The liver may not hurt until cirrhosis. Moreover, every day almost every person deals with risk factors for liver disease. Fatty foods are dangerous. Alcohol is dangerous. Medicines are dangerous. After all, coronavirus is a danger. How can we understand what is happening to the liver if it does not give any signals? We'll talk about this further.
What are ALT and AST in blood biochemistry
Let's look at the abbreviations and find out what enzymes are hidden behind them:
- ALT or ALT – alanine aminotransferase – is an enzyme that is present in the cells of various organs. Most of it is in the liver and kidneys. When organs are damaged, ALT enters the blood. The presence of an enzyme in the red liquid may indicate the development of jaundice. ALT analysis is one of the “liver tests”, the results of which indicate problems with the organ, namely, its destruction. A large amount of enzyme in the blood may indicate not only liver disease. If your ALT level is high, there are likely problems with other organs. We use the words “may”, “possibly” - because ALT analysis is the primary diagnosis. Based on it alone, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis. More research is needed.
- AST or ASAT - aspartate aminotransferase is an enzyme that is found in the greatest quantities in the liver, kidneys, and myocardium. It, like ALT, enters the blood during tissue destruction. An increase in AST is a sign indicating possible liver disease. A complete diagnosis is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis.
Thus, AST and ALT are enzymes that are found primarily in the liver and kidneys in the body. They are involved in the synthesis of many useful substances. If the organs in which aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase are located are destroyed, the enzymes enter the blood. This is revealed through analysis.
What do increased indicators mean?
A significant increase in AST activity is observed in myocardial infarction, insufficient blood circulation, shock, hypoxia, acute viral or toxic hepatitis, necrosis or damage to liver cells.
A moderate increase in AST activity can be detected in liver cirrhosis, obstructive jaundice, metastases, acute pancreatitis, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, with damage to skeletal muscles, after injuries or surgical interventions. In children, protein activity may increase in the presence of inflammatory processes in the body. An increase in aspartate aminotransferase concentrations is sometimes observed during pregnancy.
The use of hepatotoxic drugs or drugs that cause cholestasis (slowdown or complete cessation of bile secretion) can also provoke an increase in AST. Usually this condition is regarded as temporary.
Normal ALT and AST in a healthy person
Indicators differ for people of different genders and ages. More details are described in the tables.
| Patient gender/enzyme | ALT | AST |
| men | up to 45 U/l | up to 37 U/l |
| women | up to 34 U/l | up to 30 U/l |
A child's enzyme levels are constantly changing. They are:
| Age/enzyme | ALT | AST |
| less than 5 days | up to 49 | up to 97 |
| from 5 days to 6 months | up to 56 | up to 57 |
| from six months to a year | up to 54 | up to 82 |
| up to 3 years | up to 33 | up to 48 |
| from 3 to 6 years | up to 29 | up to 36 |
| up to 12 years | up to 39 | up to 47 |
If the patient is older than indicated in the last line of the table, you need to focus on the norms for men and women.
You need to know that there is also the Ritis coefficient, which determines the ratio of enzymes to each other. Normally, it is 1.3 - that is, this is how much less AST in the blood plasma should be compared to ALT.
The Ritis coefficient is useful in identifying myocardial problems. AST is most abundant in this muscle. If the aspartate aminotransferase level approaches the alanine aminotransferase level, then most likely the problem should be looked for in the heart area.
Rules for preparing for research
Liver enzymes are included in the biochemical analysis. The material is taken from a vein in the morning, and the patient must be hungry.
After disinfection of the puncture site of the blood vessel, 5-10 ml of blood is drawn into the syringe. The material is then sent to a laboratory where the plasma is separated from the cells. Using special reagents, the level of transaminases is determined. Analysis answers are issued every other day.
To obtain reliable data, certain preparation guidelines must be followed. These include:
- the interval between food and analysis should be at least 8 hours;
- three days before the study, you should give up alcohol, fatty foods, and limit physical activity;
- In two weeks, you must stop taking medications that affect the liver. If cancellation is not possible, the doctor should take this into account when interpreting the analysis.
In addition, the study is not carried out within three hours after radiography, physiotherapeutic procedures, rectal examination and ultrasound diagnostics.
To keep liver enzyme levels normal, it is recommended to eat healthy, control physical activity, avoid alcohol, and remember to have regular medical checkups.
Symptoms of increased ALT and AST
Signs are divided into primary and late. First, the following manifestations of an increase in AST and ALT occur:
- nervousness;
- itching;
- poor sleep;
- weakness of the body;
- decreased appetite, which leads to weight loss.
Late symptoms:
- darkening of urine;
- stool discoloration;
- yellowish tint to the skin and whites of the eyes;
- swelling of the arms and legs;
- nausea;
- general poor health.
If the primary symptoms can indicate both problems with elevated levels of ALT and AST, and other disorders in the body, then later ones clearly indicate that not everything is in order with the liver. Additional diagnostics are required to make an accurate diagnosis. For example:
- coronavirus test;
- blood test for hepatitis B and C;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- heart diagnostics;
- clinical blood test;
- study of the concentration and quality of thyroid hormones;
- liver biopsy.
If after coronavirus there are elevated levels of ALT and AST enzymes, contact the LaSalute clinic. It has all the necessary equipment to establish an accurate diagnosis, as well as specialists who are involved in the rehabilitation of people who have suffered from coronavirus.
For what diseases besides hepatitis is testing prescribed?
Alanine aminotransferase level testing is carried out if:
- diseases of the hepatobiliary tract, when not only the liver, but also the bladder and bile ducts are involved in the pathological process;
- damage to the pancreas;
- viral hepatitis;
- hemolytic jaundice;
- myocardial infarction;
- cirrhotic liver damage;
- diseases of skeletal muscles (progressive muscular dystrophy, metabolic disorders);
- myocarditis.
For preventive purposes, analysis can be prescribed:
- people who have been in contact with a patient with viral hepatitis;
- donors planning to donate blood;
- those suffering from diabetes;
- obese patients;
- people who abuse alcohol;
- when taking hepatotoxic drugs;
- in the presence of a family history of liver diseases.
Indications for biochemical analysis to determine AST levels include:
- liver diseases (cirrhosis, steatosis, echinococcosis);
- pathology of the circulatory system (hemolytic jaundice);
- heart diseases;
- renal failure;
- icteric syndrome and cholestasis against the background of obstructive jaundice;
- autoimmune diseases;
- encephalopathy to determine the cause of central nervous system dysfunction;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- oncopathology of malignant origin;
- long-term use of hepatotoxic medications (antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs);
- preoperative preparation;
- control over the dynamics of treatment.
A biochemical analysis to determine the level of transaminases is prescribed if there are complaints:
- from the liver, pain in the area of the right hypochondrium, dyspeptic disorders in the form of nausea, vomiting, bloating and intestinal dysfunction (constipation, diarrhea). Yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, spider veins, discoloration of stool, darkening of urine and the appearance of dilated veins in the abdomen may also be observed;
- pancreas pain in the area of the left hypochondrium with irradiation to the lumbar region, repeated vomiting, flatulence, severe weakness and diarrhea as a result of impaired digestion of food;
- heart pain behind the sternum of a burning nature, which spreads to the shoulder blade, arm and neck. It is possible that cardiac arrhythmias and decreased blood pressure may occur. The patient has chills and fear of death;
- skeletal muscles, severe weakness and changes in body shape due to muscle atrophy.
Which doctor should I contact?
You should start by visiting a therapist. This doctor interviews and examines the patient and decides which specialist needs to be contacted. Options:
- Cardiologist, if after Covid the AST level increased more than ALT. This indicates that, most likely, there are problems with the myocardium.
- Endocrinologist, if the virus has negatively affected the liver or kidneys.
Help from other specialists may be required.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. This leads to a worsening of the condition. Then you still have to contact a doctor. But time will be lost. In such a situation, specialists are not always able to help in any way.
How to increase AST
In general, low AST levels in the blood are normal and should not be a cause for concern. Vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to low AST levels, so if you notice a decrease in this enzyme, it is worth knowing your vitamin B6 level.
Older people may be particularly susceptible to low AST levels, as they are often at increased risk of malnutrition. Vitamin B6 supplements tend to help increase AST in older patients. []
Stages of determination and normalization of ALT and AST
A blood test allows you to identify the problem - to establish that the amount of enzymes is not normal. If there is more ALT and AST in the vessels than they should be, it is necessary to undergo a full examination to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Next, you should undergo therapy using the methods outlined by the specialist. In order not to worsen the situation, all medications should be taken exclusively as prescribed by a doctor.
You can undergo diagnostics, determine the level of enzymes in the blood and determine which organs the coronavirus has caused complications at the LaSalute clinic. There is all the necessary diagnostic equipment and experienced specialists work here.
AST functions
Aspartate aminotransferase is one of the key enzymes that catalyzes the reversible transfer of the α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism.
At the macro level, this transport pathway influences the overall metabolism of amino acids and fats (fatty acids). It also plays a partial role in detoxification (urea cycle) and gluconeogenesis. [, ]
At the micro level, a direct chemical reaction that AST accelerates to convert an amino acid (aspartate) and acid (alpha-ketoglutarate) into another acid (oxaloacetate) and amino acid (glutamate). This conversion is vital for other metabolic processes such as the urea cycle, the glucose cycle and breakdown (glycolysis). [, ]
High AST level
One of the main signs of existing health problems is elevated AST levels ( above 40 U/l ). There are a number of physiological conditions and diseases that can lead to elevated AST levels, including:
- Rhabdomyolysis: This is a process of muscle breakdown in the body that causes large amounts of AST to be produced from the muscles. In addition, this process causes the release of protein (myoglobin), which is difficult for the liver to utilize. This situation leads to the production of increased amounts of AST, which increases the value of AST in the blood. Rhabdomyolysis can occur during strenuous exercise. [, ]
- Viral and alcoholic hepatitis is one of the main reasons for the increase in AST in the body. Inflammation of the liver increases the production of AST, and its significant increase in the blood helps to diagnose hepatitis. Long-term alcohol use (alcoholism) can also increase AST. [, ]
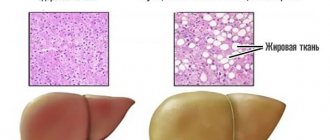
- Fatty liver also leads to increased AST levels, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease ( NAFLD ). Excessive alcohol consumption, together with obesity or separately, can lead to the development of liver steatosis (fatty infiltration, also called liver hepatosis). []
- Age (aging). A study of 602 healthy people found an age-related increase in mean ALT (alanine aminotransferase) levels. This increase in ALT with age was also associated with an increase in AST values. It is believed that AST scores may increase with increasing age . []
- Floor. A study of adults in a specific region of China examined the course of metabolic syndrome. Although this was not the main finding of this study, the scientists did notice that AST levels were higher in men than in women. []
- Medicines. Some medications, such as painkillers, chemotherapy drugs, and statins (to lower blood pressure), may increase AST levels. This increase in AST has generally been associated with stress on the liver caused by long-term use or too much medication. [, , ]
- Other diseases that may be accompanied by an increase in AST: myocardial infarction, acute pancreatitis, acute hemolytic anemia, acute kidney disease, dermatomyositis, trauma or wounds.