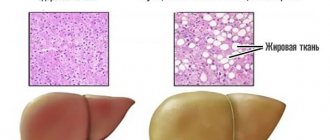
An ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm that contains fluid inside. The pathology is quite common and is diagnosed in 30-50% of women of childbearing age. With the onset of menopause, the risk of developing a cyst decreases significantly.
The reason for its formation is said to be chronic pathologies of the genital organs and hormonal imbalance.
If treatment is not carried out in time, the cyst can increase in size, lead to compression of healthy tissue, a decrease in the supply of follicles, hormonal disorders and infertility. In addition, the danger of a neoplasm lies in the possibility of its tissues degenerating into malignant ones. Therefore, if conservative therapy does not bring the desired result, ovarian laparoscopy is performed.
Types of hysteroscopy
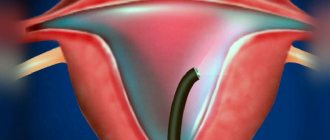
Today it is difficult to imagine diagnosing diseases of a woman’s reproductive organs without hysteroscopy. It is used to identify gynecological pathology using the endoscopic method in most clinics. Menstruation should not be late after hysteroscopy.
Depending on the goals and objectives set for the functional diagnostics doctor, the following options for hysteroscopy are distinguished:
1. Diagnostic. It involves a visual examination of the inner surface of the uterus using optical instruments. This procedure allows us to identify pathological processes in the endometrium and uterine cavity. During such a study, the integrity of the uterine mucosa is not compromised. 2. Surgical. This endoscopic intervention allows for surgical treatment of various diseases of the uterus and cervical canal. With its help, endometriotic heterotopias, polyps, and myomatous nodes are successfully removed. 3. Control. Performed for the purpose of dynamic monitoring of the progress of treatment. This examination allows you to determine the degree of its effectiveness, timely record relapses of the disease, and monitor the condition of the uterine mucosa after surgical treatment or conservative therapy.
Different types of hysteroscopes, which differ in size and degree of magnification, help to assess the condition of the endometrium, as well as conduct microscopic diagnostics after obtaining biological material intended for histological examination. Using microhysteroscopy, you can perform highly effective endoscopic operations, which are possible thanks to multiple image magnification. After this type of hysteroscopy, periods may occur earlier than expected.
Since the cervical canal does not allow the hysteroscope tube to pass through, it has to be expanded with Hegar dilators. A sterile liquid or carbon dioxide is injected into the uterine cavity so that the relief of the endometrium is better visible. As a means of stretching the uterine cavity, doctors usually use saline solution of sodium chloride, dextran, dextrose, sterile distilled water or sorbitol.
Types of ovarian cysts
Based on the reason for the development of formation and the type of tissue that makes up the cyst, they are divided into the following types:
- Follicular. The cyst is a mature follicle that has not ruptured due to a cycle disorder.
- Luteal. They develop from the corpus luteum when fluid accumulates inside.
- Endometrioid. Formed from endometrial cells.
- Thecalyuteinaceae. Their development is associated with progesterone deficiency in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Mucinous. They are distinguished by a multi-chamber cavity and a bumpy surface. There is mucus inside the cyst. Their difference lies in the possibility of rapid growth.
- Paraovarian. They are formed from ovarian tissue on its outer wall.
- Dermoid. They are formed from the epithelium that has entered the ovary during the girl’s prenatal development.
Each of these cysts has its own developmental characteristics and prognosis. When removing an ovarian cyst using laparoscopy, the doctor strives to preserve healthy ovarian tissue as much as possible, since the functioning of the organ, the patient’s hormonal background and her ability to conceive in the future depend on this.
Indications and contraindications for hysteroscopy
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed if the following uterine pathology is suspected:
- endometrial polyp;
- adenomyosis;
- submucous uterine fibroids;
- intrauterine constrictions;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- various defects in the anatomical structure of the uterus;
- suspicion of perforation of the uterine wall or the presence of a foreign body in its cavity;
- suspicion of malignant neoplasm;
- signs of intrauterine fistula;
- algodismenorrhea;
- synechiae in the uterine cavity.
Quite often, such an examination is prescribed for infertility. Hysteroscopy on the eve of in vitro fertilization allows you to assess the condition of the uterus, identify pathologies that may interfere with embryo implantation, and verify the physiological readiness of the organ for the IVF procedure. Relative indications for hysteroscopy may include irregular menstruation, bleeding from the genitals, miscarriage and the need to monitor the effectiveness of hormonal therapy.
Surgical hysteroscopy is performed for polyps of the uterus and cervical canal, myomatous nodes located in the submucosal layer of the myometrium, and adenomyosis. It is carried out to remove remnants of the intrauterine device, fertilized egg, and foreign bodies. Another effective treatment method that minimizes damage to uterine tissue is laser ablation, which is also performed using a hysteroscope.
If there are the following contraindications, performing hysteroscopy is unacceptable:
- cervical stenosis;
- heavy uterine bleeding;
- acute inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs;
- pregnancy;
- malignant neoplasms of the cervix;
- third and fourth degrees of vaginal purity.
If you perform hysteroscopy, neglecting the fact that there are contraindications, then serious complications may develop after it, which are unsafe for the woman. In this case, menstruation after hysteroscopy may come late or be excessively heavy.
Why do menstrual irregularities occur?
Despite the fact that there are no results of large-scale studies that would confirm the negative impact of the new coronavirus infection on women’s reproductive health, doctors do not deny the presence of consequences of covid. Doctors note that the uterus and ovaries contain ACE enzymes, which facilitate the penetration of the virus into the cells of the reproductive organs.
But cycle failure is not a necessary consequence or symptom of the virus. Menstruation may disappear or be delayed due to:
- Stress
. Constant, prolonged nervous tension promotes the synthesis of the stress hormone (cortisol) and suppression of estrogen production. This causes delayed menstruation or amenorrhea. In addition, stress affects the level of prolactin, which, in turn, reduces the concentration of dopamine, which transmits signals to the parts of the brain responsible for regulating the cycle. In this case, the woman will complain of spotting between menstrual periods. - Fluctuations in hormonal levels
. This can lead to the growth of existing fibroids and cysts or provoke an exacerbation of endometriosis. In this case, the patient may notice an increase in the amount of discharge or a delay in menstruation. - Physical inactivity
. The closure of gyms, self-isolation, and remote work from home contribute to a decrease in the physical activity of citizens. This has a bad effect on the endocrine system, which affects the functionality of the genital organs. - Blood thickening
. It has been noted that after Covid, women’s blood becomes thicker. This causes a delay in menstruation and the appearance of clots in the discharge. - Directing the body's resources to the functioning of the respiratory system
as more important for life. In this case, support for the reproductive organs is postponed until recovery, so the patient’s discharge may be scanty or stop altogether.
In some women, coronavirus causes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and lack of appetite. As a result, the body loses weight by losing fat tissue. Sudden weight loss leads to a decrease in estrogen production, which will disrupt your cycle.
Appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist
Preparation for hysteroscopy
On the eve of hysteroscopy, the patient undergoes a gynecological examination. It allows the doctor to determine the condition of the vagina and cervix. The gynecologist also takes a smear from the vagina for bacteriological and cytological examination. Also, the woman must provide the results of a general blood and urine test, coagulogram, determination of blood group and Rh factor, RW, the presence of antibody titres to hepatitis C and B, as well as the causative agent of HIV (AIDS). An electrocardiogram is taken and fluorography is performed on her. After this, the patient is examined by a therapist, who, if necessary, prescribes consultations with specialized specialists.
In order to avoid complications of the postoperative period after hysteroscopy, I recommend that a woman follow these rules:
- do not use vaginal suppositories, tablets and sprays for one week preceding the procedure;
- refrain from intimacy for two days before hysteroscopy;
- do not drink alcohol on the eve of the examination;
- stop taking medications that are not recommended by your doctor.
Depending on the presence of a particular pathology, hysteroscopy is performed at different phases of a woman’s menstrual cycle. If the procedure is prescribed to diagnose uterine fibroids, then the study must be carried out a few days after the end of menstruation. In the second phase of the cycle, a study is carried out to diagnose endometriosis and identify the causes of infertility.
Course of the postoperative period
In most cases, hysteroscopy is quite easily tolerated by patients. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is rarely accompanied by uterine bleeding or pain. It does not require any rehabilitation measures.
After surgical hysteroscopy, the patient requires medical supervision for some time. She is prescribed anti-inflammatory combination drugs to prevent bacterial infections. Additionally, the doctor evaluates the nature of the discharge after hysteroscopy. Most often they are bloody and scanty, and after some time they stop on their own.
To relieve pain in the perineum or lower abdomen, doctors recommend that patients take non-opiate painkillers in the first days after hysteroscopy. Analgesics can be taken only in case of severe pain. Minor pain that may occur after hysteroscopy goes away on its own within a couple of days.
A woman after hysteroscopy should follow the following recommendations:
1) refrain from coitus for a couple of weeks after hysteroscopy; 2) for the same period of time, stop using tampons and vaginal suppositories; 3) refrain from taking a bath, visiting a bathhouse, sauna, or swimming in a pool.
Laparoscopic surgery - wedge resection of the ovaries
This operation involves maximum removal of hyperplastic ovarian stroma. The ovarian tissue is grabbed with atraumatic forceps in the area of one of the poles or in its middle part in a place remote from the ovarian hilum, then fixed in a comfortable position. Using an electrode, a wedge-shaped section is cut off to the ovarian hilum, 2 x 1.5 cm long and 1 x 1.5 cm thick. The edge of the cut-off area is grabbed with forceps, everted, cut off wedge-shaped and removed from the abdominal cavity through one of the trocars. Hemostasis is achieved using a monopolar or bipolar coagulator, and a protective film is formed on the resected surface. As a result of resection, the volume of the ovary is reduced to normal size.
Menstruation after hysteroscopy
The first menstruation after hysteroscopy can begin in 25-50 days. A woman should pay attention to the nature of the discharge. If they become abundant, and their color or consistency changes, this may be a sign of a pathological process in the uterine cavity. The pungent smell of the first menstruation after hysteroscopy usually indicates inflammation in the uterine cavity, and in combination with the black color of the discharge, it often indicates endometriosis. If surgery was performed during hysteroscopy, then this day is considered the first day of menstruation. After hysteroscopy, the first menstruation lasts longer than usual. The reason for this is damage to the endometrium.
If you need to perform a hysteroscopy, please contact the IVF Center clinic in Yekaterinburg. Our procedures are carried out by experienced specialists who have extensive experience in performing diagnostic and surgical procedures. We provide care to patients with many gynecological diseases and monitor them in the postoperative period.
The nature of the discharge after removal of a uterine polyp
After endometrial curettage, most patients report spotting and spotting for 7-10 days, which is considered a physiological norm. Such a reaction of the body to intervention manifests itself as an adaptogenic mechanism and should only cause concern if it persists for a long period. Sometimes the discharge takes on a brown tint, which indicates the patient’s blood clotting ability is normal.
Also, many women experience leucorrhoea mixed with blood, which may be a variant of the normal immune response. If vaginal discharge acquires an unpleasant odor or contains pus, this is a signal to contact a medical institution where hysteroscopy was performed. Most often, such manifestations form against the background of an infectious process and are accompanied by a significant increase in body temperature. It should be taken into account that subfibrile temperature (up to 38) for several days after manipulation is also a normal postoperative condition.