Principle of the method
As a result of the Sulkovich test, it becomes clear whether the baby has hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia. The causes of both diseases include an unbalanced diet and (or) the presence of pathological changes in the body.
A urine test according to Sulkovich in an infant is necessary when prescribing vitamin D for preventive purposes. There is a special need for such measures for children born in autumn or winter, that is, during those periods of time when the sun shines less intensely. Natural luminary is a natural source of fat-soluble vitamin, which belongs to the steroid type prohormones, whose functions include the exchange and absorption of Ca and P.
These processes are vital for humans because their body is not able to independently produce cholecalciferol (D3) and ergocalciferol (D2). These forms of vitamin D are not the only ones; there are also D1, D4 and D5. The formation of these elements is stimulated by ultraviolet rays that hit the skin. Vitamin D can enter the body through food.
An accurate determination of the daily dose for an infant is necessary to restore balance in the event of a lack of the “solar” element. Moreover, it should not cause excess vitamin levels in the body, as this is also fraught with problems. The Sulkovich reaction during diagnostics gives a result that cannot be considered unambiguous. After all, it can be influenced by many factors, for example, the consumption of prohibited products before collecting biological material.
If the results of the Sulkovich test reveal a lack of calcium, then rickets is suspected. What it is? This is a disease that causes bones to form improperly. Excessive vitamin D levels cause hypercalcemia, which provokes hormonal imbalances, damage to the circulatory and skeletal systems, gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system, as well as diseases of unknown etiology, for example, sarcoidosis.
Sulkovich's test: Features, Indications, Preparation and collection, Decoding
Sulkovich's test is a medical test, the results of which can be used to diagnose impaired calcium metabolism. The method is semi-quantitative, so exact numbers cannot be determined. The method of analysis and interpretation of the result is the same for all people, regardless of gender and age. All this ensures high accessibility of the study.
Peculiarities
Initially, you need to figure out what the Sulkovich test is. The laboratory assistant adds the reagent of the same name to the urine and looks at the degree of turbidity. Oxalic acid (which forms the basis of Sulkovich's reagent) and calcium salts react and precipitate. It is this that allows for a visual assessment of a cloudy liquid.
Advantages of the method:
- Time. The high reaction speed allows you to get results literally within one minute.
- Simplicity. A minimum of manipulations and reagents - you just need to combine two substances;
- Price.
Flaws:
- Specificity. The analysis does not reveal a specific pathology. Only the relative amount of calcium excreted by the kidneys.
Indications
After the initial examination of the patient, the endocrinologist, therapist or urologist decides on the need for a Sulkovich urine sample.
The main indications for prescribing the test are the following conditions:
- Diagnosis of rickets in a child;
- Monitoring the level of vitamin D absorption in infants;
- Routine examination of a child up to 12 months;
- Convulsive syndrome of unknown cause;
- Suspicion of progression of an extensive oncological process;
- Tuberculosis of muscles and bones;
- Disturbance in the functioning of the parathyroid glands.
Preparation and collection
Sulkovich's urine test is a sensitive test that is influenced by many external and internal factors. Therefore, we try to limit everything that can affect the result from the outside as much as possible. The doctor tells you how to collect urine correctly during your consultation.
Approximately three days before the test, you must stop eating foods with high levels of calcium (dairy products, green vegetables, canned fish, sesame seeds, etc.). Coffee and alcohol. Excess animal protein will also distort the analysis result. Intense physical activity should be limited.
Biological material is given on an empty stomach. The first third of the morning urine portion is not collected. The rest of the morning urine in its entirety is suitable for the test.
Urine must be delivered to the laboratory no later than 2 hours later. If transportation is carried out in winter, care must be taken to ensure that it (the biological material) does not become overcooled.
If you are taking any medications or dietary supplements, you must inform the laboratory.
If the results obtained deviate greatly from the norm, the analysis is retaken. But daily diuresis is already used, in which only the average portion is taken.
Decoding
Performed by a laboratory assistant after examining urine.
After a urine sample according to Sulkovich has been performed, the interpretation may not show pronounced abnormalities. In this case, the possibility of calcium metabolism disorders in the body can be excluded. Accordingly, subsequent diagnostics are carried out in a different direction.
The results are interpreted in the laboratory, and the data are entered into a special form in the form of pluses or minuses. If the Sulkovich test shows 3 pluses, the leading specialist will tell you what to do. The number of advantages is determined by the rate of turbidity and the level of urine transparency.
In children and adults, the Sulkowicz test can be positive or negative. The norm is “+” or “++” on the form. If there are more pluses = the calcium level is higher than normal.
Urine according to Sulkovich in children normally also shows two plus signs. If there are more of them, then there is a possibility that the vitamin D content in the body is exceeded, or more calcium is excreted than it should be physiologically. When the Sulkovich test is 1 point, the pediatrician will tell you what this means. Most often this indicates normality.
If the study was prescribed for an adult patient, then the 3 or 4 pluses on the form indicate:
- overdose of vitamin D;
- taking certain medications (antacids, glucocorticosteroids, furosemide);
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- kidney disease;
- osteoporosis;
- oncological process.
A negative result is determined by:
- unbalanced diet;
- lack of vitamin D;
- rickets (in children);
- hypoparathyroidism;
- hypoalbuminemia;
- hypomagnesemia;
- chronic renal failure;
- some oncological processes;
- taking certain medications (oral contraceptives, aspirin, indomethacin, hypochlorothiazide).
Why is hypercalcemia dangerous?
The condition in which the body finds itself when there is excess calcium is very dangerous. It is accompanied by many diseases, for example, hypervitaminosis, hormonal disorders, sarcoidosis, tumors, etc. Excess calcium leads to damage to all organs and systems, but the bones, central nervous system, intestines and blood vessels are most affected. The pathological condition is expressed by impaired consciousness (up to coma), muscle weakness or tension, arterial hypertension, decreased heart rate, the appearance of kidney stones, and deterioration of glomerular filtration. Since calcium is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, an increase in its level leads to digestive disorders, including nausea, vomiting, and constipation. In the skeletal system, tissue compaction occurs, which is accompanied by movement disorders and pain.
Deviations from the norm
An excess (hypercalcemia) or deficiency (hypocalcemia) of calcium in the body indicates poor nutrition or the presence of pathologies.
Hypercalcemia
Reasons for a sharply positive result: excess vitamin D, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, hyperparathyroidism, diabetes mellitus, impaired renal tubular function, inflammation of the intestine, ulcerative colitis, osteoporosis, benign tumor of the parathyroid gland, cancer of the blood, breast, lungs, lymphatic tissue, sarcoidosis, multiple myeloma, hypercortisolism syndrome. Excess calcium in urine can be caused by increased dietary intake (milk-vegetable diet), vitamin D, antacid medications, furosemide, and glucocorticoids.
Signs of hypercalcemia include:
- lack of appetite, weight loss;
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation;
- thirst and frequent urination;
- fatigue, weakness, drowsiness;
- memory loss, deterioration in concentration;
- mental disorders (ranging from mild behavioral changes and depression to personality changes and dementia);
- deposits of calcium salts on the walls of blood vessels;
- urolithiasis disease;
- renal failure;
- arrhythmia.
Often hypercalcemia does not appear clinically for a long time.
Hypocalcemia
A decrease in calcium levels in the body is usually the result of a lack of vitamin D, hypoparathyroidism (decreased activity of parathyroid hormone), decreased concentration of albumin in the blood, malabsorption syndrome, hypomagnesemia, hyperphosphatemia, liver disease, chronic renal failure, pancreatitis, metastatic cancer.
Hypocalcemia can be caused by taking anticonvulsants, diuretics, phosphates, oral contraceptives, aminoglycosides, and antitumor drugs.

The test consists of adding Sulkowicz's reagent to urine, resulting in the formation of a sediment
Hypocalcemia in the early neonatal period (early hypocalcemia) can be caused by cessation of calcium supply from the mother, functional immaturity of the parathyroid glands in the child, perinatal stress (asphyxia, placental rupture, birth trauma of the central nervous system). Low calcium levels in newborns may also be due to maternal hyperparathyroidism or diabetes. Moderate hypocalcemia of newborns usually occurs in children fed with unadapted formulas high in phosphorus, patients with viral gastroenteritis, and born to mothers who had severe vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy. Late neonatal hypocalcemia may occur in very preterm infants born with very low birth weight.
Clinical signs of low calcium levels in the body:
- involuntary painful muscle contractions;
- tetany, carpopedal spasm;
- muscle twitching;
- tremor of the chin and fingers;
- clonic foot spasms;
- positive Chvostek and Trousseau symptoms on neurological examination;
- paresis of the limbs;
- pain in bones and joints;
- laryngospasm, frequent shallow breaths with retraction of intercostal spaces, inspiratory stridor;
- bronchospasm;
- vomit;
- insomnia, neuroses;
- heart rhythm disturbances.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Indications for the test
The Sulkowicz test is a method that helps to recognize pathologies affecting the genitourinary, endocrine, digestive and nervous systems. Oncologists also consult him. This is due to the fact that high-quality differential diagnosis without the Sulkovich test is hardly possible.
Indications for testing in adults and children differ slightly. For children, this laboratory test is prescribed if there is suspicion of:
Recommended topic:
Decoding urine analysis in children
- pancreatitis;
- granules in the lymphatic system, kidneys, liver;
- tremor of the limbs;
- tuberculosis;
- Wilson's disease;
- hypoparathyroidism.
For adults, the list is somewhat longer; sarcoidosis and tetany are added. For cancer patients, the benefit of such screening is expressed in the detection of tumors of the producing type, which can arise in any organ of the human body.
Indications
A urine test for calcium in children is practically no different from a similar study for adults. However, in most cases, this analysis is carried out in the pediatric department so that the calcium content in the body of infants can be quickly and effectively checked. This is a very important procedure that will allow timely measures to be taken to prevent osteomalacia, which is popularly called “softening of the bones,” in which the baby’s skeleton develops incorrectly, resulting in the likelihood of various diseases.
With elevated Ca levels, convulsive manifestations may occur, which poses a serious health hazard. If this component is deposited in large quantities in the bones, then the skeleton is inhibited in its development. An adult may be referred for a Sulkowicz test if the following diseases are suspected6
- sarcoidosis;
- hypoparathyroidism;
- pancreatitis;
- tuberculosis;
- Wilson's disease;
- seizures; convulsions;
- hyperparathyroidism.
For newborn children, this study is mandatory, especially important for those babies who are born in winter, when there is an acute lack of sunlight. They promote phosphorus-calcium metabolism, and also regulate the content of these components in the body, but the quality and speed of formation of the bone skeleton depend on them, and they also regulate the mental and physical development of the baby
The Sulkovich analysis must be carried out in the presence of the following diseases:
- pancreatitis;
- hypoparathyroidism;
- formation of granules in the tissues of the liver, kidneys, lymph nodes;
- systematic tremor of the lower and upper extremities, as well as various convulsions;
- tuberculosis of bones, kidneys and lungs;
- suspicion of Wilson's disease, a congenital failure of the metabolic process of a component such as copper.
The sample is analyzed by visually determining the turbidity of the biological fluid, but at the same time it is mixed with a special solution. This product contains oxalic acid. If calcium is present in the urine of a child or adult, then the process of precipitation of an insoluble type is activated. It can be visually identified as a specific clouding. It should be noted that this reaction has several forms.
Reasons for deviations
A high concentration of calcium in urine may indicate the presence of problems in the body such as:
- hyperparathyroidism is a disease of the endocrine system, which is based on an increased level of parathyroid hormone productivity;
- sarcoidosis;
- Paget's disease (bone problems);
- disorders of the kidneys;
- hypercalcemia - exceeding the permissible level of Ca in the blood;
- poor quality formations;
- excess vitamin D in the body;
- Fanconi syndrome (caused by dysfunction of the renal canals, resulting in poor calcium absorption);
- the presence of stones in internal organs;
- leukemia;
- diabetes.
A low concentration of calcium in urine indicates:
- problems with digestion of food, causing diarrhea and vomiting;
- problems with the kidneys (impaired filtration);
- lack of vitamin D by the body;
- hypoparathyroidism.
- X-ray of the spine - what does it show? Find the answer here!
- Ultrasound of axillary lymph nodes shows what
- What does an MRI of the cervical-thoracic spine show?
- What does an oak from a vein show?
Disease Prevention
Urine submitted for Sulkowicz tests provides useful information for doctors and parents of children. It is possible to prevent the development of a number of diseases or stop their progression in the initial stages. These include:
- tremor of the upper extremities;
- tremor or cramps of the lower extremities;
- Wilson's disease (a congenital disorder associated with copper metabolism that can destroy the central nervous system and internal organs of a person);
- pancreatitis;
- hypoparathyroidism;
- tuberculosis (affecting the kidneys, bones and lungs);
- formation of granulomas (affect the liver, kidneys, lymph nodes), etc.
Also, the Sulkovich test in an infant allows you to diagnose benign or malignant neoplasms. After all, cancer cells provoke excessive calcium production.
With the help of analysis, you can detect problems in the endocrine system of a small child, pathologies of the urinary tract, kidney dysfunction, etc.
This analysis can significantly help the patient in identifying serious disorders and preventing their development and further occurrence. The test is especially recommended for newborns, although age is not an indicator for analysis.
Collection of biological material for analysis
Urine for the Sulkowicz test must be collected, with the opportunity to immediately deliver it to the laboratory. Otherwise, after 2 hours it will become unsuitable for research. Collecting biological material from an infant and newborn is quite difficult. The most accurate result is determined by the Sulkovich test using urine accumulated over a day, but it is impossible to carry out a similar procedure with a child who cannot understand what exactly is required of him.
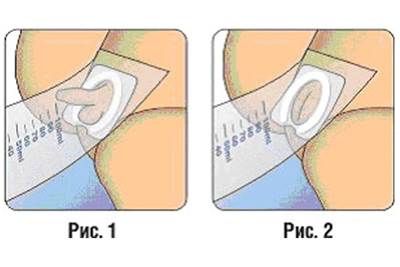
Urine collection
How to collect urine from a baby? To implement this plan, urinals were developed. These are devices that are attached to the child’s genitals using Velcro, without causing pain.
When prescribing the Sulkovich test for the first time, a one-time urine collection is allowed; subsequent laboratory testing requires daily biological material. This is because the second analysis is intended to clarify the meaning obtained earlier.
Features of sample collection
Collecting biomaterial for analysis according to Sulkovich is quite simple. By following a few rules, you can easily understand how to collect samples and send them for research:
Urine for the Sulkowicz test is collected using sterile transparent measuring containers, which are sold at any pharmacy. This is true for those children who go to the toilet on their own. Special urine collectors are provided for infants. Please note that they are universal, especially for boys and separately for girls. The idea is to attach them to the genitals and put a diaper on top. Urine collectors are transparent bags with adhesive tape. Due to this design, they can be easily attached to children. When the child pees there, you can pour the urine into a previously prepared sterile container. Before collecting urine, the baby’s genitals must be washed. It is best to use purified water and active detergents. Only the latter should not contain foaming additives or flavorings. Otherwise, they may get into the samples and not give a positive or negative reliable answer during the study. In children, morning samples are required for testing. It is not recommended for your baby to eat or drink before going to the toilet. The normal process of urination involves three stages. This is the first, middle and last urine output. It is advisable to collect the middle portion and the last one, but for children it is difficult to guess the stage. Whenever possible, be sure to follow the rules. How much urine do you need? There is no norm as such. This means that you need to donate as much as the baby can give. This amount of urine should be tightly closed with a lid in the container and immediately sent to the laboratory. If urine is collected more than 2 hours before sample collection, the calcium value may be incorrect.
It is extremely important to obtain a sample from the child that is as fresh as possible.

For analysis, in addition to following the collection algorithm, it is necessary to follow certain nutritional recommendations. In order to obtain the correct reaction from the baby’s diet, you need to exclude:
- puff pastry;
- baked goods;
- tea;
- chocolate;
- spices;
- fermented milk and dairy products.
Also, for children under one year old and for older children, physical activity should be minimized. These recommendations must be followed at least 2 days before the scheduled delivery of urine samples.
Why is calcium assessment so important?
The importance of calcium for the human body is difficult to overestimate. Most of this trace element is found in teeth and bones. Disorders in calcium metabolism can be detected using blood or urine tests. The Sulkovich test makes it possible to determine the degree of this disorder. The amount of calcium released from the body can be used to judge the condition of the kidneys and metabolism in bone tissue.
Monitoring urine calcium levels is very important, especially in infants. This is due to the fact that a lack of this microelement can lead to improper formation of bone tissue. That is, the structure of the bone tissue becomes more fragile, which subsequently leads to skeletal deformation.
Excessive levels of calcium in children's urine can cause bone destruction or the development of seizures. This is very dangerous and requires immediate medical treatment. In addition, excess calcium, deposited in the skeletal system, leads to slower bone growth.
The main use of the Sulkowicz test is in pediatrics, since almost immediately after birth, doctors prescribe vitamin D for children to prevent the development of rickets.
Rickets is a very common disease that is dangerous. Vitamin D is needed to regulate phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the human body. If there is not enough calcium, then softening of the bones can occur, which negatively affects the baby’s skeleton. If there is an acute deficiency or absence of calcium, then rickets often develops. Newborns are at risk of serious health complications that cannot always be eliminated.
If rickets develops in childhood, then over time, the child receives high bone compliance or crooked limbs. Often even the child’s head becomes square in shape, and the fontanel does not heal for a very long time.
When a doctor prescribes the use of vitamin D, he must accurately take into account the daily amount of the norm, since otherwise a complication will arise that leads to the development of pathologies.
It is very important to monitor the calcium level in an infant, since excess, as well as deficiency, has an extremely negative effect on health. Bones cannot grow properly, and pathological processes with them lead to irreversible processes.
The baby must have a normal calcium level; in order to achieve it, you need to adjust your diet or resort to medications.
Absorption and excretion of calcium
Calcium is present in our daily diet. About 40% of the total amount of calcium salts (carbonates, phosphates, etc.) entering the body with food is absorbed in the intestines. The initial part of the duodenum is responsible for their absorption.
The absorption process occurs against the concentration gradient and requires energy expenditure from enterocytes (intestinal epithelium). This process is regulated by calcitriol (the active form of vitamin D), which stimulates the synthesis and transport of calcium transport proteins.
During the day, approximately 400 mg of Ca is excreted from the human body in stool and 100 mg in urine. It is the presence of calcium in the urine, its increased concentration, that is the object of study with the Sulkovich test.
| What increases calcium absorption? | |
| Vitamin D | The active form of vitamin D (calcitriol) in the body stimulates the synthesis of calcium transport protein in intestinal epithelial cells |
| Parathyroid hormone (parathyroid hormone) | An increase in the level of this hormone in the blood leads to increased synthesis of the active form of vitamin D (increased activity of 1a-hydroxylase in the kidneys) and increased absorption of the microelement |
| Acidity | A decrease in acidity leads to increased absorption of calcium salts, as their solubility increases. In an alkaline environment, absorption decreases as insoluble salt is formed |
| Diet rich in proteins | As protein levels in the daily diet decrease, absorption decreases. |
| Amino acids | Some amino acids (lysine, arginine) increase calcium absorption by increasing the solubility of its salts |
| Sugars and organic acids | Organic acids produced by intestinal microflora during the fermentation of sugars increase the solubility of calcium salts and increase their absorption |
| What reduces calcium absorption? | |
| Phytic acid | Phytic acid is found in cereals; when it interacts with calcium, it forms insoluble salts, reducing the absorption of the mineral. |
| Oxalates | Oxalates are present in leafy vegetables |
| Dietary fiber (fiber) | Excess dietary fiber in the diet leads to decreased absorption of calcium in the intestine and increased excretion in stool. |
| Increasing consumption of phosphates, magnesium | |
| Taking glucocorticoids (steroids) | Taking glucocorticoids is accompanied by a decrease in calcium transport into intestinal epithelial cells |
Table 1 - Factors affecting calcium absorption
After absorption in the intestine, calcium ions enter the blood plasma. In the plasma they are in three equilibrium states: free, bound to proteins and bound to anions.
- 1Half of blood calcium is in free, ionized form. It is the ionized form that is metabolically active and is responsible for maintaining the normal functional state of nerve fibers, the permeability of cell membranes, muscle contraction and hormone secretion.
- 240% of the total is in a protein-associated state (most often in association with albumin).
- 310% is associated with plasma anions (bicarbonate, phosphate, lactate, citrate).
| Age | Male gender, mg/dl | Female gender, mg/dl |
| 1-14 years | 9.6 – 10.6 | 9.6 – 10.6 |
| 15-16 years old | 9.5 – 10.5 | 9.1 – 10.3 |
| 17-18 years old | 9.5 – 10.4 | 9.1 – 10.3 |
| 19-21 years old | 9.3 – 10.3 | 8.9 – 10.1 |
| 22 and older | 8.9 – 10.1 | 8.9 – 10.1 |
Table 2 - Level of calcium in blood plasma depending on age
The main functions of the microelement in the body:
- 1Development of bone tissue (skeleton, teeth). For the normal formation of the skeleton, a huge amount of trace elements is required.
- 2Bones are also a calcium reservoir. Osteoblast cells are responsible for bone mineralization, and osteoclasts are responsible for resorption, which lead to the leaching of microelement salts from the skeleton.
- 3Excitation and contraction of myocytes (muscle tissue cells). Ca ions, interacting with troponin, trigger myocyte contraction. They also reduce the excitability of skeletal muscles (with a decrease in the level of Ca in the blood, convulsions can develop).
- 4Conduction of nerve impulses.
- 5The microelement is one of the key links in the blood coagulation system.
- 6The mineral is necessary for the release of hormones (insulin, parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, vasopressin) from the cells of the endocrine glands.
- 7Activation of pancreatic enzymes, blood coagulation system, renin (an enzyme responsible for the regulation of blood pressure).
1.1. How does calcium get into the urine?
The main structural unit of the kidney is the nephron, which consists of a network of tubules densely intertwined with a capillary network. Each kidney has more than one million nephrons. Calcium enters the primary urine through filtration of blood plasma in the renal glomerulus.
From the lumen of the nephron tubules into the surrounding capillaries, the nutrients and microelements necessary for the body, including Ca, are reabsorbed. This creates secondary urine, which a person releases when urinating.
An increase in the level of Ca in the blood plasma is accompanied by an increase in its concentration in primary urine. The maximum threshold concentration of a microelement in plasma at which its complete reabsorption from primary urine in the nephron tubules will occur is 7.5 – 9.0 mg/dl.
Consequently, if the plasma contains a slightly higher concentration of Ca (a level of no higher than 10-10.5 mg/dL is considered normal), then its salts are found in the secondary urine. Exceeding the physiological threshold leads to a pronounced increase in the concentration of the microelement in the excreted urine.
Preparing for the test
Before donating urine, you need to familiarize yourself with the rules for preparing for the Sulkovich test. The main place in them is occupied by the list of prohibited foods, ignoring which leads to an incorrect value for the obtained indicator. You should stop consuming the following foods and drinks three days before your test.
- Fermented milk and dairy products.
- Greenery.
- Chocolate.
- Pastries made from butter or puff pastry.
- Sweet dishes.
- Fruits, particularly bananas.
- Mineral water.
- Alcohol.
- Strong tea
- Juices.
- Coffee (regardless of type).
You also need to forget about physical activity for a while and, if possible, avoid stressful situations. Women should postpone the Sulkowicz test if they have started their menstrual periods.
Where is the research conducted?
The diagnostic procedure must be performed in specialized laboratories that have a state license and good reviews. These include, for example, “Sinevo”, “Invitro”. Helix operates according to high international standards
It is important that they use such high-quality reagents that are produced by Gemotest
The price of this analysis may vary in different institutions, but not very significantly. In this case, it is better to choose a good quality diagnostic. Before donating biological fluid, you should receive instructions on preparing for the procedure, collecting material, and correct delivery. This will help to avoid mistakes when interpreting the result and to find out the true state of the patient’s health.
How to collect the analysis correctly?
When directly collecting biological material, you need to follow the following algorithm:
Recommended topic:
Urine analysis during pregnancy
- Buy a sterile urine container with a screw-on lid.
- Carry out hygienic treatment of the genitals using regular soap, which does not contain additives, including fragrances.
- Collect urine from the second and third streams (the first is not necessary).
- Close the container without touching the inside. It is treated with a preservative to preserve liquid.
- Deliver the urine to the laboratory for a Sulkowicz test.
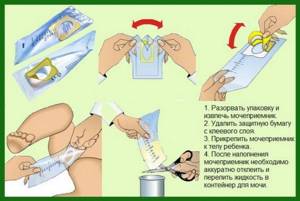
The main condition is to comply with the time of urine collection. This should happen in the morning. You should not eat or drink before the procedure. The fence rules are mandatory for both adults and children.
The boy should place a pre-prepared container under the stream, and the girl should simply place it in the pot. It is advisable to first show the child the device and explain why it is needed. Then everything will be done correctly and without unnecessary emotions.
How to collect urine from infants
Many parents have significant difficulties in the process of collecting urine for analysis from infants. It is quite difficult to track the process of urination in this situation; in fact, it is spontaneous.
Squeezing urine out of a diaper or diaper, or pouring urine from a pot is strictly prohibited due to the introduction of a large number of foreign impurities, including pathological ones, into the sample.
Moreover, only the morning portion is suitable for collection, respectively, taken before the first morning feeding. What to do in this situation?
The optimal scheme for collecting biomaterial includes the following points:
- In the morning, at least 4 hours should pass between feeding and urine collection. If necessary, set yourself an alarm clock to monitor the situation;
- To directly collect biomaterial, you can use a special urinal, which is a soft, sterile bag with a convenient hole. Using the available Velcro, it is fixed between the child’s legs, after which the process of urination occurs. It should be taken into account that the collection should be carried out in an upright position of the baby’s body in order to prevent potential mixing of the biomaterial with fecal matter.
Carrying out analysis
Sulkovich's test is carried out as follows: a reagent containing ethanedioic acid is added to the patient's urine; in everyday life it is called oxalic acid. Urine is a waste product of the metabolic process, excess fluid and minerals. The interaction of ethanedioic acid with the latter, in particular with calcium, leads to the formation of a precipitate (turbidity), on the basis of which the result of the Sulkovich test is determined.
Its interpretation can be carried out in different ways, it directly depends on the specialist. Therefore, the data obtained during decoding are taken into account as relative indicators. The Sulkovich test is always supplemented with other laboratory tests: biochemical analysis of urine and blood. Detection of creatinine and other elements will clarify the clinical picture.
What is Sulkowicz's test?
A laboratory test of urine, which can be used to determine the presence of calcium in urine, is called the Sulkowicz test. It shows how much of a given element is excreted from the body. Its overestimated or underestimated value indicates the presence of a number of diseases or that it is necessary to pay attention to the daily diet. Typically, this type of test is prescribed for infants who are suspected of having rickets.
The main reasons why a doctor may refer a patient for analysis using the Sulkowicz method are:
- intake of vitamins A and D in quantities exceeding the norm;
- assumption of the presence of rickets;
- the likelihood of developing Besnier disease;
- possible presence of oncological formations;
- suspected hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Purpose and principle of the Sulkowicz test in children
Rickets is a severe disabling disease that occurs due to a lack of calcium in the body or a violation of its absorption due to a lack of vitamin D. Children in infancy are more often affected; symptoms develop gradually and may not be clearly expressed until the baby begins to grow vigorously, sit, walk.
As the load on the bones increases, their deformation develops and skeletal function is disrupted. Nervous system disorders, muscle atrophy, and digestive disorders occur. Treatment of a developed disease is quite difficult and lengthy, and is not always effective.
That is why a urine test for calcium content is regularly taken from children, starting from the newborn period, in order to identify the slightest deviations and take action. Increased calcium in the urine is the result of the fact that it is not completely absorbed by the body; its content in the blood is also increased. Accordingly, more of it enters the urine.
Decoding the results
Sulkovich's reaction is deciphered visually. The visual determination of turbidity is expressed using points, and the result is recorded using pluses. Insoluble sediment (if present) receives a score from 1 to 4. The average value of the indicator is considered the reference value. Obtaining such a result from the Sulkovich test indicates the absence of deviations in the amount of vitamin D and refutes suspicions of the presence of hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia.
Score decoding of the Sulkovich test:
- 0 points – lack of calcium in the body, a bad indicator. Possible rickets in a child and hypoparathyroidism in an adult. There is a possibility of a malignant tumor that has metastasized, pathological absorption, convulsive syndrome, hypoalbuminemia, and kidney problems. The patient is registered, special attention is paid to children.
- From 1 to 2 points – a normal ratio of minerals, characterized by maintaining balance. No additional action is required.
- From 3 to 4 points – exceeding the upper limit of the reference value, presumably hypercalcemia or increased influence of the parathyroid gland. The possibility of further detection of osteoporosis, sarcoidosis, colitis, diabetes mellitus, and leukemia is noted.
If it is impossible to determine the result, it is recorded as doubtful, and the test is repeated after 3-4 days. It is also possible to get an erroneous result. It can be both positive and negative. It is affected by:
- Taking medications. An increase is caused by antacids, vitamin D itself (multivitamins containing it), Furosemide and glucocorticoids. The opposite effect is possible when using Indomethacin, oral contraceptives and Aspirin.
- Inclusion of prohibited foods in the diet. The consequences of this step are different: heart problems, loss of concentration, nausea, vomiting, polyuremia, general weakness.
After performing the Sulkovich test, the attending physician prescribes additional laboratory tests. If they confirm the result obtained earlier, then he selects treatment, during which the effect of the measures taken is monitored. This is only possible using the same Sulkovich test. In the absence of the expected effect, the complex of therapeutic measures is revised, that is, other medications and procedures are selected.
The patient is required to strictly comply with all prescriptions, timely take control tests and inform the specialist about changes in well-being. You should also eat right, because eating prohibited foods will significantly reduce the benefits of the treatment measures taken.
Functions of calcium
Calcium is necessary for every cell of the body, being part of many enzymes and ensuring the transport of substances across cell membranes. We list its main functions and tasks:
- Structural element of bones.
- Regulates the process of blood clotting.
- Provides impulse transmission in nerve cells and myocytes.
- Increases metabolic rate.
Calcium is especially important in childhood. With its deficiency, which is often observed due to a lack of vitamin D, the dangerous disease rickets develops. Its symptoms are a violation of the formation of the skeleton and irreversible pathology of the nervous system. Therefore, monitoring calcium concentrations is most often used in early childhood.
Indications for the Sulkovich test
The analysis is prescribed not only for children, but also for some conditions in adults. The indications are:
- Preventive examination of all children under 1 year of age.
- For children over one year of age with suspected rickets and other pathologies associated with microelement deficiency.
- To confirm the diagnosis of sarcoidosis in adults. The calcium level is significantly increased.
- In case of overdose or excess intake of vitamins A and D from food.
- In oncology for diagnosing tumors, most of which produce calcium.
- In the complex diagnosis of thyroid diseases (hyper- or hypothyroidism).
- The presence of seizures or patient complaints of tremors of the limbs.
- For tuberculosis (lungs, bones, kidneys).
- If Wilson's disease (congenital disorder of copper metabolism) is suspected.
- Formation of granulomas in various organs.
- For pancreatitis, hypoparathyroidism.

Sulkowicz test
Analysis methodology
Sulkovich's test does not require complex equipment and expensive drugs. Urine in a test tube is mixed with a reagent (oxalic acid) in a ratio of 2:1. Usually 5 ml of urine and 2.5 ml of acid are mixed. Calcium forms a salt - calcium oxalate, which precipitates. The solution itself becomes milky in color. The results are assessed by the amount of sediment and the rate of sedimentation in the test tube. The laboratory technician describes the result using the following terminology:
- “–” — turbidity is completely absent. This is an unfavorable situation, indicating a lack of vitamin D or pathology of the parathyroid glands.
- “+” - insufficient turbidity of urine, which is considered a normal variant. In combination with clinical symptoms, the doctor may assess this result as the initial stage of hypocalcemia and prescribe small doses of vitamin D for correction.
- “++” is optimal urine turbidity, which is considered normal and does not require intervention.
- “+++”—turbidity is more intense than expected. This means increased calcium levels and increased production of vitamin D.
- “++++” - severe turbidity of the solution. Indicates a disease or excess calcium intake from food or bone tissue.
Despite the lack of quantitative results, the Sulkowicz test is rarely misinterpreted. The amount of sediment differs sharply in the appearance of the solution, which does not give the laboratory assistant any reason to doubt one or another interpretation.
Interpretation of urine analysis according to Sulkovich
To evaluate, you need to take morning urine. A very important condition is to take tests on an empty stomach, otherwise a high-quality diagnostic study will not be carried out. The interpretation of the analysis is determined by the level of urine turbidity. If the result is negative, it indicates the presence of hypoparathyroidism. Thus, both calcium and vitamin D are insufficient in the human body. Hypocalcemia may also be present, but such a diagnosis is determined subject to parallel blood testing for reliability.
A negative result may mean:
- lack of ergocalciferol in the human body;
- disruption of the functioning of the thyroid gland and decreased production of hormones;
- defect in magnesium metabolism;
- metastases of a malignant tumor in the prostate gland that have penetrated into the bones;
- chronic and acute kidney failure, which is characterized by the release of diluted urine;
- use of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal medications, diuretics containing hydrochlorothiazide;
- a hemotest determined intolerance to products containing calcium.
One or two points, that is, + or ++, is the established average norm in urine, indicating low calcium content.
Three and four points (+++ or ++++) indicate excessive release of calcium from the body during bladder emptying. For example, when a patient has hyperparathyroidism, approximately 200 milligrams of this macronutrient are washed out of his body in the urine in 24 hours. Deviations from the norm require additional diagnostics and effective therapy.

Evaluation of results
A clinical laboratory technician visually assesses the degree of change in urine clarity and expresses it in points (from 0 to 4) or in the number “+”
- 0(-) - there is no turbidity, the test is negative, the amount of calcium in the urine is below normal or absent altogether. Characteristic of hypoparathyroidism, tetany, pathological absorption and rickets.
- 1 (+) - weak, slightly milky-white turbidity of the urine gives reason to say that the calcium level is within acceptable limits and the test did not reveal any disturbances in calcium mineral metabolism.
- 2(++) - moderate cloudiness of urine indicates an increase in the level of calcium in the urine, but is not a 100% sign of the development of a pathological condition.
- 3(+++) and 4(++++) - significant and pronounced turbidity of urine is observed due to the high calcium content in it and is characteristic of hypervitaminosis with vitamin D, hyperproduction of parathyroid hormone in hyperparathyroidism and tumors of the parathyroid gland, kidney diseases, long-term treatment with glucocorticoids.
There are 2 possible options for distorting the results:
- Inflated results occur due to improper preparation - collecting urine after a meal; when consuming calcium and vitamin D supplements the day before the study.
- Reduced results may appear with various diets with an increased phosphorus content, a shift in the acid-base balance of urine to the alkaline side and, as a result, the acidic Sulkovich reagent will be neutralized by alkaline urine.