There is a strong opinion that ultrasound during pregnancy is harmful. Even the most obedient expectant mothers are very worried about the need to do frequent checks, believing that this could harm the baby. It is believed that if the expectant mother is frequently examined, this will inevitably affect the development of the child, making him predisposed almost to cancer, genetically inferior and lagging behind in physical and mental development.
First, let's figure out what ultrasound is?
This is a sound so high that it is beyond human perception. These are ordinary sound waves, like conversation or music, for example, but the frequency of vibration of these waves is higher than the human ear can hear. Like any sound, it penetrates obstacles, partly being reflected from them (shout in the mountains, they will return an echo to you, the same thing happens with ultrasound). An ultrasound machine emits a signal, and it is reflected (echoes) from different tissues with different strengths; it is this echo that is recorded, turning into a picture. The effect on the fetus is due to these sound waves. It is unlikely that the embryo can hear them; he is a future person, and his hearing will be human, unable to hear such high-pitched sounds. It must be said that until 16-17 weeks the hearing organ is not at all developed enough to hear at least some sounds. Often during the examination you can see how the baby turns away from the sensor, but this is more likely due to its pressure on the anterior abdominal wall than the influence of the ultrasound itself on the fetus.
Physics of Ultrasound
To begin with, I propose to talk about what kind of beast “Ultrasound” is and how it differs from other sounds.
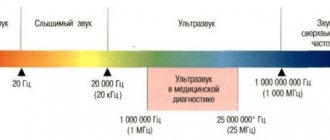
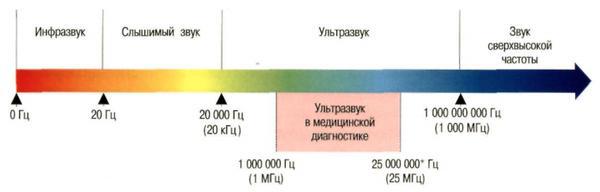
Ultrasound is vibrations from 20 kHz to 1000 MHz, inaudible to the human ear. Ultrasound diagnostics uses a narrower frequency range: from 1 to 25 MHz. Audible spectrum from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. If ultrasound were audible, it would sound 1000 times higher and thinner than the squeakiest mosquito.
The power of modern diagnostic ultrasound is from 15 to 730 mW/cm2. In obstetric studies, an average power of 180 mW/cm2 is used. For example, modern smartphones have a limited radiation power of 200 mW, Wi-Fi points of 100 mW, while the process of exchanging information between devices (maintaining communication) occurs on average 1000 times per second. At the same time, in an ultrasound diagnostic system, the sensor emits an average of 20 times per second, i.e. 80 percent of the time it is in receiver mode, emitting nothing.
Thus, irradiation of the measuring point with ultrasound power of 200 mW/cm2 is 50 times lower than 200 mW of a cell phone.
The average duration of an ultrasound examination is 20-30 minutes.
From the point of view of physics and biophysics, ultrasound has a number of mechanisms of action on body tissues.
Thermal mechanisms. Heating of tissues in the area of ultrasound exposure due to molecular relaxation, internal friction and relative movement of medium particles is negligible to cause a significant increase in tissue temperature.
If in the average output power mode the ultrasound device emits 250 mW/cm2, converting all the energy into heat, heating the fetal tissue, and there is no leakage of this heat, then in 300 seconds of radiation (and approximately the same amount of energy the sensor emits in 30 minutes of research) to heat the fetus and the uterus will be used (250 mW * 300 sec) 75 Joules, or 17.93 calories. This is enough to heat 17.92 ml of water by 1 degree. For example, let’s imagine a uterus with a fetus at 20 weeks as 3 liters of water. In this case, the radiation energy of the ultrasound device is enough to heat the uterus and fetus by less than 0.006 degrees. And this is under IDEAL conditions of an IDEAL model.
Cavitation (mechanical manifestation), which refers to the process of growth and oscillation of gas bubbles in the field of an acoustic wave, usually occurs in cases where high-power ultrasound is used in continuous radiation mode. Theoretically, cavitation can also occur when using diagnostic ultrasound. But only theoretically.
In modern medicine, the effects of cavitation are used in minimally invasive surgery. In this case, it is high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), which uses much more powerful ultrasonic waves. Using HIFU, the following types of surgical treatment are performed:
- removal of uterine fibroids while preserving the uterine body;
- removal of a prostate tumor;
- treatment of heart diseases (atrial fibrillation);
- destruction of kidney and gallstones (shock wave lithotripsy);
- simulation of regenerative processes in nerve fibers;
- surgery for pathologies of the pelvic and abdominal organs.
The thin beam of ultrasound waves used in HIFU has much greater power than the waves used in ultrasound. But even with the use of such power, in order to bring intracellular structures to a boil (this is how the destructive effect on tumors is achieved), long-term continuous exposure to more than 20,000 W/cm2 (100,000 times stronger than diagnostic ultrasound) is required. For example, surgery to remove uterine fibroids lasts more than 3 hours.
The effect of ultrasound on pregnancy
The effect on the fetus is associated with the mechanical effect of ultrasound. Indeed, it is used in the treatment of various diseases during physical therapy and even for cleaning teeth. Moreover, it is used by the military, for example, on submarines. Knowing this, you can’t help but think: is it worth the risk? But by analogy with ordinary sound, imagine your sensations at a disco, or next to a plane taking off, where the decibels are off the charts, or in a quiet room where a loved one whispers affectionate words in your ear... About the same difference between the ultrasound that is used in the above situations and what the device emits. Thus, the harm of this device is greatly exaggerated by people who do not understand the very essence of the study.
Ultrasound is harmful because...
Most often they try to compare ultrasound with radio waves or electromagnetic radiation. This is similar to comparing red to square. The nature of these wave oscillations is fundamentally different, the effects are different, so comparisons of this kind are incorrect.
“The safety of ultrasound has not yet been proven, so it is better to avoid it.”
If the experience of using it for more than 50 years, the presence of not only children, but also grandchildren of those who were examined by ultrasound, the absence of any reliable evidence of the harm of diagnostic ultrasound on humans does not convince you, you should probably refuse ultrasound. According to WHO (“Safety of ultrasonography in pregnancy: WHO systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis.”), the only difference in children who received a dose of diagnostic ultrasound in utero was a slightly higher number of left-handed boys. That's all! It is also worth considering the presence of radiation from cell phones, radio stations, television antennas, GPS and Glonass satellites, all electrical appliances, main electrical wires, as well as the Earth’s magnetic field. I also advise you to pay attention to experiments conducted to study the influence of magnetic fields on the development of embryos. There it was shown that frogs and rats placed in a Faraday cage, excluding any electromagnetic influences, developed with pronounced malformations and mutations.
“Ultrasound doesn’t give a guarantee, what’s the point of doing it?”
Nothing in medicine is 100%. When determining the sex of the baby both at 11-12 weeks and at 30 weeks, I never give a guarantee. My favorite phrase “I won’t give 100% even after giving birth” is already known by a good half of Moscow.
However, if we do not consider casuistic cases and variants of clinical cretinism, the average “accuracy” of ultrasound examination is 85-90%.
K. Nicolaides indicates that when examining the size of the cervical fold in a study for Down syndrome, the sensitivity is 33.5% and the specificity is 99.4%. The likelihood ratio is 55.8%, which is not high, but when combined with other signs and symptoms, it is a very accurate result. For some this is too little. For others, it's better than complete ignorance. The final decision rests with the pregnant woman, no doubt.
“Although it is stated that a person does not perceive high-frequency sounds, the violent reaction of the fetus to ultrasound remains unexplained (it is not observed in all women, by the way). When the sensor moves across the mother’s belly, some babies begin to move intensely.”
Firstly, it is worth mentioning that there is no objective evidence that during an ultrasound the child moves more actively than at any other time in life. Agree, everything here is quite subjective: some mothers’ babies violently kick their father’s hand, others calm down when their father’s hand touches their stomach; Some people are sleeping during CTG, others are going on a rampage. It's the same with ultrasound. Only during the ultrasound does the woman also lie on her back and focus on the baby’s behavior, which in itself is important.
What processes affect a woman undergoing an ultrasound? The ultrasound itself, the force of pressure on the stomach, everything? No, there is also emotional pressure on the pregnant woman, which is accompanied by the release of a corresponding portion of hormones. Most likely, the baby reacts to them.
My patients know how important emotional support is. I try to have a positive attitude towards my patients, reassure them and destroy established harmful misconceptions. You can read their reviews, there are many of them on the Internet. If the mother is calm, then the child will be calm.
When the baby turns away and covers his face, this is not his attempt to hide from the ultrasound, but reflexive movements during periods of wakefulness. The child is in a relaxed state in the aquatic environment. Flexor muscles are stronger than extensors, so the natural position is one in which the arms are bent at the elbows and pressed either to the chest or to the face.
“Ultrasound, which was considered harmless, can damage the genetic apparatus. Moscow researchers came to this disappointing conclusion under the leadership of Petr Petrovich Garyaev, a senior researcher at the Department of Theoretical Problems of the Russian Academy of Sciences.”
This opinion is based on the work of P.P. Garyaev’s “Wave Genome”, in which the author claims that the frequency of ultrasonic vibrations causes delayed genetic deviations, in other words, mutations. But due to the complete lack of evidence, the scientific community did not accept Garyaev’s work. Later, the presence of scientific degrees in P.P. Garyaev, was also declared invalid.
I can even admit that there is a bit of common sense in the theory expressed, but the author himself has discredited himself so much with lies that it makes no sense to analyze his theory.
“It’s better not to do an ultrasound, they will definitely find something there. The less you know the better you sleep."
Every person has the right to receive information and to refuse it. If a person refuses the opportunity to find out in advance about possible problems with the child’s health (developmental defects that require correction immediately after birth), to see the shortening of the cervix and save the pregnancy, this is his right.
“Okay, ultrasound is harmless, but Doppler is definitely harmful to your health.”
There are no fundamental differences in the effect on tissue. Yes, during Doppler examination, ultrasound beams are focused at one point. However, even with this, the tissue exposure remains much less than the minimum fixed dose.
Ultrasound during pregnancy, yes or no?
It is worth remembering that this is a fairly young research method, and we do not know the long-term consequences of exactly how ultrasound can affect pregnant women and future generations. Perhaps these fears are unfounded, but you should not insist on conducting 3D and 4D ultrasounds, in which the ultrasound power is greater, just to see your baby - a routine examination is enough. On the other hand, it was ultrasound that became the research method that revealed the unborn child to prying eyes, and made it possible to timely notice serious deviations in the development of the fetus and take measures to prevent complications of both pregnancy itself and childbirth. You can refuse an ultrasound scan during pregnancy; there is no law that would force a person to do this or that examination. But on the other hand, perhaps this very ability can save you and your child from serious complications, because how else can you suspect, for example, abnormal fetal positions, congenital malformations in the fetus, placenta previa and other problems that can lead to real disasters...?
The material was prepared by ultrasound doctor E.V. Tishkovskaya
Ultrasound during pregnancy.
Ultrasound examination is the reflection of ultrasonic waves from organs with different intensities. As a result of high-frequency mechanical vibration, a characteristic black and white picture appears on the monitor screen, which shows the fetus in motion and allows you to capture the image for measurements.
The main purpose of ultrasound during pregnancy is to determine the condition of the fetus and woman, diagnose signs of pathological changes and analyze possible hereditary congenital pathologies of the fetus.
Depending on the stage of pregnancy, during an ultrasound, indicators of the condition of the fetus are determined. Diagnostics can be planned or unscheduled.
Scheduled ultrasounds.
A routine ultrasound is performed in every trimester of pregnancy.
In the first trimester the following is determined:
- gestational age;
- fetal size;
- determining the risk of developing Down syndrome;
- condition of the uterus and appendages with the presence of pathologies.
- fetal size and development;
- Heart rate;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
- degree of maturity of the placenta and its localization;
- gender of the child.
- fetal size and development;
- growth rate;
- position and presentation of the fetus;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
- developmental defects;
- blood flow in the uterus and umbilical cord using Doppler.
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding from the genital tract;
- discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the expected duration of pregnancy;
- determination of the condition of the cervix;
- determination of fetal position;
- changing the activity of fetal movements to exclude hypoxia;
- monitoring the condition of the fetus after therapy;
- placenta previa.
- cell division processes;
- chromosome divergence;
- organ laying;
- brain development.
- effective;
- safe;
- inexpensive;
- allowing you to visualize the fetus and judge its condition.
During the study in the second trimester, the following is determined:
- fetal size and development;
- Heart rate;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
- degree of maturity of the placenta and its localization;
- gender of the child.
During the third trimester of pregnancy determines:
- fetal size and development;
- growth rate;
- position and presentation of the fetus;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
- developmental defects;
- blood flow in the uterus and umbilical cord using Doppler.
Unscheduled ultrasounds.
Unscheduled ultrasounds can be performed at any stage of pregnancy. Possible indications for additional research include:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding from the genital tract;
- discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the expected duration of pregnancy;
- determination of the condition of the cervix;
- determination of fetal position;
- changing the activity of fetal movements to exclude hypoxia;
- monitoring the condition of the fetus after therapy;
- placenta previa.
Indications may expand depending on the individual characteristics of the woman and child.
What information does ultrasound provide in early pregnancy?
- The very fact of pregnancy - with the help of ultrasound it is possible to see the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity on the screen. The procedure can be carried out 3-5 days after the expected conception, by which time the egg reaches a size of about 2-3 mm.
- The exact time of conception - the specialist is also able to determine the size of the fetus, sometimes there is an error of 1-2 weeks.
- The location of the embryo egg - it is very important to make sure that the pregnancy began correctly, intrauterine, and not vice versa (this can be seen 7-10 days after the delay appears).
- Number of fertilized eggs - you can see the number of embryos already at 3-4 weeks of pregnancy. Around this time, the mother can hear the first heartbeat of her child or children.
- The viability of the embryo , and specifically the work of its heart and the appearance of other organ rudiments.
- The sex of the child - such data cannot be obtained at the first ultrasound, but by 12-13 weeks the ultrasound already makes it possible to see the development of the child’s genital organs.
cost of services
Ultrasound
| ULTRASOUND EXAMINATION GYNECOLOGICAL | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (abdominal) | 1400 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (transvaginal + abdominal) | 2500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (transvaginal) | 1400 rub. |
| Ultrasound to determine pregnancy (up to 12 weeks) | 1600 rub. |
| Ultrasound pregnancy 1st trimester | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound pregnancy 2.3 trimester | 2000 rub. |
| Doppler ultrasound | 800 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands (days 5-7 of the cycle) | 1200 rub. |
| Folliculometry | 900 rub. |
| Cervicometry | 1100 rub. |
| CTG (cardiotocography) | 1500 rub. |
How do you prepare for the first ultrasound during pregnancy?
The answer to the question “how to prepare a pregnant woman for the first ultrasound” depends on the research methodology. If we are talking about an intravaginal ultrasound, you should also take a condom with you in addition to a diaper. The procedure is performed on a full bladder, for which a few hours before the examination, you need to drink two glasses of non-carbonated liquid. Such measures are necessary to ensure that the uterus is more clearly visualized on the monitor. The entire examination takes about 10-15 minutes and does not cause the slightest discomfort. It is worth remembering that the information about the fetus obtained at the first ultrasound is quite relative, since the size of the fetus is still very small.
A convenient way to view the capabilities of city clinics
When making a step-by-step selection of a medical center that is convenient for subsequent visits to the necessary specialists, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of various medical institutions in Moscow, which can be done by visiting our Help Desk for private clinics “Your Doctor”.
By determining the complexity of the provision of services, the site allows you to identify the most appropriate option for a visit, clarifying the criteria for the competence of personnel, technical equipment and laboratory capabilities, and also provides data on the description of the diagnostic and therapeutic procedures performed.
Useful information on the topic of gynecologist:
- How to get tested for gynecological diseases?
- What diseases does a gynecologist treat?
- What tests can be done by a gynecologist?
- How to prepare for an appointment with a gynecologist?
- Where to go with a gynecological problem?
- What symptoms should you consult a gynecologist for?
- How does an appointment with a gynecologist go?
- Female doctor
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections in women
- Diagnosis of gynecological diseases
- Treatment of female diseases
- Pediatric gynecologist
- How is a gynecologist examined?
- Paid gynecologist
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Author:
Kasabov Alexander Vladimirovich Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Ultrasound Doctor
Back to section
When does an ultrasound show pregnancy?
At a gestation period of more than 3 weeks, an ultrasound scan can already show pregnancy. At such early stages of fetal development, the transvaginal method of examination is usually chosen as it can give more accurate results. When using the transabdominal method of examination, an accurate result can be obtained only at the 4-5th week of gestation. At the same time, such early diagnosis of pregnancy should be carried out in a complex: in addition to ultrasound, it is necessary to conduct a blood test to detect the level of hCG (a hormone secreted by the placenta when pregnancy occurs).