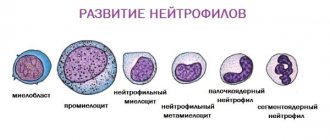
General information
Leukocytes - what are they?
The answer to the question “what are leukocytes?” is not as clear as it seems at first glance. To put it simply, leukocytes are white blood cells that are involved in protecting the body from bacteria, viruses and other harmful agents. This concept also includes a heterogeneous group of blood cells of different morphology and significance, united by the presence of a nucleus and the absence of color.
What are leukocytes responsible for?
The main function of white blood cells is specific and nonspecific protection against all types of pathogenic agents and participation in the implementation of certain pathological processes, that is, they are responsible for the “protection” of the body.
Blood structure
All types of leukocytes can actively move and penetrate through the capillary wall into the intercellular space, where they capture and digest foreign agents. If a lot of such agents penetrate the tissue, then the leukocytes, absorbing them, greatly increase and are destroyed. This releases substances that provoke the development of a local inflammatory reaction, which is manifested by swelling, increased temperature and hyperemia of the inflamed focus.
Where are leukocytes formed in humans and how long do they live?
Carrying out the function of protecting the body, a large number of leukocytes die. To maintain a constant quantity, they are continuously produced in the spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes and tonsils. Leukocytes usually live up to 12 days.
Where are leukocytes destroyed?
Substances that are released when white blood cells are destroyed attract other leukocytes to the area where foreign agents are introduced. By destroying the latter, as well as damaged cells of the body, white blood cells die en masse. The pus that is present in inflamed tissues is an accumulation of destroyed white blood cells.
What are white blood cells also called?
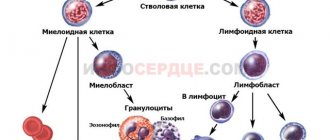
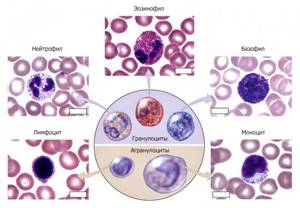
There are 3 main synonyms for the described cells in the literature: white blood cells, white blood cells and leukocytes. They are classically divided into granulocytes and agranulocytes . The former include eosinophils , neutrophils and basophils , the latter – lymphocytes and monocytes .
The "Family of Defenders" includes:
- Neutrophils are the main white blood cells that specialize in eliminating cellular aggression (bacteria), in the fight against which they usually die, forming compactions (infiltrates) and/or foci of septic inflammation (ulcers).
- Lymphocytes - perform the functions of recognizing foreign agents and transmitting information about them to responsible cells, and also provide antiviral protection.
- Monocytes (macrophages) are “eaters” of large cells that are too heavy for neutrophils.
- Basophils - regulate vascular permeability, prevent allergic and inflammatory reactions, affect blood clotting.
- Eosinophils – fight allergies and poisons (toxins) released by parasites, such as helminths.
leukocyte blood test results mean A general analysis with a leukocyte formula shows the qualitative composition and percentage of leukocytes to the total number of blood cells. Deviations from the norm make it possible to identify pathologies in the early stages.
Norm of leukocytes in the blood
How many leukocytes should a healthy person have?
The normal number of white blood cells in the blood is measured in units (that is, cells) per liter of blood. It is also worth understanding that the content of leukocytes is not constant, but changes depending on the state of the body and the time of day. For example, the concentration of leukocytes usually increases slightly after meals, in the evening, after physical and mental stress.
The normal level of leukocytes in the blood of an adult over 16 years of age is 4-9·109/l. Considering the amount of blood in the adult human body, we can say that there are from 20 to 45 billion white blood cells circulating there.
What is the norm of leukocytes in the blood of men?
The above value is taken as the normal level of leukocytes in men (more precisely, leukocytes 4.4-10). In the body of males, the number of leukocytes is subject to much weaker fluctuations than in other groups of patients.
What is the normal number of leukocytes in women?
In women, this indicator is more variable and leukocytes of 3.3-10·109/l are taken as the standard. The figures for this indicator may fluctuate depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle and the state of hormonal levels.
Normal white blood cell count in pregnant women
It is known that many blood parameters in pregnant women are altered, therefore, values that are overestimated for ordinary patients are considered to be the norm for leukocytes. Thus, according to various authors, an increase in the number of leukocytes to 12-15·109/l should not cause concern and is physiological for this condition.
The norm of leukocytes in the blood of a child
The norm of the indicator described in this section in children directly depends on age.
| Age | Normal value (unit 109/l) |
| 11 – 16 years | 4,5 — 13 |
| 6 – 10 years | 4,5 — 13,5 |
| 4 – 6 years | 5 — 14,5 |
| 34 years | 5,5 — 15,5 |
| 6 – 24 months | 6,6 — 11,2 |
| 1-6 months | 7,7 — 12 |
| 8-14 days | 8,5 — 14 |
| 1-7 days | 9 — 15 |
| newborns | 10 — 30 |
Leukocyte formula
The blood test also calculates the percentage of different types of leukocytes. Absolute cell values are additionally designated by the abbreviation “abs.”
Classification of leukocytes by groups
In a healthy person, the leukocyte formula looks like this:
- band neutrophils – 1-6%;
- segmented neutrophils – 47-72%;
- eosinophils – 0.5-5%;
- basophils – 0.1%;
- lymphocytes – 20-37%;
- monocytes – 3-11%.
In children, during the development process, 2 so-called “crossovers” of the leukocyte formula occur:
- the first at the age of 5 days, when the lymphocyte/neutrophil goes from 20%/60% to 60%/20%;
- the second at the age of 4-5 years, when the reverse crossover occurs to the lymphocyte/neutrophil of 20%/60%, after which the content and proportions of this ratio should correspond to those of an adult.
WBC level norms and deviations
The total content of white cells in the blood of the same person may vary depending on functional conditions and time of day. A slight decrease in white blood cells may be observed with physical and/or emotional exhaustion (fatigue).
An increase in leukocyte levels is observed with mental or muscle overstrain, after eating, under the influence of heat or cold. In addition, the relative norm of maintenance has gender and age dependence.
Leukocytosis - what is it?
“What is leukocytosis” and “leukocytosis - what is it?” are the most frequent queries on hematology topics on the World Wide Web. So, leukocytosis is a condition characterized by an increase in the absolute number of leukocytes per liter of blood more than an established physiological indicator. It should be understood that an increase in leukocytes in the blood is a relative phenomenon. When interpreting a general blood test, one should take into account gender, age, living conditions, diet and many other indicators. In adult patients, a leukocyte count exceeding 9·109/l is considered leukocytosis.
Elevated leukocytes in the blood - what does this mean?
In simple terms, leukocytosis indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. The reasons why leukocytes in the blood are elevated are physiological and pathological in nature, respectively, and leukocytosis is physiological and pathological.
Physiological (which means that does not require treatment) increased levels of leukocytes in the blood can occur for the following reasons:
- hard physical labor;
- food intake (can “spoil” a blood test, causing an increased number of leukocytes after a meal to reach 12·109/l);
- dietary characteristics (food leukocytosis can also occur if the diet is dominated by meat products, some components of which the body perceives as foreign antibodies - this means that leukocytes in the blood will be increased due to the development of an immune response);
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- taking cold and hot baths;
- after vaccination;
- premenstrual period.
An increased level of leukocytes in the blood of a pathological nature requires examination or, at a minimum, re-analysis after 3-5 days to exclude counting errors. If leukocytes in the blood are elevated and physiological causes have been excluded, then an increase in the number indicates the presence of one or more of the following conditions:
- infectious disorders ( meningitis , sepsis , pneumonia , pyelonephritis and others);
- infectious disorders affecting immune cells (infectious lymphocytosis or mononucleosis );
- various inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms ( phlegmon , peritonitis , abscess , boil , appendicitis , infected wounds - these are the most common causes of an increase in the described indicator in the blood);
- inflammatory disorders of non-infectious origin ( systemic lupus erythematosus , rheumatoid arthritis and others);
- myocardial infarction , lung and other organs;
- extensive burns;
- malignant neoplasms (in the presence metastases in the bone marrow, leukopenia );
- large blood loss;
- proliferative diseases of hematopoiesis (for example, leukemia , when white blood cells are increased to 100·109/l or more);
- splenectomy;
- diabetic coma, uremia.
In addition, when there are a lot of leukocytes in the blood, this means that in rare cases one can suspect poisoning with aniline or nitrobenzene . Many leukocytes in the blood appear in the initial stage of radiation sickness .
There are a number of insufficiently studied conditions of the human body, in which leukocytes and ESR and body temperature rises slightly. After a short period of time, these indicators return to normal. These abnormal conditions do not have any noticeable manifestations.
Causes of elevated leukocytes in the blood of women
In women, as stated earlier, there are many more physiological reasons for the level of leukocytes to be higher than normal. What does it mean? The fact is that hematological parameters in women are much more dynamic and subject to change. Most often, a physiological increase in the indicator is observed during the premenstrual period and during pregnancy, but after childbirth it decreases to normal values. Otherwise, the causes of leukocytosis in women are identical to those described above.
Elevated white blood cells during pregnancy
The norm during pregnancy for the described indicator is, according to various authors, up to 15 and even 18·109/l. Leukocytosis during pregnancy is a fairly common phenomenon, reflecting the reaction of the mother's immune system to the presence of the fetus. If white blood cells are elevated during pregnancy, the patient's condition should be closely monitored due to the increased risk of premature birth. Also, we should not forget about the “traditional” causes of leukocytosis: inflammation, infections, somatic diseases. White blood cells that are elevated after childbirth usually return to normal within 2-4 weeks.
High white blood cells in a child
In general, in pediatrics it is believed that if a blood test shows leukocytes 14·109/l in a healthy patient, then you should be wary, order a repeat test and draw up an examination plan. The reasons for elevated leukocytes in a child’s blood can be varied, so patients in this category always need to have a repeat test.
The most common reason why a child’s white blood cell count is elevated is the presence of childhood infections (including elementary ARI , when blood counts are changed within a few days after recovery), mainly of a bacterial nature.
They are also high in children with other diseases (which are more common in children than in adults), for example, leukemia (colloquially “blood cancer”) and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis . The reasons for the described phenomenon in a newborn are described below.
High white blood cells in a newborn
If leukocytes are elevated in a newborn, this is not always a sign of disease (as, for example, increased bilirubin ). Their normal level in the blood immediately after birth can reach 30·109/l. However, it should decrease quickly during the first week. The issues of increasing leukocytes in a newborn (infant) should be dealt with by an experienced neonatologist.
Symptoms of leukocytosis
Leukocytosis in children and adults, leukocytosis in newborns and pregnant women never causes characteristic signs of changes in well-being and cannot be detected during instrumental examination. Moderate leukocytosis in itself is a symptom and without collecting an anamnesis, examination by specialists, or ordering tests, it does not have any special clinical significance.
How to lower and how to raise leukocytes in the blood
Patients are often interested in how to quickly lower or how to quickly increase leukocytes in the blood. At the same time, on the Internet you can find a lot of useless and sometimes dangerous methods for raising or lowering the level of leukocytes using folk remedies.
It is important to understand: an elevated or increased level of leukocytes does not require urgent reduction to normal; a comprehensive, thorough examination of the patient and a search for the cause of this phenomenon are needed. And when the cause is eliminated (cured), the leukocyte count will return to normal.
Types of leukocytes
Cells of the leukocyte series have several functions, each group is responsible for certain functions of the body. There are five of them in total
:
- neutrophils
, aimed at destroying bacteria and related problems; - lymphocytes
, responsible for the general condition of the immune system, putting up a kind of barrier; - eosinophils
, an increase in which indicates the presence of a serious allergen in the blood and suggests allergy testing; - basophils
- a reconnaissance group that recognizes infections and gives orders for destruction; - monocytes
- cells that destroy remaining foreign particles.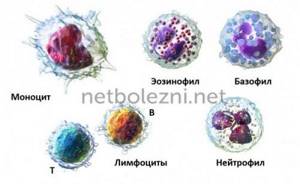
Leukocytes are commonly called white blood cells. If you look through a microscope, you find that they are purple with a pink tint.
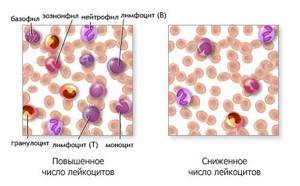
Low leukocytes in the blood - what does this mean?
If there are few leukocytes in the blood, this means that there has been a decrease in the number of white blood cells below 4000 per 1 mm3 (including both granulocytes and agranulocytes ), called leukopenia .
Indicator of the number of leukocytes in the blood
It doesn’t matter whether white blood cells are low in women or men, the reasons for this phenomenon do not differ by gender. So, the following possible reasons for the low level of this indicator:
- damage to bone marrow cells by a variety of chemicals , including drugs;
- hypoplasia or bone marrow aplasia ;
- lack of certain vitamins and microelements ( iron , folic acid , vitamin B12 and B1 copper );
- radiation exposure and radiation sickness ;
- acute leukemia;
- myelofibrosis;
- hypersplenism;
- plasmacytoma;
- myelodysplastic syndromes;
- pernicious anemia;
- metastases to the bone marrow;
- typhus and paratyphoid fever ;
- sepsis;
- carriage of herpes virus types 7 and 6 ;
- anaphylactic shock;
- collagenoses;
- taking medications ( sulfonamides , a number of antibiotics , thyreostatics , NSAIDs , cytostatics , antiepileptic and oral antispasmodic drugs ).
Also, when leukocytes are below normal, this means that the patient should exclude thyroid disease.
If white blood cells are low in a child's blood, this may be a symptom of influenza , malaria , typhoid fever, measles , brucellosis , rubella or viral hepatitis . In any case, leukopenia is a serious phenomenon that requires urgent analysis of its causes.
Factors that reduce leukocytes
A low white blood cell count (leukopenia) is a sign of a weak immune system. The reasons may be low cell production in the bone marrow, a lack of micro- and macroelements and the presence of systemic diseases. The most common factors of leukopenia include:
- alimentary (food) deficiency;
- B12 folate deficiency anemia;
- long-term (sluggish) infectious processes with depleted immunity;
- diseases of the liver and spleen, other disorders of the digestive organs;
- taking a number of medications;
- hormonal and/or metabolic dysfunctions;
- autoimmune diseases;
- leukemia in the initial stage or other oncology with metastases to the bone marrow;
- radiation (radiation) damage.
Blood test readings should be deciphered by a qualified medical professional. Early detection of any abnormalities in the leukocyte profile plays a significant role in identifying the actual cause and preventing the development of diseases.
Elevated leukocytes in a smear in women, causes
Leukocytes normally in a smear from the urethra do not exceed 10 units in the field of view, from the cervix - do not exceed 30 units, from the vagina - do not exceed 15 units.
An increased content of leukocytes in a smear may indicate bacterial infections ( gonorrhea , mycoplasmosis , syphilis , genital tuberculosis chlamydia and others), trichomoniasis , HIV , herpes , papillomavirus , cytomegalovirus , candidiasis , dysbacteriosis , allergies , genital irritation and basic non-compliance hygiene rules before collecting material.
Leukocytes in urine are increased, reasons
The normal content of leukocytes in the urine of men is 5-7 units per field of view, in women - 7-10 units per field of view. leukocyturia in medicine . Its cause can be both failure to comply with personal hygiene rules and serious illnesses (inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract, urolithiasis , tuberculosis , carbuncle , systemic lupus erythematosus and others).
Leukocyte norms in adults in an extended blood test
| Categories | Values | Unit measurements |
| Neutrophils | 55 | % |
| Lymphocytes | 35 | % |
| Monocytes | 5 | % |
| Basophils | 1 | % |
| Eosinophils | 2,5 | % |
Considering the various physiological (normal) possibilities for deviations in the level of white blood cells, it is recommended that the test be taken in the morning, on an empty stomach.
In women of reproductive age, the number of peripheral leukocytes also increases during periods of menstrual bleeding and ovulation.
Neutrophils are increased
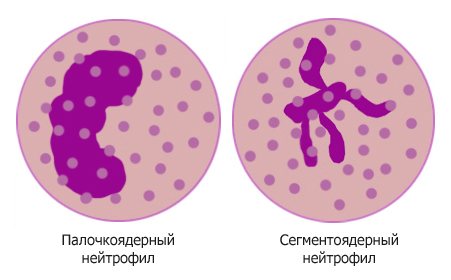
Neutrophils
The normal number of neutrophils in a blood test is:
- for rods 1-6% (or 50-300·106/l in absolute values);
- for segmented ones 47-72% (or 2000-5500·106/l in absolute values).
Neutrophilia - what is it?
A condition in which there is an increase in the number of neutrophils in the blood is called neutrophilia . It can occur during inflammatory purulent processes, infectious acute diseases, insect bites, myocardial infarction , after severe blood loss, and with physiological leukocytosis .
Neutrophils are elevated in adults and children
In general, the reasons for the development of the described condition are similar in people of all ages. It is also known that pronounced neutrophilia is characteristic, as a rule, of bacterial infection . So, if elevated neutrophils in the blood, this means that:
- elevated band neutrophils in an adult or child indicate mild infection or inflammation;
- band neutrophilia with the detection of metamyelocytes against the background of general leukocytosis is observed in purulent-septic complications ;
- neutrophilia with the detection of young leukocytes (promyelocytes, myelocytes, myeloblasts) and the absence of eosinophils indicates a severe course of purulent-septic and infectious diseases and can worsen the patient’s prognosis;
- the causes of increased band neutrophils with the appearance of a large number of destroyed segmented forms indicates suppression of bone marrow activity caused by severe infectious disorders, endogenous intoxication or other reasons;
- the appearance of hypersegmented neutrophils can be caused not only by radiation sickness or pernicious anemia , but in rare cases it is observed in practically healthy patients;
- an increase in segmented forms against the background of eosinophilia (neutrophilic surge) is characteristic of chronic inflammatory processes, myeloproliferative diseases and acute infections.
Increased neutrophils in the blood during pregnancy
The condition when neutrophils are abs. moderately increased, that is, up to 10,000·106/l in a pregnant woman can be interpreted (subject to the exclusion of pathological conditions) as a variant of the norm, called neutrophilia of pregnant women . It occurs due to the response of the immune system to the process of fetal growth and is characterized by an increased content of band granulocytes . In case of neutrophilia in pregnant women, it is necessary to monitor and regularly do a general blood test, since these changes can also signal the risk of premature birth.
Neutrophils are reduced
Neutropenia is a condition when neutrophils in the blood are reduced to 1500·106/l or less. Occurs more often with viral infections. Neutropenia is usually associated with roseola , hepatitis , mumps , adenovirus infection , rubella , influenza viruses , Epstein-Barr , Coxsackie , infection with rickettsia and fungi . The described condition also occurs with radiation sickness , treatment with cytostatics , aplastic and B12-deficiency anemia , and agranulocytosis .
Basophils are increased
The normal number of basophils in a blood test is 0.1% (0-65·106/l in absolute values). These cells take an active part in the allergy and the development of the inflammation process, neutralize poisons from insect bites and other animals, and regulate blood clotting.
Basophils are higher than normal - what does this mean?
Basophilia is an increase in the number of basophils above normal. The reasons for the increase in basophils in an adult and the reasons for the increase in basophils in a child have no fundamental differences and differ only in the frequency of occurrence in different age groups of patients.
So, an increase in the number of basophils occurs in the following diseases:
- blood diseases ( polycythemia vera, chronic myeloid leukemia, acute leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis );
- ulcerative colitis , chronic inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract;
- chronic sinusitis;
- myxedema;
- hemolytic anemia;
- allergic reactions;
- Hodgkin's disease;
- taking antithyroid drugs, estrogens .
Monocytosis
Monocytosis is a condition when an adult or child has an increased number of monocytes . Elevated monocytes in an adult (the norm is 90-600·106/l or 3-11% in the leukocyte formula ) or a child can be detected with the following pathologies:
- sarcoidosis , brucellosis , syphilis , tuberculosis , ulcerative colitis ;
- infections and the recovery period after acute infections;
- acute leukemia of the monocytic and myelomonocytic type, multiple myeloma, myeloproliferative diseases, lymphogranulomatosis;
- endocarditis , rheumatoid arthritis , systemic lupus erythematosus , periarteritis nodosa ;
- intoxication with tetrachloroethane or phosphorus .
Reasons for the highest rates
If some indicators of the leukocyte formula are exceeded tens of times, then this is a signal of serious diseases that require immediate, strong drug treatment. For example, neutrophilic leukocytosis with numbers of 50-100*109 units/l indicates myeloid leukemia.
The reasons may be:
- tuberculosis;
- sepsis, severe infection;
- malignant tumors;
- severe forms of hepatitis.
A significant excess of the norm of eosophils indicates a struggle with a constantly exposed allergen, for example, some regularly taken medication.
Stable, persistent monocytosis becomes a harbinger of chronic forms of tuberculosis or progressive cancer.
A change in leukocyte counts is only a consequence of ongoing internal struggle processes. When the cause is identified through additional examinations, doctors make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. To ensure a clear clinical picture, a repeat blood sample is scheduled 2-3 weeks after the violations are detected.
Changes in blood eosinophil levels
These cells play an important role in the development and suppression of allergic reactions : from elementary nasal congestion ( allergic rhinitis ) to anaphylactic shock . An increase in the number of eosinophils in a blood test is called eosinophilia , and a decrease in their number is called eosinopenia.
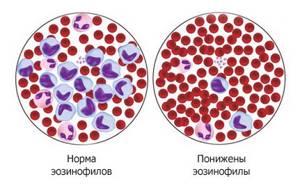
Level of eosinophils in the blood
Eosinophilia occurs in a fairly extensive list of diseases, including:
- allergies and bronchial asthma ;
- tumors;
- infestation with parasites;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- chronic myeloid leukemia;
- scarlet fever;
- treatment with antibiotics , sulfonamides or PAS .
In the vast majority of cases, a decrease in the number of eosinophils below the normal level is associated with increased adrenocorticoid activity, leading to retention of eosinophils in bone marrow tissue. The presence of eosinopenia in the postoperative period indicates how severe the patient's status is.
Changes in the level of lymphocytes in the blood
An increase in the content of lymphocytes (lymphocytosis) is observed when:
- bronchial asthma;
- chronic radiation sickness;
- whooping cough, tuberculosis;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- drug addiction;
- after splenectomy ;
- chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Lymphopenia is observed in the following cases:
- malformations of the organs of the lymphoid system;
- slowing down lymphopoiesis ;
- acceleration of lymphocyte ;
- agammaglobulinemia;
- thymoma;
- leukemia;
- aplastic anemia;
- carcinoma , lymphosarcoma ;
- Cushing's disease;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- treatment with corticosteroids;
- AIDS;
- tuberculosis and other diseases.