Pelvic ultrasound is one of the types of ultrasound used for accurate and early diagnosis of diseases of the genitourinary system associated with impaired vascular activity.
This study is indispensable during pregnancy: it allows you to assess the state of blood flow in the placenta and listen to the baby’s heartbeat. In the diagnostic and treatment department you can undergo duplex and triplex scanning using modern equipment that meets international diagnostic standards. We have experienced doctors who will help identify even minor violations and give recommendations.
How the research is carried out
There are 3 ways to perform ultrasound examination:
- Abdominal. In this case, the sensor is placed on the surface of the abdomen. The method is suitable for women in late pregnancy, for girls who are not sexually active, and for men when examining the bladder.
- Transvaginally. Through the vagina in women. This method provides a more complete amount of information about the veins and arteries of a woman’s internal genital organs. It makes it possible to place the sensor as close as possible to the organ being studied.
- Transrectal. Through the rectum. The study is recommended to clarify the diagnosis after abdominal ultrasound in girls and when diagnosing prostate diseases in men. Diagnostics is performed with an ultra-thin sensor and therefore does not cause virtually any discomfort.
The method that will be the most appropriate and informative in each specific case will be determined by the medical doctor during the appointment. You will also be able to ask all your questions - our specialists will certainly tell you about all the intricacies of conducting the study.
| № | Name of service | price, rub. |
| 1 | Color duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities/upper extremities. | 2 100 |
| 2 | Color duplex scanning of the arteries of the lower extremities / upper extremities. | 2 100 |
| 3 | Ultrasound color duplex scanning of the vessels of the lower extremities (veins and arteries). (UZDG, UZDS, UZAS, DS of vessels...) | 3 200 |
| 4 | Triplex scanning of the vessels of the upper extremities (veins and arteries). | 3 200 |
| 5 | Duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic vessels of the neck for children over 1 year old and adults. (BCA of veins and arteries, USDG of extracranial, extracranial parts of the brain). | 2 100 |
| 6 | Transcranial color duplex scanning of brain vessels. TCD for children over 1 year old and adults. Intracranial examination of the vessels of the head. | 2 500 |
| 7 | Duplex scanning of the vessels of the brain and neck with functional tests for children from 1 year and adults. | 3 200 |
| 8 | Renal vessels and abdominal aorta (duplex scanning of veins and arteries). | 1 800 |
| 9 | Triplex scanning of the abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava | 1 500 |
| 10 | Ultrasound of the pelvic vessels (Doppler study of blood flow in the uterus and appendages). Transvaginally. | 1 700 |
| 11 | Neurosonography with Doppler analysis. NSG or ultrasound of the brain for infants. | 1 500 |
| 12 | Ultrasound video recording on DVD. | 500 |
| 13 | You can order duplex scanning of blood vessels and other studies at home, see the page “Ultrasound at home” |
How is Doppler sonography performed?
The study is no different in preparation from a regular ultrasound of the pelvic organs. If it is prescribed by a gynecologist, then an ultrasound scan can be performed twice - in the first and second half of the menstrual cycle. The most informative days are days 5-7 of the cycle and 5-7 days after ovulation. Your doctor will give you exact recommendations when prescribing an ultrasound scan.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs with Doppler ultrasound lasts about 20-40 minutes, depending on the method and area of examination. Diagnostics takes place:
- Transabdominal - through the anterior abdominal cavity.
- Transvaginally - through the vagina.
- Transrectally - through the rectum.
The received data is visualized on the monitor and recorded on the hard drive. Based on the final result, the ultrasound room doctor issues a conclusion, and the attending physician interprets them. In many cases, Doppler ultrasound is performed in conjunction with conventional ultrasound or duplex scanning to evaluate the vessels. If necessary, other diagnostic methods can be used to clarify the diagnosis: MRI, radiography.
You can get a consultation or make an appointment for an examination by calling the clinic administrator on duty by phone or leaving a request for a call at a convenient time.
When is it appointed?
Ultrasound and Dopplerography of the genitourinary system is performed for both women and men. For non-pregnant women, the indications for the procedure are:
- menstrual irregularities;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- inability to get pregnant within a year;
- repeated miscarriages;
- detection during examination and routine ultrasound of a neoplasm in the uterus or bladder, changes in the thickness of the walls of these organs;
- urinary disorders.
Pregnant women undergo duplex scanning:
- on routine ultrasound (such a study is recommended at 20-25 weeks and mandatory at 30-34 weeks);
- when the fetus lags behind in development or gains weight very quickly;
- in case of Rh conflict;
- in case of multiple pregnancy;
- if the fetus is in abnormal position on the eve of birth.
Ultrasound ultrasound during pregnancy is required in the presence of diseases that contribute to the development of pathology in the veins and arteries:
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension;
- renal failure;
- liver diseases.
For men, the study is prescribed for:
- infertility;
- erectile dysfunction;
- changes in the testicles (reduction, enlargement, appearance of compactions in them);
- prostate diseases.
Dopplerography of pelvic vessels
Ultrasound with Doppler - what is it? Why is Doppler sonography needed?
These questions are of interest to patients to whom the attending physician has prescribed this diagnostic method. The essence of the Doppler effect is that ultrasonic waves are reflected from moving objects with a changed frequency. This frequency shift is proportional to the speed of movement of the located structures - if the movement is directed towards the sensor, then the frequency increases, if away from the sensor, it decreases. An interesting fact: in nature, this effect is used by bats and dolphins to determine the speed of a moving object.
Dopplerography includes duplex scanning, which provides information about the size of arteries and veins, their capacity, and the direction of blood flow; color or triplex scanning, which allows, thanks to the color image on the monitor, to study the speed of blood flow in the vessels. Recently, ultrasound examination with contrast agents has also been used.
The method is safe and painless for humans, can be performed in almost any condition of a person, children, pregnant women, has virtually no contraindications, and multiple studies over time are possible.
In recent years, a lot of attention among obstetricians-gynecologists and urologists has been paid to the so-called chronic pelvic pain syndrome, and here it is necessary to study the blood flow in the pelvic organs.
It should be recalled that the small pelvis is anatomically a cavity limited in front by the pubic fusion, behind by the sacrum, and on the sides by the pelvic bones.
Ultrasound and Dopplerography of the pelvic organs is performed for both women and men.
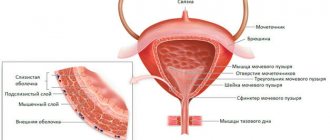
The pelvic organs include:
- Bladder with ureters
- Rectum
- In men - the prostate gland, spermatic cords and seminal vesicles
- In women - the uterus, ovaries, vagina.
Many pathological changes in these organs are accompanied by impaired blood flow through the arteries that supply blood to these organs, or the veins that take venous blood from them. These vessels include: in women - the uterine and ovarian arteries, through which blood flows to the uterus and its appendages. In men - the inferior vesical artery (supplies the prostate), venous plexuses of the prostate, veins of the spermatic cord, arteries and veins of the penis. Dopplerography of these vessels makes it possible to clarify the degree of vascular disorders in the following diseases:
- Congenital anatomical anomalies of the uterus and appendages
- Pipe welds
- Uterine fibroids
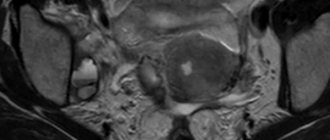
- Tumors of the body of the uterus and ovaries - by the speed of blood flow one can judge the benignity or malignancy of the neoplasm;
- Female and male infertility;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the uterus and endometrium;
- menstrual irregularities;
- adenoma and malignant tumors of the prostate gland;
- inflammatory processes in the prostate - acute and chronic prostatitis, prostate abscess, vesiculitis;
- varicocele - (varicose veins of the spermatic cord);
- impotence associated with vascular pathology.
The most important area of application of ultrasound is the examination of pregnant women. During pregnancy, duplex scanning is performed:
- on routine ultrasound (such a study is recommended at 20-25 weeks and mandatory at 30-34 weeks);
- With fetal hypo- or hypertrophy (when the fetus lags behind in development or gains weight very quickly);
- in case of Rh conflict;
- in case of multiple pregnancy;
- if the fetus is in abnormal position on the eve of birth.
Timely and high-quality ultrasound examination with Dopplerography is an important element (and sometimes the only method of safe non-invasive diagnosis) for various pathological conditions, dynamic monitoring of the condition of the mother and fetus at all stages of pregnancy, differential diagnosis of gynecological and andrological diseases, male and female infertility, erectile dysfunction in men.
In our clinic, ultrasound examinations with Dopplerography are carried out by experienced specialists with many years of experience, using the latest expert-class equipment.
Preparation
- Routine Doppler ultrasound of the pelvic organs is done on the 7th day from the start of menstruation in women. Men can take it whenever they want.
- If an abdominal ultrasound examination is planned, it is necessary for 3 days before it to adhere to a diet that reduces gas formation (refuse fruits, vegetables, milk and carbonated drinks).
- Transrectal and transvaginal examinations do not require any preparation.
To undergo a pelvic ultrasound scan at a medical clinic, make an appointment by phone or online. You can also order a study at home - just call!
Description
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs makes it possible to detect diseases of the genitourinary system in women and men. The method of performing a pelvic ultrasound is selected depending on the organ or group of organs that should be given special attention. The most informative and least comfortable types of pelvic ultrasound from the point of view of patients are transrectal (through the rectum) ultrasound in men and transvaginal (through the vagina) in women. This is due to the fact that the closer the sensor is located to the organ being examined, the less interference occurs and the less dispersion of ultrasound occurs. In some cases, a transabdominal ultrasound (through the abdomen) is sufficient. Color Doppler mapping is part of the ultrasound procedure that significantly increases the diagnostic value. With its help, the doctor diagnoses abnormalities in the condition of the vessels of the pelvic organs. During pregnancy, it is carried out to study the arterial and venous blood flow of the placenta, umbilical cord and fetus. Dopplerography evaluates the direction of blood flow, the throughput of blood vessels, and can detect atherosclerosis, stenosis (narrowing) of the arteries, and deep vein thrombosis. During transabdominal ultrasound, the patient is in a lying position - the procedure takes approximately 15-20 minutes. During a transvaginal pelvic ultrasound, a probe is inserted into the vagina - the procedure takes approximately 5-10 minutes. During transrectal ultrasound, the patient is in the lateral decubitus position with the knees drawn up to the chest; The sensor is inserted into the rectum, and the procedure lasts about 20-25 minutes.
What does the study show?
A special feature of duplex scanning is its extensive diagnostic capabilities. Doppler provides real-time functional information about the ability of a vascular segment to conduct blood and the linear velocity of venous blood flow. Whereas ultrasound scanning provides additional information about anatomical details due to differences in acoustic impedance. Sonography identifies:
- structure of the venous basin of the small pelvis;
- communication of vessels with each other, the degree of their tortuosity and expansion;
- the presence of calcifications, the size of sclerotic plaques and blood clots in the gonadal and uterine veins.
Thus, during the ultrasound examination, the most informative picture is obtained about the size of the lumen of the pelvic veins, the presence of pathological reflux and other vascular pathologies.
Indications for use
Transvaginal pelvic ultrasound is prescribed in the following cases: • detection of cysts and other neoplasms of the pelvic organs (including malignant); • assessment of reproductive function, determination of the causes of infertility; • determining the cause of abnormal vaginal bleeding or menstrual irregularities; • diagnosis of unexplained pelvic pain; • diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. Ultrasound is a valuable basic method for diagnosing adenomyosis, uterine fibroids, an important additional method for diagnosing hyperplastic processes of the endometrium, the development of adhesive disease, etc. Men undergo transrectal ultrasound of the pelvis in the following cases: • detailed examination of the prostate gland if deviations from the norm are detected during its transabdominal examination ( even if only an increase in prostate size is detected); only with the transrectal method of examination is it possible to exclude early signs of a prostate tumor; • age over 45 years, even in the absence of changes in transabdominal ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
What will an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the pelvic organs show?
During duplex/triplex scanning of the vessels of the pelvic organs in men, the doctor examines the vessels of the prostate and prostatic plexus, in women - the uterine, ovarian, spiral arteries, and endometrial vessels of the uterus. In addition, the iliac and arcuate veins and arteries are examined in all patients.
The examination allows you to study the structure of blood vessels, their patency, the condition of the vascular wall, as well as various indicators of blood flow.
Using duplex/triplex scanning, you can identify atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels, blood clots, compression of blood vessels, and also diagnose:
- ovarian cysts and tumors,
- uterine fibroids,
- volumetric formations in the wall and cavity of the uterus,
- some inflammatory diseases of the uterus and ovaries,
- varicose veins of the pelvis,
- varicocele,
- prostatitis,
- prostate abscess,
- prostate adenoma,
- prostate cancer,
- congenital anomalies.
In our ultrasound center you can urgently perform an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the pelvic organs.
Indications for ultrasound examination of pelvic organs vessels
The pelvic organs in women include the bladder, uterus, its appendages, cervix, ovaries; in men - bladder, prostate gland, spermatic cords, seminal vesicles. The normal functioning of these organs largely depends on their high-quality blood supply, and any changes in blood circulation are usually associated with pathological complications.
Indications for duplex/triplex scanning of the vessels of the pelvic organs are:
- infertility in men and women,
- miscarriage,
- suspicion of the presence of tumor formations,
- urinary disorders,
- erectile dysfunction in men.
Indications for ultrasound examination
Ultrasound is prescribed in the presence of symptoms of diseases of internal organs and tissues. Widely used to identify benign and malignant tumors, as well as to detect metastasis of cancer cells. Ultrasound is used for preoperative examination and postoperative monitoring.
Angiology and karyology
Doppler ultrasound measures the direction and speed of blood movement and determines blood pressure. Diagnoses various heart conditions, including heart valve problems and congestive heart failure, and assesses damage after a heart attack. Cardiac ultrasound provides images of the cardiovascular system and helps measure the movement of heart tissue.
Ultrasound diagnostics allows:
- examine the walls of blood vessels;
- determine deep vein thrombosis;
- accumulations of plaques and clots;
- control tumors and congenital vascular injuries.
Sonography is used to monitor decreased, absent, or increased blood flow in various organs. Information obtained from a Doppler ultrasound image can determine whether a patient is a suitable candidate for a procedure such as angioplasty (widening of the arteries).
Emergency conditions
Used to evaluate traumatic wounds, fluid accumulation around the heart, internal bleeding, etc. Gastroenterologists use ultrasound to obtain images of the spleen, kidneys, bile ducts, gallbladder, liver, aorta, inferior vena cava, pancreas and other abdominal organs.
Sonography detects swelling or infection in the appendix area.
Pediatrics and pregnancy
Ultrasound in newborns is performed in the soft spot on the skull (fontanelle) to monitor for brain damage or abnormalities, genetic disorders, cerebrovascular disease, bleeding, hydrocephalus. Sonography is also used to examine the baby's hip and spine.
Ultrasound during pregnancy is a standard component of prenatal follow-up care. Obstetric ultrasound helps monitor the health of the child and mother.
Urology and gynecology
In urology, ultrasound helps examine the amount of urine remaining in the bladder after urination and the health of organs in the pelvic area, including the uterus and testicles. A urological ultrasound is performed to examine the kidneys or bladder for stones.
Orthopedics
Diagnoses problems with soft tissues, muscles, blood vessels, tendons and joints. Muscular skeletal sonography can be used to study connective tissue, bony surfaces, soft tissue masses, nerves, muscles and tendons.