Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is a modern, safe and highly informative method for diagnosing diseases of internal organs. It is based on the ability of soft tissues to reflect sound waves that are generated by the device and sent down by a special sensor. The procedure is absolutely painless and can be used from the very birth of the baby. Specialists at the Profimedica clinic perform ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs for children of any age. Preparing a child for an abdominal ultrasound is one of the stages of a quality examination. Our doctors explain in detail to parents exactly how to prepare their baby to obtain the most accurate test results.
Is it necessary to prepare a baby before an abdominal ultrasound?
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, as well as preparation for examination of a child, are interdependent concepts. Carrying out high-quality diagnostics of the abdominal organs involves temporary fasting before the procedure. Depending on the patient’s dietary habits, it is necessary to refuse to eat:
- 3 hours in advance for newborns and breastfed infants;
- in 3.5-4 hours for babies on artificial formulas.
Children under 1 year old eat frequently. To minimize the baby's discomfort, it is recommended to plan a visit to the doctor so that an ultrasound examination of the abdomen is carried out immediately before the next feeding. This increases the information content of the procedure, which is easier to tolerate.
Progress of the procedure
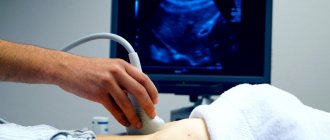
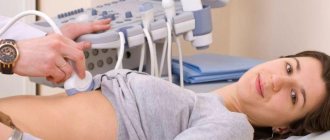
This ultrasound is performed on children in the same way as on adults. The child needs to open the abdominal area (it is advisable to come in clothes that allow this to be done easily, that is, not a jumpsuit, not a bodysuit, etc.). The sonologist will apply a special hypoallergenic gel to the tummy and move the sensor over the desired areas. The child will need to turn on his right side and then on his left side at some point. An older child will be asked to inhale and not breathe for a while. The examination itself is painless; if pain or discomfort occurs during the procedure, this also indicates diseases of the internal organs in this area.
Children from 1 year of age: preparation for abdominal ultrasound
The preparation of young patients over the age of one year includes several more restrictions. During this period, it is important not only to avoid eating before the procedure, but also to monitor the baby’s diet over the last 2-3 days. Eating foods that increase gas formation and stimulate intestinal motility may distort the results of the examination.
What should you avoid?
In order to prepare your child for the procedure using ultrasound of the abdominal organs, 2-3 days before diagnosis, it is recommended to exclude the following foods from the diet:
- fresh grapes;
- legumes;
- cabbage;
- onion;
- mushrooms;
- Jerusalem artichoke;
- whole milk;
- carbonated drinks.
Children aged 3-4 years and older should also avoid eating fried foods. These products stimulate increased gas formation and intestinal motility. This reduces the diagnostic information content. The distended colon displaces adjacent structures, making visualization difficult.
Additionally, you need to refrain from eating 4-8 hours before the procedure. The older the little patient, the longer he can go without food. It is advisable not to drink water 1 hour before the examination.
Products permitted before testing
In preparation for an ultrasound, the child is switched to a light diet. You are allowed to eat simple, easily digestible food. Doctors at Profimedica recommend paying attention to the following products that are approved for consumption:
- porridge cooked in water;
- boiled fish (low-fat) and chicken;
- boiled chicken eggs;
- dairy products.
High-quality preparation for the examination is an important aspect of a full diagnosis. Following simple rules increases the information content of ultrasound examination. This is the key to establishing the correct diagnosis and allows, if necessary, to quickly select adequate treatment for diseases of the abdominal organs.
Types of research
Classic ultrasound of the abdomen gives a detailed idea of the size, structure of parenchymal and hollow organs. An ultrasound is performed:
- Liver;
- Pancreas;
- Spleen;
- Ultrasound of the bladder;
- Gallbladder with definition of functions;
- Small intestine;
- Large intestine;
- Gallbladder;
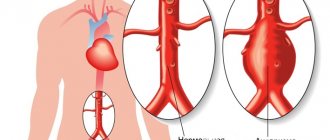
- Abdominal aorta;
- Intestines;
- Stomach.
The method is completely safe and does not cause discomfort or pain. You can undergo an ultrasound as prescribed by a doctor or at your own request if there are disturbing symptoms. Compared to other diagnostic procedures such as CT and MRI, ultrasound diagnostics are cheaper, faster, simpler and do not use ionizing radiation.
Ultrasound of the liver
The doctor prescribes a liver examination if there are certain symptoms that may indicate that the patient is not well. Among them is discomfort in the right hypochondrium, which manifests itself more strongly after drinking alcohol, fatty foods, smoked and fried foods.
A signal to perform an ultrasound of the liver may be a lump detected during palpation - this may be a tumor, the exact location of which and its inherent signs will be identified by the doctor using ultrasound. It is important to undergo an examination after a course of therapy if hepatitis and other diseases are detected.
Ultrasound of the pancreas
Sonography makes it possible to identify the size of an organ, its inherent shape, and the presence of changes in structure and structure. Attention is paid to the location of the pancreas relative to other structures and vascular formations. If pathological changes are identified, the study expands the boundaries, and the question arises of using additional diagnostic methods.
Inflammation of the pancreas can manifest itself in reduced size of the organ if it becomes chronic. This may also be indicated by excessive tissue scarring and calcifications. Cysts formed in the structure of the organ are reflected during examination as compacted areas with clearly defined boundaries.
Ultrasound of the spleen
Prescribed when liver pathologies are detected. And also if there is a suspicion of injuries resulting from falls, mechanical shocks and bruises. Indications for the procedure include leukemia, the formation of compactions and tumors, diseases of an infectious nature (syphilis, tuberculosis, sepsis).
For the examination, the patient is placed on his back. A special gel is applied to his stomach, on which the ultrasonic signal transducer glides more easily. The session takes 15 minutes, and the results are immediately available. For better visualization, the doctor may ask the patient to turn on their side or assume another position that makes it easier to view.
Ultrasound of the bladder
The reason for performing an ultrasound of the bladder may be a long-term change in the color of urine, which is not associated with eating foods and medications that can affect its tone. The doctor should be alerted to the patient's complaints about pain and discomfort when urinating, the release of a small amount of fluid with frequent urge to go to the toilet.
It is recommended to undergo an examination if pain appears in the suprapubic region, bloody discharge in the urine and flakes visible from the side in the liquid. As a result of viewing the internal structures, stones, foreign bodies in the organ, neoplasms and other anomalies may be detected.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of functions
The procedure is preceded by a trial choleretic breakfast, with the help of which it is easier for the doctor to examine the organ. The study is carried out in several stages, when after 10-15 minutes a specialist examines the organ with ultrasound at rest and after exercise. The patient is asked to lie on his back, and when necessary, move to his side, on all fours, or stand up straight.
Ultrasound of the bile duct shows whether cholecystitis or cholelithiasis exists, and reveals biliary dyskinesia. A quick and painless examination reveals five degrees of abnormality. Such accuracy allows you to subsequently draw up a competent therapeutic protocol and achieve good results in the treatment of the disease.
Who interprets the research results and how to obtain them?
An ultrasound diagnostic specialist will analyze and interpret the images obtained during the study. He will prepare a medical report for the pediatric specialist who referred you for an ultrasound scan. In some cases, additional research and consultations with other specialists may be required. Your doctor will explain the exact reason for this need, if it arises. You may also be advised to have repeated ultrasound examinations to determine the effectiveness of treatment or to monitor your child's condition.
How will the child be positioned during the procedure, and how will he feel?
During the abdominal scan, your child will lie comfortably on a couch, face up, next to the ultrasound machine. The doctor may ask you to turn the child on his side if it is necessary to check an organ adjacent to the side (liver, spleen, stomach, kidneys).
Ultrasound examinations are painless and easily tolerated by most infants and children. The child will feel warmth and slight pressure from the device’s sensor moving across the gel-lubricated skin. He will also hear pulsed sounds emitted by the sensor. Once the examination is completed, the gel will be gently removed from the surface of the skin using regular wipes. An ultrasound examination usually lasts about 30 minutes.
The procedure does not disrupt the child’s daily routine in any way. If the doctor did not identify any pathologies and did not give special recommendations, then after the ultrasound you can do normal activities, walk, attend clubs, school, play sports, eat, etc.
Advantages of ultrasound over other examination methods
The safety of ultrasound does not involve radiation exposure to the body and has no absolute contraindications. If necessary, the examination can be carried out several times in a row in a short period of time.
Painless ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic method that does not require the use of painkillers. The procedure is quick and does not cause any discomfort to small patients.
Efficiency
With the help of ultrasound, you can literally examine the brain, internal organs, joint-muscular apparatus, that is, all the main structures of the body, in just half an hour. A high-tech diagnostic method allows you to detect even minor deviations from the norm.
In what cases is abdominal ultrasound used?
- First of all, ultrasound scanning of the abdominal organs is performed as a preventive examination in the postpartum period. This is necessary to assess the condition of the baby’s internal organs, including their location, size, structure, to exclude congenital diseases and developmental abnormalities
- Preventive ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity of a newborn is mandatory for children who were at risk of receiving a birth injury, after a difficult birth, or cesarean section.
- An abdominal ultrasound, if indicated, is performed to diagnose the cause of pain or colic in a child’s tummy, which may be caused by a hernia, intestinal obstruction, pancreatitis, gallstones or kidney stones, abscesses or appendicitis.
- the procedure can help determine the causes of regurgitation in children
- Using ultrasound diagnostics, you can also determine an increase in the size of the abdominal organs, detect the accumulation of fluid in the tummy, and gas retention in the intestines
- Ultrasound helps guide other types of examinations when a medical instrument must be precisely positioned in the part of the body being examined (for example, when taking a tissue sample)
- Doppler ultrasound is a research method that is used mainly for diagnosing vascular pathology of the abdominal organs. It helps the doctor see and evaluate
- blockage of blood flow (for example, blood clots),
- vasoconstriction,
- congenital vascular malformations,
- decreased or absent blood flow in various organs,
- increased blood flow to certain areas in inflammatory diseases,
- testicular torsion, leading to decreased blood flow.
Indications for the study
Immediate ultrasound is required for abdominal pain, prolonged nausea, vomiting, bloating, unexplained weight loss, injury, fever of unknown origin. Ultrasound diagnostics is prescribed as part of a set of measures when identifying a tumor to clarify its nature.
Ultrasound is an imaging method. It is often resorted to when a biopsy is necessary, but the organ is located deep. In this case, it is necessary to view the structures of the abdomen and the needle placed in it, aimed at taking biological material, which is later sent for histological and cytological analysis.