Many women are interested in whether it is possible to conduct an ultrasound during menstruation. This question becomes relevant if, for example, an ultrasound examination is routinely prescribed by the attending physician. In such situations, you often have to wait a month, calculating the day of the examination in advance, which can be difficult, especially with an irregular cycle. So, can an ultrasound be performed during menstruation?
What is transvaginal ultrasound?
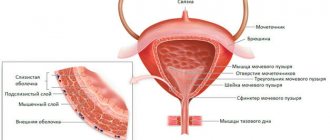
The main difference between intravaginal ultrasound and the transabdominal method is the insertion of an ultrasound probe into the vagina. At the same time, the principle of operation of the device remains unchanged. The device emits high-frequency ultrasonic waves, which are partially reflected from tissues and recorded by a transducer. Since the pelvic organs and the ultrasound sensor during vaginal ultrasound are separated only by a thin vaginal wall, the device collects more accurate information than during a transabdominal examination. The obtained data is displayed on the monitor in the form of a contrast image, which allows you to control the research process and monitor the condition and operation of the organ under study in real time.
Detailed, clear images are obtained due to different levels of absorption and reflection of ultrasound by different types of tissue. Numerous studies have proven the safety of ultrasonic waves for the body and make it possible to repeat the procedure without risk to health.
To conduct an intravaginal ultrasound, an oblong-shaped sensor is used, slightly larger than a tampon. Before inserting the device into the vagina, the sonologist puts a condom on it and lubricates it with a sterile gel, which ensures continuous transmission of the signal. To obtain a three-dimensional image of organs and accurate information about the structure of tissues in various areas, when conducting an intravaginal ultrasound examination, the doctor uses rotational movements, which may cause slight discomfort to the patient.
In gynecology, ultrasound is used to make a diagnosis, monitor pregnancy, and control treatment. Examination of internal organs through the abdominal wall is used more often. But the transabdominal method provides limited information about the pelvic organs, while intravaginal ultrasound gives a clear picture of the condition:
- Bladder;
- vagina;
- ovaries;
- uterus and its cervix;
- fallopian tubes
When is the best time to do a transvaginal ultrasound?
A transvaginal ultrasound may be prescribed by a doctor to clarify the diagnosis after a transabdominal examination. Intravaginal ultrasound is prescribed for:
- pain in the pelvic area;
- menstrual irregularities;
- pathological vaginal bleeding;
- the presence of signs of inflammatory pathologies of the pelvic organs (endometriosis, endometritis, etc.) or neoplasms in them (cysts, tumors, polyps);
- early pregnancy monitoring;
- suspicion of pathological processes in neighboring organs (soft tissues of the pelvis, lower parts of the digestive tract, bladder);
- suspected varicose veins of the small pelvis;
- menopause;
- delayed or impaired sexual development in girls;
- prescribing intrauterine, vaginal or oral contraceptives;
- study of anomalies of the anatomical structure of internal organs (duplication or absence of the uterus, vaginal atresia, etc.);
- infertility, to determine its cause.
Intravaginal ultrasound is most effective for monitoring pregnancy in the early stages, when the position of the uterus does not allow obtaining all the necessary data on the condition of the fetus and amniotic structures by examining them through the abdominal wall. Vaginal ultrasound during pregnancy is prescribed for:
- fetal heart rate checks;
- setting the exact date of pregnancy;
- diagnosing ectopic pregnancy and establishing the site of implantation of the embryo (on the ovary, in the fallopian tube or in the abdominal cavity);
- monitoring pregnancy with an increased risk of miscarriage;
- assessing the condition of the placenta.
What day after menstruation is best to do an ultrasound?
The doctor decides when it is best to do an ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries, based on the preliminary diagnosis. When conducting a preventive examination and for diagnosing most functional pathologies of the uterus and ovaries, an intravaginal ultrasound should be performed on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle, immediately after the end of menstruation.
If the doctor suspects endometriosis, an ultrasound examination is performed after ovulation, when the endometrium is thickest and foci of pathological changes are best visible. When undergoing folliculometry, the procedure is repeated several times during one menstrual cycle with an interval of 2-3 days. If there are urgent indications, abnormal bleeding during menstruation, or to monitor the progression of the disease over time, the patient may be prescribed a transvaginal ultrasound during menstruation.
Exceptions to the general canons
They do not always wait until days 5–10 of the cycle to conduct an ultrasound examination. Moreover, when treating a number of gynecological ailments, ultrasound data obtained on other days is necessary. The examination cannot be delayed either in extreme situations when a woman’s life is in danger.
Indications for ultrasound during bleeding:
- uterine hemorrhage or heavy discharge during menstruation - may indicate dangerous pathologies of the endometrium;
- risk of miscarriage;
- acute inflammatory processes of the reproductive organs;
- suspected tubal pregnancy;
- complication after abortion;
- suspicion of uterine fibroids or hyperplasia, polyps, cysts (up to 10 mm in size) - ultrasound is indicated on days 1 - 3 of the cycle;
- injuries, burns of the pelvic organs;
- intense pain of unknown origin.
If a woman is carrying a child, the appearance of bloody discharge may indicate a threat of miscarriage, and therefore an ultrasound in this situation is performed urgently. Echography provides a complete assessment of the condition of the fertilized egg and the reliability of its implantation into the mucous membrane of the inner wall of the uterus.
An ultrasound is performed during menstruation if folliculogenesis needs to be examined. The procedure helps to record and evaluate all stages of follicle maturation and its migration from the ovary. The study is prescribed on days 1–4 of the cycle and continued until the 15th day. This data is necessary for the diagnosis and treatment of female infertility and cycle disorders.
Preparing for a vaginal ultrasound
No special preparation is needed for a gynecological ultrasound. An intravaginal ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs lasts about half an hour. Depending on the reason for the examination, the doctor may recommend emptying the bladder or, conversely, filling it before the procedure by drinking about a liter of non-carbonated liquid an hour before the procedure (for bladder examination). When performing a transvaginal ultrasound during menstruation, it is necessary to remove the tampon while using it.
To undergo an ultrasound examination, the patient must undress from the waist down and lie on the couch with her knees bent. During the procedure, a woman may feel slight discomfort or pressure in the vagina. If painful sensations occur, you should inform your doctor.
What gynecologists advise
If you experience any unusual, uncomfortable or painful sensation in the pelvic area, you should consult a gynecologist so as not to trigger a painful condition or allow pathology to develop. During the consultation, the doctor will determine when it is right to do a pelvic ultrasound in this particular case - urgently or in accordance with the menstrual cycle.
At the same time, we must remember that timely prevention is the best way to combat diseases. And at least once a year, devote time to your health: undergo consultations with specialists, undergo general tests and perform simple and safe diagnostics, such as ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system.
Is it possible to eat before an ultrasound of the pelvic organs?
You may eat before undergoing a transvaginal ultrasound examination. But a few days before the procedure, you should avoid eating foods that contribute to increased gas formation:
- flour products;
- legumes;
- milk and fermented milk drinks;
- cabbage, radishes, turnips;
- grapes, apples, pears;
- carbonated drinks, etc.
The large amount of gases in the intestines makes it difficult to obtain an accurate image of the organs being examined. When experiencing flatulence, a woman needs to take a drug that normalizes gas formation processes.
Gynecological ultrasound: vaginal or transabdominal?
The main advantage of transvaginal ultrasound in gynecology is its high accuracy in displaying the structure of the tissues of the pelvic organs, giving the doctor the necessary information about their functional state. Intravaginal sonography allows you to obtain detailed data on the condition of the tissues of the cervix and body of the uterus, ovaries, and visualize both fallopian tubes, while transabdominal examination allows you to examine only the left one.
Unlike transabdominal ultrasound, vaginal ultrasound makes it possible to detect and study areas of altered endometrium, which in many cases makes it possible to recognize endometriosis without performing a diagnostic operation - laparoscopy.
Despite the high information content of vaginal ultrasound, its use is not always possible. Transvaginal ultrasound is not prescribed for virgins due to the likelihood of damage to the integrity of the hymen. Vaginal ultrasound examination also cannot be used:
- if the patient is allergic to latex;
- in the later stages of diagnosed cervical cancer (due to the risk of bleeding);
- in the acute phase of diseases accompanied by inflammation, tissue swelling and severe pain (the study should be postponed until recovery or alternative methods should be used);
- in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy (due to the risk of premature contractions).
If there are contraindications to vaginal ultrasound, the doctor may prescribe transabdominal sonography or other diagnostic methods. Also, both types of examinations can be prescribed simultaneously to obtain the maximum amount of data on the condition of the pelvic organs through examination in different planes.
The results obtained during the study are interpreted by a sonologist, after which he gives his opinion and refers to the appropriate doctor to prescribe the necessary treatment.
1
0
2
Article rating:
5 out of 5 based on 6 ratings
Author: Shulga Tatyana Alexandrovna
Ultrasound diagnostics (USD) doctor. First category. Work experience 27 years.
Decoding the results
After an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs, the woman is given a conclusion that describes the condition of the uterus, endometrium, left and right ovaries, cervix, fallopian tubes, retrouterine space and veins. If pathological changes are detected during the examination, the doctor must indicate their nature, location, nature of the structure and other features. He can also suggest the cause of such changes, but the final diagnosis is made only by the attending gynecologist. At the same time, he takes into account not only the results of ultrasound, but also the features of the clinical picture, as well as the results of other studies.
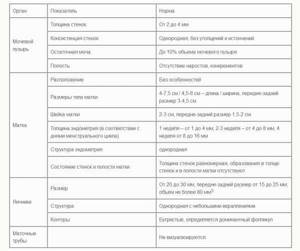
Normally, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs does not visualize the fallopian tubes, Douglas and retrouterine spaces. The uterus has a pear-shaped shape, a uniform structure and smooth, clear contours. The endometrium is visualized as a clear line with a homogeneous hyperechoic structure. The cervix normally has a homogeneous structure, has a length of 35-40 mm, and the diameter of the cervical canal does not exceed 3 mm. The condition of the ovaries depends on the phase of the cycle. In any case, normally they should have a uniform structure, clear, bumpy contours. Healthy pelvic veins are not dilated and do not show signs of tortuosity.
Thus, ultrasound of the pelvic organs is a very informative diagnostic procedure that allows one to detect almost any deviation from the norm in the condition of the female genital organs. And the simplicity of its implementation, accessibility and absolute safety make the method widely in demand.
0 0 votes
Article rating