Colonoscopy is the most informative diagnostic tool and allows you to detect a wide range of diseases of the colon (ulcers, polyps, malignant tumors), as well as remove some of them during the examination. Since a regular colonoscopy can be accompanied by unpleasant sensations, sleep colonoscopy (using medicated sleep) is popular in Nearmedic clinics - a method in which the patient is completely free from pain.
In addition, colonoscopy allows you to:
- simultaneously carry out an ultrasound examination (necessary if there is a tumor in the intestinal wall);
- diagnose cancer at an early stage;
- perform a high-quality biopsy in any part of the intestine, which greatly increases the efficiency of the study.
The appearance of this diagnostic method in the arsenal of doctors helped reduce the mortality rate from colon cancer by 20 times (according to the World Health Organization).
General indications for the procedure
Doctors consider two groups of indications for the procedure - diagnostic and therapeutic.
Diagnostic:
- suspicions of the presence of neoplasms in the large intestine;
- Crohn's disease;
- intestinal obstruction and chronic constipation;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- presence of an unknown source of bleeding.
Treatment indications:
- removal of polyps;
- straightening of the intestine during intussusception;
- stop bleeding.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
2-3 days before the test - stick to a diet without vegetables, fruits and bread.
Further preparation is possible (to choose from) with two drugs Fortrans and Flit-Phosphosoda.
We purchase Fortrans at the pharmacy, the quantity depends on the patient’s weight, further according to the instructions:
If the study is scheduled for 9-10 a.m., then from 4 p.m. on the eve of the study the patient begins to take Fortrans.
Each sachet of the drug is dissolved in 1 liter of boiled water and every 15 minutes the patient drinks 1 glass (250 ml) of the solution. In 4 hours (from 16 to 20 hours) you need to drink at least 3-3.5 liters (in the presence of chronic constipation - at least 4 liters) of Fortrans solution. If the study is scheduled for 11-12 o'clock, then the patient begins taking Fortrans from 18 o'clock on the eve of the study, and finishes taking it by 22 o'clock in the same regimen.
On the morning of the test, do not drink or eat. There is no need to do enemas.
We purchase Fleet-Phospho-Soda at the pharmacy, follow the instructions:
The drug is used in adults and adolescents over 15 years of age. No dose adjustment is required for elderly patients.
You should start taking Flit Phosphosoda on the day before your scheduled endoscopic or x-ray procedure. If your appointment is scheduled before noon, it is recommended that you follow the instructions for a morning appointment. If your appointment is scheduled for the afternoon, it is recommended that you follow the instructions for an afternoon appointment.
Anesthesia (anesthesia) for colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a procedure for examining the large intestine, as well as the final part of the small intestine, using a thin flexible fiberoptic device consisting of a light source and a camera that produces an image on a television screen.
Anesthesia for colonoscopy
Different clinics in our country use different types of anesthesia for colonoscopy. It is not so rare that a colonoscopy is done without any anesthesia at all, although this medical procedure is quite unpleasant and painful. Sometimes a colonoscopy is performed under local anesthesia, where the tip of the colonoscope is lubricated with a local anesthetic. However, local anesthesia for colonoscopy does not provide sufficient comfort for the procedure.
The most optimal and most often used type of anesthesia for colonoscopy in European countries is sedation. Sedation causes a state similar to sleep, while anxiety and fear go away, and all sensations are dulled as much as possible. Midazolam or propofol are most often used for sedation during colonoscopy. Both of these anesthetic drugs have their advantages and disadvantages. The advantage of midazolam is that its use does not evoke in the patient any memories of the procedure. The disadvantage of midazolam is the longer period of awakening after its use. Propofol ensures rapid awakening after sedation, at the cost of some risk of retaining memories of the past colonoscopy.
Another type of anesthesia used during colonoscopy is general anesthesia (anesthesia), which ensures that the patient is completely unconscious. If sedation provides comfort in 95-99% of cases of its use, then anesthesia during colonoscopy guarantees 100% comfort. However, we should not forget that anesthesia during colonoscopy is associated with a greater risk of complications of anesthesia than when using sedation techniques. Various drugs from the group of anesthetics can be used to administer anesthesia during colonoscopy. Anesthesia for colonoscopy should be carried out only in an operating room, which has all the necessary equipment to ensure complete safety of the procedure.
Thus, performing anesthesia during colonoscopy is not rational, since the risk from it exceeds the risks associated with the colonoscopy procedure itself, so the most optimal is to perform colonoscopy under sedation.
Indications for colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is most often performed for gastrointestinal bleeding, as well as for suspected development of inflammatory or malignant neoplasms of the colon. Also, another indication for colonoscopy is an unmotivated decrease in hemoglobin in elderly patients.
Features of colonoscopy
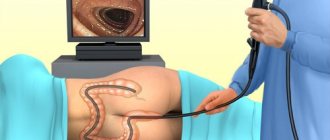
During a colonoscopy, a probe is inserted through the anus into the colon to visually examine the inside of the intestine. A colonoscopy may involve some surgical procedures, such as removing a polyp, or taking a small sample of colon tissue for examination (biopsy). However, most often a colonoscopy is performed for diagnostic purposes.
Colonoscopy time
The duration of the procedure is from 15 to 60 minutes.
Complications of colonoscopy
Overall, the risk of complications during colonoscopy is extremely low, only about 0.35%. Possible complications of colonoscopy include perforation, bleeding, postpolypectomy syndrome, reaction to anesthetic, and infection. Of the possible complications of anesthesia during colonoscopy, the most common are the development of an allergic reaction to anesthetics, as well as the occurrence of respiratory problems.
Performing a colonoscopy
The duration of the procedure is 20-30 minutes. The patient must come to the procedure with an escort.
- the patient lies on his left side, pulling his knees to his chest;
- the doctor carefully inserts the colonoscope;
- Air is pumped into the intestines to straighten the folds while simultaneously advancing the colonoscope (can be painful without anesthesia);
- During the study, if indicated, polyps can be removed, bleeding can be stopped, and a biopsy can be performed.
Proper nutrition after colonoscopy
The main method of preventing negative consequences and restoring intestinal functions after colonoscopy is following a proper diet. Foods that can be consumed include:
- Low-fat varieties of meat and fish.
- Boiled eggs, steamed omelettes.
- Vegetable broth.
It is important to consume enough fluid - at least 2 liters daily. It is better to drink plain clean water or green tea. All dishes must be prepared by boiling or baking, and additionally chopped before use. Solid foods should be introduced gradually, no earlier than one day after the endoscopic examination.
Meals should be divided, in small portions of 5-6 meals per day. This will allow the intestines to easily adapt to normal loads.
Indications for the use of colonoscopy during sleep
Colonoscopy with sleep is used both at the request of the patient, who is not ready to endure possible pain, and for medical reasons:
- age from 5 years;
- the presence of adhesions in the intestines that occurred after surgery on the abdominal organs;
- low sensitivity threshold up to painful shock with loss of consciousness.
Colonoscopy with sedation involves the use of mild sedatives - the patient does not feel pain, but remains conscious and can follow the doctor’s instructions. The main advantage of this method is the easy recovery from a sedative state. The anesthesiologist stays with the patient throughout the procedure to avoid side effects and to maintain the desired degree of sedation.
Colonoscopy during sleep under anesthesia, when the patient is immersed in a medicated sleep, during which he does not feel or remember anything that happens.
There are a number of contraindications for this method:
- severe heart failure;
- neurological/psychiatric diseases in the acute stage;
- acute diseases of the bronchi and lungs;
Most often, specialists use gentle sedation, since it is quite sufficient for this procedure, while the patient is conscious and helps the study.
FGDS with anesthesia: which method is better
Gastroscopy is a non-invasive examination of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach and some parts of the intestines. The procedure is carried out using a special probe. This is an optical device with a camera. The image from it is transmitted to the display, which allows for timely detection of pathologies.
Given that the tube with the camera is inserted through the mouth, discomfort during the procedure is common. To eliminate discomfort, our clinic performs FGDS with anesthesia. This reduces the gag reflex, calming the patient.
There are 3 types of pain relief during gastroscopy:
- local - by irrigating the larynx with an anesthetic;
- light sedation – the patient falls into a shallow sleep and quickly wakes up after the session;
- general anesthesia - this method is not recommended for this procedure, since immersion in a deep narcotic sleep is fraught with complications.
Our clinic provides local anesthesia for FGDS. This is the safest method of eliminating unpleasant sensations. There are no side effects. The decrease in sensitivity of the larynx disappears a few minutes after completion of the diagnosis.
Light sedation is also possible. In this case, the patient is immersed in a state of superficial sleep by administering Midazolam, Propofol or similar drugs. But FGDS under anesthesia of this type is carried out if there are indications:
- a strong gag reflex that does not allow insertion of a probe;
- increased sensitivity of the larynx;
- panic fear of performing gastroscopy;
- the patient's wishes in the absence of contraindications.
To perform sedation, preliminary laboratory diagnostics and a detailed medical history will be required. This will eliminate contraindications, making the procedure safe.
Colonoscopy in the network of NEARMEDIC clinics
Colonoscopy during sleep in our clinics is carried out using modern digital video endoscopes using advanced techniques in accordance with European and Japanese standards. The team consists of an endoscopist, an anesthesiologist, and junior medical staff. An informative result is provided within 10-20 minutes after the procedure. Biopsy results are provided in 5-7 days.
For all questions and to sign up for the procedure, you can call +7 (495) 6 171 171 or fill out the feedback form on the website.
Drug sedation during endoscopy
The advantages of performing an endoscopic examination under medical sedation are obvious - the patient does not experience discomfort, pain, and behaves calmly. This allows the doctor to conduct a full examination, concentrate on conducting the study and not be distracted by persuasion and explaining to the patient how to behave correctly.
The principle of such research is simple. Before the procedure begins, the anesthesiologist administers a special sleeping pill intravenously to the patient, and the person falls asleep. Only after this the doctor begins the examination. At the same time, drug-induced sleep is deep, so a person does not experience any discomfort or unpleasant sensations. And when the effect of the drug wears off (usually it lasts no more than 30 minutes, this is enough to conduct an examination), the patient wakes up.
There is no discomfort at this stage either. Medication-induced sleep is not anesthesia, it is much easier to tolerate, after it there is no lethargy or lethargy, or problems with orientation.
In what cases is sedation acceptable?
The decision about whether gastroscopy can be done during medicinal sleep or not is made by the doctor. As a rule, an emergency procedure is not done with sedation, since there is no time to select and administer the drug. Also, the doctor does not have a diagnosis or additional examinations that are necessary to understand whether sedation is dangerous for the patient.
How to prepare
In order for the research to proceed quickly and be informative, it is necessary not to forget about the set of rules:
— If you are planning to carry out the endoscopic examination you need under conditions of drug sedation/sleep, then you need to first talk with an anesthesiologist.
— Undergo the necessary examination, which the doctor will indicate to you.
— Colonoscopy and/or gastroscopy with or without sedation is done only on an empty stomach. It is necessary that at least 7-10 hours pass between the last meal and the study.
— Thoroughly and completely prepare for the planned study.
— It must be said that tobacco smoke affects the reliability of the examination results, so suppress the desire to smoke 2-3 hours before the manipulation.
- Stop drinking alcoholic beverages for 2 days, and stop drinking coffee, energy drinks and other caffeine-containing liquids and products a day before.
— If you have catarrhal symptoms from the oro- and nasopharynx (cough, runny nose) or residual symptoms of acute respiratory infections, it is better to reschedule the study to another day (as soon as you have fully recovered).
— Provide adequate transport to send you home, where you should never be left alone. The absence of transport and a person looking after you at home for at least the coming night is a contraindication to conducting a study using anesthesia drugs (except local anesthetics) on an outpatient basis.
Rules for performing gastroscopy in a dream
There are a number of rules that will help to avoid complications after the procedure during medicated sleep.
— This type of endoscopic examination is carried out only in the presence of an anesthesiologist. His task is to select a suitable drug, introduce and remove the person from drug-induced sleep, and monitor you during the study.
— Before starting the examination, the patient needs to remove contact lenses, dentures, jewelry and glasses, unbutton or remove clothes that are restricting you - a tie, a bra, a belt on trousers.
- Be sure to warn your doctor about any chronic diseases you have and the medications you have been taking for the last few weeks; if you are allergic to something, be sure to tell them about it.
What you should not do after undergoing drug sedation/sleep
Drug sedation/sleep may affect your ability to react correctly and quickly to current events, which can lead to serious consequences, including: and legal nature. Therefore, within 24 hours after the study, you should not:
· drive a car or other vehicles
· make any important decisions or sign legal documents
· take alcohol or sleeping pills