Author
Kremleva Yulia Viktorovna
Leading doctor
Candidate of Medical Sciences
Ultrasound diagnostic doctor
until September 30
We're giving away RUR 1,000 for all services per visit in September More details All promotions
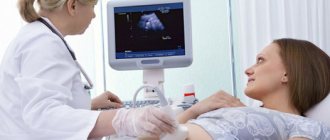
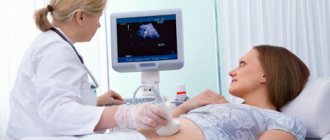
Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs
in women is a modern and informative method used to assess and monitor the condition of the female reproductive system at different periods of life. A pelvic ultrasound includes examination of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
Pelvic organs in women - list
Women usually receive an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs from a gynecologist. Using an ultrasound machine, the doctor determines the condition of tissues in:
- Bladder;
- uterus;
- cervix;
- fallopian tubes;
- ovaries.
It is not only patients who receive ultrasound referrals. Women expecting babies are sent for ultrasound three times during pregnancy. Each trimester has its own control week, during which the doctor is obliged to assess the state of fetal development.
Preparation for the procedure
Before performing a pelvic ultrasound, preparation is simple but necessary. It is recommended to perform the most preliminary actions before the abdominal examination:
- In two to three days (preferably a week), you need to start following a certain diet
- The last meal before the test should be no later than six o'clock the evening before
- It is recommended to use drugs to remove food debris from the intestines or do an enema
All these actions are necessary to avoid the accumulation of gases in the intestines, flatulence and bloating, which will interfere with obtaining the clearest image. If the patient has problems with gas formation or constipation, then he should consult with a doctor about which medications are best to use before the test.
When adjusting your diet before performing an abdominal pelvic ultrasound, you must adhere to the following rules:
- You can eat foods that are easy to digest:
- Porridge
- Low-fat fish and meat dishes
- Hard cheeses
- Boiled eggs or omelet
- Weakly brewed tea
- Vegetables (cabbage, potatoes and others)
- Legumes (beans, corn, peas)
- Milk and dairy products (cottage cheese, kefir)
- Fatty foods, including meat and fish
- Coffee
- Alcohol
- Carbonated drinks
- Fast food and sweets
- Brown bread, pastries
Immediately before the test (an hour), you need to drink half a liter or a liter of water, since a filled bladder provides the best echolocation.
Transvaginal examination does not require special preparation. It should be remembered that before it you need to empty your bladder. It is also important to pay attention to personal hygiene.
This method is not used during monthly bleeding, but if necessary, it can be performed during this period of time.
Transrectal ultrasound requires a bowel movement, which requires an enema several hours before the test. You can use cleansing preparations the day before (you should consult your doctor about this).
It is usually carried out with an empty bladder, but in some cases it may be necessary to fill this reservoir with urine (investigation of the causes of infertility, erectile dysfunction). Then before the analysis you need to drink about 4 glasses of water or other unsweetened and non-carbonated liquid.
Before any of the studies, it is not recommended to smoke, take alcohol or other toxic substances.
Features of ultrasound examination
Using an ultrasound machine, a specialist can only assess the condition of non-hollow organs, that is, those that are not empty inside. In this connection, it is necessary to provide additional consultation to patients regarding the condition of the bladder. So, if you want to examine its walls for chronic cystitis or other pathology, you need to fulfill a mandatory condition - to carry out a full urinary diagnosis, which is not very convenient for those who suffer from incontinence. In this case, urine will act as a reflection of ultrasonic rays, and the bladder will be examined.
If other organs are to be examined, the bladder should be empty so as not to block the view.
Bladder
It is a muscular organ that, when unfilled, has a sac-like formation, and when filled, it has the appearance of a ball. The volume of the organ can vary, depending on the degree of filling, water load, as well as the frequency of emptying and some health problems.
On average, the volume of the bladder is within 200 ml; when the urination reflex appears, the volume can reach up to 800 ml. In pathological conditions, stretching of the organ is allowed, creating a volume of 1500 ml.
It consists of three components, which are the membranes of the organ:
- This is a serous layer that covers the outside of the organ, and the degree of coverage depends on the filling.
- The muscle layer, which is multidirectional muscle fibers that ensure complete removal of urine from the organ.
- The mucous membrane, which is expelled from the inside of the organ, thereby preventing urine from irritating the structures.
Other components of the organ and their work:
- The organ receives two ureters that connect the kidneys and bladder. They carry secondary urine, which accumulates in the organ and is subsequently removed to the outside.
- The urethra also emerges from the organ. It is through this that urine is removed into the environment. The female urethra has some features compared to the male one. This is largely due to the structural features of the pelvic organs, as well as the genital organs. In the female body it is wider and shorter.
- As the organ fills, the uterus gradually shifts relative to its physiological location. If the uterus is located in a typical position, tilted anteriorly, then when the bladder is full, it tends to straighten.
- In front of the bladder is the symphysis pubis , which is a bony structure, and behind it is the uterus. There may be intestinal loops on the sides. Below is the urogenital diaphragm.
The main function of the bladder is to create a reservoir that allows urine to accumulate in its cavity, preventing its constant removal into the environment. It also removes urine from the body.
What does a pelvic ultrasound show?
Using ultrasound you can determine:
- The position of the organ in the pelvic cavity: is it displaced?
- What are the dimensions of the organ?
- Is it properly developed? Are there any anomalies in shape or size?
- Myometrial structure.
- Endometrial thickness.
- Presence of scar tissue.
- Dinu and width of the cervix.
- Condition of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- Presence of fertilized egg.
- The presence and absence of fetal development pathologies.
The simplicity and safety of this type of research has deservedly made this method one of the most popular.
Rectum
This is the final section of the digestive tract. This organ is located in the pelvic area, nearby there are neuromuscular and vascular fibers. In front of the rectum are the vagina and uterus, as well as the ovaries.
Due to this close arrangement, problems associated with the rectum or uterus can imitate each other, which sometimes complicates the clinical picture.
Structure of the rectum:
- This organ has the shape of a cylinder and, relative to other parts of the digestive tract, is a significantly expanded formation. That is why one of the sections of the rectum is also called ampullary.
- Their wall consists of muscle fibers of various directions, most of them are circular muscle fibers, and also to a small extent longitudinal. They perform the main function of the organ.
- The rectum, as a pelvic organ, has a high degree of blood supply.
- Particular importance is given to the final part of the rectum - its sphincter. It has some of the most powerful circular muscles.
The rectum as an organ has few functions, among which the main one is the removal of feces from the body into the environment:
- Products of nutrient processing after passing through the overlying sections of the large intestine accumulate in the ampullary section of the rectum.
- After the accumulation of the required amount of feces occurs, a reflex irritation of the organ occurs, creating an evacuation reflex.
Are there any restrictions for ultrasound diagnostics?
When a woman suffers from pain during menstruation, or her cycle is unstable for a long time, the gynecologist gives a referral for an ultrasound. To obtain information about the condition of the fallopian tubes and follicles, it is important to conduct the examination on days 5-7 from the first day of the cycle, that is, from the day of menstrual bleeding.
But if you want to find out the cause of problems with conception, research must be carried out at least three times:
- from the 8th to the 10th day from the beginning of menstruation;
- from the 14th to the 16th day from the first day of bleeding;
- from the 22nd to the 24th day of the cycle.
For pregnant women, there are also certain time frames for assessing the condition of the fetus. Conducting an ultrasound examination at other times is not considered informative. Each trimester of pregnancy has its own weeks for diagnosis:
- from 10th to 14th week;
- from the 20th to the 24th week;
- from the 30th to the 34th week.
If there are suspicions of pathologies, the number of studies can be increased to determine the condition of the fetus over time.
Prevention
In many cases, in order to avoid complications from the pelvic organs, preventive measures should be followed, which consist of several rules for lifestyle changes.
Among them are:
- Regular visits to a specialist to prevent the development of diseases of the pelvic organs. As well as timely treatment in the event of complaints punishable by damage to these parts of the pelvis.
- Preventing the occurrence of infectious or nonspecific inflammatory processes. To do this, measures should be taken to protect sexual intercourse, especially with unverified persons. The only method of protection at present is a condom, which protects the body from germs entering it from the male genitals.
- Compliance with personal hygiene measures and timely treatment of chronic diseases not only of the pelvic organs, but also of other body systems.
- Prevention of hormonal disorders. To do this, first of all, you should take a responsible approach to issues of contraception. It is the termination of pregnancy that leads to serious hormonal disorders, including the development of inflammatory complications. That is why every woman should pay great attention to the condition of the pelvic organs and maintaining their health.
What does a pregnant ultrasound tell you?
Pregnant women can refuse a routine examination with an ultrasound machine, but this is not recommended, because this painless type of diagnosis allows you to find out about very important changes in the child’s body, in particular, whether he has Down syndrome. According to the regulations of conduct, a medical worker is obliged to notify future parents about a serious genetic disease that entails disability from birth. In this case, the woman is given a complete plan of action if she decides to terminate the pregnancy. The antenatal clinic is obliged to provide all necessary medical care, regardless of the long period of time.
If there is a risk of miscarriage, the gynecologist will monitor the condition of the cervical canal, the length of the cervix and the location of the placenta.
Additionally, ultrasound can easily detect oligohydramnios, as well as:
- quality of blood flow, its intensity;
- location of the umbilical cord for entanglement;
- fetal heart rate;
- fetal presentation.
With the help of a modern three-dimensional imaging system, the expectant mother can see the face of her unborn child, which always cheers up a pregnant woman.
Survey results
Based on the image displayed on the screen, the doctor explains the results, makes a diagnosis and assesses the size of the organs and their echogenicity. A full conclusion is made only by a specialist who examines the size, location of the female organs, and determines whether there are follicles, formations, or stones. After the procedure, the doctor explains in writing or orally all the information about the compliance of the size of the internal organs with the standards, their condition and the presence of formations. If there are deviations from normal values, this indicates the presence of diseases. Lumps that are detected during examination can diagnose cancer. If round structures appear on the image, this may indicate the presence of cysts. Changes in the size of internal organs occur with polycystic disease, and deviations in echogenicity indicate the presence of fibroids.
At the same time, as mentioned above, only a specialist can accurately diagnose the disease. The result of the ultrasound is provided on a photo card or disk, at the request of the patient. A pelvic examination protocol is also provided. The procedure is painless, with its help you can determine the presence of diseases and find out about pregnancy. A pelvic ultrasound is a mandatory procedure for every woman, but for correct diagnosis you need to choose a qualified specialist!
Ultrasound methods
There are two types of sensors that are used for research. One is called transabdominal. It is enough for a specialist to apply it tightly to the body so that the ultrasound waves begin to show the internal organs.
Another type of sensor is called transvaginal. Based on the name, it is easy to guess that it is inserted into the vagina to look at the organs from a different angle. To conduct such a study, the doctor places a condom on the sensor to ensure sterility. Budgetary institutions often ask patients to buy it for themselves if the deposited funds are not enough to provide the office with consumables.
In addition, there are stationary and mobile devices. Ultrasound diagnostic rooms are equipped with stationary ones. The doctor can take the mobile device with him to visit patients at home. Modern ambulances are also equipped with such equipment.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- MEDSI clinics use modern ultrasound equipment for all types of ultrasound examinations (more than thirty types)
- All devices are certified and suitable for patients of any age and gender
- Doctors of the highest qualification categories will interpret the results and make the diagnosis most accurately, and will also help prepare for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs
- Clinics are conveniently located in all districts of Moscow - more than twenty diagnostic centers
- If necessary, an emergency examination can be carried out
If you experience sudden bleeding or pain in the abdominal area, do not hesitate and consult a doctor - phone 8 (495) 7-800-500.
How the study is conducted and what you need to know
Carrying out diagnostics, as a rule, does not require special preparation, with the exception of the condition of the bladder, which the doctor will warn you about in advance. When a patient enters the office, she should remember that it is advisable to turn off her mobile phone during the examination.
After presenting her documents to the doctor, the woman can go to the couch. If the examination is carried out with a transabdominal sensor, it is not necessary to undress completely - you just need to lower your pants or lift your dress so that the lower abdomen is free from clothing.
When examined with a transvaginal probe, the patient must completely remove pants, tights and underwear. Her position on the couch is lying on her back with her knees bent.
It should be noted that neither one nor the other sensor causes any discomfort. The procedure is completely painless.