Features of devices for diagnosing diseases of the small intestine and colon
In our clinic, examinations are carried out using stationary ultrasound equipment of expert and high class. It allows you to get a good quality image. The results of the study can confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the intestine is performed in B-mode (from the English brightness - brightness). On the screen, the doctor sees a black and white two-dimensional image in one plane. For examinations in our clinic, convex ultrasound sensors are used, which operate at a frequency of 2-7.5 MHz. They allow penetration to a depth of 25 cm. The doctor will determine the exact operating frequency of the device depending on your build.
This is interesting! The first ultrasound of the intestines was performed by the English scientist John Wilde in 1949. He used this diagnostic method to determine the thickness of the intestinal wall. For this development, the scientist was called the “father of medical ultrasound.”
To examine the rectum, a rectal ultrasound sensor is used, which has a small thickness. The sterility of the device and painless insertion helps to preserve the special condom.
How to do endoscopy of the rectum with a proctoscope
Usually the study is performed in the knee-elbow position on the couch. A special device in the form of a metal tube with a diameter of about 1.2 cm with an optical system is inserted through the anus. Rectoscopy, in the absence of inflammation of the anal canal, is painless. During the examination, some discomfort may occur when air is forced inside. Rectoscopy differs from colonoscopy in that only the rectum is examined, and the rest of the colon remains unexamined, and therefore we recommend that you always sign up for a total colonoscopy. In the absence of contraindications and the patient’s personal desire, the use of anesthesia is allowed. The duration of the study ranges from 5 minutes to 30 minutes
.
Types of intestinal ultrasound methods
Diagnosis of intestinal diseases in our clinic in Moscow is carried out in two ways:
- transabdominal
- rectal
Your doctor will perform a transabdominal ultrasound using a standard transducer. This procedure is performed through the anterior abdominal wall and is completely painless. It can be carried out in 3 stages:
- With an empty organ.
- With a full intestine.
- With a full bladder.
This approach makes it possible to examine the large and small intestine in dynamics, but requires more time for diagnosis.
Examination of the rectum through the anterior abdominal wall is difficult. The pelvic bones and nearby organs interfere. To get a good result, your doctor will suggest you perform a rectal ultrasound. The procedure is painless, may be accompanied by slight discomfort, but lasts 10-15 minutes.
Rectal ultrasound examination requires special preparation. The doctor will insert the ultrasound sensor into the rectum to a depth of 12-18 cm, determined by special divisions on the device. This method allows you to check the intestines without a colonoscopy and detect inflammatory changes, stenosis and other pathologies.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
In this case, information about the intestines is collected using special technical devices. They help to determine not only the nature and localization of the pathological process, but in some cases even to collect biological material and remove formations. More information about the morphological diagnosis of the stomach and intestines can be read in the book by Aruin L.I.
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a test that examines the colon. Diagnostics is carried out using a long flexible probe to which a video camera is attached. During the examination, the specialist can see the patient's intestines from the inside. The attached video camera allows you to take photos and videos. First, the colonoscope is placed in the anus and the probe is gradually moved deeper along the intestine.
Doctors may prescribe a colonoscopy for chronic anemia and sudden weight loss
The study allows you to study in detail the condition of the mucous membrane, assess the functioning of the organ, including motor function. The specialist has the opportunity to examine inflammatory processes and neoplasms. Colonoscopy combines not only diagnostic but also therapeutic measures. For example, if a polyp is discovered, the doctor can remove it immediately. Also during the study, you can take a sample of biomaterial for histological analysis.
During a colonoscopy, the doctor can stop bleeding, cut adhesions, remove a foreign object, and expand the lumen of the organ. Experts recommend examining the large intestine in the following cases:
Preparation for intestinal irrigoscopy
- for persons over fifty years of age, colonoscopy is recommended for preventive purposes;
- hereditary predisposition to polyps;
- diagnosed cancer in close relatives.
The doctor may refer you for a colonoscopy if there are certain patient complaints, for example, the appearance of blood in the stool.
Such a symptom may indicate not only the presence of hemorrhoids or anal fissures, but also more serious pathologies: tumors, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis.
Pus and mucus in stool is another reason for a colonoscopy. Pain in the abdomen that occurs after eating, before defecation, during movement, or bending may be an indicator of intestinal dysfunction. Constant constipation is a prerequisite for the occurrence of pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract.
Abnormal bowel movements may be a symptom of existing pathologies, which can be detected by endoscopic examination. Another reason for a colonoscopy is alternating constipation and diarrhea. These signs may be present in irritable bowel syndrome, colitis and cancer pathologies.
Important! A colonoscopy literally allows you to look inside your intestines.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. A special office is equipped for this purpose. The patient lies on his left side, with his legs pressed to his stomach. The anorectal area is treated with an antiseptic. For better passage of the probe through the intestine, the initial section is lubricated with a special substance. During the procedure, patients sometimes feel fullness, pressure and moderate pain.
To straighten the mucous folds, the intestines are filled with air. At this point, cramping pain and bloating may appear. Colonoscopy requires special preparation. The effectiveness of the procedure depends on the conscious attitude of the patient. To remove feces and areas of semi-digested food from the intestinal walls the night before, the patient should drink Fortrans.
To prepare a medicinal solution, the dry powder is diluted with boiled water. Three days before the test, foods that contribute to increased gas formation should be excluded from the diet:
- White cabbage;
- legumes;
- whole milk;
- fatty and fried;
- nuts;
- fresh baked goods;
- mushrooms;
- vegetables and fruits.

It is important to avoid gas-forming products on the eve of the procedure.
You should also avoid drinking coffee, alcohol and any drinks that have coloring properties. The patient should not have dinner the day before; the last meal should be no later than 14.00. There are contraindications to colonoscopy:
- diseases of the coagulation system;
- acute infections;
- exacerbation of inflammatory processes;
- pregnancy;
- massive bleeding;
- peritonitis;
- intoxication;
- heat;
- severe heart pathologies.
Recently, virtual colonoscopy has become increasingly popular. Computed tomography allows you to recreate a three-dimensional image of the intestine. Air is pumped through a tube in the rectum and a scan of the abdominal organs is performed. Unlike the classic version, visual colonoscopy has a number of advantages:
- there is no need to use endoscopic instruments;
- the possibility of performing treatment for patients with diseases of the coagulation system and cardiac pathologies;
- gentle, comfortable procedure;
- there is no need for anesthesia.
Despite the fact that colonoscopy is an effective diagnostic method, it is not always possible due to existing contraindications. In such cases, alternative methods are used, for example, anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, irrigoscopy, capsule endoscopy.
Capsule endoscopy
The essence of the study is to use a wireless camera, which the patient must swallow like a pill. It takes thousands of pictures, which are transferred to a recording device. The technique allows you to study hard-to-reach departments that cannot be reached using standard instrumental methods.
Capsule endoscopy provides complete information about the condition of the mucous membrane and venous wall of the gastrointestinal tract. The procedure is carried out in large centers, as expensive imported equipment is used to carry it out.
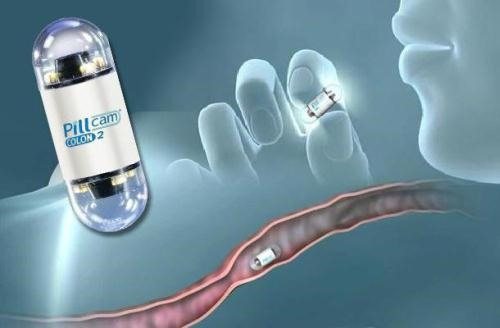
Capsule endoscopy allows you to examine the small intestine without a colonoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy
The procedure allows you to examine the condition of the lower portion of the sigmoid and rectum. The sigmoidoscope allows you not only to study the internal state of the organ, but also to carry out some procedures, for example, removal of polyps, cauterization of tumors, removal of a foreign body.
During the procedure, the patient takes a knee-elbow position. After a digital examination of the rectum, the device is inserted into the anus. The procedure takes no more than five to ten minutes and in most cases is well tolerated by patients.
So, early diagnosis of the intestine allows you to identify dangerous pathologies and successfully cope with them. To assess the condition of the intestinal tract, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are used. Based on the results obtained, the doctor conducts a differential analysis and makes a diagnosis.
Who is indicated for intestinal ultrasound?
Doctors at our clinic conduct examinations of the small intestine and large intestine for acute and chronic diseases. They are manifested by the following symptoms:
- acute abdominal pain
- chronic pain syndrome
- frequent intestinal disorders
- belching, bitter taste in mouth
- flatulence, intestinal colic
- the appearance of blood, mucus in the stool
- weight loss
- signs of anemia in blood tests
Ultrasound examination is also prescribed for patients who have had colon cancer to exclude recurrence of the disease. Patients whose bowel curvature was found during rectoscopy require sonography to clarify the diagnosis.
Note! Ultrasound of the intestines in men is done for prostate cancer to exclude tumor growth into the rectum. This diagnosis helps to choose treatment tactics and the scope of intervention.
Women often experience hemorrhoids during pregnancy. According to statistics, the disease manifests itself from the 2nd trimester. By the time of birth, the expansion of the nodes becomes pronounced and can cause bleeding. To clarify the diagnosis, a rectal ultrasound is prescribed. During the examination, the doctor will distinguish inflammatory changes and enlarged hemorrhoids.
Primary signs of bowel cancer
Like many other oncological diseases, intestinal cancer in the initial stages manifests itself with subtle and subtle symptoms, which often go unnoticed:
- certain changes in intestinal motility;
- general weakness, fatigue, loss of body weight that does not have natural causes;
- anemia;
- the presence of blood in the stool;
- changes in taste preferences, the appearance of aversion to certain foods.
The presence of such signs and symptoms of bowel cancer, as a rule, does not cause concern for patients. This oncopathology in the early stages can be detected by chance, when the patient undergoes an endoscopic examination for a completely different reason. Most often, intestinal cancer is detected in late, advanced stages, requiring long-term and complex treatment.
Early diagnosis of colon cancer ensures timely initiation of treatment, which increases the patient’s chances of recovery and maintaining quality of life. Therefore, if you have at least one of the above signs of this disease, you must immediately consult a doctor and undergo a thorough examination.
Diagnosis and treatment of oncological diseases is carried out in one of the leading centers in Moscow - the Yusupov Hospital.
Diseases that ultrasound diagnostics of the intestine can help detect
In Moscow, checking the digestive tract using ultrasound is a fairly common method of diagnosing the adult population. The equipment in our clinic allows us to identify acute or chronic diseases.
Diagnosis of the small intestine determines functional disorders. These are diseases that are associated with genetic characteristics or neuropsychic activity. These functional disorders include:
- irritable bowel syndrome
- functional constipation
- functional diarrhea
- bloating
Ultrasound can also help identify Crohn's disease. The lesions are localized in the terminal part of the ileum, but sometimes the disease affects the entire digestive tract. Ultrasound helps identify intraperitoneal abscesses and enlarged lymph nodes, which are a complication of the disease.
Doctors at our clinic recommend doing an ultrasound of the intestines if appendicitis is suspected. Inflammation of the appendix is an insidious disease that disguises itself as other pathologies: intestinal or renal colic, colitis, cholecystitis. To avoid unnecessary surgery, it is recommended to do an ultrasound.
Examination of the colon is aimed at detecting tumors and inflammatory processes. Doctors visually distinguish these two pathologies. The tumor has the appearance of a delimited focus. Inflammation of an infectious or non-infectious nature looks like a long, thickened section of an organ.
By the way! Functional disorders of the colon are difficult to diagnose. The colon is normally distended with gases; it is impossible to distinguish this condition from pathology.
When examining the abdominal cavity, the doctor may detect fluid, abscess, or cystic formations. But when examining the small intestine, it is difficult to determine its sections: the loops are layered on top of each other.
Rules for preparing for examination of the small intestine
Diagnosis of diseases of the small intestine and colon requires special training. Gases that are normally found in the organ cavity distort diagnostic results.
It is recommended to go on a special diet 3 days before the scheduled ultrasound to reduce the amount of gas. Avoid foods that can cause fermentation and release gases from the diet. These include legumes, bread, milk. You should also limit your consumption of fatty foods.
If you have indigestion, your doctor will recommend a drug that will help cope with unpleasant symptoms:
- festal
- mezim
- pancreatin
- Creon
The day before the procedure, sorbents are taken. Examination of the small intestine is carried out no earlier than 7 hours after eating. If you have planned a rectal ultrasound, then in the evening you need to do a cleansing enema at home.
How is an intestinal ultrasound performed?
The technique of transabdominal and rectal examination is different. Through the anterior wall of the abdomen, the ileum, sections of the colon, sigmoid, and rectum are examined.
The doctor will ask you to undress to the waist and lie on your back on the couch. A water-based gel is applied to the sterile sensor. It removes the air gap between the sensor and the skin.
If you are worried about abdominal pain, diagnosing intestinal diseases begins with painless areas. Only at the end of the examination, the doctor presses the sensor on the area of appendicitis or inflammation in order to better examine it.
The colon is examined in three states:
- Empty bowel after an enema.
- A contrast liquid is injected into the intestinal cavity through a thin tube; it contours the walls.
- The bowels are emptied again and the condition is assessed.
For a rectal ultrasound, a cleansing enema is first performed. The manipulation does not take much time and is painless. It uses sterile rectal nozzles, which are processed after each patient.
After cleaning the rectal area, the doctor will ask you to undress from the waist down and lie on your side on the couch. The legs are bent at the knees and hips. A disposable condom is put on the disinfected sensor and the gel is applied. The doctor carefully inserts the sensor into the rectum. During an ultrasound, the transducer is rotated to examine all areas of the organ.
After checking, the device is carefully removed and the condom is thrown away. The nurse treats the sensor with a special antiseptic solution. This prevents the risk of patients becoming infected with various types of infections.
Diverticulosis and its treatment
Diverticulitis is the presence of a diverticulum
, which is a sac-like cavity formation that communicates with the small intestine through an opening.
There are several types of localization of diverticulitis in the small intestine:
- Diverticulum 12 – duodenum;
- Meckel's diverticulum localized in the upper ileum;
With diverticulosis, bloating, diarrhea, bad breath, and pain in the abdominal area are observed.
To diagnose this disease, EGD and capsule videoscopy are used. X-rays of the small intestine, CRT and angiography are also done.
For diverticulosis, diets No. 4 and No. 3, symptomatic therapy and probiotics are prescribed. All appointments are made by a specialist gastroenterologist based on the obtained tests and research data.
Who should not be tested using ultrasound?
There are no contraindications for ultrasound of the digestive tract. This research method does not provide radiation exposure, because not associated with x-ray exposure. Ultrasound is safe for both adults and children. The advantage of this diagnosis is that it can be done even for pregnant women, at the same time several times during the gestation period. Modern devices used in our clinic also give accurate results in this case.
Ultrasound of the intestine during pregnancy is a safe way to diagnose its condition and detect appendicitis. The inflamed appendix in pregnant women is often located on the side of the abdomen, under the liver, simulating intestinal colic. Colonoscopy during pregnancy is contraindicated, but ultrasound diagnostics is safe for the fetus. In preparation for childbirth, such a diagnosis also gives the observing doctor an understanding of how the fetus is positioned in relation to the internal organs.
It's important to know what! It is impossible to limit yourself to only ultrasound without colonoscopy when tumors and Crohn's disease are detected. These diseases require histological confirmation of the pathology.
Main symptoms of bowel cancer
The appearance of more significant signs of an intestinal tumor is noted as the tumor grows:
- the presence of blood is observed in the stool: both individual streaks and completely colored stool;
- the presence of pus and mucus is noted in the stool, causing an unpleasant odor in the stool;
- patients begin to worry about constipation, which is replaced by diarrhea;
- blood pressure decreases, the blanching of the skin disappears, and attacks of cold sweat occur periodically - when the tumor is localized in the cecum;
- development of nausea and vomiting, which does not bring relief and is accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- the appearance of pain arising in the projection of the neoplasm onto the abdominal wall;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement after defecation;
- long absence of bowel movements, which can last several weeks. The abdominal wall becomes hard and painful;
- Over time, general oncological symptoms develop and secondary tumors appear.
The manifestations of intestinal cancer depend on a number of factors, primarily on where the malignancy is localized.