrasound is one of the main diagnostic tests that should be performed several times during pregnancy . Ultrasound examination allows you to continuously monitor the development of the fetus and monitor the functions of the female reproductive organs. What is important, it is very important for the expectant mother to be able to see the baby on the ultrasound .
What is fetal ultrasound?
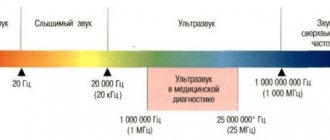
Ultrasound uses ultrasound waves that are reflected from internal organs. The doctor conducting the examination holds a sensor from which waves are emitted - every obstacle encountered (for example, internal organs, bones ) is displayed in black and white on the screen in real time. Ultrasound scanners allow you to accurately measure the organs being examined and evaluate their structure.
In the case of fetal ultrasound examination, the first examination is carried out vaginally, and the next one is carried out through the abdominal wall. During a transvaginal examination, the patient is placed on a couch, her legs are bent at the knees , and the doctor inserts the oblong head of the scanner into the vagina . Subsequent ultrasound examinations of the fetus are carried out similarly to abdominal ultrasound examinations - the patient lies on a couch with her legs , and the doctor applies the gel to her stomach and moves the head of the device along it.
In the first weeks of pregnancy , the fetus is so small that a vaginal sensor must be used. Thanks to a transvaginal examination, pregnancy and the embryo can be assessed whether the embryo is implanted correctly. The doctor also checks the woman's reproductive organs to rule out possible anatomical defects.
How often should an ultrasound be done during pregnancy?
In addition to the initial transvaginal ultrasound , which is performed around the 10th week of pregnancy , at least three abdominal ultrasounds These are very important examinations, thanks to which the doctor responsible for pregnancy can regularly check how the fetus is developing and whether the woman’s body is properly preparing for childbirth .
Between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy, a so-called genetic ultrasound - at this stage of pregnancy the doctor can assess the anatomy of the fetus and its size. The gynecologist takes precise measurements of the fetus, which allows early detection of genetic and developmental defects. He can also estimate your due . The next ultrasound examination of the fetus should be performed between 18 and 22 weeks of pregnancy . During this examination, the doctor re-evaluates the fetus's structure - this time he may also closely examine the baby's internal organs, including his heart . The doctor also examines the placenta and checks the amount of amniotic fluid. The last ultrasound examination of the fetus is carried out between 28 and 32 weeks of pregnancy , when the gynecologist evaluates the positioning of the baby and placenta, as well as re-measurement of the baby's body - also from the point of view of birth defects that may only appear at this stage of pregnancy .
If a woman does not give birth before the end of the 40th week of pregnancy , a repeat ultrasound to assess the position of the baby, its weight and head volume. The doctor also pays attention to the cervix , which shortens before childbirth . If everything is in order, the woman should see her doctor at the end of 41 weeks - if a natural birth has not yet occurred, she will have to be induced at the hospital .
Published in Pregnancy and pregnancy management Premium Clinic
Norms of the latest ultrasound
For ultrasound at 30-34 weeks of pregnancy, there are certain standards recorded in special plates. Do not be afraid of minor deviations in indicators from standard figures: this extremely rarely indicates any developmental disorders. If the mother has any doubts about the baby’s condition, the attending physician will explain the ultrasound results in detail and allay all concerns.
Standards for the last ultrasound during pregnancy include the following parameters:
- fetal presentation;
- fetometry indicators (child’s circumference and length of tubular bones);
- internal organs;
- biophysical profile (assessment of the baby’s posture, breathing, movement);
- placenta indicators;
- amniotic fluid;
- mother's pelvic organs.
Indicators of fetal fetometry on the third ultrasound are biparietal diameter (BPD), head circumference (GC), abdominal circumference (AC), fronto-occipital size (FOR). The length of the hip, shoulder and overall weight of the child are also assessed.
During the final ultrasound, the doctor examines the child’s internal organs and skeleton: brain structures, spine, face, lungs, heart and tummy.
To assess the condition of the mother and her readiness for childbirth, placenta indicators are of great importance. First of all is the location. It is optimal if the placenta is attached to the posterior wall of the uterus, but other localization is also possible. The only pathology is previa, when the placenta is too close to the cervix and practically blocks the exit from the uterus. The specialist also looks at the thickness of the placenta at the site of attachment and maturity.
Ultrasound objects in late pregnancy
- Cervical parameters: the cervix smoothes normally 14 days before birth. If smoothing of the cervix is observed earlier than expected, then we can talk about insufficient closure ability of the cervix
- In the prenatal period, the tone of the uterus increases - this is a physiological norm.
- The placenta in late pregnancy has stage 3 of maturity. Overlapping of the pharynx with the placenta, incorrect positioning of the fetus are indications for cesarean section. Calcification at the end of pregnancy is normal.
- Water should normally contain the required amount and be transparent. Turbidity of the water is allowed, the content of meconium in it, a small or increased amount of water is not always a pathology.
- The expectant mother is full of hopes and worries, she is overwhelmed with a range of emotions. To ensure that the last months of waiting for the heir pass only on positive notes, if you have any doubts about the normal course of the pregnancy, you can undergo an ultrasound in any private clinic and get another specialist.
The “Your Doctor” help desk for private clinics will help you choose a medical center and sign up for diagnostic procedures.
Useful information on the topic of gynecologist:
- How to get tested for gynecological diseases?
- What diseases does a gynecologist treat?
- What tests can be done by a gynecologist?
- How to prepare for an appointment with a gynecologist?
- Where to go with a gynecological problem?
- What symptoms should you consult a gynecologist for?
- How does an appointment with a gynecologist go?
- Female doctor
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections in women
- Diagnosis of gynecological diseases
- Treatment of female diseases
- Pediatric gynecologist
- How is a gynecologist examined?
- Paid gynecologist
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Author:
Kasabov Alexander Vladimirovich Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Ultrasound Doctor
Back to section
In the examination room
Once it has been established which department the pregnant woman or woman in labor is being sent to, she is transferred to the appropriate examination room. Here the doctor, together with the midwife, conducts a general and special examination: weighs the patient, measures the size of the pelvis, abdominal circumference, the height of the uterine fundus above the womb, the position and presentation of the fetus (cephalic or pelvic), listens to its heartbeat, examines the woman for the presence of edema, and measures arterial blood pressure. pressure. In addition, the doctor on duty performs a vaginal examination to clarify the obstetric situation, after which he determines whether labor is occurring, and if so, what its nature is. All examination data is entered into the birth history, which is created here. As a result of the examination, the doctor makes a diagnosis, prescribes the necessary tests and prescriptions.
After the examination, sanitary treatment is carried out: shaving of the external genitalia, enema, shower. The scope of examinations and sanitization in the examination room depends on the general condition of the woman, the presence of labor and the period of labor. Upon completion of sanitary treatment, the woman is given a sterile shirt and gown. If labor has already begun (in this case, the woman is called a woman in labor), the patient is transferred to the prenatal ward of the birth block, where she spends the entire first stage of labor until pushing, or to a separate birth box (if the maternity hospital is equipped with such). A pregnant woman still awaiting childbirth is sent to the pregnancy pathology department.
Why do you need CTG during childbirth? Cardiotocography provides considerable assistance in assessing the condition of the fetus and the nature of labor. A cardiac monitor is a device that records the fetal heartbeat and also makes it possible to monitor the frequency and strength of contractions. A sensor is attached to a woman’s stomach, which allows the fetal heartbeat to be recorded on a paper tape. During the study, the woman is usually asked to lie on her side, because when standing or walking, the sensor constantly moves away from the place where it is possible to record the fetal heartbeat. The use of cardiac monitoring allows for timely detection of fetal hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) and labor anomalies, assessment of the effectiveness of their treatment, predicting the outcome of childbirth and selecting the optimal method of delivery.