What are ALT and AST in blood biochemistry
Let's look at the abbreviations and find out what enzymes are hidden behind them:
- ALT or ALT – alanine aminotransferase – is an enzyme that is present in the cells of various organs. Most of it is in the liver and kidneys. When organs are damaged, ALT enters the blood. The presence of an enzyme in the red liquid may indicate the development of jaundice. ALT analysis is one of the “liver tests”, the results of which indicate problems with the organ, namely, its destruction. A large amount of enzyme in the blood may indicate not only liver disease. If your ALT level is high, there are likely problems with other organs. We use the words “may”, “possibly” - because ALT analysis is the primary diagnosis. Based on it alone, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis. More research is needed.
- AST or ASAT - aspartate aminotransferase is an enzyme that is found in the greatest quantities in the liver, kidneys, and myocardium. It, like ALT, enters the blood during tissue destruction. An increase in AST is a sign indicating possible liver disease. A complete diagnosis is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis.
Thus, AST and ALT are enzymes that are found primarily in the liver and kidneys in the body. They are involved in the synthesis of many useful substances. If the organs in which aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase are located are destroyed, the enzymes enter the blood. This is revealed through analysis.
Reasons for the increase
Among the factors for the growth of the indicator, the following points should be mentioned.
Hepatitis
Chronic or acute inflammation of the liver. It occurs relatively frequently and leads in the number of identified cases among all organ pathologies.
It also occupies one or the main positions in the conditional ranking of diseases of the digestive tract.
There can be several types, depending on the origin. For example, toxic, medicinal or infectious, viral. Most often, the disorder occurs in binge alcoholics and drug addicts. Although not only.
The disease is accompanied by a system of symptoms. The following points can be found in the clinical picture:
- Discomfortable sensations in the right side of the abdomen. They occur especially often and indicate problems with the whole body. Unpleasant sensations, pressing, shooting. They are not cutting, this is an indication of gallbladder disease and a completely different question.
- Heaviness in the abdomen of unknown origin. It is often impossible to detect the exact localization of discomfort.
- Bitterness in the mouth. Due to the intensive discharge of bile and its return to the initial parts of the digestive tract.
- Increased body temperature. Not always and not everywhere. Depends on the form and duration, the neglect of the pathological process.
- Digestive disorders. Dyspeptic phenomena. Be it heartburn, belching and other conditions.
- In acute hepatitis, the concentration of ALT in the blood exceeds the norm by 20-50 times.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting or at home. According to the decision of a hepatologist or gastroenterologist. Hepatoprotectors are prescribed.
For viral etiology of the disorder, special medications are used. In particularly difficult cases, radical measures cannot be avoided. But this is rather an exception to the rule.
Therapy is most often lifelong. The disease does not go away completely. This is a permanent state that you need to learn to exist with.
In addition, a low-fat diet is prescribed. The goal of recovery is not so much a total cure as achieving stable remission.
Cirrhosis of the liver
A logical continuation of the pathological process of an inflammatory nature, hepatitis.
ALT (ALAT) is always elevated, since the disorder is determined by the gradual but steady destruction of liver tissue and the death of organ cells. This is an irreversible phenomenon; nothing can be done about it. Just slow it down, and only for a while.
If we are talking about the initial stages of a pathological process, there is a good chance of stopping the progression and thereby saving the patient’s life. But this is rarely possible. Mainly due to late seeking medical help.
The disease is characterized by a number of pathological manifestations. Among them are:
- Pain in the right side, under the ribs. It is impossible to distinguish between cirrhosis and hepatitis in this case. Special diagnostics are needed.
- Bitterness in the mouth.
- Wound healing disorders. Coagulation factors, special substances involved in blood coagulation, are produced in this organ. Problems begin even with small scratches. Not to mention anything more.
- Increased body temperature.
- Disruption of the vascular walls. Externally, this manifests itself as varicose veins. Characteristic spiders and stars form on the skin. This is a clear indication of the onset of a pathological process. Especially if there are other symptoms.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Dyspepsia.
- Discoloration of stool.
The disorder is difficult to treat. At the initial stages, hepatoprotectors are used. As the disease progresses, their meaning is lost.
A radical recovery measure is a liver transplant. Possible only in the very first stage of the disease. Then it is not performed because severe bleeding begins.
In the case of hepatitis and cirrhosis, ALT in a blood test increases as a result of cell breakdown - the substance is actively released and enters the bloodstream. Then it is recorded using laboratory analyzers and techniques.
Liver cancer
Oncology develops against the background of a systematic inflammatory process as a result of viral damage, drug addiction, alcoholism, and the reason for the increase in ALAT is the destruction of liver tissue.
There are also spontaneous, idiopathic variants. When the exact cause cannot be determined.
The disease is deadly and can be treated well only at the initial stage. When the tumor is still small. But there is a serious problem here.
It is very difficult to detect neoplasia at the initial stage. This is due to the deep location of the structure and its camouflage.
The results of a conventional ultrasound cannot make a diagnosis. And MRI is prescribed only when indicated; no one suspects that the cause of the pain may be cancer. The problem is insufficient diagnosis and low qualifications of doctors.
Symptoms of the pathological process, in general, resemble those of cirrhosis or hepatitis. There are still the same severe pains and discomfort in the right side. There are also problems with digestion, health and well-being in general.
But to prove the oncological nature of the disorders, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis. Something almost no one ever does.
At the initial stage of oncology, cancer is well treated. The tumor is removed. Some healthy tissue is also excised. This is the so-called resection. For greater accuracy.
If necessary, if it makes sense, radiation and chemotherapy are prescribed. The results are fast and high quality. Recovery takes up to several months.
Then you need to have a contrast-enhanced MRI every six months or more often. To exclude relapses of the pathological process. This is the only way to fight.
Hepatosis
Dystrophic process in the structures of the largest gland in the body. Occurs mainly in cases of severe metabolic disorders. Also found in patients who drink.
The bottom line is this: if alanine aminotransferase is elevated, this means that in the course of a pathological change, destruction of functional liver tissue and replacement of normal cells with fatty cells is observed.
The condition is somewhat reminiscent of cirrhosis, only the process is much slower.
The disease is well treated in the early stages. The main problem is that most of them have no symptoms. The condition progresses very slowly and does not make itself known.
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a hepatologist. If there is no specialist, a gastroenterologist is involved. Hepatoprotectors are prescribed.
A mandatory measure for correcting the pathological process is diet. Low in fat, with a predominance of plant foods in the diet.
Then everything depends on the doctor’s decision. You can develop a menu individually.
The prognosis is favorable only at the initial stage of the pathological condition. Then the prospects are vague and not completely clear.
In fatty hepatosis, ALT exceeds the norm slightly; plateau effects and a gradual decrease in concentration are observed. Because there are fewer and fewer functional cells, and the previous reserves of the substance are removed from the blood.
There are almost no critical indicators, since the disease progresses slowly and does not lead to massive cell death here and now.
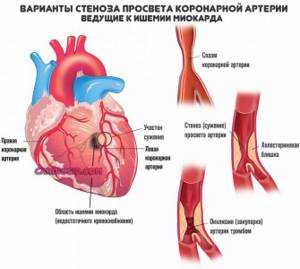
Heart attack
Acute emergency condition. The death of functional structures—cardiomyocytes—is typical for it.
This is a very dangerous violation. It is fraught with the death of the patient in the short term. Even if they survive, many become disabled and suffer from complications.
The symptoms of the pathology are quite typical. But they are difficult to distinguish from those with angina pectoris.
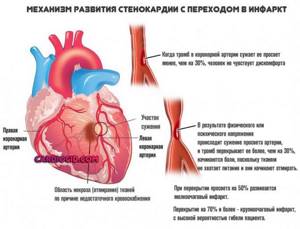
Among the manifestations are:
- Severe chest pain. They can radiate to the arm, left side, or jaw. Character - pressing or burning, baking. This is a typical symptom of an ischemic process. How to understand that it is the heart that hurts - read here.
- Respiratory disorders. Feeling of lack of air.
- Arrhythmias of different types.
- Panic attacks. Feeling of intense fear.
- Psychomotor agitation.
- Heaviness in the chest.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle. The so-called cyanosis.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Impaired consciousness.
A person risks dying in a matter of hours if he is not transported to a hospital. Symptoms of heart attack in women are described in detail here, in men here.
Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist. Organic nitrate group drugs and protectors are prescribed. Also other means as needed.
Laboratory indicators, however, need to be correctly deciphered.
Explore two levels. If alanine aminotransferase is elevated, and AST is even higher, this means that the problem is clearly from the heart. Diagnosis must be carried out quickly. The clock is counting. And sometimes - for minutes.
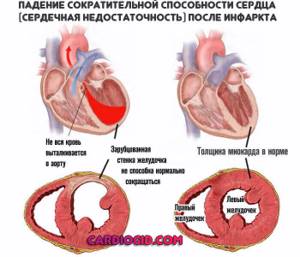
Heart failure
ALT is elevated when other diseases of the cardiac structures are present: this may include coronary heart disease and other coronary disorders (insufficient blood circulation without signs of a heart attack).
Conditions of this kind are often united by common clinical manifestations.
Among the features of the pathological process:
- Severe periodic chest pain. They appear and go away on their own.
- Dyspnea.
- Disturbances of normal rhythm. Tachycardia, fibrillation, extrasystoles. Anything. Depends on the specific diagnosis.
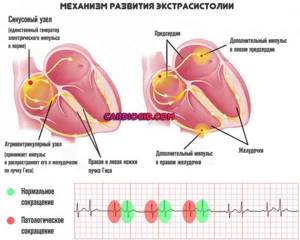
- Loss of consciousness. Fainting.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle.
- Pale skin.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Exercise intolerance.
These are all signs of heart disease. Treatment depends on the clinical situation. Antihypertensive drugs, cardioprotectors, organic nitrates, and glycosides are prescribed. There are plenty of options.
The decision remains with the attending physician.
Attention:
When coronary blood flow is impaired, ALT increases gradually and very rarely over a wide range. Usually there is slight growth that is barely noticeable. This should be alarming.
In case of liver diseases, laboratory indicators are much worse.
Skeletal muscle disorders
This also happens, although not as often. The condition mainly occurs in patients who have been in a hospital bed for a long time, bedridden.
Obvious degenerative processes begin. Since the enzyme is actively synthesized in skeletal muscle, everything is pretty clear.
Symptoms are usually invisible or absent altogether. Recovery as such is impossible. Unless you conduct sessions of passive or active physical therapy. To maintain muscle nutrition, then the cells will not die.
As soon as physical activity returns, everything will be restored.
An ALT test shows the condition of the liver, heart and skeletal muscles. Other changes are also possible.
There are also temporary deviations from the norm. For example, as a result of physical activity, after smoking, stress.
There are other diseases that are not reflected in the list above. For example, gallbladder pathologies.
Normal ALT and AST in a healthy person
Indicators differ for people of different genders and ages. More details are described in the tables.
| Patient gender/enzyme | ALT | AST |
| men | up to 45 U/l | up to 37 U/l |
| women | up to 34 U/l | up to 30 U/l |
A child's enzyme levels are constantly changing. They are:
| Age/enzyme | ALT | AST |
| less than 5 days | up to 49 | up to 97 |
| from 5 days to 6 months | up to 56 | up to 57 |
| from six months to a year | up to 54 | up to 82 |
| up to 3 years | up to 33 | up to 48 |
| from 3 to 6 years | up to 29 | up to 36 |
| up to 12 years | up to 39 | up to 47 |
If the patient is older than indicated in the last line of the table, you need to focus on the norms for men and women.
You need to know that there is also the Ritis coefficient, which determines the ratio of enzymes to each other. Normally, it is 1.3 - that is, this is how much less AST in the blood plasma should be compared to ALT.
The Ritis coefficient is useful in identifying myocardial problems. AST is most abundant in this muscle. If the aspartate aminotransferase level approaches the alanine aminotransferase level, then most likely the problem should be looked for in the heart area.
Material under study
Deoxygenated blood
Interpretation of research results contains information for the attending physician and is not a diagnosis. The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis using both the results of this examination and the necessary information from other sources: medical history, results of other examinations, etc.
Units of measurement: U/l.
Reference values:
| Age, gender | Reference values |
| 0 - 1 year | <56U/l |
| 1 – 4 years | <29U/l |
| 4 – 7 years | <29U/l |
| 7 – 13 years | <37U/l |
| 13 - 18 years old | <37d/l |
| >18 years old male | <41U/l |
| >18 years old female | <33U/l |
Symptoms of increased ALT and AST
Signs are divided into primary and late. First, the following manifestations of an increase in AST and ALT occur:
- nervousness;
- itching;
- poor sleep;
- weakness of the body;
- decreased appetite, which leads to weight loss.
Late symptoms:
- darkening of urine;
- stool discoloration;
- yellowish tint to the skin and whites of the eyes;
- swelling of the arms and legs;
- nausea;
- general poor health.
If the primary symptoms can indicate both problems with elevated levels of ALT and AST, and other disorders in the body, then later ones clearly indicate that not everything is in order with the liver. Additional diagnostics are required to make an accurate diagnosis. For example:
- coronavirus test;
- blood test for hepatitis B and C;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- heart diagnostics;
- clinical blood test;
- study of the concentration and quality of thyroid hormones;
- liver biopsy.
If after coronavirus there are elevated levels of ALT and AST enzymes, contact the LaSalute clinic. It has all the necessary equipment to establish an accurate diagnosis, as well as specialists who are involved in the rehabilitation of people who have suffered from coronavirus.

References
- Interpretation of a biochemical blood test for liver pathology: A manual for doctors / M. G. Ipatova, P. V. Shumilov, Yu. G. Mukhina. M.: PrimaPrint, 2021.
- Ivashkin V.T., Shirokova E.N., Mayevskaya M.V. et al. Clinical recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association and the Russian Society for the Study of the Liver for the diagnosis and treatment of cholestasis // Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. 2015. No. 2.
- Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of liver diseases / V. S. Kamyshnikov. M.: MEDpress-inform, 2013.
- Brief clinical recommendations for the correction of hepatotoxicity induced by antitumor chemotherapy: - Larionova V. B., Gromova E. G., Zeynalova P. A., Snegova A. V. - 8 p.
- Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of von Willebrand disease.
- Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cholestasis. - Moscow 2013.
- Drug-induced liver damage (clinical recommendations for doctors) V. T. Ivashkin, A. Yu. Baranovsky, K. L. Raikhelson, L. K. Palgova, M. V. Mayevskaya, E. A. Kondrashina, N. V. Marchenko , T. P. Nekrasova, I. G. Nikitin. — St. Petersburg, 2021.
- Letter of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 2, 2021 N 15-4/10/2-7675 On the direction of clinical recommendations (treatment protocol) “Acute fatty liver degeneration in pregnant women: intensive care and obstetric tactics.”
Which doctor should I contact?
You should start by visiting a therapist. This doctor interviews and examines the patient and decides which specialist needs to be contacted. Options:
- Cardiologist, if after Covid the AST level increased more than ALT. This indicates that, most likely, there are problems with the myocardium.
- Endocrinologist, if the virus has negatively affected the liver or kidneys.
Help from other specialists may be required.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. This leads to a worsening of the condition. Then you still have to contact a doctor. But time will be lost. In such a situation, specialists are not always able to help in any way.
Complexes with this research
Pregnancy planning.
Clinical indicators 3,260 R Composition Blood biochemistry. 13 indicators Optimal biochemical blood test RUR 1,830 Composition
Fitness control of sports nutrition Assessment of liver function, hormone levels and metabolism when taking sports nutrition 2,590 RUR Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Advanced male anti-aging diagnostics RUR 21,270
- Nutritionist recommends RUB 3,870
- Women's check-up No. 1 10,550 RUR
- Expanded hospital complex RUB 3,860
- Advanced anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUR 18,460
Stages of determination and normalization of ALT and AST
A blood test allows you to identify the problem - to establish that the amount of enzymes is not normal. If there is more ALT and AST in the vessels than they should be, it is necessary to undergo a full examination to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Next, you should undergo therapy using the methods outlined by the specialist. In order not to worsen the situation, all medications should be taken exclusively as prescribed by a doctor.
You can undergo diagnostics, determine the level of enzymes in the blood and determine which organs the coronavirus has caused complications at the LaSalute clinic. There is all the necessary diagnostic equipment and experienced specialists work here.
What may affect the results
An increase in AST levels can be observed even in healthy people if the rules for preparing for the analysis are not followed. For example, blood should not be donated if during the day the patient experienced severe emotional distress, heavy physical exertion, underwent fluorography, X-ray examination or any physiotherapeutic procedures, ultrasound or rectal examinations of any spectrum. The result can be affected by the intake of alcohol and a number of medications, in particular, antitumor and choleretic drugs, antibiotics, barbiturates, contraceptives, sedatives, vitamin A and others, as well as recent heart surgery.