Types of urine tests:
A general urine test is the most common and common test. This test is prescribed when the first symptoms of the disease appear and for preventive purposes.
There are also special urine tests for a child, which are prescribed only for diagnostic purposes. For example, a urine test according to Nechiporenko (if cystitis, glomeronephritis, pyelonephritis is suspected), Zimnitsky test to assess the condition of the kidneys, Sulkovich test (a screening test to determine the amount of calcium in the body), Rehberg test (to assess the efficiency of the kidneys), urine test for hormones , urine culture for sensitivity to antibiotics , etc.
The amount of urine may increase (polyuria) with:
- Consuming large amounts of liquid;
- Eating foods that increase diuresis (watermelon, pumpkin);
- Kidney diseases (pyelonephritis);
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Dystrophies.
A decrease in the amount and volume of urine (oliguria) can occur with:

- Limiting fluid intake;
- Increased sweating;
- Diarrhea;
- Vomit;
- Kidney disease;
- Circulatory failure.
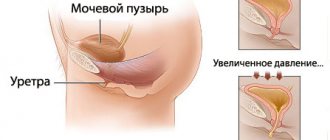
Urinary retention in the bladder can occur due to:
- prostate cancer and adenoma;
- prostatitis;
- narrowing of the urinary canal;
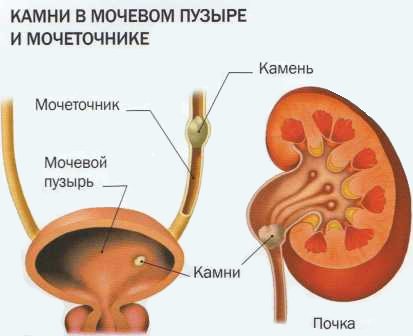
- obstruction of the bladder outlet by a stone.
The predominance of nighttime urine volume over daytime (nocturia):

- chronic pyelonephritis;
- chronic renal failure;
- heart failure.
Cessation of urine excretion (anuria) or excretion of no more than 50 ml per day:
- general condition disorders (shock, blood loss, decreased blood pressure);
- renal causes (poisoning with kidney poisons, transfusion of incompatible blood);
- disruption of urine flow from the kidney (stones, tumor).
Normally, daytime diuresis prevails over nighttime in a ratio of 3:1.
Daily volume measurements allow us to suspect problems in various organ systems.
For men and women, the daily diuresis rate is different.
This is due to differences in metabolic rate and hormonal processes.
In order for metabolic processes to proceed at a normal speed, it is necessary to consume at least 500 ml of liquid per day.
On average, the recommended amount is 1 – 2 liters.
How to properly prepare a child for a general blood test, how to collect urine for analysis.
In order for the results of a child’s urine test to be reliable, it is necessary to properly prepare the child for the test. On the eve of the urine test, you should not feed your child vegetables and fruits that can change the color of the urine (beets, carrots). Urine for research is collected in a special sterile plastic container or urine bag (for collecting urine from infants), which can be bought at a pharmacy or taken from a diagnostic laboratory. Before collecting urine, be sure to wash your child. Girls are washed from front to back, then, with a cotton swab dipped in warm water, wash the area between the labia. For boys, when washing, the foreskin is pulled back, exposing the head of the penis.
For a general urine test, it is best to take morning urine. The baby releases the first portion of urine into the toilet, and you must collect the rest of the urine in a container. If you collected evening urine, then you need to store the jar with the material in the refrigerator so that the main indicators do not change.
Daily diuresis of a pregnant woman
During pregnancy, a woman’s body receives a double load.
It does not occur immediately, but as the fetus grows.
An increase in the volume of circulating fluid leads to an increase in the need for water support.
This can lead to fluid accumulation in a woman's body.
Because of this, swelling develops.
During fetal growth, waste products enter the maternal bloodstream.
This forces a woman’s kidneys to work harder.
The volume of daily urine increases.
On average, the figure is 60–80% of fluid consumed.
Pregnant women note an increase in the frequency of urination.
This is due to fetal pressure on the bladder.
Norms of urine tests in children
The normal urine test results for a child depend on the type of analysis and the age of the child. The color of a child’s urine is normally rich yellow, from straw to amber yellow, the urine should be transparent, the smell should not be pungent, there should be no protein in the urine or traces of protein are detected, there should be no glucose (sugar) in the urine, red blood cells Normally, they are not detected or are single in the preparation, leukocytes are normally up to 5 in boys and 8-10 in girls in a single portion of urine, the epithelium is normally single, mucus is practically not found normally.
Change in urine color due to medication
Some drugs are excreted from the body by the kidneys along with urine. Some of them are capable of changing its normal color:
- a red color may occur when taking the antibiotic rifampicin, antipyretics - amidopyrine and antipyrine, as well as the laxative purgen, which contains phenolphthalein;
- Pink color of urine can be caused by long-term use of high doses of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin);
- a dark brown color may occur during treatment with phenyl salicylate;
- the blue-green color is caused by triamterene, which is used to enhance renal blood flow;
- Orange urine color occurs when taking the vitamin riboflavin.
What to do if the urine test shows leukocytes or red blood cells?
An increase in leukocytes in a child’s urine or the appearance of red blood cells is a reason to consult a doctor. Since untimely treatment of the causes that caused these deviations from the norm is very dangerous.
The presence of red blood cells in a child’s urine (hematuria) indicates that blood is mixed into the urine. Most causes of hematuria require careful evaluation and treatment. Red blood cells appear in glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, kidney tumors, cystitis, urolithiasis, intoxication of the body, injury to the kidneys or bladder, etc.
If there is an increased number of white blood cells in a child's urine, make sure that you wash the child thoroughly. The reasons leading to an increase in the level of leukocytes in the urine are a child’s urinary tract infection, a kidney infection, inflammation of the child’s external genitalia, metabolic disorders, etc.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
This is a water-soluble vitamin, which is an essential nutrient, an antioxidant and an important coenzyme for many biochemical processes in the human body.
Research method
High performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS).
Units
µg/ml (micrograms per milliliter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 8 hours before the test; you can drink clean still water.
- Completely avoid taking medications 24 hours before the test (in consultation with your doctor).
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Ascorbic acid is a water-soluble vitamin necessary for many biological processes in the body. It is not synthesized in the human body and accumulates in tissues in minimal quantities, so its reserves must be constantly replenished with food. The main sources of ascorbic acid are plant products: rose hips, black currants, citrus fruits, green vegetables (especially broccoli), tomatoes, potatoes, peppers.
Vitamin C has a powerful antioxidant function and neutralizes free radicals in cells, protects against oxidative stress. It is a coenzyme for many metabolic processes. It takes part in the formation of collagen, carnitine biosynthesis, iron absorption, and the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine. In addition, ascorbic acid is necessary for wound healing and tissue growth, for the functioning of the adrenal glands, the secretion of hormones and interferons, the metabolism of folic acid, tyrosine, and phenylalanine. It increases the absorption of iron, reduces the concentration of cholesterol in the blood and helps reduce high blood pressure. Ascorbic acid helps strengthen the body's protective properties and enhances the immune response to infectious diseases.
Smoking, hemodialysis and stress increase the body's need for vitamin C.
When consuming more than 2 g of vitamin C in one dose, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea may occur, and 3 g may cause increased liver enzymes. Excessive amounts of vitamin C are excreted in urine and feces. At the same time, the level of oxalates in the urine increases, which, in kidney pathology, contributes to the formation of urinary tract stones.
With a deficiency of ascorbic acid, the formation of connective tissue is disrupted, intradermal, intraarticular and intracavity hemorrhages occur, inflammation and bleeding of the gums, joint pain, hair loss, dry skin, severe weakness and fatigue, and emotional instability. With insufficient intake of vitamin C in children, bone growth is impaired.
In economically developed countries, cases of scurvy (vitamin C deficiency) are rare and affect poor people or people who abuse alcohol. Cases of vitamin C deficiency have been reported with strict adherence to a macrobiotic diet.
With malabsorption syndrome (impaired absorption of nutrients from the digestive tract), metabolic disorders occur, which are manifested by signs of multivitamin deficiency.
What is the research used for?
- To diagnose vitamin C deficiency (scurvy).
- For differential diagnosis of conditions accompanied by increased bleeding and impaired wound healing.
When is the study scheduled?
- When examining a patient with suspected vitamin C deficiency (with gum inflammation, increased bleeding, delayed wound healing).
- When examining a patient with intestinal absorption disorders.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 4.00 - 20.00 µg/ml.
Reasons for increased vitamin C levels:
hypervitaminosis caused by increased consumption of ascorbic acid (temporary, since excess vitamin C is quickly removed from the blood).
Reasons for low vitamin C levels:
- scurvy (vitamin C deficiency);
- malabsorption (impaired absorption of nutrients in the intestines);
- alcoholism or drug addiction;
- pregnancy;
- hyperthyroidism;
- renal failure;
- rheumatic diseases;
- oncological diseases.
What can influence the result ?
- Gender (in women, the content of ascorbic acid in tissues and biological fluids is higher than in men).
- Smoking (nicotine reduces the half-life of ascorbic acid).
- Presence of concomitant pathology.
- Use of certain medications (acetylsalicylic acid, barbiturates, oral contraceptives, estrogens).
- Ingestion of toxic substances (nitrosamines, pesticides) and heavy metals.
Also recommended
- Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin)
- Vitamin B9 (folic acid)
- Vitamin K (phylloquinone)
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid)
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxal 5-phosphate)
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
- Vitamin A (retinol)
- Vitamin E (tocopherol)
- Complete blood count (without leukocyte formula and ESR)
- Coprogram
Who orders the study?
Therapist, general practitioner, pediatrician.
Literature
- Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 16th ed. NY: McGraw-Hill; 2005: 2607 p.
What can affect the analysis result?
The amount of urine that is released per day can be influenced by certain factors.
The patient is recommended to keep a diary in which he will monitor the amount of fluid he drinks.
In particular, you can mark food and medicine in it.
During the test period, you should avoid eating diuretic products, pickles, and spicy foods.
Any medications that cannot be stopped should be discussed with your doctor.
It is worth noting the time you take medications in your diary, this will help avoid false indicators.
Reasons for changes in urine volume in pathologies
Increased urine output occurs in a variety of conditions:
- Increased body temperature;
- Hydronephrosis;
- Conn's syndrome;
- Psychosomatic disorders in children;
- Increased levels of parathyroid hormone;
- OPN.
A decrease in diuresis volume occurs for prerenal, renal or postrenal reasons.
Prerenal factors include processes that occur without involving the genitourinary system.
This may be a sharp decrease in circulating fluid, spasm of blood vessels due to shock conditions, or acute thrombosis of arteries and veins.
Cardiovascular pathologies can indirectly affect a decrease in daily urine volume.
Renal causes lie in the pathology of the kidneys themselves.
This may be direct damage to the kidney tissue or impaired circulation through the renal arteries.
The reasons may be:
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Vasculitis;
- Kidney injury;
- Toxic effect of substances;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Nephrotic syndrome.
The decrease in diuresis is based on dysfunction of the renal tubules.
Changes in the function of the ureters are among the postrenal factors of oliguria.
Ureteral obstruction can be caused by several reasons.
Blood clots, stones, and strictures can impede the passage of urine.
There may be external pressure from the uterus, which has increased, for example, during pregnancy.
Tumor formations can also put pressure on the wall of the ureter.
This leads to disruption of the outflow of urine from the kidneys.