- Home >
- Directory >
- Which MRI should I do for headaches?
Do you suffer from frequent and debilitating headaches?
Don't put off visiting your doctor! Headaches do not always indicate serious and dangerous diseases, but such a possibility cannot be ruled out. To detect such a pathology or confirm its absence, the doctor may prescribe you an MRI - a modern and effective diagnostic method that can detect the smallest foci of pathology!
If you have any questions, ask our specialist! Ask a Question
Types of MRI for headaches
The first MRI for headaches will probably be an MRI of the brain. An MRI of the cervical spine may also be needed: this is where the cause of migraines sometimes lies, sometimes accompanied by dizziness and nausea.
Which MRI do you need to undergo? Only a neurologist can answer this question. A visit to a specialist will not only bring you closer to recovery, but will also help you save money if another study is indicated for you - for example, ultrasound duplex scanning of blood vessels.
By diagnostic area
Types of MRI examinations are divided depending on which part of the body is being diagnosed. The following groups are distinguished:
- Head and neck. Includes examination of the brain, pituitary gland, head as a whole, including the cervical spine, and thyroid gland. It also allows you to assess the condition of the optic nerve, auditory nerve, and pathology from ENT practice.
- Bones and joints. Makes it possible to identify arthritis, joint tumors, tendon ruptures, and ligament damage. Depending on the indications, specific joints are examined.
- Abdomen. Allows you to determine the condition of the liver and kidneys, spleen and gall bladder, ducts, intestines, mediastinum and lymph nodes.
- Small pelvis. It is especially often prescribed in gynecology and surgery to detect adnexitis, endometriosis, and bleeding of unknown etiology. In men, the procedure is indicated for vesiculitis, scrotal tumors, and prostate diseases.
- Spine. Allows you to separately assess the condition of all parts of the spinal column. Necessary for injuries, neoplasms, circulatory disorders.
- Rib cage. Includes examination of the heart, lungs and bronchi, and mammary glands. When assessing the heart, the condition of the valves and blood vessels is determined, and anomalies are identified.
- Vessels. A particularly informative examination method. Allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels in the brain, in the cervical region, in individual organs, as well as coronary vessels. Contrast is used if necessary.
Very rarely, depending on the indications, a whole body examination may be used.
What does a brain MRI show?
MRI of the brain, the main type of MRI for headaches, will help identify the cause of the pain, which lies in the brain itself. It can be:
- Cerebrovascular accident
- Damage to brain tissue after injury, oxygen deprivation
- Inflammation of the frontal sinus
- Meningitis
- Benign and malignant tumors
These pathologies can cause painful headaches, and they need to be identified as early as possible: some of them are deadly, and early diagnosis significantly increases the chances of a successful recovery! Take care of your health! Schedule an MRI of the brain today!
What are the different types of MRI of the brain?
The objectives of the study are clarified by a specialist (attending physician, radiologist). The differences between types of brain MRI are determined by the region of interest. The quality of the images depends on the power of the tomograph. Performing diagnostics on open devices is not so informative. Minor changes may not be noticeable in images. Closed medium- and high-field tomographs provide highly detailed images. Doctors recommend studying the structures of the brain and cerebral vessels using devices with a magnetic field strength of at least 1.5 Tesla.
The need for contrast enhancement is determined by the attending physician or radiologist. During native examination, pathological changes may not be visible in sufficient detail. To draw conclusions about the nature and characteristics of the development of abnormalities, the radiologist uses various MRI modes. Contrast enhancement is recommended in controversial situations. The attending physician prescribes tomography with gadolinium preparations if tumors, inflammatory and infectious processes are suspected, if it is important to obtain the most accurate results in the shortest possible time.
To study cerebral vessels, a special angiography mode and contrast are used. MRI is not considered the most informative method for studying arteries and veins, but is used to clarify the diagnosis.
The Magnit DC uses modern high-tech equipment (Siemens tomograph). The clinic's staff includes experienced radiologists who are fluent in the intricacies of MR diagnostics. To make an appointment and receive additional information about the procedure, call +7 (812) 407-32-31.
MRI of the cervical spine for headaches
MRI of the cervical spine will identify or exclude the following pathologies:
- Osteochondrosis
- Spondylosis
These diseases can create pain in the neck and back of the head that radiates to the head.
At the MART clinic on Vasilyevsky Island
- Experienced doctors (including those practicing in the USA and Europe)
- Prices affordable for everyone
- Expert level diagnostics (MRI, ultrasound, tests)
- Daily 8:00 — 22:00
Make an appointment
By type of tomograph
Today, only two types of tomographs are used. An open device is optimal for patients who experience discomfort during a procedure in a confined space. As a rule, it is used for claustrophobia, as well as when examining children. Can also be used for overweight patients.
The closed apparatus is presented in the form of a tunnel. A closed space may cause fear in the patient, but this method is more accurate.
There are different types of MRI and it is important to understand what their differences are. This is especially true for patients who wish to undergo examination on their own without a doctor’s referral. In other cases, the specialist himself prescribes the required type of examination with or without the use of contrast.
Why do an MRI for headaches?
There are other diagnostic methods: laboratory tests, ultrasound... Why do an MRI? The answer is simple: MRI allows you to visualize brain tissue that is inaccessible to other studies, while MRI is absolutely harmless (unlike CT).
Therefore - do not tolerate pain! Make an appointment at the MART Clinic and find out the cause of your discomfort! Experienced doctors, an expert-class open tomograph and affordable prices are at your service!
Sign up at the MART medical center in St. Petersburg (see map) by phone, or leave a request on the website.
By the presence of contrast agent
Traditionally, MRI is performed without the use of a contrast agent. That is, the patient is positioned on the table and scanning begins immediately. Layer-by-layer images are obtained, which are combined into a three-dimensional model.
You can get an even brighter picture through contrast. That is, two types of MRI studies can be distinguished: with and without contrast. The use of a contrast agent makes it possible to examine all vascular structures, identify clots, and also determine the presence of tissues with impaired blood supply. The most commonly used is gadolinium. It enhances the magnetic signal, which improves the quality of pictures.
All substances used for testing can be divided into several groups:
- Substances that are once introduced into the vascular bed in full. As a rule, these are compounds of manganese or iron with oxygen.
- Dosed administration of a substance. Allows you to evaluate the speed of contrast propagation through tissues.
- Oral medications. Used to assess the condition of the digestive organs.
Despite the fact that MRI with contrast has a higher price, the procedure is in demand due to its greater information content.
What to do if you have a headache?
You've probably experienced headaches more than once. If you are reading these lines, perhaps your headache has become more frequent and intensifying? We recommend that you do not suppress recurring headaches with pills taken without a doctor’s prescription, because this will not get rid of its root cause. Remember that self-diagnosis based on articles and advice found on the Internet is of dubious value: firstly, it is not known who exactly wrote the recommendations for relieving headaches - perhaps it was a person who did not have a medical education, and secondly, such Recommendations are always of a general nature and may not suit you due to your individual characteristics.
There is no need to risk your health if you experience frequent headaches; an MRI will make it possible to confirm or exclude a number of different diseases. Don't waste time that can be used for diagnosis. After all, a headache, as we have already found out, can be a symptom of many diseases (some of which often have serious consequences).
And if you still doubt whether you need to do an MRI for a headache, we recommend that you read the article about in what cases MRI and CT of the brain are prescribed.
What will an MRI show for dizziness?

It is fair to wonder why this type of diagnosis is prescribed quite often and is recommended to almost everyone? Meanwhile, this is not surprising, because such a brain scan is much more accurate and safe than x-rays, which have not lost their relevance over many years. After all, there are not many diagnostic methods that do not expose the patient to radiation or any painful intervention in the problem area of the body.
MRI is relevant in cases of frequent headaches, migraine attacks, and sudden loss of consciousness. Sudden, severe disturbances in vision and hearing may also be an indication for tomography. This study will detect the disease even at the earliest stage. A disease that manifests itself in this way can be either a tumor or some completely curable vascular disease.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that the preliminary diagnosis of the doctor and the conclusion of the specialist after the MRI may not coincide. There is no need to panic about this. A reasonable solution would be to consult with a therapist or neurologist based on the conclusion. If the preliminary diagnosis and the final diagnosis have common treatment methods, it is necessary to begin to strictly adhere to them. Everything in the human body is interconnected, and these treatments may well be effective.
When is an MRI prescribed?
During the examination of the head, not only the brain itself is examined, but also the bones of the skull, organs of vision and hearing (after all, the cause of the disease may be hidden in their condition). The volumetric image shows the entire area under study, including problem areas. Based on these data, the doctor draws conclusions about the disease.
As a rule, MRI is prescribed for brain tumors, insufficient development of its areas, blockage of blood vessels, but other diseases may also be detected along the way, albeit less serious, but also preventing one from living a full and peaceful life.
Diagnosis of headache
Diagnosis of headaches is carried out in two or three stages.
At the first stage, a neurologist examines the patient and collects an anamnesis and either prescribes therapy (medication, physical therapy) or resorts to additional consultations with highly specialized specialists (otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist). In the second, the patient may need to undergo a number of examinations, including an MRI. On the third stage, with the help of the examinations, the neurologist receives a complete picture of the identified changes, correlates them with the existing neurological symptoms and clinical picture of the patient and, based on all of the above, prescribes a complete, most adequate treatment. Among modern diagnostic methods that examine the brain, in the vast majority of cases it is magnetic resonance imaging that makes it possible to determine the cause of the headache. MRI of the brain is a leading study in the diagnosis of headaches - this is facilitated by the high contrast of images obtained from magnetic resonance imaging, as well as the ability to scan in three mutually perpendicular planes, which makes it possible to identify any structural changes in the brain, including early stages of their development.
Interesting facts about MRI
| Did you know that... |
| Thanks to the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance, on which the operating principle of the MRI device is based, two Nobel Prizes in physics were received: for NMR in molecular beams (1944) and for NMR in liquids and solids (1952). |
Magnetic resonance imaging is indispensable in identifying tumors of any location and stage. The images obtained by MRI clearly show the size of the tumor, its location (intracerebral, extracerebral), structure (homogeneous, heterogeneous), growth pattern (infiltrative - malignant or expansive - benign), shape and other important data. In addition, MRI most accurately shows the relationship of the tumor with its surrounding structures. Due to the fact that MRI is a completely safe procedure (it does not use harmful ionizing radiation), it is suitable for all patients, including cancer patients.
Thus, to make a clinical diagnosis and plan therapy, a neurologist needs the results of magnetic resonance imaging. MRI for headaches is a diagnostic method that will quickly and painlessly provide a specialist with data about the cause of your headaches.
Causes of headaches
The brain has a very complex structure. Many nerve cells and neural connections are responsible for transmitting impulses and regulating all processes in the body. Cephalgia occurs as a result of tissue compression, oxygen starvation (ischemia), trauma, metabolic disorders, etc. The causes of regular headaches can be:
- migraine;
- tension headaches;
- high or low blood pressure;
- sinusitis, otitis and other infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- brain tumors (benign or malignant);
- degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the cervical spine (osteochondrosis, spondylosis);
- neuroinfections;
- increased muscle tone in the cervical region;
- vascular pathology, etc.
Many other pathologies can manifest as cephalalgia. If you often have a headache without an objective reason, an MRI of the brain will help determine it.
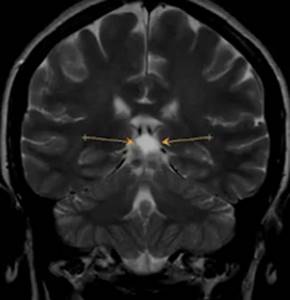
Pineal cyst on MRI as a cause of headache (indicated by arrows)
How is a tomography done?
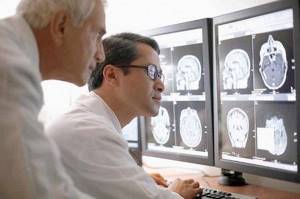
Brain tomography can be performed in two ways - with or without contrast. Contrast is needed when it is already known that the patient has a serious disease - a special substance additionally illuminates the tissue, making it more convenient to observe changes that can often appear during oncology or during the recovery process after complex injuries. The solution is administered intravenously (in addition to it, a sedative may also be administered if the patient is very nervous before the examination. Then the couch with the person lying on it is placed in the turned on tomograph.
And here there is one more nuance - tomography can be carried out in an open specimen, and not only in a closed one. This makes life much easier for people suffering from claustrophobia - the fear of closed spaces. As soon as such a person finds himself in a small enclosed space, panic begins to overcome him: trembling, perspiration appears, the heartbeat quickens and the muscles involuntarily contract. While during this study, the person being examined must be absolutely calm and not make unnecessary movements.
Therefore, such diagnostics are not carried out for those who suffer from mental disorders (even if they do not have active, violent manifestations) or hyperkinesis (this feature often appears against the background of cerebral palsy - the muscles of the face and body are almost constantly in motion, the person constantly twitches and shudders, but he cannot control it).
The examination lasts an average of 40 minutes, after which the patient leaves the office. A few minutes later he is given a report from a radiologist, who usually recommends going to a neurologist to determine measures to monitor his further condition. In some cases, dizziness can be eliminated with medication, but you should always consult a doctor before starting therapy. This rule should not be neglected.
If the case of the disease is too advanced (for example, a patient in the terminal stage of brain cancer with multiple metastases), then tomography can take an hour and a half. You need to be prepared for this and make plans in advance so that there is enough time “with reserve” for the procedure.