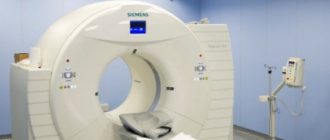
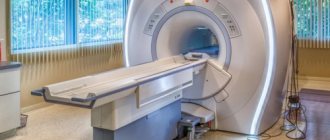
Magnetic resonance imaging is a diagnostic method based on obtaining layer-by-layer “slices” of the area under study. This technique allows you to visualize different organs and parts of the body with high quality. MRI is based on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance. If we describe the principle of operation in simple words, we can say that an MRI machine is a large magnet that affects the entire human body, as a result of which the response of atomic nuclei, namely the nuclei of hydrogen atoms, changes. These changes are recorded by the device and converted into image format by special algorithms. Simply put, the method is based on the level of “saturation” of various tissues and organs with hydrogen.
- Safety
- What does an MRI show?
- Indications and contraindications
- Preparation and execution
How is an MRI examination performed?
To conduct the study, the patient is placed in a lighted and ventilated magnet tunnel 1.6 meters long and 60 cm in diameter.
Throughout the scan, the examiner remains in the next room, able to observe and communicate with the patient via voice communication. The patient should try to lie still. Sometimes the operator asks you to hold your breath for a few seconds to take a picture - this way the image quality is as high as possible. Do not plan any urgent matters after the study. The study can take from 10 minutes to 1 hour depending on the volume and complexity of the study. If necessary, you are given the opportunity to have a person close to you with you throughout the duration of the study.
According to indications, we use special contrast agents (omniscan). The need to use contrast agents is determined by the doctor and is paid additionally.
In what cases is MRI performed?
Scanning is used in all areas of medicine. MRI is done for:
- making a primary diagnosis;
- comprehensive examination of the body;
- surgical planning;
- monitoring the condition of a patient undergoing treatment.
The optimal diagnostic method is chosen by the doctor. MRI is often done in cases of suspected tumor. The study shows a detailed picture of the area of interest, where it is possible to examine the slightest changes. The images allow us to make an assumption about the nature of the neoplasm: dangerous tumors are characterized by blurred boundaries and growth into surrounding tissues, benign pathologies are clearly differentiated from neighboring structures and have a capsule. The final diagnosis is made based on the results of a biopsy.
Signs of a malignant tumor on an MRI of the brain
In some cases, contrast enhancement is used - the injection of a special drug into a vein to improve visualization. From the blood vessels, the drug spreads into the intercellular space and selectively (depending on the type and phase of the pathological process) accumulates in the altered tissues.
MRI with contrast allows you to:
- perform differential diagnosis of diseases;
- determine the boundaries of tumor spread;
- clarify the number, size and location of metastases;
- plan treatment (including stereotactic radiosurgery, etc.);
- assess recurrence or continued growth of the tumor after surgery or radiation;
- get a complete picture of the condition of the arteries and veins (in most cases, MRI of the vessels of internal organs can be performed without contrast);
- determine the phase of activity of multiple sclerosis and other demyelinating processes.
Not everyone can be examined with an MRI. This diagnostic method is not used if the patient has a pacemaker (the magnetic field can disrupt or stop the operation of the device). The study is not carried out for people with:
- electronic or ferromagnetic implants of the middle ear - there is a risk of device failure and injury to the hearing organ;
- large metal elements in the body - endoprostheses (MRI is done only with titanium structures), plates, etc.;
- ferromagnetic fragments and other foreign bodies;
- Ilizarov apparatus;
- vascular clips, stents (due to the risk of internal bleeding);
- infusion pumps for supplying medications (there is a possibility of damage to the microcircuit or batteries).
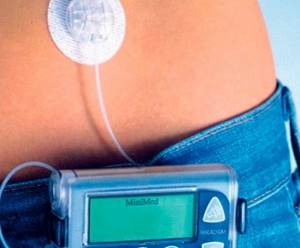
Insulin pump
Relative contraindications to MRI are the subject’s body weight of more than 150 kg (the restriction applies to closed-type devices), claustrophobia (if the patient is afraid of closed spaces, it may be necessary to put the patient into medicated sleep), conditions that prevent maintaining a stationary position during the scanning process, pregnancy in the first trimester.
Contrast drugs should not be used by expectant mothers, people with severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys (a blood test is sometimes required to determine the condition of the filtration organs), or intolerance to the components of the drug.
Indications for MRI diagnostics
Neurology and neurosurgery:
- tumors of the brain and spinal cord;
- disorders of cerebral and spinal circulation;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- malformations of the brain and spine.
Traumatology and orthopedics:
- joint injuries and diseases (including arthritis);
- injuries and inflammatory diseases of the spine;
- osteochondrosis, tumors of bones and soft tissues.
Gynecology:
- pathology of the uterus and appendages (tumors, cysts, inflammatory diseases, dyshormonal conditions).
Urology:
- tumors of the bladder, prostate gland;
- inflammatory diseases of the bladder, prostate gland;
- urolithiasis disease.
Gastroenterology:
- tumors of the liver, pancreas, spleen;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- pancreatitis;
- cholelithiasis.
When is MRI medical services needed?
Magnetic resonance imaging shows the smallest nuances - in the image you can examine in detail the structure of the skeleton, the condition of the internal organs and soft tissues. A tomogram will help the doctor detect tumors, congenital organ abnormalities and other problems that concern the patient. MRI is chosen as an examination method almost always when the maximum amount of information is required.
Tomography results will help to detect the cause and assess the degree of damage to organs, joints, bones and vertebrae when:
- injuries;
- pain of any location and intensity;
- preparation for operations;
- managing treatment and monitoring progress.
These are not necessarily just complex conditions or injuries. Sometimes, to determine the cause of “ordinary” chronic lower back pain, to which the patient has become accustomed over many years, it is necessary to examine all the internal organs and tissues in this area - this can only be done with the help of an MRI of the tailbone and lumbar spine.
In the image, the doctor can see all sorts of problems and damage:
- tumors, changes in organ size and tissue volume;
- hernias, protrusions;
- rachiocampsis;
- degenerative-dystrophic lesions;
- foci of inflammation;
- disorders related to the spinal cord;
- autoimmune lesions of the central nervous system.
Medical MRI services are safe, which is an additional big advantage of this procedure. During X-rays, the patient is exposed to some harmful radiation. Therefore, x-rays have more contraindications.
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to make diagnoses in various fields of medicine, so almost any doctor can send a patient for the procedure.
Preparing for the study
When going for an MRI, it is better not to use decorative cosmetics, because... Some types of cosmetics contain metal particles and this may affect the quality of the study.
- During an MRI examination, you must lie still for 10 to 50 minutes, depending on the tasks. Therefore, MRI examinations are usually not performed on children under 6 years of age and patients with severe involuntary uncontrolled movements,
- MRI examinations of the brain, spine, and joints do not require any preliminary preparation from the patient.
- MRI of the abdominal organs is performed on an empty stomach (5-6 hours after eating). It is necessary to exclude not only food intake, but also try to abstain or limit fluid intake at least 2 hours before the test.
- MRI of the pelvis is best performed with a full bladder. To reduce intestinal motility, it is recommended to take 2 tablets of Espumisan the day before or take 2-3 tablets of No-shpy 1 hour before the test (if there are no contraindications to taking these drugs).
- When heading for an MRI, you must remember that during the examination you will need to remove all metal jewelry and accessories, and watches.
- If you have difficulty staying still due to pain or are claustrophobic, please let us know when booking.
- We kindly ask you to choose clothing without metal elements (buttons, locks, jewelry) to undergo the study.
How much does an MRI cost?
In our center, MRI is performed on an open tomograph - during the procedure, the patient lies on an open couch and watches the doctor’s actions. A closed tomograph is a tunnel in which the patient is placed while the images are taken. For many, such a tunnel becomes a stressful factor, but an open tomograph is suitable for absolutely everyone.
In the price list we have indicated all areas of MRI, but remember that you must first consult a doctor. This examination method may be optimal for you, but there are other diagnostic methods. Your case is individual!
You can sign up for an MRI of the back and lower back, as well as other parts of the back, based on the recommendation of a specialized doctor, ask questions and schedule a consultation with the specialists of our center by calling +7 (391) 229-80-85.
Contraindications to the MRI procedure
The presence in the body of medical devices that involve electronics (such as a pacemaker or ear implant). The MRI magnet may cause malfunctions in their robot.
- The presence of unfixed foreign metal bodies of any location (the presence of metal teeth does not affect the possibility of conducting the study). Metal can cause blur in a clear MRI image, thereby preventing the examination of the desired organ (metal prostheses, clips, fragments).
- Patients whose weight exceeds 110 kg cannot be examined with our device.
- Pregnancy during the 1st trimester. If the patient is pregnant or may be pregnant, she must inform the doctor conducting the study. MRI is much safer than computed tomography and radiography because This method does not use ionizing radiation (X-rays). However, MRI causes some heating of the body, so they try not to do MRI in the first 3 months of pregnancy unless absolutely necessary. In the second and third trimester, MRI is considered safer, but if it is possible to postpone the scan until after birth, wait until the end of pregnancy.
- Mental inadequacy or serious condition of the patient;
MRI of the spine
Examination of the spine is always important - many diseases originate in the back area. Muscle tension, vertebral displacement, hernias and other problems certainly affect a person’s health and bring discomfort.
MRI of the back helps to see the condition of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, spinal cord and other skeletal elements. The problem may be hidden in internal organs, muscles and other soft tissues. Sometimes an MRI is performed with contrast - before the procedure, the patient is given an injection with a special substance that colors the tissue and allows you to more accurately see the volume and damage to organs, tissues and bone structures in the image. MRI of the spine is performed in three projections in order to reflect the most complete picture.
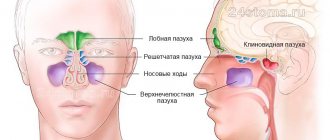
MRI of the cervical spine is recommended for headaches, dizziness and numbness of the neck and head. Also, if a crunch or other symptoms occur when turning your head, consult a doctor - tomography will help establish the cause and assess the condition of the joints, blood vessels and tissues. The neck receives a huge load every day. It is reinforced by the need to constantly look at the screen of a smartphone or laptop. Often the neck compensates for the curved position of the back, taking on the load of overstrained spinal muscles. All this can cause pain and problems in the cervical spine.
MRI of the thoracic spine helps to identify scoliosis, kyphosis, the presence of herniated discs, and injuries in the ribs.
MRI of the lumbosacral region and coccyx shows the presence of pathologies in this area. The procedure will show why the patient feels severe pain, numbness in the legs, and limited mobility in the lower back and hips.
What do you need to take with you to the procedure?
- You need to have with you all medical documentation related to the area of interest: postoperative statements, data from previous studies, such as MRI (images and reports, if available), ultrasound, SCT. A referral from your primary care physician is encouraged. The doctor needs this information before performing a diagnostic procedure in order to think through and optimally plan the course of the magnetic resonance examination.
- Voluntary medical insurance policy, if your research is paid for by the Insurance Company;
- Identification;