The volume of urine that is formed during the day (daily diuresis) in an adult normally averages 1500 milliliters. The amount of diuresis is determined by the ratio between glomerular filtration and tubular reabsorption of water. Depending on the state of water balance in the body, diuresis, as well as the concentration of final urine, vary widely (mainly due to changes in water reabsorption). During dehydration (vomiting, increased sweating, diarrhea, increased swelling, and sometimes accumulation of fluid in the serous cavities), a decrease in diuresis begins to develop: a small volume of highly concentrated urine is released. Otherwise, with overhydration (excessive fluid intake), a state of water diuresis appears, in which up to 2-2.5 liters of weakly concentrated urine are formed during the day.
Also in medicine there is such a thing as forced diuresis. What is it? Forced diuresis is the accelerated removal of toxic substances from the body. This is achieved by simultaneously introducing a large volume of fluid into the body (up to one liter of saline solution) and prescribing diuretics (for example, furosemide, the purpose of which is to increase diuresis) according to the instructions.
Another interesting phenomenon is cold diuresis. It makes us urinate more in the cold. A decrease in temperature and the frequency of visiting the toilet are related exponentially. The colder it gets, the more a person feels as if the urine has become heavy and begins to put more pressure on the walls of the bladder. Don't let this bother you. Cold or nervous excitement are often the causes of frequent urination.
The amount of urine may increase (polyuria) with:
- Consuming large amounts of liquid;
- Eating foods that increase diuresis (watermelon, pumpkin);
- Kidney diseases (pyelonephritis);
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Dystrophies.

A decrease in the amount and volume of urine (oliguria) can occur with:

- Limiting fluid intake;
- Increased sweating;
- Diarrhea;
- Vomit;
- Kidney disease;
- Circulatory failure.
Urinary retention in the bladder can occur due to:
- prostate cancer and adenoma;
- prostatitis;
- narrowing of the urinary canal;
- obstruction of the bladder outlet by a stone.
The predominance of nighttime urine volume over daytime (nocturia):

- chronic pyelonephritis;
- chronic renal failure;
- heart failure.
Cessation of urine excretion (anuria) or excretion of no more than 50 ml per day:
- general condition disorders (shock, blood loss, decreased blood pressure);
- renal causes (poisoning with kidney poisons, transfusion of incompatible blood);
- disruption of urine flow from the kidney (stones, tumor).
Normally, daytime diuresis prevails over nighttime in a ratio of 3:1.
Daily volume measurements allow us to suspect problems in various organ systems.
For men and women, the daily diuresis rate is different.
This is due to differences in metabolic rate and hormonal processes.
In order for metabolic processes to proceed at a normal speed, it is necessary to consume at least 500 ml of liquid per day.
On average, the recommended amount is 1 – 2 liters.
Classification of violation
Disturbances in urine production manifest themselves most clearly in changes in the amount of diuresis. Based on the reason that caused them, these changes can be divided into
:
- renal, caused by pathological processes occurring in the kidneys directly;
- extrarenal, provoked by disorders of systemic hemodynamics, urinary tract function, as well as the system regulating urine production.
Weather also has an impact on this process. In a healthy person, the amount of urine decreases in the heat. And with copious fluid intake, an increase in urine volume is observed. And this should not be confused with pathology.
What should the daily diet be for older people? After all, it is known that they often encounter a disorder, as a result of which doctors prescribe the necessary pills for them. Nocturia (failures in the urinary system) is one of the most common diseases. The main symptom: excessive urine output at night. While in a healthy person, on the contrary, diuresis during the day is two to three times greater than at night.
According to the mechanism of occurrence, pathological changes in diuresis are caused by impaired reabsorption or filtration.
To detect and diagnose kidney disease (urolithiasis), the Rehberg test (endogenous creatinine clearance) is often used. How is it carried out? There are certain rules for this. The patient should drink 400-500 ml of water or weak tea on an empty stomach, and then urinate (this portion of urine is poured out). The time of urination is accurately noted. Exactly after 1 hour, urine is collected (completely). In the middle of this hour, the cubital vein is punctured and 5-8 ml of blood is obtained. Minute diuresis is determined based on the volume of urine collected. Creatinine concentration is determined in blood and urine. Filtration and reabsorption are calculated using special decoding formulas. The cost of this analysis ranges from 200-500 rubles.
Urolithiasis can cause a more serious disease - renal pyelectasis. It is treated depending on the severity. Only a doctor can prescribe effective treatment methods. In addition, if you are overcome by another viral infection, do not endure the disease on your feet - you definitely need bed rest, the disease does not go away without a trace. Do not forget that the kidneys are your weak point, and a common cold can leave a deplorable mark on them.
Daily diuresis of a pregnant woman
During pregnancy, a woman’s body receives a double load.
It does not occur immediately, but as the fetus grows.
An increase in the volume of circulating fluid leads to an increase in the need for water support.
This can lead to fluid accumulation in a woman's body.
Because of this, swelling develops.
During fetal growth, waste products enter the maternal bloodstream.
This forces a woman’s kidneys to work harder.
The volume of daily urine increases.
On average, the figure is 60–80% of fluid consumed.
Pregnant women note an increase in the frequency of urination.
This is due to fetal pressure on the bladder.
Diuresis during pregnancy
It is very important to calculate daily diuresis in pregnant women. Normally, it is about 60-80% of the liquid drunk. With pathology, edema of the lower extremities may form (negative diuresis predominates). After fasting days and normalization of the diet, they pass. Doctors say that normally, as much as a woman drinks, that much should come out, because everything that doesn’t come out will go into edema. Therefore, what is the calculation formula? For this, a method for tracking diuresis can be used, such as a table, which is quite convenient to collect data and calculate. It records the time of fluid intake and elimination along with the volume. Basically, diuresis in pregnant women is disrupted at 22 weeks, when the fetus is large. An enlarged uterus puts pressure on the kidneys, making urination difficult. Women often wonder what they can drink during pregnancy and how much fluid they should drink per day. To keep records correctly, you need to remember that water is found not only in drinks, but also in soups, main courses, desserts and even bread. The main task is to calculate it correctly. For example, yogurt is most often charged at 50%, i.e. 200 ml yogurt = 100 ml liquid. Many products have the liquid percentage listed on the packaging. Doctors advise eating more foods that have a diuretic effect. The most popular are watermelon and melon, buckwheat. Many berries are also diuretic, such as blueberries, which have a positive effect on treatment.
The method for calculating the daily diuresis of a newborn is based on the indicators of a special table that can be found on the Internet. Therefore, measuring urine output is not difficult. Monitoring the measurement of diuresis in children is necessary, since quite often they have urinary disorders. The environment in which a child grows plays a significant role. Very often, violations can arise for the following reasons: reluctance to go to the toilet due to an exciting game, incomplete emptying of the bladder, delaying urination as much as possible when urinating, as well as such bad habits as urinating “for .
Volume of daily urine in infants
The metabolism of children is completely different from that of adults.
Children in the first month of life receive fluid from their mother's milk during breastfeeding.
Or dosed from a bottle - with artificial feeding.
As you gain body weight, the required amount of food increases.
Accordingly, the water load increases.
Up to six months, children tend to urinate frequently up to 20–25 times a day.
The daily volume of urine at this age ranges from 250 to 450 ml.
After 6 months, the child’s rate of weight gain decreases.
At the same time, the amount of food he receives is still growing.
But during this period of time, the baby gets acquainted with new food - complementary foods.
Taken together, the restructuring of the body leads to a decrease in the number of urinations per day to 15–16.
In this case, the daily volume of urine remains between 300 and 500 ml.
Sex in facts and figures
Imagine that at this very minute, when you are reading my page, four thousand people on the globe are having sex! Impressive? In search of little-known and interesting facts, I dug through a bunch of literature and Internet sites for you. And this is what happened. With love, your Eva Adams.
AT WHAT SPEED DOES SPERM SHOOT? 1-2 teaspoons of sperm are released during ejaculation. The average man produces 32 liters of sperm in his entire life. 7 kcal is contained in one teaspoon of sperm. 45 km/h is the average ejaculation speed. 10 cm is the length of the path of sperm to the egg. “Zhivchiki” pass it in 2.5 seconds. From 10 to 17.5 cm is the length of the male penis, from 7.5 to 17.25 cm is the circumference of this organ. 2.5 cm is the size of the smallest male penis. 35 cm is the size of the longest male penis. On average, 11 erections during the day and 9 erections at night occur in men per day. From 2 minutes to 2 weeks - the time required for repeated erection.
HOW LONG DOES A KISS LAST? From 30 seconds to 5 minutes is the average duration of a kiss. 25 facial muscles are used when kissing. 55 seconds is the approximate difference between a kiss from your sister and your girlfriend. 31 hours 18 minutes 33 seconds is the record for a continuous kiss, which belongs to an Italian couple. 56% of women and 44% of men around the world enjoy kissing. 9.7% of women and 10.7% of men do not kiss during intimacy. 1% of the world's population have very short tongues, so they cannot kiss.
STANDARD FOR WOMEN'S BREASTS 60% of men consider the ideal breast to be a breast that can be held in the palm of your hand. 25% of women dream of enlarging their breasts by two sizes. 45% of women are completely satisfied with the size of their breasts. 30% of the stronger sex dream of girls with a bust size of 3 or more. Only 10% are crazy about small breasts. Busty women become pregnant 2-3 times more often: on favorable days, the content of estradiol (an indicator of reproduction) is one third higher. 1 in 5 thousand women in the world have three or more nipples.
BEST TIME FOR LOVE The most popular time for sex is Saturday evening, the most unpopular is Monday afternoon. 400 million people have sex every day. 4 thousand people are making love at the moment. Men and women make love 2 hours a week, 5 days a year and 6.5 months in their entire lives. 15 minutes. The average sexual intercourse lasts 10-12 minutes. Prelude continues, 3-5 minutes. - sexual intercourse, 30 sec. - orgasm. 17-25 years old is the peak of male sexuality, 27-35 years old is the peak of female sexuality. 67% of couples regularly practice traditional sex, 30% - oral, 3% - anal. The average Russian couple makes love 150 times a year and ranks third among Europeans in this indicator (ahead of Hungarians - 152 and Bulgarians - 151). 60% of couples in the world have sex without continuing the relationship. 3/4 of the population are satisfied with their sex life. A man thinks about sex 2 hours a day and a woman 10 minutes. 20% of men and women have sex only at night, 20% only in the morning. For 50%, the time of day for making love does not matter.
FREQUENCY OF ORGASM From 4-5 mm to 1 cm - the total length of the clitoris, from 2 to 20 mm - the diameter of the clitoris. 40% of girls experience vaginal and 60% clitoral orgasm. 30% of women experience orgasm rarely or never. 20% of women have an orgasm with every sexual intercourse. 95% of men end every sexual intercourse with ejaculation.
SEXUAL DESIRES 58% of men and 74% of women accompany sex with lewd comments. 43% believe that a scantily clad woman is sexier than a naked woman. 43% of men and 45% of women dream of sex on the side. 51% of men admit to their partners that they dream about others during sex. 60% of men have sex in the missionary position, while the rest prefer the knee-elbow position (doggy style). On average, a single man has 7 casual partners per year and a woman has 1 casual partner. 19% of men condemn sex before marriage. 47% of men and 28% of women cheat on their spouse. 40% of guys cheated on their girlfriends an average of 6 times. 10% of women would rather give up chocolate than sex. 37% of women take the initiative in bed.
AGE IS NOT A HINDER TO SEX! 45% of women get maximum pleasure from sex after the age of 40, 50% of men - at the age of about 30. At the age of 14-15, boys lose their virginity; at 16-17, girls lose their virginity. 73% of men and women can have sex at age 70, 15% of women over 80 continue to have sex. About 60% of men and 42% of women masturbate.
NON-TRADITIONAL LOVE 11% of the world's population by the age of 45 have experienced same-sex sex. 9% consider themselves bisexual. Every 5 women dreams of trying sex with a girl. 12% of women and 23% of men consider themselves to be gay. 28% of men and 13% of women have had group sex at least once. 60% of girls dream of having group sex. 10% of couples aged 25 to 60 years old changed partners.
Daily urine volume in children from 1 year to 7 years
After a child turns one year old, his body is already adapted to the environment.
The number of urinations is already 10–12.
Urine volume is from 500 to 600 ml.
The child's body still continues to grow rapidly.
But the pace is already significantly lower than that of an infant.
When a child reaches three years old, the number of urinations decreases to 7–9 per day.
This frequency will continue until the child reaches 7 years of age.
The only difference is the volume.
From 3 to 5 years, the daily volume of urine is from 600 to 700 ml.
After 5 and up to 7 years it increases to 650 - 1000 ml.
Daily urine volume in children from 7 to 13 years
At the age of 7 years, the child’s body has slow metabolic processes.
Until the age of nine, the number of urinations will remain up to 7–8 per day.
After 9 years of age, on average, urine output occurs 6 to 7 times.
At this age, the child can already consciously control the level of thirst and fluid intake.
Changes also occur in the daily volume of urine.
For children from 7 to 11 years old it ranges from 800 to 1400 ml.
After 11 years, the volume increases slightly to 1000 - 1600 ml.
Next, the child’s body is already undergoing changes that are associated with hormonal changes during puberty.
Excretory and metabolic processes acquire characteristics similar to those of an adult.
Determination of daily urine volume
Determination of daily urine volume
Daily diuresis is the total amount of urine excreted by a person in 24 hours, taking into account the fluid consumed during this period. This test is necessary to determine normal kidney function.
For analysis, the patient must collect urine in a special container throughout the day. It is recommended to store this container in a cool, dry place until transport to the laboratory.
The composition of urine includes water and breakdown products of chemicals such as protein, creatinine, sodium, etc.
If the level of substances exceeds the permissible norm or the urine contains foreign chemical elements, this may be a sign of kidney disease or other ailment.
Analysis of the daily volume of urine gives the doctor the opportunity to diagnose pathology.
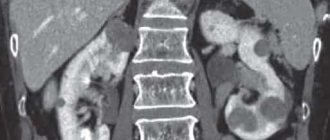
Other methods such as ultrasound, computed tomography, biopsy and angiography of the renal arteries are also used to diagnose kidney disease.
Principles of the urinary system
Together with food, a person receives valuable substances that feed the body with energy. After the body receives nutrients, part of the breakdown products is excreted through the excretory organs, the other part remains in the blood and is purified through the kidneys.
The urinary system regulates the salt and water balance in the body and helps maintain it at the proper level. Urea is formed as a result of the breakdown of animal and plant proteins and is then excreted from the body through the kidneys.
The kidneys play an important role in regulating blood pressure and producing the glycoprotein hormone erythropoietin, without which the formation of red blood cells is impossible.
The urinary system and its functional role
- The kidneys are a paired organ that is located in the lumbar region under the ribs on both sides of the spine. The kidneys rid the body of toxins, which are excreted in the urine and provide optimal levels of salts and other substances. Produced in the kidneys, erythropoietin forms bone marrow red blood cells. The kidneys are involved in regulating blood pressure.
- A nephron is a functional and structural unit of the kidneys. Consists of the renal corpuscle, responsible for filtration, and tubules. In the nephron, when urea and other substances enter, primary urine is formed.
- The ureters are two hollow tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder to transport urine. Disruption of this process in the form of urine flowing from the bladder to the kidneys can cause infection.
- The bladder is a triangle-shaped muscular organ located at the bottom of the abdominal cavity. It is a storage reservoir for urine before its direct removal from the body. To retain urine, the walls of the bladder can stretch and, conversely, contract to push urine out through the urethra.
- Sphincters are a pair of muscle rings that create obstacles to the outflow of urine.
- The nerves of the bladder perform the function of notifying the need to empty the organ.
- The urethra is a channel for removing urine from the body.
Useful information about urine:
- On average, an adult accumulates between 700 and 2000 ml of urine per day. The amount directly depends on the volume of liquid and food consumed during the day.
- In a healthy person, urine does not contain microorganisms, fungi, viruses and is sterile.
- During the night, half of the total volume of urine excreted per day is formed.
- There is a protective coating on the walls of the bladder that prevents the growth and development of microorganisms on it.
Indications for daily diuresis
Daily urine output is a quick test for diagnosing renal dysfunction. It is prescribed to determine the amount of creatinine that passes through the kidney filter, as well as to measure the amount of protein lost during the day, as well as hormonal secretion and minerals.
Like any other organ, pathologies can be detected in the kidneys.
Kidney diseases can be both acute and chronic.
Acute pathology appears instantly and can be cured.
Chronic diseases take a long time to develop and can cause kidney failure. The causes of pathologies, as well as their symptoms and treatment methods, may be different.
Diseases that cause kidney damage:
- diabetic nephropathy – kidney damage in people with diabetes;
- Essential hypertension – high blood pressure causes chronic kidney damage;
- systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic inflammatory disease that provokes damage to the skin, kidneys, joints and nervous system;
- infectious diseases of the urinary tract;
- difficulty or blockage of urine flow;
- hereditary nephritis or Alport syndrome - causes deafness and blindness, kidney damage;
- nephrotic syndrome is a kidney pathology in which protein appears in the urine, protein levels in the blood decrease, and cholesterol levels increase. Accompanied by swelling;
- polycystic kidney disease - a genetic disease characterized by the formation of cysts with fluid in the kidneys;
- cystinosis is a hereditary pathology in which an abnormal amount of a protein component, cystine, is formed in the cytoplasm of cells;
- interstitial nephritis - inflammation of the structure of the kidney tissue and tubules;
- pyelonephritis is an infectious kidney inflammation that affects the kidney tissue and pelvis.
As a diagnosis, daily diuresis is prescribed in combination with other procedures. In addition to the above, there are other reasons for prescribing a 24-hour urine test, which can be identified by the attending physician.
Disturbances in daily diuresis that affect the result.
As a rule, the procedure for collecting 24-hour urine is simple, safe and does not require outside intervention. Violation of the basic rules for collecting urine can significantly affect the initial result of the analysis. For example:
- if not all urine excreted in the specified period of time was collected;
- if you went outside the day and collected excess urine;
- if for some reason urine spills from the container;
- violation of storage conditions during the procedure;
- taking medications and eating foods that should be excluded during the analysis.
Preparation before taking a 24-hour urine test.
- Consultation with the attending physician about the procedure and the opportunity to ask questions.
- Your doctor may set a specific time for you to start collecting urine.
- For your convenience, during daily diuresis, it is recommended to spend this day at home.
- If there is a possibility of pregnancy, notify your doctor.
- You must provide your doctor with complete information about all the medications and vitamins you are taking.
- Individual recommendations for preparing for the procedure can be prescribed in accordance with the patient’s health condition.
Daily diuresis can be prescribed in combination with other medical procedures or on an outpatient basis.
The procedure for collecting urine during daily diuresis:
- You will first be given a container for analysis. Most often, a special brown plastic container is used. It is most convenient to use a urinal or bedpan to collect urine.
- It is recommended to start collecting urine in the morning, but you can start at a time convenient for you. The main thing is to strictly adhere to the 24-hour collection schedule.
- There is no need to save urine during the first morning urination session. Start counting from next time.
- It is recommended to store the collected urine for 24 hours in a cool place, possibly in the refrigerator.
- It is advisable to carry out the last urine collection at the same time as the first.
- Upon completion of the procedure, the urine collected in the container must be transported to the laboratory.
As a rule, there are no restrictions or rules for the patient after taking a 24-hour urine test. On an individual basis, the doctor may prescribe repeated daily diuresis.
Reasons for changes in urine volume in pathologies
Increased urine output occurs in a variety of conditions:
- Increased body temperature;
- Hydronephrosis;
- Conn's syndrome;
- Psychosomatic disorders in children;
- Increased levels of parathyroid hormone;
- OPN.
A decrease in diuresis volume occurs for prerenal, renal or postrenal reasons.
Prerenal factors include processes that occur without involving the genitourinary system.
This may be a sharp decrease in circulating fluid, spasm of blood vessels due to shock conditions, or acute thrombosis of arteries and veins.
Cardiovascular pathologies can indirectly affect a decrease in daily urine volume.
Renal causes lie in the pathology of the kidneys themselves.
This may be direct damage to the kidney tissue or impaired circulation through the renal arteries.
The reasons may be:
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Vasculitis;
- Kidney injury;
- Toxic effect of substances;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Nephrotic syndrome.
The decrease in diuresis is based on dysfunction of the renal tubules.
Changes in the function of the ureters are among the postrenal factors of oliguria.
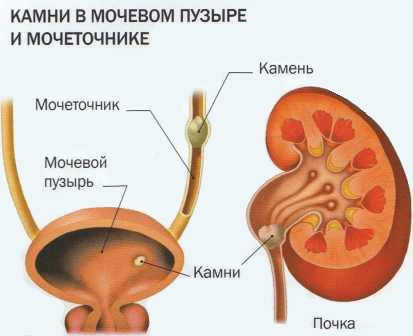
Ureteral obstruction can be caused by several reasons.
Blood clots, stones, and strictures can impede the passage of urine.
There may be external pressure from the uterus, which has increased, for example, during pregnancy.
Tumor formations can also put pressure on the wall of the ureter.
This leads to disruption of the outflow of urine from the kidneys.
Signs of violations
Changes in daily diuresis can be detected by interviewing and examining the patient.
Polyuria is characterized by a frequent urge to urinate.
In this case, a large amount of urine is released.
It has a light yellow color.
Can be almost transparent.
This indicates decreased urine density and low concentrating ability of the kidneys.
Manifestations of anuria include headache, dyspepsia, and itching of the skin.
There is an urge to urinate, but is often unsuccessful.
Voluntary urine output is not observed.
Sometimes there is no urge, and the patient is tormented by constant thirst.
Ishuria is accompanied by difficulties in performing the act of urination or its impossibility.
Feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
The appearance of swelling, weakness and drowsiness.
For pregnant women, when diuresis is impaired, protein appears in the urine.
This is the main sign that indicates problems with the urinary system.
There is a sharp jump in body weight and an increase in edema of the lower extremities.
Possible increase in blood pressure.
Urine is released frequently, in small volumes, and patients are thirsty.
Free consultation with a urologist
What is a 24-hour urine test (24-hour diuresis)?
Daily urine analysis (daily diuresis) is a simple test that allows you to determine the volume of urine excreted during the day. The test is non-invasive (meaning no damage to the skin is required). A 24-hour urine sample (24-hour urine output) is used to assess kidney function.

A 24-hour urine test (24-hour urine output) is determined by collecting the patient's urine for 24 hours in a special container. The container must be kept in a cool place until it is delivered to the laboratory for analysis.
Urine consists of water and dissolved chemicals such as sodium, potassium, urea (a breakdown product of protein), and creatinine (a breakdown product of muscle tissue) and others. Typically, urine contains a certain amount of these waste products. If the amount of these substances exceeds normal limits, or if there are other substances in the urine that should not normally be present, then this may be a symptom of kidney damage or other pathology. The results of the analysis of daily urine (daily diuresis) provide information that will help the doctor establish and confirm the diagnosis.
Other diagnostic tests that are used to detect kidney disease include renal ultrasound (renal ultrasound), renal CT scan, renal biopsy, and renal arteriogram.
How does the urinary system work?
The body takes nutrients from food and converts them into energy. After the body has received the necessary nutrients, waste products are eliminated from the body through the intestines or remain in the blood and are then filtered by the kidneys.
The urinary system maintains water-salt balance, allowing the body to function normally. The kidneys also remove urea from the blood. Urea is formed by the breakdown of proteins in the body, which are found in meat, poultry and some vegetables.
Other important functions of the kidneys include regulating blood pressure and producing erythropoietin, a hormone that is necessary for the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
Parts of the urinary system and their functions:
- The two kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located below the ribs on either side of the spine. The kidneys remove liquid waste from the blood, which is excreted from the body in the form of urine, and maintain the balance of salts and other substances in the blood. The kidneys produce erythropoietin, a hormone that is involved in the formation of red blood cells. The kidneys are also involved in regulating blood pressure.
- The structural and functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. Each nephron consists of a glomerulus formed by capillaries and renal tubules. Urea, along with water and other waste substances, passes through the nephron, where urine is formed.
- The two ureters are narrow tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The muscles in the wall of the ureters continually contract and relax, forcing urine into the bladder. Every 10 to 15 seconds, urine alternates from the ureters into the bladder. If urine backs up from the bladder through the ureters into the kidneys, an infection may develop.
- The bladder is a hollow, triangular-shaped organ located in the lower abdominal cavity. The bladder is held in place by ligaments that attach to other organs and bones of the pelvis. The walls of the bladder relax and expand to hold urine, and then contract and flatten, pushing urine out through the urethra (urethra). A healthy adult bladder can hold up to two cups of urine for two to five hours.
- The two sphincters are circular muscles that prevent the flow of urine by closing around the opening of the bladder.
- Bladder nerves – signal the person to empty the bladder.
- The urethra (urethra) is the tube that carries urine out of the body.
Urine Facts:

- Adults excrete approximately 750 – 2000 milliliters of urine per day, depending on the amount of fluid and food consumed.
- The volume of urine produced at night is half the volume of urine produced during the day.
- Normal urine is sterile. Urine contains liquid, salts and waste, but there are no bacteria, viruses and fungi in it.
- The bladder wall is sealed from urine and toxic substances by a coating that prevents microorganisms from attaching and growing to the bladder wall.
Indications for analysis of daily urine (daily diuresis).
A 24-hour urine sample (24-hour urine output) is a quick, simple diagnostic test that can help identify problems with kidney function. A 24-hour urine test is performed to determine the amount of creatinine that is filtered by the kidneys, as well as to determine the daily protein losses, secretion of hormones and minerals. Analysis of creatinine clearance allows you to assess the excretory and metabolic function of the kidneys.
Like all organs in the human body, the kidneys are susceptible to various diseases. Kidney diseases can be acute or chronic. Acute kidney disease has an abrupt onset and is most often reversible. Chronic kidney disease develops slowly over months or years and can lead to chronic kidney failure. The causes, symptoms, treatment and outcomes of acute and chronic kidney damage vary.
Conditions that can cause kidney damage include, but are not limited to:
- diabetic nephropathy is a complication of diabetes mellitus
- hypertension – high blood pressure leads to chronic kidney damage
- systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin, joints, nervous system and kidneys
- frequent urinary tract infections
- long-term urinary tract obstruction or blockage
- Alport syndrome is a hereditary disease characterized by deafness, progressive kidney damage and decreased visual acuity
- nephrotic syndrome is a condition that has several different causes. Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by protein in the urine, low protein in the blood, high cholesterol and swelling
- Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder characterized by the appearance of numerous fluid-filled cystic formations in the kidneys
- cystinosis is a hereditary disease in which the amino acid cystine (a protein component) accumulates in the lysosomes of kidney tissue cells
- interstitial nephritis - inflammation of the internal structures of the kidneys
- pyelonephritis is an infectious and inflammatory disease that affects the pelvis and kidney tissue, simultaneously or in turn.
Analysis of 24-hour urine (24-hour diuresis) is performed along with other diagnostic procedures, such as cystometry and cystography.
Your doctor may have other reasons for recommending a 24-hour urine output test.
Complications of 24-hour urine analysis (24-hour diuresis)
Analysis of 24-hour urine output is a safe procedure that usually does not require outside assistance.
The accuracy of a 24-hour urine test (24-hour urine output) can be affected by various factors, which include, but are not limited to:
- collection of not all urine that is excreted during the day
- going beyond the 24-hour period and collecting excess urine
- spilling urine from a collection container
- improper storage of urine during the collection of daily analysis
- taking certain medications and/or eating certain foods
There may be other factors depending on your health. Discuss any possible concerns with your doctor before your procedure.
Before analyzing 24-hour urine (24-hour diuresis)
- Your doctor will explain the procedure to you and invite you to ask any questions you may have regarding the analysis of 24-hour urine (24-hour urine output).
- No special preparation is required before analyzing 24-hour urine (24-hour urine output)
- You may be instructed to start collecting your 24-hour urine sample at a specific time.
- If possible, choose a time to collect your 24-hour urine sample (24-hour urine output) so that you can be at home during the 24-hour period.
- If you are pregnant or suspect that you are pregnant, tell your doctor.
- Tell your doctor about all medications, including vitamins and herbal remedies, that you take.
- Depending on your medical condition, your doctor may prescribe other special preparations for you.
During the collection of a daily urine test (daily urine output)
A 24-hour urine test (24-hour urine output) may be done on an outpatient basis or as part of a check-up during your hospital stay. The procedure for testing 24-hour urine (24-hour urine output) may be modified according to your condition and your doctor's practice.
Typically, 24-hour urine analysis (24-hour urine output) is collected as follows:
- On the eve of collecting a daily urine test (daily urine output), you will be given one or more containers for collecting and storing urine. Typically a brown plastic container is used. A bedpan or urinal can be used to collect a urine sample. You should collect all urine during the day in a container provided to you, which should be stored in a cool place.
- Collection of a 24-hour urine sample (24-hour urine output) can begin at any time during the day. However, it is best to start collecting a daily urine test in the morning. It is important to collect all urine over the subsequent 24-hour period.
- Do not save the first morning urine. Note the time that will be the start time of daily urine collection (daily diuresis).
- All urine, after the first specimen, must be collected and stored in a cool place, on ice or in the refrigerator for the next 24 hours.
- Try to urinate again at the same time, 24 hours after the start time and complete the process of collecting a 24-hour urine sample (24-hour urine output), but if you were unable to urinate at the same time, this is not a problem.
- Once the collection of daily urine (daily urine output) is completed, containers with urine must be delivered to the laboratory. If you collect a daily urine test at home, you will be given recommendations on when and how to deliver the container with urine to the laboratory.
- The collection of daily urine analysis is completed. Depending on your health, you may be asked to collect 24 hours of urine over several days in a row.
After analyzing daily urine (daily diuresis)
There is no need to follow special rules after collecting daily urine (daily diuresis).
However, your doctor can give you additional recommendations after analyzing 24-hour urine and prescribe additional examinations depending on your specific situation. The article is for informational purposes only.
For any health problems, do not self-diagnose and consult a doctor! Author:
V.A. Shaderkina is a urologist, oncologist, scientific editor of Uroweb.ru. Chairman of the Association of Medical Journalists.
What can affect the analysis result?
The amount of urine that is released per day can be influenced by certain factors.
The patient is recommended to keep a diary in which he will monitor the amount of fluid he drinks.
In particular, you can mark food and medicine in it.
During the test period, you should avoid eating diuretic products, pickles, and spicy foods.
Any medications that cannot be stopped should be discussed with your doctor.
It is worth noting the time you take medications in your diary, this will help avoid false indicators.
How is urine collection performed?
It is recommended to start collecting urine for the day at 6–7 am.
The first urination is not collected, starting from the second, urine is collected.
A container with a total volume of up to 3 liters is used for collection.
It may have graduations for more comfortable counting of quantities.
Starting from the second portion, the patient collects urine hourly into the indicated container.
Before each act of urination, hygienic treatment of the genitals is carried out.
To do this, use ordinary water; it is not recommended to wash with soap, as this will upset the alkaline balance.
The end of the analysis occurs exactly after 24 hours.
Before 6 p.m., daytime diuresis is considered, and after that, nighttime diuresis.
The quantity can be indicated on a special form.
Why is the first portion of urine not taken into account?
The first portion is not included in the analysis, so it can be used for other studies, if they are prescribed.
The reason is that night urine has a high density and concentration of minerals after sleep.
Features of daily urine collection in children
The analysis in children does not differ significantly.
For newborns and infants, whose urination is quite difficult to control, there are special pads.
These are plastic or cellophane bags with an adhesive surface.
Made from hypoallergenic materials and comfortable to wear and use.
Overlays of different shapes have been developed for boys and girls.
The adhesive surface is placed on the perineal area in the projection of the urethra.
The pad should be tightly fixed, then a diaper is put on the child.
The pads are changed every hour.
The entire contents of the bag are placed in a large container with a measuring scale.
You need to record the amount of each serving, then calculate the daily and nightly volume.
Collecting urine in children is a rather labor-intensive procedure; this study is usually carried out in a hospital.