Clinic » Services » Pregnancy management » Pregnancy progress by week
Pregnancy is a very special state for a woman. The expectant mother must not only register in a timely manner and be observed by a specialist, but also devote a lot of time to self-education. It doesn't matter what week you are pregnant right now. In any case, the guidance we offer will be useful and will help you better understand your own condition. With our help, you can find out what changes occur in the fetus from the first to the fortieth week, how the child develops, what happens to his weight, the formation of body parts, and growth. We have tried to provide a detailed description of the course of pregnancy week by week.
Our guide to pregnancy will become your assistant and will help you find out what exactly happens to the body in the first weeks, and what changes await you in the future. We described the features of a woman’s well-being during this important period and the specifics of fetal development.
Find out the cost of a consultation and make an appointment with a doctor by phone:
+7 or
Make an appointment
1-4 weeks
The egg grows and matures in the ovary before conception. Ovulation is the movement of a mature egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube. Ovulation occurs in the middle of the cycle. When a mature egg and sperm unite, fertilization occurs, and from this moment the development of the future baby begins.
At week 4, the size of the embryo is only 2-4 mm. As a rule, a woman does not feel anything and often does not even realize that pregnancy is occurring.
You can read more about the first weeks of fetal development here.
Why is it necessary to track fetal femur length?
The femur bone is a hard organ that reaches the greatest size in thickness and length compared to other bones. It is responsible for the balance of the human body, so the heaviest load falls on it. This explains the fact that the femur is the most commonly damaged bone.
When measuring fetal thigh length (hereinafter referred to as HF), it is important to monitor the dynamics of its growth. Based on the results of the ultrasound, the diagnostician makes a conclusion about whether this indicator corresponds or does not correspond to the gestational age of the child. This information makes it possible to timely diagnose developmental disorders and predict the likelihood of their occurrence. This is especially important when one of the baby’s future parents has an anomaly of the femur, since these abnormalities can be inherited.
DB is checked against a table of reference values. Based on this indicator, in a number of cases the question of the advisability of taking special therapeutic measures before delivery is decided.
5-8 weeks
The embryo grows, almost a million new cells are formed every minute. By the end of the seventh week, it will already reach one centimeter in length. By the end of the eighth week, the unborn baby will grow to 1.5-2 cm. At this time, primitive nerve pathways begin to form in his brain. During an ultrasound examination with CRT (coccygeal-parietal size) more than four centimeters, the specialist will be able to determine the heartbeat.
You can read more about the features of weeks 5-8 here.
The concept of biparietal head size and BDP norm according to weeks of pregnancy
Biparietal size (BPR, BPD, BPD) is the distance between the parietal bones of the fetal head, or the “width” of the skull. When measuring fetal BPD, the ultrasound device sensor should be positioned so that the baby's head is visible from above. Goals for measuring the indicator:
- Clarification of gestational age. The most accurate duration of gestation according to BPD norms is determined from 13 to 22 weeks.
- Tracking child development. Each stage of pregnancy corresponds to a certain indicator. If there is a discrepancy of more than 2 weeks, a developmental disorder, brain pathology, or congenital abnormalities are suspected.
- Calculation of a child's weight. When determining body weight, abdominal circumference and femur length are also taken into account.
- Planning the method of delivery. If the width of the baby's head is much greater than the circumference of the maternal birth canal, a caesarean section is recommended.

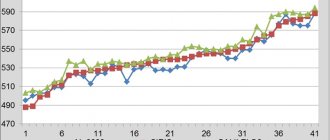
The greatest attention is paid to this index from 12 to 28 obstetric weeks. At later stages, the biparietal indicator loses its informative value, since head growth slows down and hereditary factors begin to affect the physical development of the child. The table shows the norms of fetal life expectancy by week.
| Duration, weeks | Minimum value, mm | Maximum value, mm | Average value, mm |
| 11 | 13 | 21 | 17 |
| 12 | 18 | 24 | 21 |
| 13 | 20 | 28 | 24 |
| 14 | 23 | 31 | 27 |
| 15 | 27 | 35 | 31 |
| 16 | 31 | 37 | 34 |
| 17 | 34 | 42 | 38 |
| 18 | 37 | 47 | 42 |
| 19 | 40 | 49 | 45 |
| 20 | 44 | 53 | 48 |
| 21 | 47 | 56 | 51 |
| 22 | 49 | 60 | 54 |
| 23 | 53 | 64 | 58 |
| 24 | 56 | 67 | 61 |
| 25 | 59 | 70 | 64 |
| 26 | 62 | 73 | 67 |
| 27 | 65 | 76 | 70 |
| 28 | 68 | 79 | 73 |
| 29 | 71 | 82 | 76 |
| 30 | 72 | 85 | 78 |
| 31 | 74 | 87 | 80 |
| 32 | 76 | 89 | 82 |
| 33 | 78 | 91 | 84 |
| 34 | 80 | 93 | 86 |
| 35 | 82 | 95 | 88 |
| 36 | 84 | 97 | 90 |
| 37 | 86 | 98 | 92 |
| 38 | 87 | 100 | 94 |
| 39 | 89 | 102 | 95 |
| 40 | 90 | 103 | 96 |
When clarifying the duration of pregnancy, doctors use more detailed BPR tables, which indicate the index norms by week and day. For example, a fetal head BDP of 46 mm corresponds to a period of 19 weeks. and 1 day on average (however, this figure is also acceptable at 22 weeks), at 20 weeks. and 3 days the biparietal head size will be 50 mm. Possible reasons for non-compliance with standards:
- hereditary characteristics;
- intrauterine infection;
- pathologies of the formation of cartilage tissue and bones;
- brain tumor;
- maternal endocrine disease;
- developmental delay;
- genetic abnormalities;
- parts of the brain missing or malformed.
If non-compliance with standards is detected for the first time, additional studies and a repeat ultrasound scan are prescribed after 1–2 weeks. If such deviations are confirmed, the dynamics of fetal growth, pregnancy history are studied, and possible hereditary factors are identified. The final diagnosis is made only after all possible causes have been clarified.
9-12 weeks
At the beginning of pregnancy, the unborn baby is called an embryo, but from the 9th week this term is no longer used. The fetus becomes like a smaller copy of a person; by 11-12 weeks, its heart already has four chambers, and many internal organs are formed. The future baby's limbs and fingers, nose and nostrils, eyes, earlobes are visible. By this time, the expectant mother should have ended toxicosis and feel consistently good, and the feeling of fatigue should also go away.
You can read more about the features of weeks 9-12 here.
The first day
At the first stage, the embryologist evaluates the signs of fertilization after the IVF, ICSI, IMSI or PICSI procedure. At this stage, the presence, number, symmetry, internal structure and appearance of pronuclei in the embryo are assessed.
Pronuclei are the nuclei of male and female germ cells that have not yet merged and carry a single set of chromosomes.
Based on their number and appearance, the viability of the embryo and the prospects for the occurrence of pathologies are assessed. Normally, there should be two of them, they should have relatively equal sizes, be nearby and have “nucleoli” inside - pronucleoli, also in a certain number and located in a certain way. At this stage, many pathologies can form, for example, in the presence of only one pronucleus, fertilization cannot occur, because it is this formation that is the carrier of genetic material, and we have not yet learned to reproduce without the participation of the opposite sex. There may be three pronuclei. Such embryos often carry an abnormal, triple set of chromosomes and are not viable. They usually die before implantation (attachment to the wall of the uterus) or lead to a missed abortion. Such embryos are discarded and not used in IVF programs.
17-20 weeks
In the womb, the baby grows and develops rapidly. By the end of the twentieth week, the baby's skin becomes less transparent than it was before. This occurs due to the beginning of accumulation of subcutaneous fat. The motor neurons of the brain are sufficiently developed, which allows the baby to make a variety of movements, including even putting his thumb in his mouth.
As the child's body grows, his head no longer looks so bulky.
You can read more about the features of weeks 17-20 here.
How is LZR determined and what is its significance?
When measuring the BPR, the fronto-occipital size (LOD) of the fetus is also determined. To calculate it, the distance from the frontal part of the head to the back of the head is measured along the external or internal contours. LZR is a line perpendicular to BPR. Like the BDP, or fetal head width, the fronto-occipital dimension increases as the fetus grows, so it helps clarify the gestational age.
LZR is of great importance in determining possible deviations in the development of bone and cartilage tissues and the brain. This characteristic is most informative in the second trimester of pregnancy. Measuring the fronto-occipital size allows us to identify:
- tumors in the brain;
- underdevelopment of brain tissue;
- accumulation of fluid in the ventricles of the brain;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- disruption of the formation of bone and cartilage tissue.
Timely detection of pathologies allows you to determine further tactics for pregnancy management. If diseases incompatible with life are detected, termination of pregnancy is recommended. However, some deviations can be corrected. The table shows the norms of LZR from 16 to 40 weeks of pregnancy.
| Week of pregnancy | Normal limits, mm | Average value, mm |
| 16 | 41–49 | 45 |
| 17 | 46–54 | 50 |
| 18 | 49–59 | 54 |
| 19 | 53–63 | 58 |
| 20 | 56–68 | 62 |
| 21 | 60–72 | 66 |
| 22 | 64–76 | 70 |
| 23 | 67–81 | 74 |
| 24 | 71–85 | 78 |
| 25 | 73–89 | 81 |
| 26 | 77–93 | 85 |
| 27 | 80–96 | 88 |
| 28 | 83–99 | 91 |
| 29 | 86–102 | 94 |
| 30 | 89–105 | 97 |
| 31 | 93–109 | 101 |
| 32 | 95–113 | 104 |
| 33 | 98–116 | 107 |
| 34 | 101–119 | 110 |
| 35 | 103–121 | 112 |
| 36 | 104–124 | 114 |
| 37 | 106–126 | 116 |
| 38 | 108–128 | 118 |
| 39 | 109–129 | 119 |
| 40 | 110–130 | 120 |
When comparing LZR with norms, the child’s hereditary predisposition is taken into account. Since people of different nationalities have different features of the structure of the skull, there are standards depending on the nationality of the child’s parents.
25-28 weeks
At this time, the period of most active growth ends. From the twentieth to the thirtieth week, the baby’s weight doubles; by the end of the period, the weight is already in the range of 1-1.5 kg. The baby's eyelids are not tightly closed until the twenty-eighth week, which promotes the development of the retina.
During these weeks, the child begins to distinguish tastes and hear sounds. You can note his numerous movements in response to various sounds and touches. The nervous system and brain are in a stage of rapid growth and development.
You can read more about the features of weeks 25-28 here.
Embryo 10 weeks
The baby's eyelids close. He will open them himself at 28 weeks. The respiratory system is almost completely formed. The skeleton and its structure fully correspond to a person. The arms and legs are lengthened to normal proportions. But the head occupies almost half the length of the body. This is due to the active development of the cerebral hemispheres, the cerebellum is growing. The external genitalia develop according to gender. You will soon find out if he or she is growing in your belly. The baby's blood acquires its own group and Rh factor. Height can reach 7-8 cm.
33-36 weeks
The 36th week will end for the unborn baby with a weight of 2.4-2.8 kg, his height will be approximately 48 cm. Then the baby’s weight will grow by 200 g every week. Thanks to the layer of fat cells, facial features will become rounded, and the facial muscles are already adapted for sucking. Often, during an ultrasound examination during this period, it is clearly visible how the baby tries to put his fist in his mouth or simply sucks his finger.
You can read more about the features of weeks 33-36 here.
Indicators of the mother's body
The ultrasound method also allows you to monitor the condition of the mother’s body, determining its readiness for a less painful and safe childbirth.
Cervical length
The lower narrowed part of the uterus should exceed 29 mm. The optimal value is considered to be 30–36 mm. A patient whose cervical length was insufficient (up to 26–27 mm) during a routine ultrasound examination will most likely have to be kept in hospital until delivery. Otherwise, premature delivery may be required.
Condition of pharynx
The pharynx is the opening of the upper and lower part of the cervix. One is called internal, and the other is called external. The normal ultrasound scan at 33 weeks of pregnancy suggests that there is no dilation of the pharynx - they should both be closed.
Amount of amniotic fluid
The amount of amniotic fluid must be determined. Its minimum is approximately 72–77 mm, its maximum reaches 245–265 mm. During the examination, neither high water nor low water should be observed.
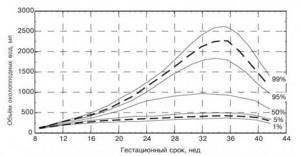
Location and thickness of the placenta
A female organ such as the placenta in the third trimester has a thickness of 35–43 mm. A deviation of 2 units to the left or right is not considered a deviation. When an ultrasound is performed, the uterine position of the structure is established - it should be located in the upper part of the hollow organ. Placenta adherence signals problems that require specialist intervention.
Placental maturity
Readiness for a full birth of the placenta is determined by its maturity. There are 4 main stages - 0, 1, 2 and 3. At the 33rd week of gestation, the mark is located between 1 and 2.
Umbilical cord length
The umbilical cord in each individual case has an individual indicator. The main thing to remember is that exceeding 70 cm can provoke the formation of loops around the baby.
The degree of supply of blood vessels to the umbilical cord
A healthy umbilical cord provides adequate blood supply and nutrition to the developing body. If the ultrasound results show 3 umbilical vessels, there is no need to talk about violations.