Detailed description of the study
Rotavirus is one of the most common pathogens of intestinal infections. This virus received its name from the word “rota”, which in Latin means “wheel” due to the similarity with this object when studying the structure of the pathogen under a microscope.
In temperate climates, rotavirus infection is seasonal; Its frequency peaks in the winter months; in summer, the disease is detected infrequently. The source of infection is usually an infected person. Transmission occurs through the fecal-oral route, sometimes through contact, for example, when using shared utensils, other household items, and toys.
The incubation period lasts on average 1-2 days. The virus penetrates the intestinal cells - enterocytes, and multiplies there. Damage to enterocytes leads to their death, which impairs the absorption of nutrients and fluids in the body and determines the development of the main symptoms of gastroenteritis.
The disease can begin acutely with damage to the gastrointestinal tract or gradually, which is less common. In the first case, nausea, vomiting, and watery diarrhea immediately appear up to 20 times a day. The stool is yellow, foamy, and has a strong unpleasant odor. Sometimes it contains mucus.
In addition, there are spastic pains in the umbilical region and lower abdomen, and a moderate increase in body temperature (usually not higher than 38 ° C). Fever usually lasts up to 2 days. The gradual onset of rotavirus infection implies the appearance of general malaise and abdominal pain, which is accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea on the 2-3rd day of illness.
On average, the disease lasts from 4 to 8 days. Certain components of rotavirus are recognized by the immune system as a foreign substance - an antigen. As a result, antibodies are produced that destroy the virus. Due to the wide variety of rotaviruses and unstable immunity to these pathogens, the body fails to develop long-term immune protection, and re-infection is possible.
Along with the classic manifestations of rotavirus infection, erased and atypical forms are distinguished, when the disease manifests itself only by fever and nausea or only diarrhea. A person can shed the virus for some time after symptoms disappear.
Children 6 months to 2 years of age and people with weakened immune systems are especially susceptible to the virus. They can develop severe dehydration (dehydration) in a fairly short period of time, which is life-threatening.
Rapid and accurate detection of rotavirus antigens in stool samples helps to understand the cause of gastroenteritis.
Rotavirus analysis
This analysis is carried out in laboratories equipped with modern technology. Feces are used as biological material for research. Preparation for the analysis is individual - check this with your doctor.
You can collect feces only after natural bowel movements. You cannot take a sample of biomaterial from diapers, after an enema, after the administration of rectal suppositories or medications that stimulate colon peristalsis, as well as feces with impurities of other biological fluids of the body.
Collect the stool sample in a sterile plastic or glass container. In our clinic you can get a sterile plastic jar for stool collection completely free of charge. It is prohibited to take a sample from the toilet. There is a special spatula for collecting stool. The amount of biomaterial should be no less than half a teaspoon.
For research it is necessary to take morning feces. The sample should not contain urine or pieces of undigested food. The biomaterial must be delivered to the laboratory on the day of collection.
Rotavirus is a serious infection common worldwide among children that causes diarrhea. The first clinical manifestations of the disease occur almost immediately after infection, in an acute form: vomiting, diarrhea with sudden frequent urges, a significant increase in body temperature. The stool is loose, watery, foul-smelling, foamy, and in some cases has a greenish or even yellow-green color. If a child has a mild form of rotavirus infection, the stool will have a mushy consistency. If the disease is severe, it is cholera-like. From the first days of infection, the patient experiences pronounced symptoms of damage to the respiratory tract - redness in the throat, pain when swallowing, runny nose. As with other viral infections, intoxication, weakness, lethargy, poor appetite, and lack of strength occur.
Not only young children suffer from this disease. Older children and even adults are at risk of becoming infected with rotavirus. However, in adults, the infection most often occurs in a milder form. This is due to more efficient functioning of the immune system, a higher concentration of class A immunoglobulins in the body, and a lower level of gastric acidity. In adults, this infectious disease in the vast majority of cases occurs in a mild form - for a maximum of 5-7 days. Rotavirus is most dangerous for young children, the elderly and people in an immunodeficient state, because the risk of developing severe dehydration syndrome and death increases significantly.
The virus is transmitted through the oral-fecal route. This is a classic disease of unwashed hands - infection occurs after eating contaminated food or through household items. Virus particles are shed in large quantities in the stool. That is why those infected with rotavirus are a dangerous source of infection even in a hospital setting. The spread of rotavirus often results in outbreaks of infection in child care facilities and pediatric departments of hospitals. In the acute period, the disease has symptoms similar to other viral infections. Therefore, without a specific study, it is impossible to determine the exact origin of this gastroenteritis - adenovirus, rotavirus or norovirus. Each patient should undergo a comprehensive evaluation for several potential pathogens.
The simplest and most effective method for determining virus antigens in stool is an immunochromatographic rapid test. It is fast, non-invasive and highly sensitive. This research can also help control and prevent outbreaks of infection. The method was developed quite a long time ago - it is based on the binding of antibodies on the membrane of the test system and immunoglobulins that are in the sample
Decoding the analysis for rotavirus
The sensitivity and specificity of the test is more than 98%. Patients with diarrheal syndrome (especially children with suspected rotavirus) should undergo testing. The study is recommended for everyone who has been in areas of outbreaks of acute intestinal infections.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: negative.
Positive result
- Presence of rotavirus infection.
- Virus carriage.
Negative result
- Rotavirus infection is unlikely.
PCR diagnostics of rotavirus, norovirus, astrovirus (qualitative)
A comprehensive molecular genetic study that allows us to identify the genetic material of pathogens of acute intestinal infections in feces (rota-, noro-, astroviruses) and establish the etiology of the disease.
Research method
Real-time polymerase chain reaction.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Cal.
How to properly prepare for research?
- The study is recommended to be carried out before starting antibiotics and other antibacterial chemotherapy drugs.
- Avoid taking laxatives, administering rectal suppositories, oils, limit taking medications that affect intestinal motility (belladonna, pilocarpine, etc.) and the color of stool (iron, bismuth, barium sulfate) for 72 hours before stool collection.
What is this analysis used for?
- For differential diagnosis of the causes of acute diarrhea.
General information about the study
Acute intestinal infections (AI) are a group of diseases caused by viruses, bacteria or parasites, which are characterized by a fecal-oral transmission mechanism.
Transmission factors: food, water, contaminated household items and dirty hands. The first symptoms appear several hours or days after infection; the onset is abrupt, with the appearance of frequent loose stools, vomiting, abdominal pain, and signs of intoxication (fever, chills, nausea). The disease can be group in nature and occur in several people who have consumed contaminated food or water.
Norovirus is the most common causative agent of AE outbreaks of nonbacterial etiology. This feature is associated with a low infectious dose and high persistence in the environment. PCR is the “gold standard” in the clinical diagnosis of norovirus infections.
Despite their somewhat lower prevalence compared to rota and noroviruses, astroviruses make up a significant group of intestinal infections, which occur with colitis in a third of patients. Group A rotaviruses are the most common cause of sporadic acute respiratory infections in children.
What is the research used for?
- To establish the etiological factor of acute intestinal infection;
- for differential diagnosis of the causes of acute gastroenterocolitis (inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract).
What do the results mean?
Reference values: negative.
Reasons for the positive result:
- presence of RNA of the causative agent of acute intestinal infections; etiology depending on the type of pathogen identified (Rotavirus A, Norovirus genotype 2, Astrovirus).
Reasons for negative results:
- no infection.
What can influence the result?
Factors distorting the result:
- long-term storage of material before it arrives at the laboratory;
- freezing the material or heat treating it;
- non-compliance with the rules for taking biomaterial and its contamination.
Important Notes
- It is recommended to conduct the study in the first 3 days from the onset of the disease.
ELISA - diagnosis of human rotavirus antigen

This is the most sensitive and specific method for diagnosing rotavirus infection, which is based on the interaction of anti-rotavirus antibodies with rotavirus antigen in stool.
Research method
One-step immunochromatographic method.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Cal.
How to properly prepare for research?
- No special diet required.
- On the eve of the study, exclude the rectal use of any medications, as well as drugs that affect intestinal motility (laxatives, enzymes, sympathomimetics).
- Feces are collected after natural bowel movements in a sterile container.
- You cannot take a sample from the toilet.
- When collecting stool, urine and genital discharge should be avoided.
General information about the study
Rotavirus infection is an acute viral disease with fecal-oral transmission, the causative agents of which are RNA-containing rotaviruses (Rotavirus). It is the most common cause of severe diarrhea in young children as well as in older adults. The source of infection is a sick person. Infection most often occurs in the cold season, the incubation period lasts from 15 hours to several days. The onset of the disease is acute, with symptoms of gastroenteritis: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and sometimes fever. If left untreated, dehydration and electrolyte and acid-base imbalance may occur.
Sometimes rotavirus infection is asymptomatic. Immunity after an infection is unstable, so re-development of the disease is possible.
The most sensitive and specific method for diagnosing rotavirus infection is the detection of the virus antigen in stool.
What is the research used for?
- To identify patients with rotavirus infection.
- To identify virus carriers.
When is the study scheduled?
- If rotavirus infection is suspected (on the 1st-4th day of the suspected illness).
- If you suspect you are a carrier of rotavirus.
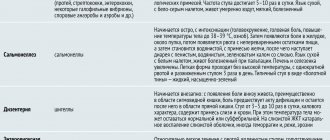
- For the differential diagnosis of diseases that occur with similar symptoms: cholera, escherichiosis, salmonellosis, food poisoning, dysentery, other viral diarrhea, etc.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: negative.
It is most advisable to conduct the study in the first 4 days of the disease, since the peak of virus shedding in feces occurs during this period.
Reasons for a positive result
- Rotavirus infection.
- Asymptomatic rotavirus infection (virus carriage).
Reasons for a negative result
- No rotavirus infection.
- A small amount of virus in the stool.




![Table 4. Major muscular dystrophies accompanied by increased CPK levels [41]](https://ddpskov.ru/wp-content/uploads/tablica-4-osnovnye-myshechnye-distrofii-soprovozhdayushchiesya-povysheniem-urovnya-kfk-41-330x140.jpg)