Ultrasound of the knee joints is an ultrasound examination of the knee that reveals hidden inflammatory processes in its structures, pathological processes that, without timely treatment, can lead to a decrease in a person’s quality of life and even disability.
The ultrasound method for diagnosing knee joints is actively used in traumatology and rheumatology. In inflammatory and degenerative dystrophic processes, the method provides the most reliable information and allows you to determine further medical tactics.
Using ultrasound, it is possible to examine soft tissue structures, clarify the presence and amount of effusion, and detect diseases at the initial stage of development.
Many connective tissue diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, occur for a long time without significant clinical manifestations. Using ultrasound, it is possible to promptly identify pathological changes and carry out effective treatment. At the CONSTANTA Clinic in Yaroslavl, you can perform an ultrasound of the knee joints using innovative technology - a modern device of the SonoScape S20/S20Pro/S20Exp/S15 ultrasound system . Our patients receive high-quality medical care, undergo diagnostics of large and small joint structures with an optimal combination of price and quality of services.
TOP 6 questions about ultrasound
No. 1. Is it necessary to undergo an ultrasound if there are X-ray results?
These studies characterize the condition of the joint from different angles. Traditional radiography evaluates bone structures, while ultrasound visualizes cartilage and soft tissue, as does MRI. If we are talking about inflammatory diseases, this examination cannot be avoided, otherwise it will be impossible to detect the source of pain.
No. 2. Is it necessary to examine two symmetrical joints with an ultrasound if one hurts?
Need to. A comparative assessment of the affected and healthy joints is more revealing than examining only the diseased joint. It allows you to detect pathological processes that do not yet have clinical manifestations, as they are at an early stage. It is especially important to examine both knee or elbow joints after injury in order to prevent the development of post-traumatic arthrosis due to microdamage to a seemingly healthy joint.
No. 3. Is it necessary to do an ultrasound of the knee if you have flat feet?
Flat feet are a risk factor for arthrosis of the knee joint, despite the fact that the disease may not bother you at all. Therefore, if the diagnosis of flat feet is confirmed, it is necessary to pay special attention to the condition of the knees, because degenerative changes in large joints often do not have clinical manifestations.
No. 4. Why is it recommended to periodically repeat ultrasound of the same joints?
Joint diseases go through several stages - exacerbation and remission. The degree of the inflammatory process changes, as does its localization. The attending physician individually determines how often the examination needs to be repeated in order to avoid complications such as synovitis or Baker's cyst. Ultrasound helps determine how much joint blockade is necessary, whether inflammatory fluid needs to be evacuated, etc.
No. 5. Will an ultrasound help with a knee injury?
In case of traumatic damage to the knee joint, it is the ultrasound examination that helps to visualize ruptures of the lateral collateral ligaments, hemorrhages, meniscal tears and disturbances in the structure of the ligaments. However, diagnosing cruciate ligament ruptures in this case is difficult, since due to their specific location they are poorly visualized.
No. 6. Will ultrasound help with rheumatism?
Rheumatism and a number of other diseases are characterized by the presence of inflammation in the joint. Ultrasound clearly visualizes inflammatory fluid in the cavity and surrounding tissues. The more it is, the more pronounced the inflammatory process. In addition, the doctor evaluates its structure. Over time, the fluid becomes viscous and thick, which indicates the duration of the disease, and not a recent exacerbation of the disease. The conclusion of an ophthalmologist often becomes decisive in such cases when choosing therapy, be it evacuation of inflammatory fluid, injections or other methods.
Ultrasound visualizes inflammation in joints well
What is the difference between MRI and ultrasound of the knee joint?
Ultrasound and MRI of the knee joint are two fundamentally different examinations. On an ultrasound, the image is visualized by treating the area being diagnosed with ultrasonic waves. Magnetic resonance imaging is a method of in-depth examination of a joint with a detailed display of all muscle-bone tissues using the effect of nuclear magnetic resonance. During an MRI, the patient is placed in a tomograph where a powerful magnetic field is created. Then the radio frequency pulse sensors are turned on. Under the influence of a magnetic field and RF, the protons of hydrogen atoms in the body's cells begin to vibrate, and this resonance is picked up by the device's computer. It processes the received data and converts it into digital three-dimensional images. This is how a series of MRI images of the knee appear on the installation screen. Since soft tissue cells contain a lot of water, MRI of the knee shows the condition of ligaments, menisci, nerve endings, and tendons better than ultrasound. However, both ultrasound and MRI of the joint do not visualize bone well. They are best examined using x-rays or computed tomography.
Advantages of the method
- You can undergo an ultrasound of the joints at any age, including during pregnancy.
- The examination is safe and painless.
- It is allowed to go for the procedure several times in a short period of time, which allows you to monitor the clinical picture over time.
- Ultrasound machines are mobile and can be used if a person is immobile.
- No preliminary preparation is required.
- The gel is hypoallergenic in nature.
In complex cases, MRI is indispensable
Decoding the research results
The patient receives an interpretation of the ultrasound diagnostics within 10-15 minutes after the procedure. Normally, all surfaces should be smooth and clear, the joint capsules look like hypoechoic structures. The doctor pays attention to the uniformity of hyaline cartilage and the quality of tissue nutrition. There should be no inflammatory effusion inside.
The ultrasound examination method allows you to detect:
- signs of infectious and inflammatory processes;
- age-related and post-traumatic changes;
- hematomas;
- degenerative-destructive changes;
- deterioration of blood circulation and nutrition of cartilage tissue;
- cysts, tumors, metastases;
- dislocations, fractures, ligament tears, meniscus injuries.
To interpret the resulting images, the specialist must have knowledge of the anatomical features of the structure of the knees and the blood circulation of nearby tissues. The CONSTANTA Clinic employs experienced diagnosticians who are well acquainted with the common problems of this anatomical zone and successfully carry out differential diagnosis, providing reliable examination results.
Damage to tendons and ligaments
Injuries to the tendon-ligamentous system occur during sports activities, falls, rare jumps and awkward movements. Ultrasound makes it possible to assess the integrity of connective tissue and detect hematomas. With partial ruptures, the contours of the tendon are preserved, but a hypoechoic zone is noticeable at the site of injury. It can also be seen between bone fragments when the patella is fractured.
Meniscus injuries
The menisci can be damaged by sudden rotation of the tibia, excessive flexion or extension of the limbs. In the first days after injury, sharp pain occurs and movement is limited. The skin is swollen and hyperemic. In this condition, the patient needs urgent medical attention. If conservative therapy is ineffective, meniscectomy must be performed. When the menisci are damaged, their contours are disrupted, hypoechoic areas and extraneous stripes appear. The appearance of effusion inside the joint is characteristic. Diagnostics must be carried out as soon as possible in order to assess the severity of the condition and, for certain indications, carry out therapeutic and diagnostic arthroscopy.
Rheumatoid arthritis
This disease is accompanied by destructive changes, the formation of osteophytes, subcutaneous nodules and nerve damage. The disease is chronic. Patients complain of morning stiffness in the joints and constant pain. Inside the knee joint, exudate accumulates, contractures and characteristic deformities appear. During the examination, specialists detect osteophytes, effusion, narrowing of the joint space and thinning of hyaline cartilage.
What knee diseases can be determined using this method?
Ultrasound is recommended for any complaints - pain, redness, swelling, crunching in the knee. With its help, you can confirm or refute the presence of injury, meniscopathy, hemorrhage, dysplasia, inflammatory pathologies, and neoplasms.
- Ultrasound allows one to predict the development of gonarthrosis by the height of the cartilage and the volume of intra-articular fluid.
- In case of injuries to the knee area, the examination will help differentiate between sprains and ruptures of ligaments, meniscal injuries and bone fractures.
- If a tumor is found in the knee, we can conclude that it is benign or malignant.
- The study reveals bursitis, synovitis, arthrosis and arthritis, tendonitis.
Ultrasound examination of the knee is important before or after surgery
Disadvantages of MRI of the knee joint
- MRI of the knee joint has a number of severe limitations. Tomography is contraindicated if the patient’s body has metal-containing implants, for example: a steel prosthesis, electronic pacemakers - neuro- or cardiac pacemakers.
- Disadvantages of MRI of the knee include the length of the procedure. It can last 30 minutes, and if the pathology is serious and contrast enhancement is required, then the scanning duration reaches 40-60 minutes.
- During the tomography of the knee joint, any movement is prohibited, as this will negatively affect the clarity and accuracy of the MRI images. Therefore, young children have to undergo MRI of the knee under anesthesia.
- MRI of the knee joint using a closed tomograph can be difficult for people suffering from claustrophobia, epileptic seizures and panic attacks.
Ultrasound of the knee: can arthrosis be detected?
Ultrasound examination allows you to analyze the following parameters:
- outlines of the joint – smooth or not, clear or not;
- bone layer - uniform or uneven, an accurate indicator of thickness;
- synovial fluid - are there any inclusions, flocculent, thread-like impurities, what is the volume compared to the norm;
- cartilage – normal or thinned;
- the joint space is widened or narrowed;
- joint capsule – is there any thickening or thinning;
- menisci – size, contours, structure, inflammation, echogenicity.
If there are no deviations from the norm in all respects, the knee joint is healthy. Otherwise, the doctor may suspect the initial stage of arthrosis and refer you for additional examinations. Pathology is also indicated by the presence of free fluid in the intra-articular cavity, a change in the volume of articular structures, and a violation of the integrity of the ligaments.
Cost difference
The affordable price of joint ultrasound allows all patients to undergo examination. You just need to make an appointment for a scan at a time convenient for you. MRI of the knee joint is a more expensive test. However, the information content of MRI of joints is certainly higher than ultrasound examination.
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the knee joint | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| Appointment with an orthopedist | 1800 rub. | free after MRI | free after MRI |
| First aid program for joints (8 studies + appointment with an orthopedist + MRI of the joint) | 13000 rub. | 7500 rub. | 7500 rub. |
| Ultrasound services of joints | price, rub. |
| Ultrasound of the knee joint | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of any two large joints | 2500 rub. |
Knee ultrasound options
To fully examine the knee joint, the ultrasound specialist uses different access points:
- Anterior access. Provides information about the thigh muscles, patella, and fatty tissue. The patient takes a supine position with the leg extended.
- Rear. In this form, you can visualize the menisci, nerves and vessels under the knee, tendons, muscles of the calves and lower legs, and the cruciate ligament. The person lies on his stomach.
- Medial. In the supine position, the patient extends the leg straight. The doctor examines the joint capsule, collateral ligaments, internal parts of the meniscus, articular surfaces of bones, cartilage, and synovial fluid.
- Lateral. For this procedure, the leg is bent at the knee 30-40°, which makes it possible to identify pathologies of the fascia lata, external meniscus and lateral ligament, and articular capsule.
During an ultrasound of the knee, the patient takes several different positions
When is MRI of the knee better than ultrasound?
Any pathology of the structures of the knee joint can be clearly seen on MRI, which in its diagnostic value is superior to both radiography and ultrasound. X-rays do not show soft tissues, and very often a knee injury is associated with damage to these tissues. Tomography visualizes occult stress fractures much better than CT, since swelling is clearly visible, which does not appear at all on x-rays. An ultrasound of the knee cannot show the ligaments and cartilaginous structures with the same level of detail and does not show the bones very well. If you have any pain in your knee or have suffered an injury, it is better to immediately go to an orthopedist or emergency room for a magnetic resonance imaging scan without wasting time. It will help you accurately and quickly identify:
- all hidden fractures, dislocation and subluxation;
- ruptures of ligaments, tendons and muscles;
- damage to soft tissues, which are characterized by inflammation;
- some systemic diseases.
The tomography procedure does not require any special preparation. You just need to choose a diagnostic center and sign up for an examination in advance. The procedure itself will take 20-30 minutes of your time, and another 30-40 minutes of waiting will be required to receive the results of the study - a series of images and an expert opinion from the doctor. Unfortunately, if you do not have medical knowledge, it will be difficult for you to understand what exactly the radiologist wrote in the conclusion, so the RIORIT clinic offers a free express consultation after an MRI of the joints with an orthopedist who will explain what was revealed during the examination in a simple way, in a language that the patient can understand and recommend therapy if necessary.
Is it possible to undergo an ultrasound for those who do intra-articular injections?
Intra-articular injections of Noltrex synovial fluid prosthesis or another drug are not a contraindication to ultrasound, but there is one limitation. It is necessary to take a break of at least five days between the injection and the ultrasound examination. Otherwise, due to insufficient visualization, the results may be unreliable.
If there are indications, you should not refuse ultrasound of the joints - an informative and reliable method. However, it should be remembered that the accuracy of the study largely depends on the competence of the specialist. If you need to obtain information not about joints, but about bones, you cannot do without X-rays or CT scans.
Indications for the procedure
The knee joint is one of the largest and most complex in the human body. It is responsible for the movement of the limb, connecting the patella, femur and tibia. Against the background of increased stress and degenerative processes, various pathologies can develop. Ultrasound helps to detect the slightest disturbances in the structure and functionality of cartilage, joints, and the functioning of blood vessels. Most often, specialists have to deal with meniscus tears or cruciate ligament injuries.
Main indications:
- knee pain;
- limited mobility;
- bone deformities;
- the appearance of local swelling, redness of the skin;
- the presence of a palpable formation;
- decreased muscle strength.
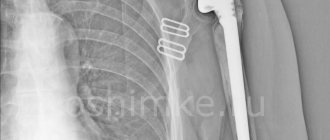
Surgery
Surgical removal of Baker's cyst of the knee joint is carried out according to certain indications:
- ineffectiveness of drug and physiotherapeutic treatment;
- excessively large size of the tumor;
- presence of signs of rupture of the cyst membrane;
- signs of necrotic changes in the popliteal fossa;
- impairment of motor functions in the knee joint.
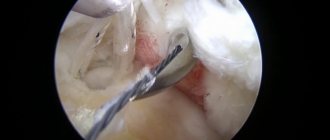
Surgical removal of the tumor is performed in one of the following ways: traditionally, using an arthroscope or laser.
Traditional removal is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor makes an incision over the cyst, isolates it and resects it. After removal, the surgical wound is inspected, the blood vessels are coagulated and sutured layer-by-layer.
Arthroscopy involves minimally invasive surgical removal of a Baker's cyst. During the operation, soft tissues are practically not injured and blood vessels are not damaged. The cyst is removed using special instruments. The entire process is displayed on the monitor, as a micro-video camera is inserted into the knee joint.
The laser provides high temperature - up to 800 ° C, with which the cyst is coagulated. The liquid contents are evacuated, and a light guide is inserted into the cyst cavity. Next, it is heated and the walls of the cavity are glued together.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Factors that contribute to the formation of Baker's cyst have been studied for many years. Modern traumatologists and orthopedists identify a number of reasons that entail the development of a neoplasm:
- Hard physical labor.
- Intense sports activities with stress on the knee joints.
- Inflammatory processes in the joint. The motor activity of the knee joint depends on the synovial fluid, which acts as a shock absorber. It washes all the structural elements of the joint and, as it were, lubricates them. During inflammation, synovial fluid leaks from the joint into the tendon bursa. She cannot return back, since the valve prevents this. This is how a cyst is formed. Moreover, the longer the inflammation lasts, the more fluid is produced in the knee joint and removed from it, the larger the size of the Baker cyst becomes.
- Dystrophic changes caused by osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis.
- Injuries - rupture of knee ligaments, damage to cartilage, meniscus.
- Excess weight, which puts excessive stress on the knee joints.