What it is?
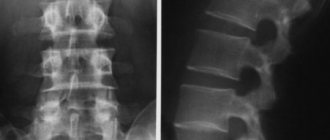
X-ray of the stomach is an instrumental technique for examining the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, which may be accompanied by the introduction of a contrast agent. A double contrast study can also be used, when additional air injection is performed. The substance that acts as a contrast is barium sulfate.
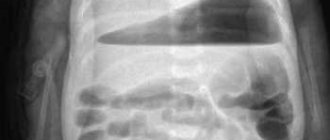
FGDS is a method of examining the gastrointestinal tract using a special device - a gastroscope. A gastroscope is a special device with a lighting device at the end. Modern devices have a camera that transmits the image to a computer screen.
How is it carried out?
Fluoroscopy begins with the use of a contrast agent. Next, a vertical study , which allows one to evaluate the passage of barium suspension through the stomach and its distribution in the folds. After this, the patient is asked to take a horizontal position in order to study the pneumorelief and the duodenal bulb. To study the stomach under conditions of complete filling, the doctor asks you to drink barium sulfate in one gulp.
When performing an FGDS, the patient swallows a special flexible endoscope and lies on his left side. With the help of swallowing movements, the probe is advanced to the stomach, after which air is pumped to straighten the walls of the stomach. After removing excess mucus, an examination of the entire mucous membrane of the walls, as well as the duodenum, begins.
Important Lidocaine is used to reduce the gag reflex and reduce sensitivity. This is the only drug that can cause allergies.
Can MRI replace EGD of the stomach?
The patient should not independently prescribe MRI of the stomach instead of FGDS. The methods are not interchangeable.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is recognized as the “gold standard” for diagnosing gastrointestinal pathologies. During the study, the condition of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum is studied in detail.
FDGS procedure
An endoscope is a flexible device placed inside hollow organs. The device transmits an image and allows for some manipulations. The endoscope forces air into the cavity, straightening the folded walls of the stomach. The doctor sees initially hidden areas. By assessing the walls of the organ, the diagnostician identifies signs of pathology development.
Using special attachments, biomaterial is obtained from the gastrointestinal tract for analysis (gastric and duodenal contents, scraping, biopsy). During the therapeutic FGDS, surgical manipulations are performed.
MRI involves layer-by-layer imaging of the area under study. The scanning technology requires complete immobility of the patient, on which the quality of the photo depends.
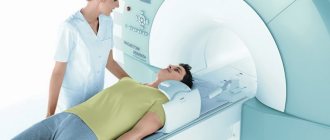
It is quite difficult to obtain an accurate image of hollow organs subject to peristalsis. Magnetic resonance imaging clearly visualizes parenchymal structures. The photographs show pathologically altered tissues. Using the method, abnormalities in the development of organs, structural disorders, and space-occupying formations (benign and malignant) are identified. Based on the scan results, the location, size of tumors, and the degree of involvement of neighboring areas are determined. The procedure is used for staging oncological processes. MRI is suitable for detecting metastases in the abdominal cavity.
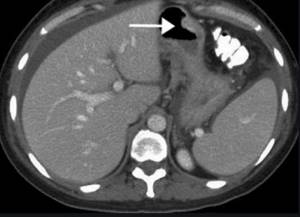
MRI of the abdominal cavity (stomach indicated by arrow)
What is the difference?

Their main similarity is that X-rays of the stomach and FGDS help the doctor assess the general condition of the organ. FGDS has one big advantage - the ability to perform a biopsy. In addition, the doctor can install a clip or administer the necessary medication. It is not possible to carry out these manipulations when performing x-rays.
The next difference is the quality of the information received. Even the most modern X-ray machine is inferior to FGDS . The fact is that the image transmitted by a gastroscope is color and has very good quality, which increases the chance of seeing various damage to the stomach that an x-ray will not show. And the last disadvantage of x-rays is the radiation that the patient receives.
But radiography also has its advantages, namely the absence of damage that may occur during FGDS and complications after the procedure.
X-rays are not accompanied by unpleasant sensations and during this procedure no allergic reaction to an anesthetic develops, because it is not used. But an allergy may occur to the contrast agent.
Medical Internet conferences
Comparative information content of gastric fluoroscopy and gastroscopy
with hiatal hernia
Scientific supervisor: candidate of medical sciences, associate professor Ilyasova E.B.
Comparative information content of gastric fluoroscopy and gastroscopy
with hiatal hernia
Scientific supervisor: candidate of medical sciences, associate professor Ilyasova E.B.
GBOU VPO Saratov State Medical University named after. IN AND. Razumovsky Ministry of Health of Russia
Department of Radiation Diagnostics and Radiation Therapy named after. NOT. Stern
Relevance. Hiatal hernia (HH) occurs in 30% of gastrointestinal diseases in middle-aged and elderly people. To diagnose hiatal hernia, many clinicians consider the use of gastroscopy sufficient and exclude fluoroscopy of the stomach from the examination plan.
The purpose of the study is to comparatively assess the information content of gastric fluoroscopy (RG) and fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) in the diagnosis of hiatal hernia.
Material and methods. The study material included 22 patients, aged from 38 to 65 years, with suspected hiatal hernia, who were treated at the Clinical Hospital named after. S.R. Peacemakers SSMU. All patients underwent: RSJ using a device with digital technology DH-90 (Apelem, France), FGDS, survey fluoroscopy (ORS) of the abdominal and thoracic cavities.
Results. In 3 (13.5%) patients with ORS of the chest and abdominal cavities, a ring-shaped shadow with thin walls and a horizontal fluid level was detected in the posterior mediastinum; a gas bubble of the stomach was visualized under the diaphragm. This shadow with RSG in a vertical position turned out to be fixed by the hiatal hernia. In the remaining 19 patients (86%), partial displacement of the stomach was determined only in the Trandelenburg position - sliding hiatal hernia. In 15 (68%) cases, gastric prolapse was noted, measuring 2x3 cm, in 4 cases - 3x4 cm, in 2 cases - 4x5 cm, in 1 case - 5x6 cm. In all 22 cases, gastroesophageal reflux (GEFR) was noted ) and signs of esophagitis, of which erosion was suspected in 4 cases. During FGDS, signs of esophagitis and hiatal hernia were detected in all cases, GEFR – in 19 patients (86%) .
The size of the prolapsed area of the stomach and its mobility were not determined. Erosive esophagitis was detected in 9 (40%) patients. In 2 patients (9%) it was possible to identify Saint's triad and Castaing syndrome (partly with the help of RSG)
Conclusions: When diagnosing a hiatal hernia, the use of FGDS or ORS of the thoracic and abdominal cavities is not enough. The advantage of RSG is that it is more accurate than with FGDS in identifying the hiatal hernia, determining its fixation, establishing the volume of the prolapsed stomach and the presence of GEFR. FGDS clarifies the presence of esophagitis and reveals erosions in the esophagus. Consequently, RS of the stomach and FGDS cannot replace each other, but should be used in combination in all cases of suspected hiatal hernia.
Advantages and disadvantages
| X-ray | FGDS | ||
| Advantages | Flaws | Advantages | Flaws |
| High level of information content (approximately 80% of gastrointestinal pathologies are diagnosed during the examination). | Possible allergic reaction to the contrast agent. | Modern equipment allows you to accurately examine the complete condition of the stomach. | Discomfort and pain during the procedure. |
| Complete painlessness | Frequent procedures increase the risk of developing cancer. | Possibility of diagnosing small erosions or polyps. | Possibility of developing a strong gag reflex. |
| Short examination period. | Not performed during pregnancy. | Ability to diagnose internal bleeding. | An allergic reaction to a pain reliever. |
| Availability. It is carried out in every clinic. | You may experience nausea and bloating after the procedure. | Carrying out a biopsy. | Risk of damage to mucous membranes. |
| Not complicated stages of preparation for the procedure. | There is a possibility of constipation due to excess amount of barium. | Entering necessary medications. | |
The doctor warns the patient in advance about all the advantages and disadvantages, which allows him to choose the most suitable procedure.
X-ray of the stomach with barium
Duration of the study
: 15 minutes.
Preparing for the study
: There is
Contraindications
: There is
Preparation of the conclusion
: 30-60 min.
Restrictions
: There is
What is a barium x-ray?
X-ray with barium sulfate is aimed at studying the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. The contrast agent makes it easier to examine the internal organs, their relief, contours, shape, and size.
The essence of the method
Hollow organs are difficult to fully visualize, so a barium mixture is injected before scanning. It colors tissues that are shaded in X-ray images. Thus, the examination picture clearly examines the walls of the large intestine, parts of the small intestine, stomach, and esophagus, and foci of pathologies are identified.
Indications
The doctor issues a referral for diagnostics for the following complaints:
- Abdominal pain.
- Unstable bowel function.
- Changes in the color and structure of stool.
- Blood in the stool.
- A sharp decrease in body weight.
- Intestinal gases.
Preparation
If barium sulfate is planned to be administered before an x-ray, the patient should prepare for the procedure in advance:
- Follow the diet for 2-3 days. You need to stop taking flour, dairy, spicy, smoked foods, legumes, black bread, and carbonated drinks. Food should be easily digestible.
- Cleanse your intestines with laxatives the day before. The dosage and number of doses is calculated according to the instructions in accordance with the weight. With proper cleansing, an enema is not necessary.
Barium X-rays are performed on an empty stomach in the morning, so you should not eat breakfast before the scan. You should leave your jewelry at home and wear loose-fitting clothes without metal inserts.
How is barium x-ray performed?
First, the doctor injects a contrast agent. Typically 400-600 ml of barium sulfate solution is given in liquid form. The patient drinks it and waits 10-15 minutes. Next, the subject takes the desired position, scanning begins, which lasts 50-60 minutes. During this time, the patient lies motionless, and the device takes from 6 to 10 pictures to assess the state of the gastrointestinal tract in dynamics. If necessary, the doctor asks you to turn over. Barium is eliminated from the body within 24 hours. To speed things up, it is recommended to drink more still water.
Where to get a barium x-ray
In the Health Clinic, located in the very center of the capital, examinations are carried out using modern, high-precision expert-class equipment. Qualified doctors with extensive experience will carefully examine the internal organs and describe the condition of the stomach.
results
Within an hour, a Health Clinic specialist interprets the images and then hands them over to the patient. The attending physician, based on the results of the examination, establishes or denies diseases such as stomach ulcers, tumors of various etiologies, protrusion of the gastric walls, intestinal obstruction, hernias, dyskinesia, etc.
Book an x-ray with barium
To sign up for diagnostics, choose any method:
- Call the clinic phone number +7 (495) 628-22-05,
- Request a call back
- Write or call via online chat, in the right corner of the page,
- Make an appointment immediately using the convenient form on the website:
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
Contraindications
You need to choose a different diagnostic method if there are the following restrictions on barium x-rays:
- Pregnancy.
- Barium intolerance.
- Bleeding in the intestines.
Price
It has become possible to get an X-ray with barium cheaply in Moscow at the Health Clinic.
Low prices, constant promotions and quality services attract visitors to our medical center. Patients of the Diagnostic Center are provided with free parking. Reservation of a place for a car is made no later than an hour before arrival at the clinic. Call
Consultation can be obtained by phone: +7
Price for stomach x-ray with barium
| Name of service | Price in rubles |
| Fluoroscopy and radiography of the esophagus with contrast | 5750 |
| Fluoroscopy and radiography of the stomach and duodenum with contrast | 5750 |
| X-ray examination of the small intestine with the introduction of a contrast agent - barium suspension passage | 6875 |
| Survey urography | 2700 |
If you do not find a service in the price list, please call us and we will provide you with the necessary information.
Indications and contraindications
Like any examination, X-rays of the stomach and FGDS have a number of indications for their implementation.
First, let’s look at the diseases for which an X-ray of the stomach is prescribed:
. An X-ray will help not only determine the location of the ulcer, but will also show its size, even in the absence of a clinical picture. On an x-ray, the ulcer looks like a kind of niche - an extra shadow. Scar formations may also be diagnosed.
Ulcer- Tumor . To diagnose cancer, examinations look for impaired gastric filling with barium, the presence of atypical relief, and the presence of an aperistaltic region (the area where motor activity is impaired).
- Gastritis . In the chronic form of gastritis, X-rays reveal enlarged gastric fields, which become more than 3-5 mm. The folds of the mucous membrane expand, causing the so-called jagged effect to appear in the image. The large amount of mucus that forms with this disease can make it difficult to fill all the folds with a contrast agent.
- Enteritis and colitis. These diseases are accompanied by impaired motor function of the stomach, which leads to faster or slower passage of barium.
- Pathologies of stomach development. The following anomalies can be diagnosed: double stomach, narrowing of sections, pyloric stenosis, large size of folds, presence of diverticula, thoracic stomach.
- Diverticula. On x-ray they look like abnormal protrusions that have the shape of a bag.
Please note: X-rays of the stomach are prescribed to monitor the condition of the esophagus and stomach if surgical treatment has been performed.
Suspicion of the presence of foreign objects is another indication for this type of examination. Among the symptoms that appear in the patient, indications for prescribing an x-ray include:
- pain during swallowing;
- localized pain in the epigastric region;
- burning sensation during swallowing;
- severe belching;
- pain in the navel area;
- malfunction of the digestive system;
- frequent attacks of nausea.
If we talk about contraindications for fluoroscopy, we can highlight the following points:
- pregnancy period . This type of examination is especially dangerous in the first trimester of gestation, when the fetus is just forming. Even small amounts of radiation can adversely affect development;
- serious condition;
- long-term internal bleeding;
- allergic reaction to contrast agent;
- allergic reaction to iodine.
If we talk about FGDS, the list of pathologies for which this type of examination is effective is as follows:
- Esophagitis . During the examination, red mucous membrane is diagnosed. In some cases, it is possible to detect the reflux of stomach contents.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Diverticula are protruding walls.
- Ulcer.
- Tumors.
Thanks to modern equipment, the doctor is able to fully examine the condition of the organ in real time, paying attention to various anomalies, which allows him to make the most accurate diagnosis.
This type of examination may be prescribed to a patient who complains of the following symptoms:
- acute and sharp pain attacks in the epigastric region that occur after eating;
- violation of the swallowing process;
- frequent heartburn;
- belching;
- vomiting with frequent repetition;
- regular bloating;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- sudden weight loss in a short period of time.
Emergency indications for FGDS are:
- Presence of gastric bleeding.
- Foreign bodies.
- Complications from ulcers or other diseases that require surgery.
If we talk about contraindications, we can distinguish absolute and relative. The absolute ones include:
- severe curvature of the spinal column;
- stroke;
- acute heart attack;
- mediastinal diseases;
- blood clotting disorder;
- enlarged thyroid gland;
- esophageal stenosis;
- asthma during exacerbation.
Relative contraindications include:
- the presence of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity, pharynx;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes;
- angina pectoris;
- mental illness.
In case of relative contraindications, FGDS is prescribed only with the permission of the doctor, as well as after the factor has been eliminated.
How to prepare?
The doctor must provide a complete list of preparatory measures before the procedures. The main points are as follows:

- It is not recommended to eat 8-10 hours before the procedure ; if there are serious digestive problems, then the last meal should be at least 12 hours before;
- Before any of these procedures smoking is prohibited , as this can cause inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- The best option would be to follow a diet that will help assess the real functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. This is especially important when performing gastroscopy.
You can learn more about preparing for an x-ray of the stomach in this article.
Alternative research methods
In addition to fibrogastroscopy and x-rays of the stomach, there are other methods that allow you to assess the condition and functioning of the organ:
- electrogastroenterography is a method that allows you to assess the motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract;
- computed tomography (CT);
- MRI;
- capsule endoscopy;
- transnasal gastroscopy;
- ultrasonography.

- study of gastric juice;
- blood test;
- urine test;
- stool examinations.
Based on the overall picture, the doctor diagnoses the disease and selects the optimal treatment option.
How does gastroscopy differ from an x-ray of the stomach?
Gastroscopy (esophagoduodenoscopy) is a type of endoscopic examination that involves examining the inner wall of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum using an instrument inserted through the mouth.
According to the order of the Ministry of Health, during gastroscopic procedures and identification of altered areas of the mucous membrane, it is necessary to take tissue sections for biopsy (histological examination). It allows you to detect cancerous degeneration of the epithelium in the early stages.
FGDS is always performed before an x-ray to avoid perforation of the organ wall, through which barium can penetrate into the abdominal cavity and cause peritonitis.
The technique is safe in terms of radiation exposure, but causes discomfort due to the need to insert a probe. Some patients are given an antiemetic drug (for example, cerucal) before the procedure to prevent vomiting and nausea.
Why is gastroscopy performed:
- X-ray examination of the internal state of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum;
- determination of wall defects;
- taking material for biopsy;
- suspicion of duodenitis, esophagitis and gastritis.
Gastroscopy is performed for additional examination of the gastrointestinal tract in case of neuroses and allergic conditions.