When determining the hematocrit number by centrifugation, it is extremely important to combine the speed and productivity of the method with the accuracy of the recorded values. This task is ideally handled by the latest generation of Centurion Scientific hematocrit centrifuges, equipped with an exclusive microrotor design and specialized software.
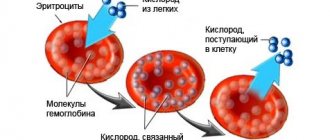
Hematocrit is the fraction of blood volume occupied by its cells (formed elements): red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Since 99% of this fraction is erythrocytes, the determination of hematocrit is essentially a measurement of the volume fraction of erythrocytes in the blood.
| Hematocrit is also the name given to y- or l-shaped microtubes (capillaries) for collecting and centrifuging blood. In professional medical terminology, instead of the term “hematocrit”, the terms “hematocrit number” or “hematocrit value” are usually used to denote the volume fraction of red blood cells. In test forms and literature you can find the following abbreviations: Hct or Ht (from Hematocrit) and PCV (from Packed Cell Volume, from English: volume of precipitated red blood cells). |
The value of normal hematocrit in humans
The body of a healthy adult contains approximately 4.5-5 liters of blood. It contains formed elements and cells - red blood cells, platelets, leukocytes, as well as a liquid part called plasma.
Some blood components, for example, red blood cells, do not have all the necessary components of a human cell, losing them during the maturation process. Therefore, red blood cells and platelets are called blood cells, not cells.
In different categories of patients, the normal values of various parameters of the blood tested will differ. So, for most men, the hematocrit will be higher: 40-41%, and in some cases it can reach up to 51%, which is due to its slower renewal.
In healthy women, the hematocrit usually ranges from 36 to 42%. This is due to physiological features - due to regular menstrual bleeding, blood is renewed more often to replenish its volume. During pregnancy, from the 20th week, the indicator begins to decrease, which is also not considered a deviation.
In children, hematocrit differs at different age periods:
- 44-62% for newborns;
- 32-43% for babies up to three months;
- 36-43% for children under one year of age;
- 35-47% (up to 52% for boys) - in the first ten years.
In subsequent years, the hematocrit norm depends on gender and practically corresponds to the values of an adult.
Methods for determining hematocrit
The indicator is determined as a percentage by calculating the amount of formed elements in whole blood. It is calculated using special instruments or manually.
Centrifugation using the Wintrobe method
The blood is exposed to centrifugal force for 10-30 minutes. The formed elements are heavier than plasma, so they settle to the bottom of the test tube. The hematocrit is determined by the ratio of sediment to the total volume of biomaterial.
Calculation of the indicator using the formula
The ratio of the number of red blood cells to the total blood volume can be calculated mathematically. To do this, the following indicators are required:
- total hemoglobin concentration (ctHB);
- red blood cell count (RBC);
- mean erythrocyte volume (MCV);
- mean erythrocyte hemoglobin concentration (MCHC).
The hematocrit number (HCT) is determined by one of the formulas:
- HCT (%)=(ctHB (mmol/l)*0.0485+0.0083)*100
- HCT (%)=0.1*MCV*RBC
- HCT (%)=ctHB/MCHC*100
Direct blood cell counting method
In a given volume of biomaterial, visible blood elements are counted manually or using hematological analyzers. The method is highly accurate, and the measurement process does not take much time - no more than five minutes, but the equipment required is very expensive.
Manual counting method
Blood collected using an anticoagulant is placed in a dry, clean tube and allowed to settle. In this case, the formed elements that have greater weight settle to the bottom of the container, and the light plasma rises to the top, forming two fractions of red and yellow colors, respectively. The hematocrit indicator can be determined by the divisions on the test tube. This method is the least accurate, its error is up to 20%, so it is currently not used in laboratories.
Centurion Scientific hematocrit centrifuges: capabilities, features and advantages
Centurion Scientific's line of medical and veterinary equipment includes PrO-Hospital PCVs and PrO-VetPCVs hematocrit centrifuges.
Hematocrit rotor BRK5401 | Both instruments are equipped with a special BRK5401 hematocrit rotor of a unique design, which allows simultaneous analysis of 24 hematocrit capillaries. In addition to seats for capillaries, the device has sockets for 12 microtubes and can be used to obtain blood plasma, material for microscopic examination of urine sediment and other purposes. Centrifugation of hematocrit capillaries in a preset mode occurs at a speed of 12,000 rpm and takes 5 minutes. Other advantages of the BRK5401 rotor include high-precision balancing, which guarantees the most stable centrifugation speed and strictly defined orientation of the spatial position of capillaries and tubes. |
The hematocrit rotor can be supplied with:
Hematocrit card reader |
|
| Plate with sealing paste |
A hematocrit rotor can be equipped not only with specialized centrifuges, but also with other models of the PrO-Hospital line, universal laboratory centrifuges CR2000, benchtop centrifuges C2012, microcentrifuge K1015. All of these devices support the BRK5401 rotor recognition function and have pre-installed programs for determining the hematocrit number.
Both Centurion Scientific's medical and veterinary hematocrit centrifuges support a different type of rotor, greatly expanding their capabilities. The general advantages of the devices also include ergonomics and increased strength of the centrifuge chamber, automatic control of speed and balance, temperature stability, innovative electronic lid lock and the presence of an emergency opening system.
At the same time, the functionality and design of the veterinary centrifuge are optimized to solve standard problems, and the capabilities of medical centrifuges are expanded to fully meet the needs of a clinical laboratory with a wide range of studies of small volumes of biomaterial.
When is a hematocrit test performed?
Most often, hematocrit is determined as part of a general (clinical) blood test. Therefore, at present this parameter of a clinical blood test is not prescribed separately. The hematocrit level changes when:
- disorder of the blood coagulation system;
- dehydration;
- anemia or polycythemia;
- bleeding.
Assessing the hematocrit level is important when determining indications for the need for blood transfusion or the effectiveness of blood transfusion, during hemodialysis, and some operations. To determine the hematocrit number, venous or capillary blood is taken.
Treatment of abnormalities
Hematocrit testing is performed routinely as part of a general blood test. The test is an economical way to diagnose and monitor hematological disorders (anemia, polycythemia), and dehydration conditions. If the final indicator deviates from the norm, then to establish the cause of the violations and prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor - therapist, pediatrician, hematologist. You can prevent the influence of physiological factors on the hematocrit index if you follow the rules for preparing for the blood donation procedure - stop smoking and heavy physical activity.
Increased hematocrit
An increase in hematocrit occurs with an increase in the number of blood cells - polycythemia - and a lack of fluid in the body. An increase in the indicator may indicate serious diseases accompanied by blood thickening and thrombotic complications.
Causes
Hematocrit increases due to stress, taking corticosteroid drugs and diuretics, traumatic shock accompanied by intense pain, as well as when climbing to high altitudes, smoking, or playing sports using anabolic steroids to gain muscle mass.
An increase in the indicator may indicate the following diseases:
- dehydration due to vomiting, profuse diarrhea, overheating or heat stroke, excessive sweating, insufficient fluids;
- heavy bleeding in the midst or immediately after it stops;
- pathologies accompanied by a decrease in blood plasma volume, for example, peritonitis, thrombosis, diabetes, burn disease;
- impaired renal function - hydronephrosis, oncology, polycystic disease;
- vitamin B12 or iron deficiency anemia;
- leukemia;
- erythrocytosis;
- defects and coronary heart disease, heart failure;
- intestinal obstruction;
- bronchial asthma, pulmonary emphysema, obstructive bronchitis.
Symptoms
An increase in blood viscosity leads to thrombus formation. The latter can manifest itself in the form of tingling or various pains and numbness in the limbs. If the cause of increased blood viscosity is not determined in time, serious complications such as myocardial infarction, stroke, gangrene and even death may develop.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out not for the changed hematocrit level itself, but for the conditions or diseases that caused these changes. In some situations, when serious causes for a slightly changed hematocrit level have been excluded, no treatment is required. But usually such situations are short-lived, in the case of physiological reasons for changes in hematocrit levels.
Preparation for analysis and collection of material
When performing a general blood test with determination of hematocrit, blood is taken in the morning, on an empty stomach. No special preparation is required for the collection procedure, but it is important to follow several recommendations: the day before the test, you should refrain from drinking alcohol, at least 8-12 hours should pass after eating, you should stop smoking and physical activity half an hour before the test, and avoid the influence of stressful factors. When talking with your doctor, it is worth informing him about the medications you are taking so that their possible effect on the hematocrit is taken into account when interpreting the results. There are no restrictions on the use of clean water.
Most often, blood for hematocrit testing is taken from the ring finger. The procedure is performed using a scarifier pen or lancet. If the doctor recommends venous blood sampling, then puncture of the ulnar vein is performed. After collection, the biomaterial is mixed with an anticoagulant to prevent the clotting process. In laboratories, two methods are used to determine hematocrit - standard centrifugation and using a hematology analyzer. Their essence lies in the fact that during the process of centrifugation (rapid rotation), heavier and more voluminous particles (red blood cells) settle to the bottom. Then the height of the bottom layer is determined and its percentage to the total height of the liquid is calculated. Preparation of the results of this study takes no more than 1 business day.
Decreased hematocrit
A decreased hematocrit occurs when the number of red blood cells or their size decreases - erythrocytopenia. The cause may also be the accumulation of water in the body when the blood becomes thinner - hyperhydration, as well as hyperproteinemia or the accumulation of proteins in the plasma, which contributes to fluid retention.
Causes
A decrease in hematocrit is facilitated by prolonged immobility, fasting or a strict diet, taking anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents, and intravenous infusions in large volumes; heavy drinking, chronic alcoholism, excessive salt intake, menstruation in women.
Also, a downward change in the indicator may indicate the following pathologies:
- iron-, B12- or folate-deficiency anemia;
- severe bleeding;
- impaired hemoglobin production in sickle cell anemia;
- fibrous degeneration of the liver - cirrhosis;
- disruption of the urinary system;
- hemolysis of erythrocytes - destruction of red blood cells due to hereditary mutation, autoimmune processes or toxic effects on blood cells;
- malaria, typhoid fever;
- oncological diseases of the bone marrow or its metastatic lesions from other organs;
- an increase in the amount of protein in plasma due to vomiting, diarrhea, blood cancer and other conditions.
During pregnancy, a decrease in hematocrit can be observed in the case of toxicosis, a very young age of the mother, multiple pregnancies, a short period of time between pregnancies, and also after the 20th week of gestation due to a physiological increase in fluid in the body.
Symptoms
A decrease in hematocrit in the blood is accompanied by hypoxia of various organs, since it is the red blood cells that normally carry oxygen throughout the body. This condition is manifested by the following symptoms:
- fast fatiguability;
- general weakness;
- drowsiness;
- increased heart rate and breathing;
- feeling of lack of air;
- headache, dizziness;
- decreased memory and concentration;
- hair loss;
- marbling or pallor of the skin.
Treatment
A decrease in hematocrit in an adult to 35-30% requires outpatient medical supervision, exclusion of possible serious diseases, and dietary adjustments with increased consumption of animal products, in particular, red meat and liver, and leafy greens. An indicator below 13% is typical for life-threatening pathologies and is usually detected in patients in serious condition in the hospital. Patient management tactics are determined by the underlying disease that led to a change in hematocrit level.
Author:
Baktyshev Alexey Ilyich, General practitioner (family doctor), ultrasound diagnostics doctor, chief physician