Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone that begins to be secreted early in pregnancy. Based on its content in the body, it is determined whether conception has occurred, how gestation is developing, and whether everything is okay with the fetus. HCG levels are determined using at-home pharmacy tests or a laboratory blood test. Can human chorionic gonadotropin tests give erroneous results?
Diagnostic tests to determine hCG levels
There are 2 main diagnostic methods for determining the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin in the body - urine and blood tests. Laboratory diagnosis is considered a more reliable way to determine whether a woman is pregnant or not. In the first weeks of gestation, the content of hCG in the body is low, but using a venous blood test, its presence can be determined with an accuracy of 99% in the very first days after implantation of the blastocyst.
The sample is taken early after the pregnant woman is registered at the antenatal clinic. If the pregnancy is the result of IVF, then the analysis is scheduled on the 14th day after embryo transfer. It will show whether implantation has occurred.
Biomaterial is submitted for analysis on an empty stomach in the morning. A few days before visiting the laboratory, a woman should give up heavy, fatty foods, not drink alcohol, and reduce smoking. The emotional state should be calm, physical activity should be stopped for a while. Some medications affect hCG levels, so they should be temporarily discontinued under the supervision of a doctor.
HCG during pregnancy: normal
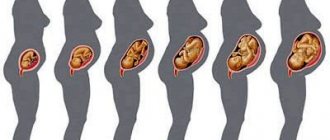
After fertilization has occurred, the outer membrane of the egg begins to produce human chorionic gonadotropin at a fairly rapid pace: in the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the hormone level doubles every two days; at 7-10 weeks of pregnancy, the concentration of gonadotropin reaches its maximum value. Next, the level of the hormone begins to progressively decrease, while no significant changes in its concentration are observed in the second half of pregnancy. That is why specialists can determine the normal course of pregnancy or identify existing pathologies in the fetus by the content of human chorionic gonadotropin in the mother’s body. The hormone level at 14-18 weeks of pregnancy may indicate existing abnormalities in the development of the fetus. In this case, the doctor prescribes a repeat test.
If we talk about the norm of hCG, it should be noted that in each laboratory its indicators differ. The concept of “norm” itself in this case is quite relative. The decisive conclusion on whether the test results comply with the norm is made only by a qualified specialist.
Can a blood test for hCG be wrong?
Although a blood test for human chorionic gonadotropin is considered one of the most reliable methods for diagnosing pregnancy, it can give false negative or false positive results.
A woman can be sure that she is not pregnant, and the test shows the presence of hCG, or vice versa. What affects the test results, and in what cases is it wrong?
Reasons for a false positive result
If the diagnosis showed the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin in the body of a non-pregnant woman, this indicates serious pathologies. Normally, the concentration of hCG should not exceed 5 mIU/ml, but if this indicator increases, but the patient is not carrying a child, she needs to undergo a thorough examination for the presence of diseases that have caused the growth of the hormone.

Reasons for false positive test results:
- Malignant tumors. Most often, human chorionic gonadotropin increases due to tumor formations of the gonads - the ovaries in women and the testes in men. A false positive result is also possible for malignant tumors of the lungs, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract.
- Bubble drift. This is a defective product of conception, in which the embryo does not develop, and the chorionic villi turn into fluid-filled blisters. A hydatidiform mole occurs when a sperm fertilizes an egg with missing chromosomes, or two male gametes penetrate into one egg. In both cases, the zygote is not viable. Women over 35 years of age are at risk.
- Chorionic carcinoma. Often, hydatidiform mole degenerates into a malignant formation - chorionic carcinoma. The tumor is formed from trophoblast, chorionic villi or germ cells of the gonads. It is usually localized in the body of the uterus, but can be located in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and metastasize to the lungs and brain.
Reasons for a false negative result
Reasons for a false negative result:
- Diagnosis made too early. Human chorionic gonadotropin reaches sufficient levels several days after blastocyst implantation. If you donate blood 2-3 days after sexual intercourse, when fertilization presumably occurred, the results will be negative, despite the fact that the woman is already pregnant.
- Risk of miscarriage. A sharp decrease in hCG in the early stages indicates that pregnancy is at risk. A miscarriage has already occurred or may occur, so the pregnant woman needs to urgently go to the hospital.
- Death of the fetus. If the test gives negative results in the middle of the term, then most likely intrauterine fetal death has occurred.
- Ectopic pregnancy. Normally, the blastocyst implants in the endometrium of the uterus. Due to a violation of the patency of the tubes, a fertilized egg can attach to the fallopian tube, or less often, go in the opposite direction and become embedded in the ovary or peritoneum. There are also cases where the embryo was attached to the cervix.
Low hCG
Low hCG is an indicator that is detected in various pathologies of pregnancy and the fetus. Although it is worth noting that false negative results obtained as a result of an incorrect gestational age or laboratory errors cannot be excluded.
Low hCG is due to the inferiority of the chorion, a decrease in its functionality, hormonal disorders of the mother and fetus, placental abruption, improper attachment of the embryo and other reasons.
Low hCG is detected in the following conditions:
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Frozen pregnancy;
- Intrauterine growth retardation;
- Risk of miscarriage;
- Fetal death;
- Chronic placental insufficiency;
- Post-term pregnancy;
- Problems of implantation after IVF (in vitro fertilization).
But human chorionic gonadotropin data cannot serve as a reason for making a disappointing diagnosis; if negative results are obtained, additional examination methods should be completed to clarify and identify the pathology.
Determination of hCG in urine, erroneous test results
Pharmacy rapid tests are the most accessible, fastest and cheapest way to diagnose pregnancy. When a woman notices a delay in her period, most often she does just such a test.
Strips, cassette tests, electronic devices, as well as blood tests, operate on the principle of detecting human chorionic gonadotropin in the body. A marker is applied to the sensitive tip of strips or electronic devices that reacts to the presence of the hormone. The hCG content in urine is slightly lower, so such diagnostic methods often give false results.
Reasons why rapid tests are wrong:
- Low test sensitivity. The presence of hCG in urine can be determined only after a delay. Different types of tests have different accuracy. Electronic devices have the greatest sensitivity; they respond to a concentration of 15 mIU/ml; they can be done on the very first day of the delay. The accuracy of strips is less; they respond to a hormone content of 20-25 mIU/ml.
- Overdue test. When purchasing a pharmaceutical device, you need to pay attention to the expiration date, which is usually 2-3 years, and storage conditions - the packaging must be intact.
- Incorrect use. Before diagnosing, you need to study the instructions. There are jet tests, the tip of which needs to be placed under a stream of urine, others need to be lowered for a few seconds into a container with collected biomaterial.

Low hCG, fetal growth restriction and placental insufficiency
Fetal growth retardation is a decrease in the weight and size of the child. Low hCG is a nonspecific marker of pathology, so other examination methods must be performed. But it is worth noting that this condition is preceded by placental insufficiency, which causes fetal hypoxia, impaired nutrition and blood supply, and other negative reactions.
Since placental insufficiency reduces all functions of the protective membrane, the synthesis of hCG also decreases. Therefore, based on the data obtained, this pathology can be suspected. Moreover, in its initial stages, a decrease in not only hCG, but also progesterone and prolactin is of diagnostic importance.
Low hCG during postterm pregnancy is also associated with placental insufficiency, since immediately before birth the functionality of the placenta begins to decrease, it ages, and therefore less hCG is produced.
What to do if the analysis result is erroneous?
If a laboratory or pharmacy test shows false results, there is no need to panic. An error can occur with any diagnostic method. The laboratory may also not follow the analysis technique, confuse the results, or enter incorrect data. Although this possibility is minimal, it cannot be excluded.
If you receive suspicious results, it is recommended to donate blood again in another laboratory or in several institutions. Only after this will doctors draw conclusions about the reasons for false-positive or false-negative diagnostic results.
Low hCG, threat of miscarriage and genetic abnormalities
The threat of miscarriage may be associated with placental insufficiency, unreliable implantation of the fertilized egg, detachment of the chorion, incorrect place of its attachment and other conditions. Most of them lead to a decrease in the functionality of the chorion and placenta, which ends in a decrease in the synthesis of hCG.
HCG can act as a marker of genetic abnormalities. Often such diseases cause a sharp increase in the level of hCG, but it can decrease, in particular with Edwards and Patau syndrome. In these cases, consultation with a geneticist is necessary.
First signs of pregnancy
The desire to carry and give birth is a dream for some, so they always try to look for signs of pregnancy in themselves. After the embryo is implanted in the uterus, the processes of its implantation and development begin there. In practice, the doctor can confirm or rule out pregnancy only 10 to 14 days from the date of replantation. But the first symptoms of pregnancy, as in women with natural pregnancy, appear no earlier than nine days later, because during this time the embryo implants into the wall of the uterus and begins to produce hCG, which causes all the subjective symptoms of pregnancy. HCG during IVF increases only during developing pregnancy up to a certain period.
The first symptoms of pregnancy, which may or may not appear, indicate its development. Such symptoms include nausea, vomiting, weakness, irritability, drowsiness, tenderness and swelling of the mammary glands, discomfort in the lower abdomen, frequent urination, changes in taste and smell.