What is all this for?
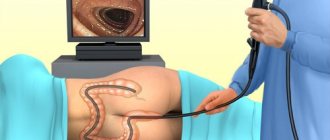
Transnasal gastroscopy (“gastroscopy without swallowing”) is performed on patients who, for one reason or another, have difficulty passing the endoscope through the oral cavity due to a pronounced gag reflex, which occurs in everyone in one form or another, when the reflexogenic zone of the tongue root is irritated. No matter how kindly and gently the doctor inserts the endoscope across the tongue, the gag reflex will still be initiated. Not to mention, if the doctor makes sudden and rough movements in this area.
Transnasal gastroscopy (“gastroscopy without swallowing”) is also performed for patients for whom sedation with propofol is contraindicated, since during transnasal gastroscopy the patient experiences minimal inconvenience. A 2007 national survey of endoscopists in the United States confirmed that unplanned pulmonary events during sedation accounted for the majority of endoscopy complications at 67%, and 72% of deaths during sedation were due to cardiac complications.
These inconveniences and complications during routine standard gastroscopy are associated with the passage of the endoscope through the reflexogenic zones of the tongue and larynx, and with inaccurate movement, various reflex states can arise that can lead to difficulty breathing (hypoventilation - insufficient oxygen supply, hyperventilation and hypercapnia - excess carbon dioxide in the blood with frequent shallow breathing, obstruction of the airways with saliva, laryngospasm - persistent prolonged closure of the vocal folds) or the occurrence of a cardiovascular reaction (tachycardia, arrhythmia, increased blood pressure, nosebleeds).
And, oh God! All this cannot happen if a transnasal gastroscopy (“gastroscopy without swallowing”) is performed. Because a thin endoscope is inserted into the nasal cavity, previously anesthetized, and descends through the nasopharynx to the mouth of the esophagus along the posterior wall, bypassing the reflexogenic zone of the root of the tongue and practically without touching the reflexogenic zone of the larynx. This explains the comfort during transnasal gastroscopy (“gastroscopy without swallowing”).
Performing gastroscopy without swallowing the probe
To conduct this study, some preparation is necessary. Three days before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude spicy, fatty, poorly digestible foods, as well as foods that lead to increased gas formation, from the diet. It is preferable to eat boiled, light food, porridges, pureed dishes. The patient must be on a fasting diet for 12 hours before the test; he can drink.
Before the procedure begins, electrodes and a receiver device are attached to the patient’s body. The patient then swallows the video capsule. The capsule moves through the gastrointestinal tract at a natural speed and takes pictures 2 times per second. The transmitting device with which it is equipped sends images to a receiver attached to the patient’s body. This process lasts about 8 hours. There is no need for medical supervision at this time; you can lead a normal lifestyle, excluding sudden movements and heavy physical activity.
The capsule is disposable and comes out naturally. At the end of the shoot, you need to come back for an appointment. The doctor reads the information from the receiving device, processes the images, analyzes them and makes a diagnosis.
How is an ultrasound of the stomach performed?
Preparation for an ultrasound of the stomach is similar to an ultrasound of the intestines: the patient adheres to a strict diet for 3 days, and the night before does not eat any food from 18.00. If there is a tendency to form gas, the patient drinks 2 capsules of Espumisan before bed. In the morning, half an hour before the procedure, you should drink a liter of water so that the walls of the stomach straighten.
There is also a method of ultrasound examination with contrast. Water is an excellent conductor of ultrasound, and without it, scanning an organ is somewhat difficult.
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. The doctor assesses the condition and thickness of the walls on an empty stomach, looking for the presence of free fluid. Then he asks the patient to drink 0.5-1 liter of liquid, and uses an ultrasound machine to evaluate changes in the expanded stomach. A third ultrasound scan is performed 20 minutes later when the stomach begins to empty. The doctor evaluates the motility of the organ and the rate of fluid loss. Normally, a glass of water (250 ml) comes out of the stomach in 3 minutes.
The patient lies on the couch on his side, the specialist applies gel to the peritoneal area and moves the sensor over the surface. Periodically, he tells the patient to change position or change his posture slightly. The doctor pays attention to the following indicators:
- position of the stomach and its size
- Has the mucous surface of the stomach expanded?
- is there thickening or thinning of the walls
- what is the state of the circulatory system of the stomach?
- contractility of the stomach
- are there inflammations and neoplasms?
The entire examination takes a maximum of 30 minutes and does not cause discomfort or pain. Ultrasound, unlike FGDS, is much easier to tolerate for children and the elderly.
After the procedure
If sedation/anesthesia is not used, you can discuss the detected changes and further tactics of examination or treatment with a gastroenterologist immediately after the examination.
If sedation is used, you will need to lie down for a few minutes until the effects of the medication wear off. After this, you will continue to consult with your doctor. Even if you feel alert, sedatives may remain in your bloodstream for up to 24 hours, so you may suddenly feel drowsy.
Drowsiness
During this time you should not:
- Drive;
- Operate complex equipment;
- Drink alcohol;
- Take sleeping pills;
- Sign contracts or legal documents;
- Stay with small children.
If the effects of the medication persist and the consultant doctor sees that there is no point in continuing the consultation, you will be contacted the next day to discuss the results of the gastroscopy and next steps.
And your gastrointestinal tract is healthy: stomach health is a matter of time
The content of the article
Let's look at medical statistics on diseases of the stomach and intestines. Alas, it is frightening, even without taking into account hidden patients who have not been examined and residents of the poorest countries where there is no access to medical services.
According to statistics:
- Almost 90% of the population of developed countries suffers from gastritis of varying degrees of neglect.
- 60% of the world's inhabitants are infected with Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium that causes inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, and is the cause of gastritis and stomach ulcers.
- In Western countries, up to 81% of citizens, according to statistics, periodically experience heartburn, which is a symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease - a disease of the esophagus that leads to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- About 14% of people have stomach ulcers.
At the age of over 60 years, the quality and length of life depends on the condition of the stomach and intestines, but it is possible to get rid of existing pathology only in the initial stages of the disease. That is why it is so important to be attentive to your health and not bring the problem to a chronic stage.
Advantages and disadvantages of gastroscopy without swallowing a probe
The advantages of video gastroscopy are obvious:
- painlessness;
- safety;
- ease of preparation and use;
- All parts of the gastrointestinal tract are examined, including parts of the small intestine (with conventional gastroscopy - only the esophagus, stomach and duodenum);
- High quality shooting, a large number of photographs;
- fewer contraindications.
However, gastroscopy without swallowing the probe also has disadvantages:
- inability to target pathology (ulcers, neoplasms, etc.);
- lack of possibility of manipulation: taking a biopsy, administering medications, removing polyps;
- insufficiently detailed filming of the stomach walls;
- the high cost of the study, mainly due to the disposable capsule.
Anesthesia and sedation
If performing gastroscopy is difficult due to the psychological status of the patient or the presence of epilepsy or organic diseases of the central nervous system, then the study is best carried out under sedation or intravenous anesthesia.
For everyone else, this may be a good way to get through the procedure without unnecessary worry and stress. Sedation for EGD is widespread throughout the world. Read more about it in our article.
General anesthesia is often used in young children, which makes the procedure easier tolerable and easier.
How to check the stomach and intestines quickly, cheaply and informatively?
There are several types of examination of the intestines and stomach, but only ultrasound diagnostics has a full range of advantages, which doctors consider invaluable and very effective in making a diagnosis.
- An ultrasound can be done urgently for any patient’s condition. The examination will take a maximum of 15-30 minutes.
- Ultrasound diagnostics are carried out painlessly, without causing psychological discomfort. Unfortunately, other methods of examining the gastrointestinal tract require very unpleasant procedures - swallowing tubes, inserting sharp instruments into the anus, sometimes to a considerable depth, ingesting liquids that cause vomiting, etc.
- Ultrasound is completely safe. The method is based on echolocation and does not require the use of X-ray and MRI equipment.
- This is one of the cheapest examinations. An examination of the gastrointestinal tract along with the rest of the abdominal organs will cost around 1 thousand rubles.
With all this, this technique is sometimes even more informative than other methods of examining the stomach and intestines. For example, unlike the endoscopic diagnostic method (using probes that are inserted inside), ultrasound reveals intestinal inflammation, thickening and protrusion of the walls, stenosis (expansion of the lumen), abscesses, fistulas, congenital anomalies (Crohn's disease), neoplasms in the early stages of development diseases.
When to see a doctor?
One to two days after your gastroscopy, you may experience a sore throat or discomfort in the abdominal area. Such minor illnesses are the norm.
You should contact your gastroenterologist immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe chest or abdominal pain;
- Defecation with black stool (a sign of bleeding);
- Constant vomiting or vomiting blood;
- Dyspnea;
- High temperature (38°C or higher).
If you need advice from a professional gastroenterologist, contact us.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
What can be replaced?
If the patient has contraindications to FGDS, the doctor prescribes an examination using alternative methods. It is considered advisable to combine several diagnostic procedures to obtain more accurate data and prevent errors at the diagnostic search stage.
Sometimes patients themselves look for an alternative to gastroscopy, experiencing discomfort or fear of the study. In such cases, it is better to coordinate your actions with your doctor and choose a diagnostic method together . After all, to make a diagnosis in each case, a different amount of examination may be required. Below we list the main alternative studies and briefly discuss each of them.
Anesthesia, anesthesia for gastroscopy
An aerosol (spray) containing lidocaine is used to relax the throat (local anesthesia). If you have previously had an allergic reaction to lidocaine, be sure to tell your doctor or nurse. You will be informed about the possibility of sedation/anesthesia during registration for gastroscopy or consultation with a gastroenterologist.
Gastroscopy is rarely indicated in young children, but if indicated, sedation and anesthesia are strongly recommended due to the lack of self-control in infants.
- Sedatives cause drowsiness and relaxation during the procedure. Patients pay less attention to unpleasant sensations and often simply forget about them (a side effect of the drug).
- Anesthesia induces sleep. An anesthesiologist is involved in this procedure.
Anesthesia during gastroscopy
For many, gastroscopy goes smoothly and without drugs. But for particularly sensitive people who cannot hold their breath during the procedure, the examination is very poorly tolerated - in this case, sedation and anesthesia become a real help for both the patient and the doctor. Sedation is also indicated for patients with panic attacks.
Since the effects of the medication will be felt for some time after the procedure, it is strongly recommended that the patient be accompanied by a relative. Health monitoring is also required in the next 24 hours. During this period you can neither work nor drive a car.
Although you may feel great and be able to do everything on your own, the reaction time after the effects of sedatives is much slower, so not only for your own safety, but also for the safety of others, it is important to follow the recommendations.
In what cases are there no analogues?

- gastrointestinal bleeding (vomiting "coffee grounds" or black stools);
- bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus (bloody vomiting);
- foreign bodies in the esophagus or stomach.
This is due to the fact that in such cases FGDS is performed not only for diagnostic purposes, but also for therapeutic purposes. it is not possible to eliminate the problem using other methods , it is impossible to replace the procedure.
It is also important to perform gastroscopy in patients with suspected gastric cancer and the need for a biopsy . After all, the patient’s management tactics depend on the results of the study.