Blood in stool
- a sign that should not be ignored.
Its presence may indicate a serious illness that requires adequate treatment: the earlier it is started, the greater the chances of success. The causes
of
blood in the stool
are bleeding, which can be caused by a wide range of factors. Blood enters the anus and exits along with the feces: this occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels in the intestines or lower gastrointestinal tract. As a rule, the losses are small, but nevertheless they are a reason to seek professional proctological help.
According to medical statistics, rectal bleeding accounts for about a quarter of all cases of bleeding from the anatomical structures of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often they are diagnosed in elderly patients, but experts emphasize that the risk of such a phenomenon increases from the age of thirty and is constantly growing. The diseases that cause them are treated by gastroenterologists or proctologists.
Causes of bloody stool
Bloody feces
is a symptom of a number of diseases of the intestines and lower gastrointestinal tract of an oncological, inflammatory or infectious nature. Experts divide the triggering factors that cause bleeding into several groups:
| Group of reasons | What are they? |
| Neoplasms of a malignant nature | Most often, they are represented by colorectal cancer, even in the initial stages of which small amounts of blood may appear. If the tumor is not treated and it disintegrates, serious blood loss is possible due to the melting of large blood vessels. |
| Pathological conditions characterized by proliferation of the colon mucosa | Abnormal growths include polyps, which are one of the most common causes of blood in the stool. This especially applies to the villous type of polyps, since they are rich in blood vessels. |
| Chronic diseases of the intestines and anus |
|
| Infections and poisoning |
|
| Congenital and acquired disruptions in local circulation | Circulatory deficiency or disturbances in the pelvic and abdominal areas, leading to the development of angiodysplasia or intestinal ischemia. |
| Complications of various diseases |
|
Infection in the intestines
The most common diseases of the small intestine are enteritis, duodenitis and adhesive disease. Tumors can form here, just like in the large intestine. Any part of the organ is affected by Crohn's disease. Diseases of the large intestine are more numerous:
- dyskinesia;
- dysbacteriosis;
- haemorrhoids;
- diverticulosis;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- obstruction;
- ulcerative colitis.
Diseases of the intestinal canal have another classification based on the etiology of the disease. According to this criterion, medicinal, toxic, traumatic, radiological, congenital and other pathologies are distinguished.
The main function of the small intestine is to nourish the body at the cellular level. When this section becomes inflamed, the absorption of essential nutrients is weakened. The following symptoms indicate this:
- bloating;
- frequent loose stools mixed with mucus, blood, or undigested food;
- rumbling in the lower abdomen;
- soreness in the area around the navel or in the abdomen on the right.
This disease develops due to the accumulation of eosinophils, blood cells responsible for allergies, in the intestinal walls. The reason for this process has not yet been clarified. The disease can be caused by pet parasites, food allergies, and helminthic infestations.
Table. Intestinal infections in which white mucus may appear in the stool.
| Name of the disease | What it is |
| Infectious lesions of the digestive tract with predominant damage to the final sections of the large intestine, provoked by Shigella (shigellosis). Causes acute systemic intoxication and can cause death of the patient. | |
| Acute inflammation of the intestines and other segments of the digestive tract caused by infection with E. coli. | |
| A type of intestinal infection that develops when salmonella bacteria enter the human body. The main route of infection is the consumption of stale eggs and poorly processed meat from sick animals. | |
| Chronic recurrent colitis with extraintestinal manifestations, symptoms reminiscent of dysentery. The main route of transmission is fecal-oral. |
Increased mucus secretion is also characteristic of helminthic infestation. Helminths that parasitize the human body feed on blood and its components, so they can damage blood vessels, which causes the appearance of mucus mixed with streaks of blood. Symptoms of helminthiasis may include anal itching, irritation and redness in the anorectal area, pale skin, and skin rashes. Some types of helminthiasis are characterized by a polymorphic rash in the form of blisters filled with exudate.
Important! To treat helminthiasis, drugs with a wide spectrum of antimicrobial and antiparasitic activity are used, for example, Pirantel. The tablets must be taken once in a dosage of 3 tablets (if the patient’s weight exceeds 75 kg, the dosage is increased to 4 tablets).
Symptoms of bloody stool
Blood in the stool of an adult
can be detected in minimal, small, medium and large volumes and have a different nature, which is due to the underlying disease.
| Disease | Symptoms |
| Anal fissures | Blood is present in a small volume and has a rich red color. When defecating, the patient experiences severe pain. |
| Hemorrhoids | The symptoms are similar to those described above, but there is no pain. The blood has a rich red color, but dark burgundy clots are also possible. |
| Diverticulitis | The blood may have a rich scarlet color if the sigmoid colon is affected, and very dark if the sections located on the right are affected. In addition to it, pain symptoms in the abdominal area and fever are observed. |
| Polyps | Bleeding is of low intensity and is detected against the background of pain symptoms in the abdominal area, as well as stool disorders. If repeated frequently, they can lead to the development of anemia. |
| Colorectal cancer | The admixture of blood is detected in the form of streaks or clots in the stool and in the initial stages of neoplasm development and has a small volume. However, if the neoplasm has disintegrated, the latter may increase. Other symptoms: pain in the abdomen, stool disorders, anemia and other manifestations of oncology. |
| Proctitis and colitis | Blood and mucus appear in the stool of an adult along with pus. Their admixture is small, but can increase in advanced forms or during exacerbation of chronic diseases. |
Reasons for men
In about 10% of men, white mucus in the stool may indicate inflammation of the seminal vesicles. This is a paired organ related to the male reproductive system and located behind the bladder along the anterior projection of the anus. The seminal vesicles perform important functions, including:
- absorption of active sperm during unrealized sexual arousal;
- secretion of substances that make up seminal fluid;
- production of fructose necessary to maintain the energy activity of sperm.
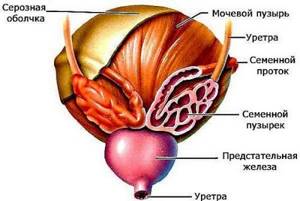
The appearance of visible, clear, white mucus in most cases is the first and only symptom of vesiculitis. Other signs may include painful urination, pain in the lower abdomen, scrotum and groin area, and a slight increase in temperature.

Note! If a man does not consult a doctor when the initial symptoms of vesiculitis are detected, he may experience erectile disorders, as well as infertility.
Diagnosis of blood in stool
The presence of a problem is determined by the attending physician, based on the patient’s complaints, medical history, and the results of:
- rectal examination;
- general blood test;
- stool occult blood test
; - colonoscopy or rectoscopy.
In order to determine the underlying disease, the appearance of which is blood in the stool, instrumental diagnostic methods are used:
- CT scan;
- Radiography with and without contrast;
- Angiography;
- Biopsy.
Blood in stool: treatment
Treatment
such a symptom as
feces with blood
is carried out individually, taking into account the underlying pathology and the amount of bleeding. If it is not significant, the doctor may prescribe a special diet that eliminates stool disorders and makes bowel movements easier. However, if blood appears systematically, anemia will need to be treated.
In any case, the underlying pathology is treated. However, if blood loss is significant, surgery and measures to restore the lost blood volume may be required. Also, endoscopic techniques using laser, coagulation, and the application of hemostatic agents give good results.
Prevention and prognosis of blood in stool
Preventive measures include timely diagnosis and adequate treatment of pathological conditions that cause symptoms such as blood in the stool. As for the prognosis, it is determined by the volume and intensity of blood loss. Often, bleeding stops on its own and no longer manifests itself, without causing serious negative changes in the patient’s condition.
The Doctor Nearby network of clinics invites you to find out the cause of rectal bleeding and undergo a course of treatment for the underlying disease in Moscow. Our clinics are located in different areas of the capital and are equipped with the latest technology. They have a powerful diagnostic base that allows them to accurately and quickly determine the cause of the anomaly and determine ways to eliminate it.
We employ proctologists with many years of practical experience. They are familiar with the symptom of blood in the stool and know how to treat the pathological conditions that cause it. After diagnostic measures, they will develop optimal treatment tactics, which will certainly achieve the desired effect: eliminate the disease and improve the patient’s quality of life.
You can make an appointment with our specialists by filling out and sending us the online form presented on the website, or by contacting our operators!
Our doctors

Kochetov Sergey Anatolievich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Perepechay Dmitry Leonidovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment

Khromov Danil Vladimirovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
35 years of experience
Make an appointment

Mukhin Vitaly Borisovich
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
34 years of experience
Make an appointment