- home
- Functional diagnostics
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound examination, echography) – scanning the human body to obtain images of internal structures and organs. High frequency sound waves penetrate tissue. Their reflected echoes come back, being converted into images on the computer monitor. Later you can get a video or photo of the area being examined. Abdominal ultrasound is a non-invasive method used in the diagnosis of a wide range of diseases and conditions.
Types of research
Classic ultrasound of the abdomen gives a detailed idea of the size, structure of parenchymal and hollow organs. An ultrasound is performed:
- Liver;
- Pancreas;
- Spleen;
- Ultrasound of the bladder;
- Gallbladder with definition of functions;
- Small intestine;
- Large intestine;
- Gallbladder;
- Abdominal aorta;
- Intestines;
- Stomach.
The method is completely safe and does not cause discomfort or pain. You can undergo an ultrasound as prescribed by a doctor or at your own request if there are disturbing symptoms. Compared to other diagnostic procedures such as CT and MRI, ultrasound diagnostics are cheaper, faster, simpler and do not use ionizing radiation.
Ultrasound of the liver
The doctor prescribes a liver examination if there are certain symptoms that may indicate that the patient is not well. Among them is discomfort in the right hypochondrium, which manifests itself more strongly after drinking alcohol, fatty foods, smoked and fried foods.
A signal to perform an ultrasound of the liver may be a lump detected during palpation - this may be a tumor, the exact location of which and its inherent signs will be identified by the doctor using ultrasound. It is important to undergo an examination after a course of therapy if hepatitis and other diseases are detected.
Ultrasound of the pancreas
Sonography makes it possible to identify the size of an organ, its inherent shape, and the presence of changes in structure and structure. Attention is paid to the location of the pancreas relative to other structures and vascular formations. If pathological changes are identified, the study expands the boundaries, and the question arises of using additional diagnostic methods.
Inflammation of the pancreas can manifest itself in reduced size of the organ if it becomes chronic. This may also be indicated by excessive tissue scarring and calcifications. Cysts formed in the structure of the organ are reflected during examination as compacted areas with clearly defined boundaries.
Ultrasound of the spleen
Prescribed when liver pathologies are detected. And also if there is a suspicion of injuries resulting from falls, mechanical shocks and bruises. Indications for the procedure include leukemia, the formation of compactions and tumors, diseases of an infectious nature (syphilis, tuberculosis, sepsis).
For the examination, the patient is placed on his back. A special gel is applied to his stomach, on which the ultrasonic signal transducer glides more easily. The session takes 15 minutes, and the results are immediately available. For better visualization, the doctor may ask the patient to turn on their side or assume another position that makes it easier to view.
Ultrasound of the bladder
The reason for performing an ultrasound of the bladder may be a long-term change in the color of urine, which is not associated with eating foods and medications that can affect its tone. The doctor should be alerted to the patient's complaints about pain and discomfort when urinating, the release of a small amount of fluid with frequent urge to go to the toilet.
It is recommended to undergo an examination if pain appears in the suprapubic region, bloody discharge in the urine and flakes visible from the side in the liquid. As a result of viewing the internal structures, stones, foreign bodies in the organ, neoplasms and other anomalies may be detected.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of functions
The procedure is preceded by a trial choleretic breakfast, with the help of which it is easier for the doctor to examine the organ. The study is carried out in several stages, when after 10-15 minutes a specialist examines the organ with ultrasound at rest and after exercise. The patient is asked to lie on his back, and when necessary, move to his side, on all fours, or stand up straight.
Ultrasound of the bile duct shows whether cholecystitis or cholelithiasis exists, and reveals biliary dyskinesia. A quick and painless examination reveals five degrees of abnormality. Such accuracy allows you to subsequently draw up a competent therapeutic protocol and achieve good results in the treatment of the disease.
What is the time frame for the research?
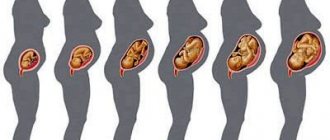
According to the plan, fetometry is prescribed to pregnant women three times in each trimester (12th, 22nd, 32nd weeks).
Unscheduled examinations are prescribed by the doctor if indicated. The first fetometry checks the expected due date, the presence of chromosomal abnormalities, and developmental defects.
Second, possible intrauterine development disorders are identified. If the position of the fetus is successful, the doctor can determine the sex of the unborn child.
Third, the baby’s health is checked, height and body weight are determined. These indicators are necessary to choose the method of birth (natural or cesarean section).
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs for children (child)
Parents are concerned about the question of whether it is possible to perform an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity on a child, and whether the procedure will cause harm. The answer is obvious - it is possible, and if necessary, with repeated monitoring. Due to the simplicity and safety of the examination, the test is prescribed for a child under 1 year of age in order to:
- Conduct an inspection of internal structures;
- Identify deviations if they exist and take measures to eliminate anomalies.
Thanks to the scan, the size of the abdominal organs, tissue composition, and structure density become visible.
First ultrasound: at 10-14 weeks (planned, screening)
Typically, 1 scheduled examination is scheduled for the 12th week of pregnancy. Already at this stage, the woman’s condition and how the pregnancy is progressing in general are easily assessed. Moreover, ultrasound reveals pathological changes in the fetus. This is important because if abnormalities are detected, termination of pregnancy may be necessary, and in the first trimester the doctor will prescribe a medical abortion, which is not dangerous to the woman’s health.
The main tasks of the first planned ultrasound:
- Determination of a special parameter - the thickness of the collar zone (the area between the soft tissues covering the spine and the inner surface of the skin, filled with fluid). Measuring this indicator allows us to identify the development of chromosomal pathologies - Down syndrome, etc.;
- Measuring the coccygeal-parietal size. The indicator determines the size of the fetus and the exact gestational age;
- Diagnosis of fetal cardiac activity is the main indicator of viability;
- Detection of multiple births;
- Assessment of the presence and development of the child’s organs;
- Determining the expected date of birth;
- Establishing the correspondence of fetal size to gestational age.
Also, the first examination allows you to assess the location of the placenta and determine the condition and tone of the uterus. Often, the first scheduled ultrasound is a significant event for a couple, since they can see their unborn child for the first time.
Indications for the study
Immediate ultrasound is required for abdominal pain, prolonged nausea, vomiting, bloating, unexplained weight loss, injury, fever of unknown origin. Ultrasound diagnostics is prescribed as part of a set of measures when identifying a tumor to clarify its nature.
Ultrasound is an imaging method. It is often resorted to when a biopsy is necessary, but the organ is located deep. In this case, it is necessary to view the structures of the abdomen and the needle placed in it, aimed at taking biological material, which is later sent for histological and cytological analysis.
Second ultrasound during pregnancy and its interpretation
The second mandatory screening for timely registration is carried out at 20–24 weeks.
This is the time when the fetus can already be examined in more detail, the features of its development are visualized more accurately, but until the 22nd week it is still possible to decide on the management of pregnancy in different directions, including abortion in case of multiple malformations, especially those incompatible with long life.
Therefore, it is better to undergo the second mandatory ultrasound in the early weeks of this period.
The second examination reveals numerous indicators of fetal development, for example, the weight and size of the child, the condition of the skeletal system, the anatomy of internal organs, and also allows us to identify possible entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord
To decipher an ultrasound, the following indicators are needed: Fetometry indicators:
- Week 20: interparietal distance: 43–53 mm, frontoccipital distance: 56–68 mm, head circumference: 154–186 mm, chest circumference 47–49 mm, abdominal circumference 124–164 mm, thigh length 29–37 mm, length tibia 26–34 mm, humerus length 26–34 mm, ulna: 28 mm, radius length 25 mm.
- Week 21: MTR 46–56, FOR 60–72, OG 166–200 mm, WC 137–177, DB 32–40, DG 29–37, DP 29–37, forearm 24–32.
- Week 22: MTR 48–60, FOR 64–76, OG 178–212, WC 148–190, DB 35–43, DH 31–39, DP 31–39, forearm 26–34.
- Week 23: MTR 52–64, FOR 67–81, OG 190–224, WC 160–202, DB 37–45, DG 34–42, DP 34–42, forearm 29–37.
- Week 24: MTR 55–67, FOR 71–85, OG 201–237, OB 172–224, DB 40–48, DH 36–44, DP 36–44, forearm 31–39.
| a week | Height, cm | Weight, gr. |
| 20 | 24,1 | 345 |
| 21 | 25,9 | 416 |
| 22 | 27,8 | 506 |
| 23 | 29,7 | 607 |
| 24 | 31,2 | 733 |
Nasal bone: 20–21 weeks 5.7–8.3 mm, 22–23 weeks 6.0–9.2, 24 weeks 6.9–10.1. The fetal heart rate at this time corresponds to the interval from 140 to 160 beats per minute.
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Ideally, an ultrasound examination when scanning the hollow organs of the digestive system is carried out after special preparation for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, when gas-forming products are excluded from the diet for three days. Otherwise, the air interferes with obtaining a detailed image of the structures.
What foods are prohibited to eat before the study?
Prohibited foods include cabbage, apples, milk, and other fruits and vegetables containing cellulose. Legumes and grains should also be avoided. The day before the study, experts indicate low-fat soup, cottage cheese, and yogurt among what you can eat. For 8-12 hours it is necessary to exclude food altogether.
Is it possible to drink water before the test?
To view the bladder and prostate in men, you need to fill your bladder (drink about 3-5 cups of liquid 1.5 hours before the exam and do not urinate). It is strictly forbidden to drink soda, energy drinks, or coffee.
For women, when asked whether they can drink water before an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, the answer is similar. It is possible and necessary, but only if the water is simple, not saturated with sugar and gases. If a transvaginal ultrasound is performed, it is not necessary to drink water.
It is important that the patient cooperates with the doctor during the examination and assumes the required position or holds his breath when asked to do so. In the event of an emergency, an abdominal ultrasound is performed without special preparation in emergency mode.
Third planned ultrasound: at 32-34 weeks
An ultrasound in the third trimester is also extremely important, as the doctor determines how the delivery will proceed. In addition, it pursues the following goals:
- determination of the position and presentation of the fetus. The position in which the baby will be will not change until birth. The method of delivery will depend on it and on the presentation. So, with a longitudinal position and a normal cephalic presentation, this is a natural birth; with a transverse or oblique position and a pelvic presentation, this is a cesarean section;
- assessment of the size and weight of the fetus;
- assessment of the size, maturity and location of the placenta;
- assessment of the quantity and quality of amniotic fluid.
How is it done and what does an abdominal ultrasound show?
An abdominal ultrasound is performed with the patient lying on his back while the doctor passes a transducer across his skin in the area of the organs being examined. To facilitate the sliding of the transducer over the body, a water-based profile gel is used, which can be easily removed with a damp cloth after the session.
In order to get a more complete picture of some organs, the doctor himself tells the patient how they do it and what an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity shows - the patient may be asked to turn over on the couch to the right or left side. The test lasts about 15 minutes. During the examination, the patient does not feel any pain. During ultrasound, the size of the organ, its structure, clarity of boundaries, and the presence of changes in tissues are visualized.
Standards for organs
- Normally, the right lobe of the liver does not exceed 125 mm, the left 70 mm. The portal vein is up to 14 mm, the thickness of the left lobe is 50-60 mm, the right one is 120-125 mm.
- The width of the gallbladder is 30-50 mm, length 60-100 mm, volume from 30 to 70 cubic meters. cm.
- Includes an interpretation of the ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, the length of the spleen, which normally does not exceed 110 mm, a thickness of 50 mm, and an index of up to 20 square meters. cm.
- The head of the pancreas is 32 mm, the body is 21 mm, and the tail is 35 mm.
- The dimensions of the urinary tract are wall thickness no more than 2 mm, the urine norm for men is 350-750 ml, for women 250-550 mm.
Main indicators of ultrasound during pregnancy
To assess the course of pregnancy, the following signs are significant:
A separate point is the measurement of the size of the nasal bone and the width of the collar zone as a risk factor for the development of chromosomal diseases (a decrease in these indicators or hypoplasia, or reduced echogenicity of the nasal bone specifically relative to indicators for a given period of pregnancy).
Among other things, the condition of the female genital organs – the uterus and its appendages – is noted. In this case, their diseases can be identified.
For the first ultrasound, they also note:
Regarding Doppler ultrasound, the following indicators are assessed:
- blood flow speed in vessels
- resistance index (RI) - the ratio between the difference in blood flow velocity in systole and diastole and systolic velocity in the vessel
- pulse index (PI) - the ratio between the difference in blood flow velocity in a vessel in systole and diastole to the average value of blood flow velocity in a given vessel
- systole-diastolic ratio (SDR) is the ratio of blood flow velocity in a given vessel during systole and diastole.
CTG indicators that are determined during the examination (carried out in the third trimester during the third planned ultrasound):
- basal heart rate (arithmetic average over 10 minutes of examination)
- oscillations (deviations from the basal rhythm)
- acceleration (increasing heart rate by 15 beats in 15 seconds)
- deceleration (decrease in heart rate by 30 beats in 15 seconds).
Prices for ultrasound of the abdominal organs
We offer attractive prices for abdominal ultrasound in Khabarovsk, and we carry out diagnostics using the latest equipment - Sonoscape s35 and LOGIQ-C5 scanners. Highly qualified doctors, mid-level staff attentive to the needs of patients, no queues and professional assistance in identifying and treating diseases - we offer all this to medical patients. The cost of our services is affordable and affordable:
| Code | Name of procedure | price |
| 7.01 | Comprehensive ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) | 1500 |
| 7.02 | Ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder | 800 |
| 7.03 | Ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder with Dopplerography of blood vessels | 1000 |
| 7.04 | Ultrasound of the pancreas | 500 |
| 7.05 | Ultrasound of the gallbladder | 500 |
| 7.06 | Ultrasound of the gallbladder with functional tests | 900 |
| 7.07 | Ultrasound of the spleen | 500 |
| 7.08 | Ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands | 850 |
| 7.09 | Kidney ultrasound | 600 |
| 7.09.1 | Ultrasound of the adrenal glands | 400 |
| 7.10 | Ultrasound of the bladder (examination with transvaginal/transrectal and abdominal sensors) | 1000 |
| 7.11 | Ultrasound of the bladder with determination of residual urine (abdominal sensor) | 600 |
| 7.12 | Ultrasound of the uterus, appendages (examination with transvaginal and abdominal sensors) | 1200 |
| 7.13 | Ultrasound of the uterus, appendages (examination with a transvaginal sensor) | 1200 |
| 7.14 | Ultrasound of the uterus, appendages (examination with an abdominal sensor) | 800 |
| 7.15 | Folliculometry (primary) | 1000 |
| 7.15* | Folliculometry (repeated) | 700 |
| 7.16 | Ultrasound of the scrotum | 600 |
| 7.17 | Ultrasound of the prostate gland (examination with an abdominal probe) | 800 |
| 7.18 | Ultrasound of the prostate gland (examination with a transrectal probe) | 800 |
| 7.19 | Ultrasound of the prostate gland (examination with transrectal and abdominal sensors) | 1200 |
| 7.22 | Doppler ultrasound of vessels of various locations (fetus; scrotum; kidneys; abdominal aorta and its branches, etc.) | 2000 |
| 7.39 | Ultrasound examination of the hip joints (children up to one year old) | 700 |
| 7.40 | Screening “Children under one year old” - neurosonography, examination of the thymus, heart, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, hip joints | 4300 |
| 7.41 | Ultrasound of the bladder | 500 |
| 7.43 | Control of the uterine cavity after m/a | 500 |
Check out the prices by studying the price list for our services. In addition to functional diagnostic services, we offer to attend an appointment with specialized specialists, whose work schedule is also presented on our website.
Second planned ultrasound: at 20-24 weeks
Examination in the second trimester is an extremely important event. By the 22nd week of pregnancy, all the internal systems and organs of the child are practically formed and active motor activity is observed, so you can assess the child’s condition and examine it in detail from all sides. In addition, this is when future parents can find out the sex of the child.
The main objectives of the second study:
- carrying out fetometry - determination of biometric indicators (length of tubular bones, circumference of the head, abdomen, biparietal and fronto-occipital size). Based on the data obtained, the child’s weight is calculated;
- identification of possible pathologies of fetal development;
- assessment of the size, maturity, structure and location of the placenta;
- conducting Doppler measurements - studies of uteroplacental circulation and blood flow in the aorta and middle cerebral artery of the fetus;
- assessment of the umbilical cord - it is possible to detect entanglement around the fetal neck, but at this stage it is not dangerous, since the child is actively moving and the situation can resolve itself;
- cervical assessment. The normal size is at least 3 cm. As labor approaches, it shortens and smoothes out. The internal opening must be completely closed. Violation of these parameters indicates isthmic-cervical insufficiency, requiring suturing of the cervix or insertion of an obstetric pessary.
Where can I get a paid ultrasound of organs?
If you are interested in where you can get a paid ultrasound of your organs, pay attention to the medical one. We work every day without lunch breaks. You can always see on the map how to find us, as well as check our opening hours, on our website.
If it’s difficult to make a decision, read the reviews of our patients, who speak about the quality of services better than any advertising. Come visit us and see for yourself. We will be glad to see you at the address on the street. Panfilovtsev, 38.
Is appendicitis visible?

Before the widespread introduction of computed tomography, ultrasound was the only way to show the inflamed appendage of the cecum. Carrying out an ultrasound allows you to find the location of the appendix already in the emergency department (in approximately 35% of cases it is not in a typical place), as well as detect symptoms of the pathological process:
- wall thickening;
- an increase in the process in transverse dimensions;
- accumulation of fluid around the appendage;
- the formation of one or more abscesses;
- violation of the integrity of the process wall;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity.
What is GBS ultrasound?
GBS (hepatobiliary system) is a complex process that performs the digestive function in the body and removes metabolic products. Changes in this system affect metabolic processes in the body, and the protective reaction to viruses and infections weakens. The GBS includes the liver, bile ducts and bladder.
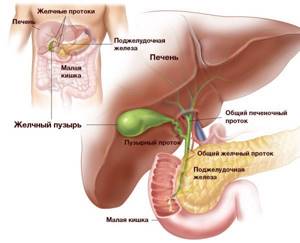
Hepatobiliary system
An ultrasound examination of the GBS is performed to assess the size and structural parameters of organs, their location and functioning. It is also possible to observe the main vessels of the liver, changes in the structure of the gallbladder and ducts.