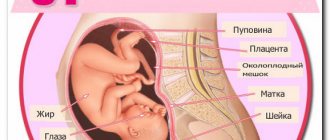
To assess the course of pregnancy and embryogenesis, there are many important criteria, one of them is the weight of the fetus.
The child’s weight is determined using an ultrasound examination; certain values are used for this:
- head circumference (HC) and abdominal circumference (AC);
- biparental size (BPD);
- fronto-occipital dimension (OFD);
- coccygeal-parietal size (CRL);
- thigh length (FL);
- diameter of the fertilized egg (internal, GS).
Let's consider what the normal weight of the fetus should be and how it is determined.
Mass factor
The weight of the fetus changes weekly and each week has its own average norms. Based on fetal weight gain, the doctor can assess the risks of pregnancy complications and identify developmental abnormalities. If the doctor suspects a violation of embryogenesis, then for confirmation and control a repeat diagnosis will be scheduled in a week or two, after which a specific diagnosis will be made and adequate measures will be taken to preserve the pregnancy, or termination will be proposed in the event that the developmental disorders of the fetus are incompatible with its life.
Of course, with such a development of events, not only weight, but also other parameters are taken into account. A deviation upward or downward indicates fetal hypoxia, exposure to external and/or internal pathogenic factors, lack of nutrients, lag or arrest of development. Therefore, by observing and monitoring the child’s weight over time, the doctor can detect the reason for underweight or overweight relative to the average normal values.
This indicator depends on the following factors:
- The functioning of the feto-placental complex, on which the child’s nutrition also depends. With premature aging of the placenta, feto-placental insufficiency develops, blood circulation in the placenta and uterus is disrupted, and the delivery of the nutrient medium for the development of the embryo is disrupted, which can result in its malnutrition.
- Poor nutrition of the expectant mother, deficiency of microelements and vitamins in the diet.
- Experiencing frequent stress during pregnancy.
- Chronic diseases of the pregnant woman, especially diabetes or obesity. Insulin affects protein metabolism; increased levels of this hormone are a factor in stimulating intrauterine growth of the child.
- Severe toxicosis.
- Maternal alcohol consumption, tobacco smoking.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Age of the pregnant woman.
- Lifestyle of the expectant mother, living conditions, including environmental conditions.
- Number of children carried.
None of these values necessarily mean you have a weight problem, they are just influencing factors.
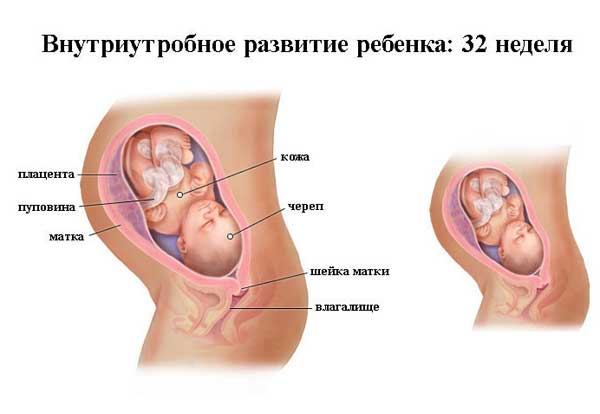
with the correction of which (if possible), the baby will develop correctly and gain the normal amount of grams.
It is believed that boys are larger than girls during intrauterine development. It is impossible not to take into account the constitution of the parents, as well as the presence of extra pounds on the mother when making calculations. Most often, children of obese mothers have less weight than women with normosthenic physique. Also, thanks to many years of observations of pregnant women, it was noticed that in women taller than 1.64 m, children are 200–300 grams larger than in women shorter than 1.58 m.
With repeated pregnancies, children are also larger by about 200 grams than during the primary gestation. Often the baby’s parameters coincide with those of the mother or father at the corresponding stage of development.
Normal weight gain in different trimesters
It is believed that acceptable weight gain during pregnancy should be calculated individually. The value of the increase can be influenced by the initial weight and age, bad habits and even belonging to a certain race. Typically, the average is an increase of 9 to 11 kg. Only a doctor can give more accurate values for the recommended weight gain, taking into account the characteristics of the pregnant woman’s body and body mass index (BMI)1.
- The first trimester is characterized by slight weight gain. Some women may even lose weight, which is associated with toxicosis. A weight gain of 1-2 kilograms is considered normal.
- The second trimester will no longer go unnoticed; the increase will be obvious. Toxicosis and constant fatigue cease to torment, and certain food preferences appear. Gaining 1 kg monthly during this period is considered normal.
- Just before giving birth, the expectant mother can see that she has become 11-16 kg larger. These numbers are considered normal. If a woman is expecting twins, the figure may increase to 21 kg.
Warning signs during pregnancy are a rapid jump in weight (sharp gain) or a complete lack of weight gain. Weight loss in the second or third trimester carries risks for the health of the mother and fetus. During this period, the baby growing in the womb simply needs nutrients, and their lack can lead to pathologies and lack of body weight.
Change by week
The baby in the mother's womb gains weight very quickly. At 7–8 weeks, the unborn baby weighs about 1 gram, this is not enough to track its size, but from this period the weight begins to grow rapidly. From the 15th week, after the internal organs of the fetus have formed, active development of the brain begins, while weight gain slows down slightly.
In the second trimester, the weekly increase is about 80 grams. Weight begins to rapidly increase again from 28–30 weeks. During this period, the weekly increase rate is up to 300 grams. As the baby grows, the uterus increases significantly, which before birth can reach 1200 grams (length up to 40 cm), in the early stages - up to 60 grams (length up to 8 cm). The ideal figure for a newborn is 3100–3600 grams.
You can find out the weight of the fetus by week of pregnancy from the table:
| Weeks of pregnancy | Approximate length of the child, centimeters | Approximate fruit weight, grams |
| 7 | 3 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 9 | 7 | |
| 10 | 9 | |
| 11 | 4,1 | 11 |
| 12 | 5,4 | 19 |
| 13 | 7,4 | 31 |
| 14 | 8,7 | 52 |
| 15 | 10,1 | 77 |
| 16 | 11,5 | 118 |
| 17 | 13 | 160 |
| 18 | 14,2 | 217 |
| 19 | 15,3 | 270 |
| 20 | 25,8 | 345 |
| 21 | 26,7 | 410 |
| 22 | 27,8 | 506 |
| 23 | 28,9 | 607 |
| 24 | 30 | 733 |
| 25 | 34,6 | 844 |
| 26 | 35,6 | 969 |
| 27 | 36,6 | 1135 |
| 28 | 37,6 | 1319 |
| 29 | 38,6 | 1482 |
| 30 | 39,9 | 1636 |
| 31 | 41,1 | 1779 |
| 32 | 42,4 | 1930 |
| 33 | 43,8 | 2088 |
| 34 | 45 | 2248 |
| 35 | 46,2 | 2414 |
| 36 | 47,4 | 2612 |
| 37 | 48,6 | 2820 |
| 38 | 49,8 | 2992 |
| 39 | 50,7 | 3170 |
| 40 | 51,2 | 3373 |
The weight of the child by week of pregnancy in this table is average and approximate, since many factors influence changes in fetal weight, and certain criteria must be taken into account when making calculations. In the early stages, the range of values is the same for almost all embryos; a noticeable difference occurs at later gestational stages.
Body length (height)
The growth process is subject to the following laws:
- An increase in body length reflects the harmonious development of the organism as a whole. Slow skeletal growth is always accompanied by slower development of muscles and internal organs.
- With age, the growth rate decreases. It occurs most intensely in the womb.
- The child grows in leaps and bounds, which alternate with weight gain.
- The parts of the body that are farthest from the head grow fastest, which makes the body proportional.
You can also measure your height at home. To do this, the baby's shoulder blades, heels and sacrum must be pressed tightly against a hard surface. You may need to press lightly on your knees to straighten your legs. The measurement is made with a tape measure or centimeter. In medical institutions, height meters are used for this.
Table of a child’s physical development by month up to one year (height gain):
| Age, months | Monthly height increase, cm |
| 1−3 | 3 |
| 4−6 | 2,5 |
| 7−9 | 1 — 2 |
| 10−12 | 1 |
The centile table of monthly growth of boys under 1 year in centimeters looks like this:
| Age, months/centile | 3 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 |
| 0 | 46.5 | 48.0 | 49.8 | 51.3 | 52.3 | 53.5 | 55.0 |
| 1 | 49.5 | 51.2 | 52.7 | 54.5 | 55.6 | 56.5 | 57.3 |
| 2 | 52.6 | 53.8 | 55.3 | 57.3 | 58.2 | 59.4 | 60.9 |
| 3 | 55.3 | 56.5 | 58.1 | 60.0 | 60.9 | 62.0 | 63.8 |
| 4 | 57.5 | 58.7 | 60.6 | 62.0 | 63.1 | 64.5 | 66.3 |
| 5 | 59.9 | 61.1 | 62.3 | 64.3 | 65.6 | 67.0 | 68.9 |
| 6 | 61.7 | 63.0 | 64.8 | 66.1 | 67.7 | 69.0 | 71.2 |
| 7 | 63.8 | 65.1 | 66.3 | 68.0 | 69.8 | 71.1 | 73.5 |
| 8 | 65.5 | 66.8 | 68.1 | 70.0 | 71.3 | 73.1 | 75.3 |
| 9 | 67.3 | 68.2 | 69.8 | 71.3 | 73.2 | 75.1 | 78.8 |
| 10 | 68.8 | 69.1 | 71.2 | 73.0 | 75.1 | 76.9 | 78.8 |
| 11 | 70.1 | 71.3 | 72.6 | 74.3 | 76.2 | 78.0 | 80.3 |
| 1 year | 71.2 | 72.3 | 74.0 | 75.5 | 77.3 | 79.7 | 81.7 |
Body length (height) of girls from 0 to 12 months, cm
| Age, months/centile | 3 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 |
| 0 | 45.8 | 47.5 | 49.8 | 50.7 | 52.0 | 53.1 | 53.9 |
| 1 | 48.5 | 50.3 | 52.1 | 53.5 | 55.0 | 56.1 | 57.3 |
| 2 | 51.2 | 53.3 | 55.2 | 56.8 | 58.0 | 59.3 | 60.6 |
| 3 | 54.0 | 56.2 | 57.6 | 59.3 | 60.7 | 61.8 | 63.6 |
| 4 | 56.7 | 58.4 | 60.0 | 61.2 | 62.8 | 64.0 | 65.7 |
| 5 | 59. 1 | 60.8 | 62.0 | 63.8 | 65.1 | 66.0 | 68.0 |
| 6 | 60.8 | 62.5 | 64.1 | 65.5 | 67.1 | 68.8 | 70.0 |
| 7 | 62.7 | 64. 1 | 65.9 | 67. 5 | 69.2 | 70.4 | 71.9 |
| 8 | 64.5 | 66.0 | 67.5 | 69.0 | 70.5 | 72.5 | 73.7 |
| 9 | 66.0 | 67.5 | 69.1 | 70.2 | 72.0 | 74.1 | 75.5 |
| 10 | 67.5 | 69.0 | 70.3 | 71.9 | 73.2 | 75.3 | 76.8 |
| 11 | 68.9 | 70.1 | 71.5 | 73.0 | 74.7 | 76.5 | 78.1 |
| 1 year | 70.1 | 71.4 | 72.8 | 74.1 | 75.8 | 78.0 | 79.6 |
Calculation based on other indicators
To determine the weight of the fetus by week of pregnancy, the most accurate diagnostic method for this case is used - ultrasound sonography. A scheduled examination is carried out three times in each trimester and unscheduled when necessary. Ultrasound allows you to perform fetometry, monitor the progress of gestation, identify the risks of possible complications, and make many other measurements,
determine vital criteria, assess the health of the mother.
There are other methods for calculating fetal weight that are less reliable than ultrasound, but they are still used. So, the height of the fundus of the uterus and the circumference of the abdomen are measured in centimeters, these values are multiplied, and the weight of the child is obtained. The error of the method is up to 200 grams since it is impossible to take into account the amount of amniotic fluid, the constitution of the mother, presentation, and genetic characteristics. This technique can only be used after 32 weeks of gestation.
The website has a convenient service for calculating the baby's weight by week of pregnancy. Several values are entered into special columns and automatic calculation shows the required parameter. The entire operation takes a minimum of time. But using this online form you can only control the required values; the main calculations are made by the doctor during examination and ultrasound examination.
If a woman does not have any special health problems during pregnancy and there are no complications, then the baby’s weight will be normal both during intrauterine development and at birth. If some values do not coincide with the data in the table, then you do not need to draw conclusions yourself; remember that everything is individual and only a specialist can make the final verdict.
Is it possible to increase fetal weight during pregnancy?
If the fetal weight is less than normal, then the first thing the doctor will advise is nutritional correction. A pregnant woman should reconsider her diet; there must be a normal balance of vitamins, trace elements, and minerals. You need to stick to the diet if it is prescribed by your doctor. Many women suffer from swelling and high blood pressure when carrying a child. In this case, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of salt, marinades, sauces, smoked foods, and fatty foods.
The correspondence of a woman’s weight to her gestational age can be calculated using a pregnant woman’s weight norm calculator.
The expectant mother should not drink alcoholic beverages that negatively affect embryogenesis. It is necessary to completely eliminate smoking, which can lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus, which leads to a decrease in its weight. There are nutritional mixtures that are recommended for women during the gestational period. This will help maintain the child’s weight at the proper level in accordance with the deadlines. The main thing that the doctor must find out is the reason for the insufficient increase, to stimulate which the pregnant woman can be hospitalized in a hospital to carry out compensatory therapy.
Useful tips
Many women, upon learning about pregnancy, decide to eat “for two”. This is a blatant misconception. You need to eat not “for”, but “for” two. It is better to give preference to the quality of products rather than their quantity. They should be rich in vitamins, microelements and nutrients. It is better to give up the constant consumption of fried, smoked, too salty and peppery foods. This will avoid problems with metabolism and the appearance of extra pounds.
Of course, you shouldn’t ignore the strong desire to eat something tasty. Sending your husband out in the middle of the night to buy goodies is an important ritual, but it should not be abused. We recommend looking at recommendations for healthy eating during pregnancy.
Pregnancy places a lot of responsibility on the expectant mother, and weight control is an important component of successfully bearing a baby!