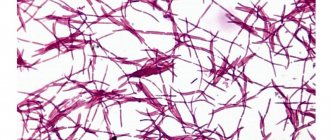
Scraping threads of mycelium in pityriasis versicolor
This is a chronic fungal disease.
It is caused by Pityrosporum ovale.
This is a yeast fungus.
It appears in places where there is increased sebum production.
Because the fungus actively metabolizes fats.
It is an opportunistic microorganism that lives on the skin of any person.
The disease does not occur due to infection.
It is called:
- increased production of sebum;
- insufficient hygiene;
- lubricating the skin with fat, for example, for medicinal purposes;
- decreased immunity;
- local use of glucocorticoids for a long time.
More often the disease manifests itself against the background of increased sweating.
Fungi prefer damp skin.
Without treatment, the disease may go away on its own within a few months or years.
It is usually not observed in patients over 40 years of age, but affects only young people.
Sometimes complicated by fungal folliculitis.
Pityrosporum ovale infection is also associated with seborrheic dermatitis.
Symptoms are usually mild.
These are spots on the skin - white on tanned skin and light brown on untanned skin.
They can be of various sizes, usually round in shape.
The lesions can merge if located nearby.
Skin flakes are taken for microscopy.
They are obtained by scraping the stain.
Staining is carried out with potassium hydroxide.
In the sample, the doctor can see mycelium threads and fungal cells.
They have a round shape.
When examined under a Wood's lamp, the glow will be green.
Sometimes it has a bluish tint.
But the glow may be absent if the patient has washed immediately before visiting the doctor.
Differential diagnosis is carried out primarily with vitiligo.
With this disease there is no peeling when scraped.
Mycelium threads are also absent upon microscopy of skin scrapings.
Pathomorphological examination reveals mycelial threads and fungal cells.
They are detected in the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
Increased proliferation of keratinocytes is observed.
There are signs of inflammation and dilated blood vessels.
When pseudomycelium is detected in a smear
Candida is also distinguished from ordinary yeast by the fact that the cellular structure of microorganisms does not have spores and pseudomycelium is present. The growth of opportunistic microorganisms is provoked by various factors, usually a decrease in immunity. Yeast-like fungi are detected in a smear during an exacerbation of candidiasis. However, in healthy women (20% of cases tested), Candida is present and to identify the type of bacteria and clarify the diagnosis, cultural diagnostics and culture on nutrient media are required.
Mycelium threads on nails
Detection of mycelium in clinical material from nails is a sign of onychomycosis.
This is a group of fungal diseases.
They can be caused by both yeast and mold fungi.
Typically, the distal or lateral edge of the plate is initially affected.
Then it spreads towards the center of the nail.
Pathogens:
- Trichophyton;
- Candida;
- Scopulariopsis;
- Aspergillus;
- Acremonium and many others.
You can become infected from another person.
It is possible that infection can spread to the nails from other parts of the body.
Sometimes fungal spores get onto the nail plates from the soil (molds).
In 80% of cases, the nail plates of the lower extremities are affected.
The diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory tests.
A scraping is taken using a curette.
The material is taken from the inner plate.
From the outside it is taken if white superficial onychomycosis is suspected.
The drug is treated with 10-30% KOH.
Dimethyl sulfoxide may be added to it.
This makes it easier for a specialist to find fungi.
Using the microscopic method you can:
- confirm the etiology of the nail disease - identify that it was the fungus that provoked the disease;
- find out whether the fungal inflammation was caused by candida or dermatophytes.

But it is impossible to determine the type of mushroom by the mycelium threads.
If such a need arises, use:
- PCR;
- sowing.
In cases where microscopy does not give results, a histological examination of the nail area is performed.
The diagnosis is confirmed using the CHIC reaction.
Are there transverse partitions in the mycelium threads?
The mycelium has septa.
But septa may be absent in pseudomycelium.
It differs from true mycelium in that during the budding process, the mother cells are not completely separated from the daughter cells.
They continue budding.
Therefore, structures appear that resemble mycelium in appearance.
It is called false.
It is unseptate, that is, not divided by partitions.
When pseudomycelium is detected, the doctor sees constrictions between the cells.
The terminal cells are smaller than those located in front of them.
Sometimes pseudomycelium consists of cells of the same type.
It is called vestigial.
In other cases, cells of different types develop in pseudomycelium.
It's called complex.
Long cells - pseudohyphae - are found.
They contain buds - one or more, round or wedge-shaped.
These buds are called blastospores.
Mycelium threads in a smear - what are they?
Spores and mycelium threads are found in candidiasis.
Only these mushrooms do not form mycelium, but pseudomycelium.
Candida can be detected in smears from:
- vagina;
- penis;
- mouth;
- anus;
- skin;
- nails
Candida can affect various structures and organs of the human body.
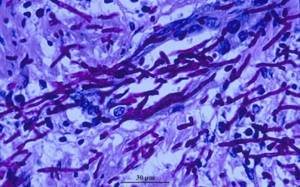
Inflammation can develop:
- on the genitals;
- in the folds of the skin;
- under occlusive dressings;
- in hair follicles;
- rectum;
- in the mouth and throat;
- on the nails.
In severe cases, invasive candidiasis develops.
It affects internal organs.
This is possible against the background of immunodeficiency, for example, with HIV.
Yeast in a smear during pregnancy
During pregnancy, not only the hormonal background changes significantly, but also the environment in the vagina due to an increase in the sugar level of vaginal secretion. If yeast is detected in a smear in women, including pregnant women, they require detailed diagnostics to exclude sexually transmitted infections, viruses and selection of appropriate treatment. Antifungal agents are toxic and affect the development of the fetus, therefore local treatment with vaginal suppositories and ointments is provided for pregnant women.

Yeast mycelium threads in a smear on the flora
Candida can be detected in a vaginal smear.
This study is called a flora smear.
Because it identifies not only mushrooms.
This smear also helps detect a number of other microorganisms.
These are opportunistic bacteria and some sexually transmitted pathogens.
The smear may reveal kidneys.
They are also called rudiments.
These are Candida spores that have just begun to grow.
Externally, this microscopic feature looks like an oval cell, on the surface of which another smaller oval began to grow.
It is located at one of the poles.
Yeasts reproduce by fission.
They form buds.
With the further formation of a large number of primordia, they form and elongate without cell separation.
Then pseudomycelium is formed.
It looks like thread.
Another name: pseudohyphae.
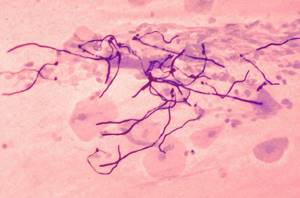
With candidiasis, threads of varying lengths are detected.
The mycelium threads can be best visualized at high magnification of the microscope.
In this case, they can be examined in detail.
Blastospores and filaments of pseudomycelium of yeast-like fungi Candida
Like Candida fungi, blastospores found in a smear indicate infection of the body with candidiasis, a disease that affects the mucous membranes and tissues of the body.
As a result of the smear, the physician can obtain information about the balance of bacteria and the presence of blastospores in the uterus and vagina. An increase in white blood cells and red blood cells indicates the presence of inflammatory processes in the body.
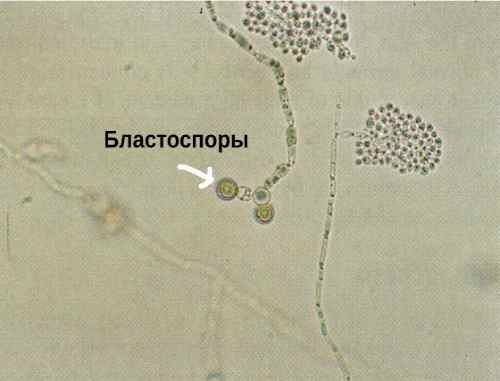
Blastospores
Blastospores are found in a smear if the body is affected by candidiasis.
Cells of this species are round or oval-shaped embryos formed from the mother organism by budding. Blastospores are usually found at cell junctions.
What can mushroom mycelium threads be confused with?
Sometimes inexperienced laboratory technicians confuse mycelium threads with villi.
They can get into the vagina from tampons.
Then these are the lint of cotton fabric.
But they can be distinguished from threads of mycelium or pseudomycelium by certain parameters.
Firstly, in size.
The villi are always larger and thicker than the hyphae.
Secondly, due to the absence of kidneys.
Unlike mushrooms, cotton threads cannot reproduce by division.
Therefore, rudiments never form on their surface.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
Acanthamoeba keratitis: symptoms, treatment and prevention, causes and routes of infection
Facultative parasite Acanthamoeba: description, structure and life cycle
Dysenteric amoeba: life cycle, structure, diagram, stages of development
Naegleria Fowlera: distribution and habitat, symptoms and treatment
Symptoms of extraintestinal amebiasis, routes of infection and treatment methods
Ways of infection with human roundworm and the main methods of combating worms
Features of threads for candidiasis
In candidiasis, the filaments are pseudomycelia rather than mycelium.
They do not have partitions.
But there are thickenings on the threads.
They appear in those areas where there are branches of pseudomycelium.
The fiber can have different lengths.
Sometimes the threads become twisted or intertwined.
Pseudohyphae can be detected in a native smear.
That is, not painted with anything.
But sometimes there are so many cells in the material that fungi are poorly visualized.
Then potassium hydroxide is added to the preparation.
The sample appears lighter when examined microscopically.
Elements of fungus become much more visible.
They are visible with a microscope magnification of 100 times.
A magnification of 400x is required to see the details.
This way the laboratory assistant can identify small and short filaments of pseudomycelium.
Budding cells and blastospores are also detected.
They are otherwise called blastoconidia.
They look like oval cells, corresponding in size to epithelial cells.
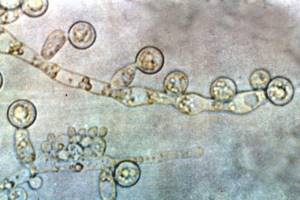
The appearance of budding forms is associated with the proliferation of fungi.
Their number may vary.
But it does not reflect the real quantitative indicators of the fungal process in the vagina.
It also does not correlate with the severity of symptoms.
Therefore, a smear on the flora cannot be used to assess the dynamic course of the disease.
This is an exceptionally high-quality test.
He gives a yes or no answer.
If mycelium threads are found, this indicates a fungal disease.
If they are not detected and the smear is clean, then the person is healthy.
What to do if there are mycelium threads in the analysis
If you have mycelium threads in your tests, treatment is required.
It is prescribed by a doctor.
The patient should not do the following:
- go home and wait until the disease goes away on its own (complications, chronicity of the process, spread of infection to other organs are possible);
- be treated with “grandmother’s” methods - they are ineffective and often unsafe;
- treatment, following instructions from the Internet, books, advice from a neighbor who had “the same thing.”
Different fungal pathologies are treated differently.
The treatment regimen is determined not only by the type of fungus.
The doctor takes into account a number of other factors: the particular course of the disease, the area of skin lesions, the severity of symptoms, etc.
If filaments of mycelium are localized in the vagina, the presence of candidiasis in other reproductive organs is taken into account.
What is prescribed for treatment
To effectively treat the disease, it is necessary to eliminate or reduce the influence of factors that can provoke the development of candidiasis, which implies thoughtful prescription of antibiotics, hormonal drugs, immunosuppressants, and giving up bad habits.
For treatment, antifungal drugs are used topically (in the form of ointment, cream, solution, vaginal tablets or suppositories) and orally (in the form of tablets, capsules, suspensions).
These include drugs such as fluconazole, etc. Antimycotic drugs are prescribed, the active ingredients of which are:
- Iconazole;
- Clotrimazole;
- Miconazole;
- Ketoconazole.
Antibacterial agents are also used (natamycin, nystatin, levorin).
Additionally, it is recommended to prescribe immunomodulators, restorative drugs, physiotherapy, as well as prebiotics (lactulose) and probiotics to normalize acidity, the composition of the microflora of the skin and mucous membranes.
Mandatory treatment of inflammatory processes, including sexually transmitted infections. With frequent relapses, additional examination is necessary.
Treatment of mycelium threads
When threads appear, treatment includes the use of antifungal drugs.
Different diseases are treated differently.
For dermatophytosis of the skin, the use of local antifungal drugs is usually limited.
Ointments and creams are used.
They may contain:
- ketoconazole;
- miconazole;
- terbinafine;
- amorolfine;
- ciclopirox and other drugs.
In severe cases, oral medications are also used.
For candidiasis, clotrimazole is used externally.
Fluconazole can be prescribed orally.
In the recurrent form, treatment can be very long.
Treatment
In the treatment of thrush, many drugs are used: local agents (suppositories, ointments, creams), systemic drugs taken orally. Systemic medications have side effects (allergies, headaches, stool disorders) and are not used during pregnancy and lactation. Systemic treatment is prescribed, as a rule, for the chronic stage of the disease; at the initial stage, local drugs are effective. Among the large selection are well-known drugs: Nystatin, Clotrimazole, Fluconazole, Miconazole, Pimafucin.