Attention!
The information in the article is for reference only and cannot be used for self-diagnosis or self-medication. To decipher the test results, contact a specialist.
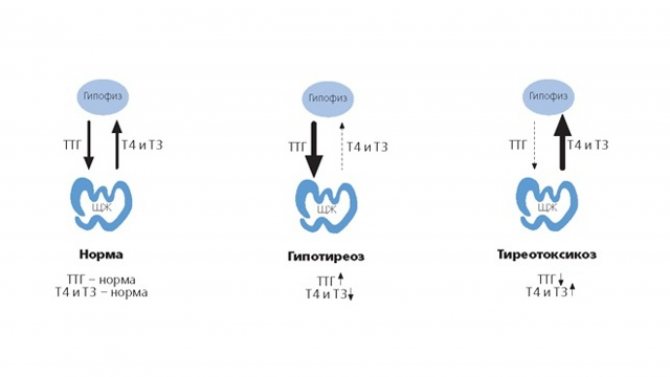
A TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone, thyrotropin) test is a laboratory test that measures the level of this hormone in the blood. Its result makes it possible to assess the quality of the thyroid gland. Most often, doctors conduct diagnostic tests to identify hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland.
Thyrotropin is
Thyrotropin is a substance produced by cells in the anterior pituitary gland. It activates the production and release into the blood of these hormones produced by the thyroid gland. The hormone triggers the growth of thyroid cells and accelerates their division. The formation of TSH is triggered by the thyrotropin-releasing factor of the hypothalamus.
This process occurs when the level of hormones circulating in the blood decreases. TSH has an inverse logarithmic relationship with the T4 content in the blood. When T4 production levels increase, TSH decreases. And if the concentration of T4 decreases, TSH production increases.
This mechanism maintains the constant content of hormones at the required level. TSH secretion is regulated by neuronal mechanisms. Its speed changes during sleep, with a decrease in temperature, and nonspecific stress.
For TSH, daily changes in concentration are typical. The highest blood TSH values are achieved between 2 and 4 am. This level remains at these values from 6 to 8 am. The minimum TSH content is recorded at 17-18 hours.
The normal rhythm of TSH production and release during wakefulness at night is disrupted. Pathologies of the thyroid gland lead to a decrease in the level of thyroid hormones in hypothyroidism or to their excess content in the blood in hyperthyroidism.
The hormone stimulates the functioning of thyroid cells. This organ is located on the front of the neck and has the shape of a butterfly. Glandular tissue produces hormones that regulate most body functions. The most important among them are metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate.
The hormone TSH regulates the production of thyroid hormones by cells through a feedback mechanism. When T4 and T3 levels decrease, the pituitary gland produces more of the hormone. This way it stimulates the thyroid cells. With a high content of these substances, the pituitary gland reduces the intensity of TSH synthesis.
This mechanism maintains a constant level of thyroid hormones, as well as metabolic stability. When connections between the thyroid gland, hypothalamus and pituitary gland are disrupted, the functioning of the endocrine glands is disrupted. Situations arise when, with high levels of T3 and T4, thyroid-stimulating hormone continues to increase.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone activates blood supply to thyroid tissue. Iodine, which its cells need to function, is more actively absorbed. This element increases the production of thyroglobulin, triiodothyronine, thyroxine.
They are responsible for the metabolism of nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) in the body. Hormones also determine the functioning of the digestive and reproductive systems. The functioning of the circulatory system and higher nervous activity depend on them. Both deficiency and excess of TSH, as well as the level of thyroid hormones, affect the condition of the human body.
Principles of therapy
The basis of treatment for hypothyroidism is replacement therapy. If a woman’s body lacks hormonal substances, they need to be replenished. Then the balance is stabilized, and you feel immediately better. But for the entire period of treatment, laboratory tests are periodically required to determine the condition of the pituitary gland and thyroid gland. If there are slight deviations, the dosage is adjusted.
Additionally, they change their diet. Products such as flour, fiber, walnuts, and cottonseed can affect the activity of replacement therapy drugs. As with any other disease, you need to drink at least 2 liters of water per day to avoid dehydration.
They refuse preservatives and carcinogens, eat healthy foods, including sea fish, seaweed, seafood, they contain iodine.
They take multivitamins to enhance systemic metabolism and establish regenerative processes. Be sure to use iodine-based preparations, as they normalize the activity of the thyroid gland and bring its function back to normal.

L-Thyroxine for replacement therapy
L-Thyroxine is a hormonal drug containing high concentrations of levothyroxine sodium. Available in tablet form. Provides the following pharmacological action:
- enhancing tissue growth and development;
- normalization of metabolism;
- improving the anabolism function of proteins and fats;
- normalization of the activity of the cardiovascular and nervous system;
- stabilization of the hypothalamus.

The drug is indicated for hypothyroidism, goiter, thyroid cancer, and deterioration of its function after chemotherapy. The dosage depends on the degree of development of the pathology and the results of laboratory tests. The drug is contraindicated in the following conditions and diseases:
- individual intolerance;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- inflammation, necrosis of the heart muscle;
- adrenal insufficiency.
Since the composition contains excipients, the product is not recommended if there is a deficiency of the enzymes that process them. Treatment during pregnancy and lactation should continue. If you stop taking the medicine, it will have a negative impact on the fetus. There may even be a miscarriage. However, the dosage is adjusted depending on the woman’s condition and test results.
How does Yodomarin affect?
Iodomarin is a drug for replacement therapy that supplies potassium iodide to the body. It is prescribed not only for the treatment, but also for the prevention of thyroid diseases. The drug causes pharmacological effects:
- regulation of metabolism;
- normalization of anabolism of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, energy;
- improving the activity of the cardiovascular system and brain;
- child growth and development.

Indications for use in the treatment and prevention of goiter, instability of thyroid hormone secretion. It can be used by both children and adults. Recommended during pregnancy to reduce the risk of thyroid dysfunction in the fetus. Adverse reactions occur extremely rarely:
- local allergy, accompanied by rhinitis, conjunctivitis, itching, burning, and skin irritation;
- Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock, dermatitis.

The drug is contraindicated for use in hyperthyroidism, thyroid adenoma, Dühring's dermatitis, and individual intolerance. The medicine is used with caution, as there is a risk of overdose. The main symptoms are dyspeptic disorders, diarrhea, dehydration, shock. It is necessary to discontinue the drug and rinse the stomach.
Eutirox against hypothyroidism
Eutirox is a medicine based on levothyroxine sodium. Used as hormone replacement therapy. It improves metabolism, normalizes the ratio of proteins and carbohydrates. The functionality of the cardiovascular and central nervous systems increases during illness. The TSH level gradually returns to normal. Replacement therapy is prescribed for life.
The drug is indicated for the treatment of hypothyroidism, goiter, and thyroid cancer, but it is also used to prevent these conditions by patients at risk.
Side effects are rare. Only an allergic reaction in the form of angioedema is possible. Then the patient is prohibited from using the drug. It is replaced with another medicine. The following contraindications for use are identified:
- individual intolerance;

- thyrotoxicosis;
- pituitary, adrenal insufficiency;
- use of antithyroid drugs by pregnant women.
The medicine is approved for use in severe heart pathologies and diabetes. The dosage is strictly regulated; laboratory blood tests are often performed to determine the amount of hormones. If the patient’s health worsens, the drug is replaced with analogues.
Why is Thyroidin needed?
Thyroidin is a natural remedy intended for replacement therapy of thyroid pathology. It is based on dried thyroid gland, which is crushed and added to tablets. Due to them, pharmacodynamic processes occur:
- organization of pituitary gland activity;
- tissue growth and regeneration;
- increased cell need for oxygen;
- normalization of energy processes in the body;
- stabilization of kidney function, nervous and cardiovascular systems, liver;
- increased cholesterol metabolism.

The drug is indicated for use in congenital thyroid deficiency. Due to this condition, inhibition of physical and mental development often develops. Thyroidin is also taken for myxedema, hypothyroidism, and diseases of the pituitary gland. It can be used during thyroid cancer, obesity, goiter.
The drug should not be used in case of Addison's disease, diabetes mellitus, exhaustion of the body, thyrotoxicosis, or coronary insufficiency.
Side effects are extremely rare. This is due to the fact that the medicine is based on natural products and there are no chemicals. Possible increased agitation, sleep disturbance, increased sweat production, tachycardia, local allergic reactions.
Traditional methods of treatment
The therapy is based on the use of traditional medicinal components. Traditional methods are an auxiliary treatment that improves the function of the thyroid gland and the general well-being of the patient. The following methods are used.
- Eating seaweed
. Take 5 g of crushed leaves. The powder is diluted with water. The solution should be used correctly before bedtime.
- Dried cocklebur
. Take 3 g of the plant and pour boiling water over it. Leave for 1 hour. Filter, drinking half a glass every day before meals.
- Coltsfoot, St. John's wort, licorice root
. The dried plants are mixed. Take 1 teaspoon. Take raw materials and pour a glass of boiling water. Place in a water bath and heat for 8-10 minutes. Take the medicine 50 ml on an empty stomach.
- Tinctures
. To raise TSH, use tincture of flaxseed, fern, nettle, celandine, and walnut. They enhance metabolism and normalize the functioning of thyroid hormones.
- Fig fruits
. Activate the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone. This will not increase the amount significantly, but with additional use of medications, your health will improve.

Many patients confuse traditional methods of therapy with the treatment of another disease. However, with hypothyroidism you need to be careful. Not all medicinal plants are suitable for therapy. For example, a decoction of licorice root will worsen the condition and increase blood pressure.
Indications for taking a TSH test
TSH testing is considered one of the most important in the hormone diagnostic program. Often the analysis is prescribed simultaneously with the T3 and T4 hormones. Indications for the purpose of the study are as follows:
- suspicion of thyroid disease;
- reproductive disorder;
- infertility;
- the presence of anovulatory cycles;
- absence of menstruation;
- an increase in the size of the thyroid gland;
- suspicion of diffuse or nodular goiter;
- manifestations of hypothyroidism;
- presence of clinical signs of thyrotoxicosis;
- poor weight gain in children;
- delayed mental and physical development in children.
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- baldness;
- insomnia;
- trembling in hands;
- decreased sexual desire;
- persistent diarrhea;
- dry skin;
- exophthalmos;
- decreased cold tolerance;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- impotence;
- constipation;
- premature sexual development.
The study is carried out to monitor the treatment of infertility and thyroid pathologies.
Why is an increase in TSH dangerous?
An increase in thyrotropin secretion is observed relatively rarely; it manifests itself as hypothyroidism or thyrotoxicosis. Symptoms usually progress quickly. High concentrations of thyrotropin in women often cause infertility, difficulties with conception, spontaneous abortion in the early stages, severe toxicosis, bleeding, fetal hypoxia, developmental delay and even fetal death. The consequence of high TSH can also be problems with the heart, vision, mucous edema, thyrotoxic crisis, atherosclerosis, and disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system. Without medical care, a woman's quality of life can seriously deteriorate.
With timely, competent treatment and strict adherence to all medical recommendations, the prognosis is generally favorable.
Preparation for the procedure
On the eve of the test for the TSH hormone in the blood, the patient is advised to be careful when taking medications and vitamin complexes containing iodine. It distorts the results of the analysis. Doctors recommend stopping taking medications that inhibit the formation of hormones two weeks before testing for hormones.
If for some reason this cannot be done, notify the laboratory assistant about the drugs used. In order for the analysis result to be reliable, preparations for it begin three days in advance. To obtain correct testing data, it is recommended to do the following:
- refusal of alcohol and soda;
- diet excluding fatty, spicy and fried foods;
- smoking restrictions;
- elimination of psycho-emotional stress;
- abstinence from sports and physical labor;
- you cannot have dinner later than 20.00;
- exclude other medical procedures (intravenous, intramuscular injections, massage);
- avoid diagnostic procedures (fluoroscopy, ultrasonography) the day before;
- cancellation of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Take a blood test for TSH on an empty stomach. You are allowed to drink a glass of still water.
What may affect the results
Before performing a TSH test, the patient is advised to exclude exposure to factors that could affect the test result or seriously complicate its interpretation. These include the following:
- Hormonal drugs that affect TSH levels. The system of connections in the thyroid-pituitary gland system is affected by medications for six weeks. Thyrotropin levels are monitored only for two months after adjustment of hormonal medications.
- Medicines. A wide range of drugs leads to an increase in concentration: Amiodarone, Atenolol Motilium and many others. Before donating blood for TSH, you should discuss with your doctor the list of medications that you take regularly. If possible, he will suggest you temporarily stop taking them.
- Severe stress. When a patient is in a long-term unresolved stressful situation or experiencing a short-term severe stressful situation can lead to variations in the concentration of thyrotropin.
- Physical exercise. Heavy physical work or high load during sports training significantly changes TSH levels.
- Infectious diseases. If you have recently suffered from an infectious pathology that significantly changes the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone, warn medical personnel about this.
- Times of Day. The level of TSH in the blood varies significantly throughout the day. Therefore, monitoring of this indicator is always carried out at the same time of day.
- Pregnancy. The content of thyrotropin increases significantly in the third trimester of pregnancy.
When the purpose of the analysis is to monitor the ongoing therapy for thyroid diseases, the day before the diagnostic procedures, the medication is stopped.
How the research is carried out
Taking a TSH test is a universal procedure that does not require special medical instruments or equipment. It is carried out in all clinical laboratories (both paid and public). It is recommended to donate blood in the morning (from 8 to 11 am). The TSH concentration is determined using a chemiluminescent immunoassay on microparticles, which has a high level of accuracy. For this purpose, blood serum obtained from the patient’s vein is used. The procedure itself does not cause severe pain, but may be accompanied by minor discomfort. As a rule, you can get results within 1-2 business days. It is important to understand that the patient receives exclusively diagnostic data, without interpretation and diagnosis. This is done exclusively by the attending physician. If the TSH test is normal , then WHO recommends conducting the next examination no earlier than in a year. If there are problems with the thyroid gland, the frequency of the procedure should be increased to 2 times a year. You can get a TSH test at the medart clinic.
TSH norm
Normal TSH levels change with age. Its values may vary among pregnant women.
| Age | Norm TSH µIU/ml |
| newborn | 1,1-17,0 |
| up to 2.5 months | 0,6-10,0 |
| from 2.5 to 14 months | 0,4-7,0 |
| from 14 months to 5 years | 0,4-6,0 |
| from 5 to 14 years | 0,4-5,0 |
| over 14 years old | 0,4-4,0 |
| over 50 years old | 0,27-4,2 |
In pregnant women, the TSH level in the analysis ranges from 0.2 to 3.5 μIU/ml
Features of thyroid-stimulating hormone

When trying to independently determine what to do if the TSH test is elevated, you should take into account the normal daily variability of its level. The range of physiological fluctuations in values can be 1-3 mU/l. The highest concentration is observed late at night - at 2-4 o'clock. Then a slight decrease occurs. Thyrotropin is secreted in a pulsating manner.
The highest concentration is also observed at 6 am, and the lowest - in the period of time preceding the evening (17-19 hours). If a woman’s standard sleep-wake pattern is disrupted, the rhythm of secretion changes and a shift occurs to a later date. The circadian rhythm normally persists in old age and during pregnancy.
Individual variability (variability) of indicators, due to the use of different methods and test systems by laboratories, is of clinical importance. When interpreting the result of the study, it is important to exclude the influence of drugs that can increase the concentration of thyrotropin.
Analysis transcript
The information presented is for reference only and the analysis should only be interpreted by a specialist.
If TSH is elevated
A decrease in TSH in the blood is detected much less frequently than an increase in this hormone. A thyrotropin content below normal is considered a sign of an increase in the concentration of thyroid hormones. It occurs with thyrotoxicosis or hyperthyroidism. The TSH level increases in the following pathologies:
- hypothyroidism (secondary, primary);
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis;
- pituitary tumors (basophilic adenoma, thyrotropinoma);
- unregulated secretion of TSH;
- lung tumors secreting thyrotropin;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- lead poisoning;
- preeclampsia;
- mental disorders;
- thyroid hormone resistance syndrome;
- juvenile hypothyroidism;
- other neoplasms of the pituitary gland;
- removal of the gallbladder;
- excessive physical activity;
- carrying out hemodialysis.
Taking many medications leads to an increase in TSH levels in the blood. These include: anticonvulsants, beta blockers, calcitonin, radiocontrast agents, iodide, morphine, rifampicin, prednisolone.
If TSH is low
A decrease in hormone levels is observed in the following cases:
- diffuse toxic goiter;
- latent thyrotoxicosis;
- hypothyroidism in pregnancy;
- thyrotoxic adenoma;
- postpartum pituitary necrosis (Sheehan's disease);
- traumatic damage to pituitary tissue;
- abuse of low-calorie diets;
- breakdown;
- starvation;
- self-correction of T4;
- TSH-independent thyrotoxicosis.
A decrease in the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone is noted when taking certain medications. These include: glucocorticoids, anabolic steroids, cytostatics, antihypertensive drugs (dopexamine, dobutamine), nifedipine, thyroxine, dopamine and other drugs.
What additional tests are prescribed?
Often, to identify pathology of the endocrine system, a more in-depth examination of the patient’s endocrine system is required. For this purpose, the following studies are prescribed, in addition to the TSH test in the blood:
- total triiodothyronine (T3 total) - its function is considered to be the regulation of energy (oxygen absorption by cells) and plastic metabolism in the body;
- total thyroxine (T4 total) - regulates energy and plastic metabolism in tissues;
- free thyroxine (free T4) - a biologically active portion of total thyroxine, which plays a major role in the metabolic process;
- free triiodothyronine (T3 free) - an active fraction of triiodothyronine not bound to plasma proteins, regulating the activity of basal metabolism, cell growth, metabolism of nutrients and microelements, as well as the activity of most body systems;
- antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) - immunoglobulins against the enzyme of thyroid cells responsible for the production of the active form of iodine;
- antibodies to thyroglobulin (antiTG) are immunoglobulins that oppose the activity of the precursor of thyroid hormones.
After TSH and other tests, in addition to a visit to an endocrinologist, you may need to consult the following specialists: therapist, surgeon, gynecologist, pediatrician, neurologist.