Modern research method
In a medical clinic, you can do rheovasography (RVG) of the vessels of the upper and lower extremities.
Rheovasography (RVG) of the upper and lower extremities is a modern method of functional diagnostics, with the help of which the intensity and volume of blood flow in the arterial vessels of the extremities is determined.
The principle of this research method is to measure the resistance of a skin area when an electric current of minimal strength (absolutely harmless), voltage and a certain frequency is passed through it using special sensors. Depending on the intensity of blood supply to the tissues, their resistance changes. The worse the blood flow, the higher the resistance of the skin and tissues. Changes in the resistance parameter are displayed on a paper tape in the form of a curved line, along which the functional diagnostics doctor determines the nature of blood flow in the area of the body being studied.
What the procedure will show
Having figured out what the essence of the diagnostic method is, people begin to be interested in how they can independently decipher the result they receive. But without the proper knowledge, this is quite problematic, because for most people, a rheogram is some kind of mathematical graph, and the impedance of biological tissues does not mean anything at all.
The basis of the picture is based on two aspects:
- sinusoids, which are presented as a steep rise, which describes arterial blood flow;
- a smooth descent, which is a reflection of the venous blood flow.
But not only this makes it possible to assess the condition of the vascular network in terms of volumes and other features of the incoming blood. It will be necessary to take into account many curves and use additional calculations, where Kedrov’s formula plays an important role.
The diagnostician will definitely take into account the regularity of the verified curve, which implies similarity between several curves. The shape and the number of secondary curves that are in a descending phase are also taken into account.
For example, it is worth analyzing the indicators characteristic of vegetative-vascular dystonia or arrhythmia. The presented ailments will be indicated by adjacent curves with different shapes.
Next, a special index is calculated, which must fit into the average statistical interval. Falling out of it threatens with suspicion of serious pathologies.
The following values specifically help identify diseases:
- level of venous outflow;
- amplitude-frequency indicator;
- measurements of the time interval for pulse wave propagation.
An experienced doctor will take into account various functional tests in order to get a detailed picture of what is happening.
Indications
RVG is necessarily prescribed based on the patient’s subjective complaints about:
- leg cramps or swelling;
- the appearance of spider veins;
- pain and/or weakness when walking, arising and disappearing for no reason;
- numbness, chilliness, paleness of the feet or hands;
- pain in the arms with light exertion or at rest,
- change in skin color,
- long-term non-healing ulcers and cracks on the feet or heels.
The procedure can also be prescribed for smokers who complain of leg pain. RVG of the vessels of the lower extremities is used for diagnosis when the following diseases are suspected:
- phlebeurysm;
- atherosclerosis of leg vessels;
- thrombophlebitis;
- Raynaud's syndrome.
How it goes
The room where the procedure itself takes place must be quite warm, since the patient is forced to take off his clothes, freeing his limbs for examination.
In order for the fixed electrodes to show accurate data, the person must lie in a motionless position. For convenience, a soft couch is available.
Before fixing the sensors, the surface fatty layer is removed from the skin. They are installed clearly according to the principle of longitudinal or transverse placement. This depends on the limbs being examined.
If the mechanical activity of the vessels of the arms is examined, then the sensors are placed in four places throughout the limb. On the legs these are the feet, legs and thighs.
Preparation for RVG of vessels
Before you begin examining the patient’s upper and lower extremities, the basic requirements preceding the rheovasography procedure must be met:
- Within 15 minutes, a person should receive complete relaxation (preliminary rest);
- 2 hours before RVH, smokers should stop taking nicotine into the body;
- 24 hours before the study, it is necessary to suspend the use of any medications by patients undergoing treatment;
- For RVH of the lower extremities, the legs should be freed from clothing.
Preparation and execution
To ensure a high-quality procedure and obtain objective results, the following preparatory measures are provided: do not take medications 24–48 hours in advance, course treatment should be temporarily suspended. It is important to give up alcohol-containing drinks for a week, eliminate physical activity, smoking and eating 3-6 hours in advance.
RVG of vessels is carried out under the condition of a static position and a relaxed state of the patient. Therefore, to restore blood flow, the patient spends a quarter of an hour before the procedure simply lying on the couch in the functional diagnostics room.
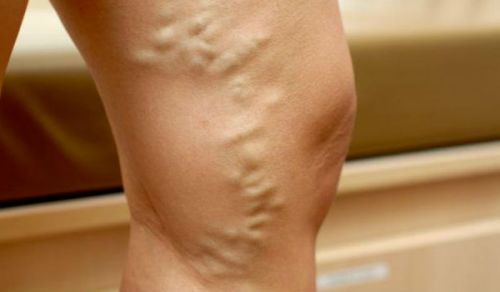
Varicose veins - indication for diagnostics
Electronic sensors are sequentially recorded on certain areas of the body. The skin is pre-disinfected with an alcohol solution. The electrodes have a strict order and absolute symmetry of arrangement. To examine the hands, two leads are used: the wrist and the forearm. The sensors are attached to the elbow and wrist areas. For legs - on the ankle joint and under the knee. The interval between the electrodes on the fingers should be 30–40 mm. The time period of the procedure usually does not exceed half an hour.
According to indications, additional RVG is performed with samples:
- Nitroglycerin. The readings are recorded after taking a certain dose of nitroglycerin, which relieves vascular spasms. In the case when the filling of blood vessels increases (compared to the initial values), the sample is interpreted as positive. This means that the disease is associated with impaired organ functionality. A negative test indicates cellular and structural (organic) lesions;
- Compression. Diagnostics with application of a compression cuff to the thigh. By increasing the pressure and then releasing the cuffs, the rate of recovery reaction and blood outflow is assessed. This test is used to diagnose deep vein diseases.
Samples
In some cases, doctors use special tests during diagnosis that help give a more accurate picture. The most common:
- Nitroglycerin test. It consists of recording vascular resistance while taking nitroglycerin tablets. The bottom line is that the study is carried out before and after the drug is absorbed. This test allows you to assess the ability of spasmodic vessels to expand. If the drug does not cause any changes in the rheogram, the test is considered negative, and the spasm is considered an organic vascular lesion (this is most often observed with vascular damage by atherosclerosis). This test is contraindicated for pregnant women and children under sixteen years of age.
- Cold test. Most often used to study microcirculation of the fingers. Such a stress test will be very informative in the development of Raynaud's disease, so it is used in special cases. After a single examination, the patient is asked to hold his hands under running cold water for one and a half to two minutes, after which the examination is repeated. The test is considered negative when blood flow and vascular pulsation are restored by the eighth minute after cooling. If nothing has changed within fifteen minutes or the restoration of blood flow occurs slowly, then the test is considered positive.
- Compression test. It is carried out after examining the vessels in a calm state. Special rubberized cuffs are placed on the limbs, which compress the tissues, as a result of which the inflow and outflow of blood is disrupted. Next, sensors are applied, the cuff is removed, and the rate of blood flow restoration is assessed. This method is considered informative if the patient has thrombosis of small and large veins.
- Turns and tilts of the head. When diagnosing pathologies of the blood vessels of the head and neck, the doctor may ask you to turn or tilt your head in one direction or another and fix it in this position for a few seconds. Such a test is necessary to monitor the blood filling of the vascular bed.
Key Indicators: What They Measure
The RVG results show a curve. Wave interpretation is based on qualitative and quantitative values. These include: the steepness of descents and ascents, intervals, amplitude, peaks.
Based on the values, control indices are derived, which are:
- rheographic - it controls the strength of blood flow in the arteries;
- arterial walls shows IE;
- IPS – peripheral resistance index;
- numerical value of venous outflow.
The most basic indicator is considered to be RI - rheographic index.
Decoding the results
Obtaining research results does not take much time.
Within 30 minutes, a specialist can decipher the received line and display the indices. RVG decoding is output in Ohms. As mentioned above, RI shows the total volume of filling of blood vessels. With readings of 0.05 Ohm and above, we can say that their condition is normal.
With deviations of one unit, mild deficiency is observed. If RI is sharply reduced, the patient is diagnosed with a blood supply disorder.
Standards for vascular tone data without deviations are calculated from 0.4. Values that do not reach the specified units are already considered violations. The lower the indicator, the lower the tone of the vascular wall.
The outflow index shows the speed of blood movement in the venous canal. RVG should range from 0.2 to 0.5. Anything that exceeds this line indicates serious illness.
The IPI responsible for counteracting vascular channels should be in the range of 0.2-0.45. In case of obvious blood flow pathologies, the index may be higher or lower than the norm.
Additional samples
Violations that were recorded during RVG do not always indicate damage.
The resulting index may have a functional nature of deviations. Often such results are obtained when preliminary preparation is not followed. There are two additional samples. They help determine what is really happening, a temporary spasm or pathology:
- Nitroglycerin. Using the drug, the rheovasography procedure must be completed several times. The first occurs before the drug is used, and the second after its action. The doctor receives data from two studies and conducts an analysis. If comparable results do not differ significantly, then we can conclude that there is a pronounced pathology on the face. In the case where the drug had an effect and the indicators improved, one-time disturbances caused are assumed.
- Compression. The essence of the procedure is to use a cuff that compresses the required area of study. As in the case of the RVG drug, the patient undergoes it twice. Before and after applying the cuff to the limbs. This test helps determine how quickly blood supply is restored when the deep veins are blocked.
The latest rheovasography devices have a large number of positive aspects. They greatly simplify the work of specialists. The system itself calculates the results, which is much faster than routine calculations.
At the same time, the patient does not receive any radiation or other negative effects on his body. The method is more than safe and informative. Due to this, this diagnosis is relevant in medical practice.