What does a biochemical blood test show?
For a patient undergoing the procedure for the first time, it will be important to find out what is included in the biochemical blood test, how the procedure is carried out, and what indicators will be examined.
The term refers to a diagnostic laboratory study of a number of substances contained in human blood, which determine the normal functioning of both each individual organ and the body as a whole. The technique allows you to evaluate metabolism for diagnostic purposes and identify some pathological processes occurring in the human body. In combination with a general blood test, a biochemical study is carried out both at the initial stages of diagnosing diseases and as a preventive measure to prevent complications. LHC is one of the most accessible ways to detect health threats early. The analysis is so informative that modern diagnosis of most diseases cannot be done without it. It is a mandatory component of screening examinations during pregnancy.
Currently, in the clinical practice of many public medical institutions, a biochemical blood test consists of general indicators, for example, total protein, cholesterol, and does not include advanced indicators. Medical provides the opportunity, depending on the doctor’s orders, to take both a standard and an extended blood test for biochemistry.
During the study, depending on the purpose, the following indicators will be determined:
- blood proteins are complex molecular structures involved in metabolism, tissue regeneration, hormone production, and the movement of substances necessary for the functioning of cells;
- blood pigments are metabolic products of protein structures involved in the systemic energy exchange of muscle fibers;
- carbohydrates, which play a very significant role in providing energy to all tissues of the human body;
- enzymes are substances synthesized by the body;
- inorganic substances - intracellular electrolytes that maintain acid-base balance, participate in the synthesis of blood plasma, normalization of water-electrolyte balance;
- Lipids are substances that enter the blood from consumed food. Partially produced in the human body during synthesis by the liver from carbohydrates.
- low molecular weight nitrogenous substances - substances produced in the human body for energy metabolism in muscle and other tissues.
How to determine a frozen pregnancy?
As a rule, women come to the gynecologists of the Miracle Doctor clinic when they observe signs and symptoms of premature termination of pregnancy:
- reduction of soreness and swelling of the mammary glands,
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen,
- weakness, chills, increased body temperature,
- symptoms of toxicosis have stopped (nausea, vomiting, dizziness, etc.),
- bloody, dark brown vaginal discharge.
The described signs do not allow one to reliably determine a frozen pregnancy at home. Any of these signs are not reliable and can occur during a normally developing pregnancy. Only a gynecologist can make a diagnosis during a face-to-face appointment.
Indications for taking a biochemical blood test
In most cases, blood biochemistry is prescribed by a doctor to establish and clarify the diagnosis. The analysis is most effective in diagnosing diseases and pathological conditions of the following organs and systems:
- urinary system;
- reproductive apparatus;
- heart and blood vessels;
- hepatobiliary system;
- musculoskeletal tissue;
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- endocrine system;
- hematopoietic systems.
You need to take a biochemical blood test when diagnosing any somatic or infectious disease, as well as if you suspect a pathology in the functioning of any of the above organ systems. Often BAC is prescribed during treatment. In this case, based on the results of the analysis, the doctor will be able to assess the dynamics of the therapy used.
Maximum accuracy, and therefore the information content of the analysis, will largely depend on the correct preparation carried out by the patient himself.
Preparing for a biochemical blood test
The effectiveness and information content of a biochemical blood test can be influenced by many factors, so patients will be interested in learning how to minimize errors as a result of biochemistry. In order for the analysis to be as informative as possible, it must be preceded by preliminary preparation. As a rule, compliance with the following measures does not present any difficulties for the patient:
- 1-2 days before the biochemistry analysis procedure, you should pay attention to your diet: you need to adhere to the principles of a gentle neutral diet, which involves excluding alcohol, fried, smoked, spicy foods, and spices from the diet. It is necessary to significantly reduce the consumption of caffeine-containing and energy drinks, and strong brewed tea.
- It is good if the patient manages to avoid psycho-emotional stress and active physical activity 24-48 hours before the test.
- On the eve of the procedure, you should avoid thermal stress on the body: baths, hot long showers, sunbathing, which can significantly affect the results of the study.
- If the patient is indicated for systematic use of medications, medications should be taken after blood sampling. If stopping taking medications is impossible for health reasons, notify your doctor about the therapy you are taking. If the purpose of the procedure is to test cholesterol, after consultation with a doctor, the patient should stop taking statins (medicines used to lower the level of “bad” cholesterol).
- You need to take a biochemical blood test on an empty stomach; the last meal before visiting the laboratory should be no later than 8-12 hours. For the most accurate interpretation of the results, in some cases the doctor may warn the patient that on the eve of donating blood for analysis, he should refrain from brushing his teeth. For example, even toothpaste can affect the carbohydrate content in the blood, because taste buds can activate insulin production, and the test result will not be accurate enough.
- An hour before the procedure, you must stop smoking.
This is important to know:
- Studies of indicators such as glucose, bilirubin, lipids, creatinine should be performed strictly on an empty stomach.
- LHC indicators can vary depending on a person’s natural biorhythms, so the analysis is recommended to be performed in the morning: the optimal time is 8-10.00.
- If the patient is undergoing a repeat test to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, it is important that it is carried out under the same conditions and preparation as the previous one.
- Drinking pure still water does not affect the test results, so you can drink before the analysis.
- The indicator standards are determined for the analysis carried out in the morning.
- LHC must be performed before any other studies: x-ray, MRI, CT, ultrasound, as well as before physiotherapeutic procedures and massage.
Failure to comply with the rules of preparation for LHC can lead to significant distortion of indicators, and, as a result, incorrect interpretation of the biochemical study.
Many patients who are scheduled for a test for the first time are interested in the progress of the procedure.
Immediately before the procedure, the patient is recommended to sit for 10-20 minutes. After this, a special rubber tourniquet is applied to the area of the arm above the elbow for better visualization of the veins. After this, the needle insertion site is treated with an antiseptic and intravenous blood is drawn into a test tube. The tourniquet is loosened immediately after blood flow begins, and the puncture site is again treated with an antiseptic. If blood sampling from the central vessel of the elbow is not possible, the wrist or inner surface of the forearm can be an alternative site for venipuncture. At the end of the procedure, the puncture site is covered with a napkin and, if necessary, sealed with a band-aid.
Tubes with collected blood are labeled and sent to the laboratory for testing.
Norm of indicators
When studying blood biochemistry standards, you can notice insignificant variability: when deciphering a biochemical blood test, the patient’s age, gender, and physiological state are taken into account. The upper and lower limits of normal were determined based on a study of healthy people. For ease of use, the norms of BAC indicators in adults are given in the table.
Biochemical blood test standards:
| Substance | Indicator name | Unit | For men | For women |
| Squirrels | Total protein | g/l | 64-83 | 64-83 |
| Albumen | 33-50 | 33-50 | ||
| SRB | mg/l | up to 0.5 | up to 0.5 | |
| Hemoglobin | g/l | 130-160 | 120-150 | |
| Pigments | Total bilirubin | µmol/l | 3,4-17,1 | 3,4-17,1 |
| Bilirubin indirect | Up to 20 | Up to 20 | ||
| Direct bilirubin | 0-3,4 | 0-3,4 | ||
| Carbohydrates | Glucose | mmol/l | 3,88-5,83 | 3,88-5,83 |
| Fructosamine | µmol/l | 205-285 | 205-285 | |
| NAV | Creatinine | 44-106 | 44-97 | |
| Urea | mmol/l | 2,4-6,4 | 2,4-6,4 | |
| Uric acid | µmol/l | 210-420 | 145-350 | |
| Enzymes | ASAT | U/l | Up to 41 | Up to 31 |
| AlAT | Up to 41 | Up to 31 | ||
| Alpha amylase | 27-100 | 27-100 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase | Up to 270 | Up to 240 | ||
| Inorganic substances | Iron | µmol/l | 11,6-30,4 | 8,9-30,4 |
| Chlorine | mmol/l | 98-107 | 98-107 | |
| Potassium | 3,5-5,5 | 3,5-5,5 | ||
| Calcium | 2,15-2,5 | 2,15-2,5 | ||
| Phosphorus | 0,87-1,45 | 0,87-1,45 | ||
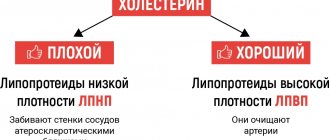
| Lipids | Total cholesterol | 3-6 | 3-6 | |
| LDL | 2,2-4,8 | 1,92-4,51 | ||
| HDL | 0,7-1,83 | 0,8-2,2 |
Decoding the biochemical blood test
The finished analysis result is handed over to the patient or transferred to the attending physician at the hospital department on a form indicating the patient’s data, the name of the laboratory and a table indicating which indicators were examined, their level and relationship with the norm.
Interpretation of the analysis results is the prerogative of the doctor. Only an experienced specialist will be able to correctly interpret the BAC indicators to make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy: the doctor takes into account the presence of concomitant diseases, the gender and age of the patient, medical history and many other factors that may influence the level of the BAC indicators.
What can a deviation from the norm in a biochemical blood test indicate?
The hemoglobin level may vary due to completely natural reasons (for example, it decreases during pregnancy or, on the contrary, increases as a result of a flight preceding the analysis or a long stay in high mountains. However, a decrease in this same indicator will tell the doctor the cause of hypotension, increased fatigue, or the patient’s complaints of night cramps in the extremities. Based on the result of the analysis, the patient may be diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia - a hematological syndrome that is characterized by a lack of iron and, as a consequence, a decrease in hemoglobin levels. Reduced hemoglobin may also indicate more serious pathologies: neoplasms of various etiologies, internal bleeding, infectious disease , disturbances in the functioning of the hematopoietic system.An increase in the indicator may indicate dehydration of the body, cardiopulmonary failure, erythrocytosis, intestinal obstruction.
Pathological values of the total protein indicator can be represented by either a reduced content or an increased one. Most often, doctors encounter a reduced indicator. Reduced protein is characteristic of such body conditions as dehydration, pregnancy and lactation, and may be a consequence of physical and psycho-emotional stress or taking certain medications. An upward deviation in the indicator indicates the development of an infectious process and intoxication of the body. With diseases such as lupus erythematosus, sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, cirrhosis of the liver, blood protein levels will certainly be elevated.
C-reactive protein is an important marker of any inflammatory process in the human body. The exception is when a woman takes systemic hormonal contraceptives; a slight increase in CRP in this case is normal.
Bilirubin in the blood may increase due to poor preparation for the test (overeating on the eve of the test, alcohol abuse). If, however, the results of the analysis, with careful preparation of the patient, indicate a deviation from the norm in the direction of increase (hyperbilirubinemia), then, most likely, pathology can be suspected of damage to the liver tissue, cholecystitis, cirrhosis, hemorrhage in the tissue. A reduced value of the indicator may indicate cardiac ischemia, tuberculosis and other chronic diseases accompanied by low levels of red blood cells.
Low glucose levels (hypoglycemia) cause energy starvation of tissue cells in the human body; most often, this pathological condition negatively affects the functioning of nerve cells and the brain. Glucose below normal is characteristic of some endocrine diseases, insulinoma, insulin overdose, and malignant neoplasms. With alcohol intoxication, use of amphetamines, long-term diets that involve a significant reduction in food intake, or long-term hormone therapy, the indicator may also differ from the norm to a lesser extent. An increased value of the indicator in the analysis can be observed in pathologies of the endocrine system, pancreas or thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, heart disease, hyperfunction of the adrenal cortex.
The determination of such an indicator as fructosamine is most relevant for patients with diabetes mellitus. Regular monitoring of this indicator allows the endocrinologist to timely adjust therapy and insulin dosing.
If the levels of creatinine and urea are outside the normal range, and, as a rule, the doctor evaluates these indicators in combination, we can conclude that there is a pathology in the functioning of the kidneys. Decreased readings have no diagnostic value. For natural reasons, a high-protein diet and increased physical activity can affect an increase in indicators. An increase in the concentration of substances in the blood appears in case of impaired renal function, including blockage of the renal pelvis, diabetes mellitus, prostate adenoma, malignant neoplasm of the prostate, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. An increase in creatinine always occurs against the background of extensive trauma or burns.
If there is a suspicion of disturbances in the functioning of the liver, the doctor will certainly write out a referral for a biochemical blood test to evaluate the indicators that are most often called liver enzymes in medical practice - alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase. Deviations from the norm of both of these indicators will become an important diagnostic sign for the doctor of inflammatory, autoimmune diseases, as well as pathologies of a neoplastic or degenerative-dystrophic nature in the organ. The cause of elevated aspartate aminotransferase levels may be myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, rheumatic carditis, acute pancreatitis. An increase in the indicator is typical for a biochemical blood test of patients in the recovery period after undergoing surgical interventions on the heart and blood vessels.
Possible causes of an increase in alpha-amylase in the blood may be pancreatitis in the acute phase, appendicitis, peritonitis, impaired renal function, poisoning of the body with chemicals, alcohol, and mushrooms. A decrease in the indicator indicates the possible development of pancreatic necrosis, hepatitis, and liver malignancy.
A decrease in alkaline phosphatase in the blood is one of the important diagnostic signs of osteoporosis, vitamin deficiency, and myxidema. An increase in the indicator can tell the doctor about the patient’s diseases such as cirrhosis, metastatic liver disease, sarcoidosis, cholangitis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis.
A deviation from the norm in total cholesterol indicates a patient’s predisposition to diseases of the cardiovascular system. A decrease in cholesterol levels can provoke the development of psychophysiological disorders: stomach ulcers, migraine-like headaches, coronary insufficiency.
Lipids in the blood allow the doctor to assess the risks of developing life-threatening pathologies such as stroke and heart attack, as well as determine the patient’s lipid profile to develop treatment tactics for atherosclerosis. Medical specialists perform a complete lipid profile, which includes not only total cholesterol, but also the content of the substance fraction in the blood plasma.
Deviations from the norm in the content of inorganic substances may indicate vitamin deficiency, poor nutrition, metabolic disorders, hormonal disorders, alcoholism, etc.
Why is second trimester screening performed?
By the beginning of the second trimester, the fetus is already sufficiently formed. Prenatal examination at this stage allows you to determine the degree of development of the child and possible deviations.
Important! According to its indications, it coincides with the first planned screening, but is considered more accurate and allows you to obtain complete information about the condition of the fetus.
Through the second screening, a number of chromosomal diseases are identified, such as Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, congenital neural tube defect, triploidy, as well as anatomical pathologies of fetal development.
How long does it take to do a blood test for biochemistry?
The accuracy of diagnosis and the prescription of correct treatment largely depend on the results of the analysis, so our clinic’s laboratory technicians try to issue a completed form with biochemistry results as quickly as possible. The medical laboratory is equipped with all the necessary equipment and instruments for studying all parameters of biochemical blood analysis. As a rule, the time from the moment of blood sampling to the patient receiving the results form can range from half a day to three days. The variability of the time period depends on the indicators being determined and the laboratory equipment used.
Innovative techniques, modern high-tech equipment from leading European manufacturers, quality control of medical procedures and manipulations used in medicine help maintain the highest standards of laboratory blood tests.
What to do if screening shows abnormalities
Some deviations from the norm do not mean that the child is sick. Often, the cause may even be an incorrectly set gestational age. In this case, the woman is recommended to undergo a repeat ultrasound scan in a week.
Important! Impairments in fetal development identified before the 22nd week of pregnancy are treatable.
In addition, screening indicators only indicate the likelihood of having a child with a pathology. A high risk is considered to be 1:100, that is, one woman out of a hundred expectant mothers with the same test results may give birth to a child with pathologies. In this case, the pregnant woman is sent for a consultation with a geneticist to prescribe additional examinations.