Color indicator is a parameter included in the general blood test. It serves as a starting point for diagnosing red lineage diseases with serious consequences. Let's figure out what a color indicator is, to identify what pathology it is needed and how it is determined.
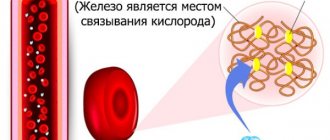
The red color of red blood cells is given by hemoglobin, a combination of protein (globin) with iron ions.
This complex acts as a carrier of dissolved gases: it delivers oxygen into the tissues and removes carbon dioxide from them back into the blood.
The color indicator reflects the level of hemoglobin in the blood cell and the degree of its saturation with iron. The more hemoglobin and carrier metal ions a blood cell can hold, the higher the color of the red blood cell and the more efficient the delivery of oxygen to the tissues.
What else can you get from the indicator?
The digital value of the color blood indicator indirectly allows us to judge the indices.
Calculated by analytical instruments:
- MCH (average hemoglobin content in the blood), the normal value of which is 27-33.3 pg,
- The average concentration of the oxygen carrier in the blood cell (the norm is 30-38%).
Thus, a color parameter of 0.86 corresponds to the lower limit of normal MCH and the average hemoglobin concentration of 30%.
Color index calculation, norm in children and adults, reasons for low and high
Calculation of the color index (or color, which is a synonym) is considered an old but important method for studying peripheral blood.
The color indicator carries information about the degree of saturation of red blood cells (erythrocytes) with a pigment containing iron and carrying oxygen - hemoglobin. It is calculated by a formula if the general analysis is performed manually or is replaced by a similar red blood cell index (MCH), which is calculated by an automatic analytical system (hematology analyzer).
Color or color indicator - norm and deviations
The color indicator is a characteristic that signals significant changes in the ratio of the main components of red blood (red blood cells and hemoglobin).
The color index norm for both adults and children, excluding children under 3 years of age, according to various sources, ranges from 0.8 to 1.1, although some authors argue that 0.8 is already too little, and 1.1 already exceeds the permissible limits borders.
The norm for CP in a child under 3 years of age is slightly lower and is 0.75 – 0.96.
The color indicator is determined as part of a general blood test performed without the participation of an analytical system. With an automatic hematology analyzer, calculating CP becomes impractical; it is gradually becoming a thing of the past, being replaced by red blood cell indices.
The most common situation is when CP is reduced (hypochromia), which gives reason to suspect the development of anemia (IDA, anemia accompanying neoplastic processes or chronic diseases of internal organs).
Then one decimal fraction tells you what diagnosis will soon be made.
Calculation in two steps
The color index is calculated using the formula: CP = hemoglobin x 3: number of red blood cells.
For example, with a red blood cell count of 4.2 x 1012/l and a hemoglobin level of 128 g/l, the color index will be 0.9 (128 x 3 and divided by 420), which corresponds to the norm (normochromia).
Meanwhile, it should be noted that normochromia does not always mean normal.
A proportionally reduced number of red blood cells and hemoglobin will also have a similar designation - normochromia, but in this case we will talk about normochromic anemia. In addition, there are other situations:
- There may be a lot of red blood cells or their number is at the upper limit of normal, for example, 4.7 x 1012/l with hemoglobin 120 g/l. When calculating the color index (120 x 3: 470 = 0.76), it is discovered that it does not fit into normal values, that is, red blood cells circulate “empty”, there are many of them, but they do not contain sufficient hemoglobin (hypochromia). This phenomenon indicates the development of anemia, the type and cause of which should be clarified by further hematological studies.
- red blood cells in the blood are normal (for example, for women 4.0 x 1012/l) or near the lower limit of normal, and hemoglobin is high (160 g/l), and after calculating the CP it turns out that it exceeds 1.0 (160 x 3: 400 = 1.2). This means that the red blood cells are excessively saturated with hemoglobin and in such a case they speak of hyperchromia - the blood of such people is thick and “heavy”.
Thus, a reduced or low color index, first of all, indicates the presence of anemia, and a high value indicates blood thickening, the cause of which also remains to be determined.
Lower values suggest serious examination
The criterion for the saturation of red blood cells with hemoglobin is the average content of blood pigment (Hb) in one red blood cell, which is calculated by the formula: SGE = hemoglobin: per number of red blood cells in one liter of blood. The indicator is measured in picograms (pg) and normally ranges from 27 to 31 pg.
The automatic analyzer measures the mean hemoglobin content in the erythrocyte (MHC) in the same units, calculating it using the formula: MHC = ten times the hemoglobin level divided by the number of red blood cells per microliter (106).
By measuring the average hemoglobin content in the erythrocyte, as in the case of cirrhosis, anemia is divided into hypochromic, normochromic and hyperchromic.
Of course, each of these indices separately cannot represent the only reliable indicator of pathology, therefore, if they decrease, the cause of the disorders should be sought.
Most often it is iron deficiency anemia, then there is a need to find a problem with the absorption or synthesis of iron, and this is a lot of all sorts of examinations, including not only blood tests, but also not always pleasant procedures, such as fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS).
This is what a fractional number that is not included in the normal values of the color index means.
How to calculate?
The color index can be calculated independently. To do this, you need to know the level of hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells, which is designated as RBC.
The formula used to calculate the parameter:
Hemoglobin level*3/the first 3 digits of the red blood cell level, inserted into the formula without a comma.
If the analyzes indicate two numbers separated by a comma, you need to remove the comma and add 0. The number 3 in the formula is unchanged. Calculation example for a hemoglobin level of 160 g/l and RBC=4.5 g/l:
160*3/450=1.06. The resulting figure corresponds to the color indicator (not measured in conventional units).
Norms
The color indicator in a healthy person is within the following values:
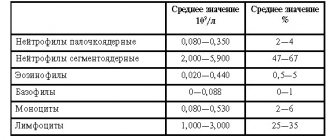
| Gender, age | Norm |
| Men | 0,86-1,05 |
| Women who are not pregnant | 0,86-1,05 |
| Pregnant | 0,85-1,0 |
| Newborn babies | 0,9-1,3 |
| 1-3 years | 0,85-0,96 |
| 3-12 years | 0,85-1,05 |
| Over 12 | 0,86-1,05 |
The condition in which the red blood cell contains the optimal amount of hemoglobin and iron and has a normal red color is called normochromia (normo + chromos - color). The deviation of the color parameter can be towards hypo- (decrease, decrease) or hyperchromia (increase).
The result is evaluated as follows:
- Hypochromia (CP 0.85 or less),
- Normochromia (0.86-1.05),
- Hyperchromia (over 1.06).
The color index norm is the same for men and women of all ages. Pregnancy is the only condition that is not a disease in which the color index is reduced in an adult. The low rate is explained by physiological anemia characteristic of the 3rd trimester.
Interesting. A higher norm is typical for a child of the first year of life. It is explained by the presence in infants of fetal red blood cells with a high concentration of hemoglobin. By adolescence, the rate becomes the same as in adults.
An altered (above or below normal) color indicator goes hand in hand with decreased red blood cells and indicates anemia.
What is the danger of hypochromia in a child?

Every day, children at an early age are depleted of iron reserves, as the growing body requires a lot of useful substances. If they have iron deficiency anemia, then such a long-term condition can lead to complications:
- Respiratory tract infections;
- Gastrointestinal diseases;
- Neuropsychic disorders;
- Decreased vision and hearing due to poor conduction of nerve impulses.
A low color index in an infant can occur for various reasons. First of all, in newborns, iron deficiency is associated with a lack of the element in the mother during pregnancy. This condition is also observed with difficult gestation, hypoxia, bleeding, abnormal development of the umbilical cord and placenta. Children who are fed formula or animal milk products rather than breast milk do not get enough iron.
If the drop in CPP is not caused by intrauterine disorders, then it is worth looking for pathologies in the child’s body. Bleeding leads to iron deficiency hypochromia:
- Esophageal hernia;
- Gastrointestinal ulcers, hemorrhoids;
- Diverticula, tumors, polyps of the intestinal tract;
- Internal bleeding in the respiratory system.
Taking hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs also contributes to the loss of hemoglobin
If iron absorption is impaired, it is important to differentiate between helminthic infestations, Crohn's disease, and dysbacteriosis.
You can recognize anemia in a child by external signs. All patients experience pale skin, moodiness, sweating, lethargy, decreased appetite, vomiting after feeding, regurgitation, insomnia, and loss of muscle tone. Up to a year, regression of motor skills may be observed. In the second half of the year, roughness of the skin, cracks on the lips, stomatitis, caries, and physical developmental delay appear.
Relationship between color indicator and red blood cell size
Cells overflowing with hemoglobin have an increased size and are called megalocytes. Their diameter exceeds 8 microns.
The higher the color index, the larger the size of the blood cell. The diameter of red blood cells with a normal color value is in the range of 7-8 microns.
If during maturation the red blood cell is not saturated with a sufficient amount of red pigment, its diameter remains reduced - 6.9 microns or less.
Such a cell is called a “microcyte,” and anemia, for which a microcyte is characteristic, is called microcytic.
Blood test online transcript for free
Laboratory analysis of blood composition (general clinical or blood biochemistry) are a very important “tool” for every doctor and occupy a special place among laboratory diagnostic methods. A blood test allows you to determine various hematopoietic disorders, identify various pathological changes in human tissues and organs, and also generally assess the condition of our body.
However, deciphering a blood test and interpreting its results requires special medical training and is extremely difficult to do on your own. However, in some cases, even before visiting a doctor, we want to understand whether everything is normal with our blood and what possible reasons could cause this or that deviation in its composition? In such a situation, our “Blood test online decoding” will help you instantly decipher the results of the study specifically based on the results of your laboratory analysis. With its help you can get general explanations about clinical blood tests.
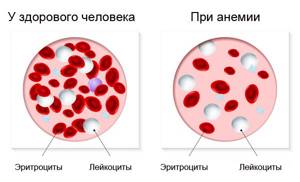
A general blood test provides valuable information about the number, size and shape of the constituent elements of blood - red blood cells, hemoglobin, platelets, and leukocytes. For each analysis indicator there is a norm - a range of normal values for these indicators. Normal values are different for men, women and children. In addition, the norm also depends on the age of the patient. Therefore, when using our “Online Blood Test Transcription” , do not forget to indicate your age and gender.
In a healthy patient, the cellular composition of the blood is within normal limits. In the presence of a disease, the values of individual indicators go beyond the normal range, since a certain disease manifests itself in a change in the composition of our blood. Even just one change in the composition of our blood can indicate the presence of several diseases. Conversely, to confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to analyze and compare the values of several indicators, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. Therefore, our service “Blood test online interpretation” provides only general information about normal values and possible causes of deviations, and cannot replace a visit to the doctor and, moreover, is not a sufficient basis for making a diagnosis.
| General blood analysis |
| Blood test biochemistry |
What does a lower level mean?
About disruption of hemoglobin synthesis.
A low value indicates hypochromic microcytic anemia (with low hemoglobin and red blood cell count).
Blood cell anemia
This type of anemia includes:
- Iron deficiency,
- Chronic posthemorrhagic,
- Sideroachrestic,
- Hypoplastic.
All of them are a consequence of low hemoglobin; they are united by a violation of the incorporation of iron ions into the erythrocyte.
Iron-deficiency anemia
Iron deficiency is the most common cause of hypochromic anemia.
The disease occurs due to:
- Insufficient consumption of animal products,
- Inflammatory process of the small intestine, leading to decreased absorption of microelements through the mucous membrane,
- Pregnancy, lactation, intensive growth in children.
Anemia in pregnant women not only worsens the woman’s condition, but also negatively affects the hematopoiesis of the fetus. It responds well to treatment with iron supplements, which are safe for the unborn child.
To make a diagnosis, you need to know the level of iron in the plasma and the total iron-binding capacity of the serum (TIBC).
Chronic posthemorrhagic anemia
The reason is constant bleeding, in which the loss of iron exceeds its intake from food.
Anemia develops with the following diseases:
- Erosive gastritis,
- Peptic ulcer disease,
- Hemorrhoids,
- Heavy, prolonged menstruation, intermenstrual bleeding due to hormonal imbalances.
Sideroachrestic
The disease is caused by a hereditary disorder of hemoglobin synthesis in the bone marrow. The body does not lack iron, it is simply unable to incorporate it into hemoglobin.
Hypoplastic
It can be determined by bone marrow puncture. In the analysis of punctate, there are damaged stem cells that are unable to absorb a sufficient amount of hemoglobin.
Color index and anemia
Depending on how low (or high) the color index is, you can judge the type of anemia.
So, if it is lowered and is less than 0.85, we are talking about hypochromic anemia. This category includes iron deficiency anemia, anemia due to a malignant tumor or chronic diseases, as well as chronic post-hemorrhagic anemia.
If it is elevated (more than 1.15), hyperchromic anemia can be diagnosed (this occurs with a deficiency of folic acid or vitamin B12), as well as polycythemia.
But even if this parameter is normal, hemolytic or posthemorrhagic anemia is possible. Also, the color index is usually normal in diseases such as chronic renal failure or hypothyroidism.
With any anemia, symptoms such as a decrease in the general tone of the body, dizziness, shortness of breath, headaches and pallor of the skin, as well as pulsation in the temples, increased heart rate, weakened memory and attention can be observed.
To clarify the type of anemia, it is also possible to undergo tests for ferritin, vitamin B12, serum iron and transferrin.
What does an increased value mean?
Lack of vitamin B12 or folic acid. As a result, red blood cells with large sizes and a high concentration of hemoglobin are formed. Blood cells with such parameters die prematurely.
Hyperchromic anemia (with a high color index) is caused by the following reasons:
- Gastritis, enteritis with atrophy of the mucous membrane, in which the protein that ensures the absorption of the vitamin ceases to be produced,
- Secretory insufficiency of the pancreas in pancreatitis,
- Severe liver dysfunction,
- Competitive consumption of vitamins by intestinal helminths,
- Long-term treatment with folic acid antagonist drugs: Methotrexate, Aminopterin, Neomycin, PAS,
- Disease of the thyroid gland with hormonal imbalance,
- A diet low in vitamin B12 and folic acid.
Important! Anemia does not always occur with a change in color parameter. In some conditions, normochromia (reduced number of red blood cells, but normal hemoglobin levels) is observed. It is characteristic of kidney disease and acute blood loss.
Prevention
Increased hemoglobin
High hemoglobin is a sign:
- Hypoxia (lack of oxygen),
- Dehydration,
- Chronic infection.
It indicates the body is working under stress and is a harbinger of depletion of health resources.
In addition to a general blood test, a biochemical test, which is also prescribed by a therapist, is informative.
He will indicate what is needed to prevent high hemoglobin:
- Rationalization of physical activity,
- Rejection of bad habits,
- Sanitation of foci of chronic infection,
- Healthy diet.
Products that lower hemoglobin:
- Plant-based meals: salads, raw vegetables,
- Seafood,
- Dietary meat,
- Legumes.