Why is a repeat procedure necessary?
Experts insist on the need to undergo this procedure. This will make it possible to completely exclude the possibility of the presence of all kinds of defects, disorders of fetal development, or to ascertain them. Those pregnant women who previously, during the first study, had any deviations from the norm were identified or whose specialist had prerequisites for suspecting them, must undergo diagnostics.
You can find out in detail from the leading doctor at what time the second ultrasound is performed. It usually needs to be completed between 20 and 24 weeks. This is a planned study.
During this procedure, the physician may identify:
- Factors that provoke pain in the lower abdomen of the expectant mother;
- Reasons for the possible appearance of bloody or watery discharge;
- Condition of the uterus, possible deviations from the required parameters;
And the use of the so-called Doppler study of the fetal cerebral vessels allows us to determine whether the child is experiencing oxygen deficiency or not.
What are they watching?
As with the first screening study, the protocol can be divided into several parts:
- information about the anatomical structures of the fetus
- fetometric parameters
- state of provisional authorities
- analysis of the female reproductive system.
Each section is necessary and contains an assessment of a number of parameters and characteristics. The final part of the protocol contains all the important information that summarizes each section.
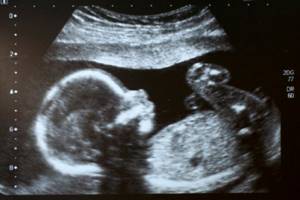
The result of this examination is an image with which a specialist can analyze fetal development and track possible pathologies
What is the difference between a repeat procedure?
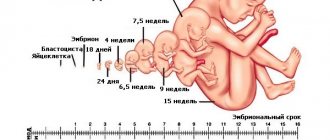
The main task of the first ultrasound examination during pregnancy is to determine the location of the embryo, as well as possible gross malformations. In addition, the parameters of the collar zone are established, whether they correspond to the norm or deviate from it.
The second procedure makes it possible to see what has formed in the period of time after the first ultrasound. What changes have occurred in the structure of the brain, how limbs and organs develop. If there are conclusions from two studies, the doctor will be able to accurately calculate the growth rate of the fetus and determine whether it is ahead of standard indicators or, conversely, behind them.
If the discrepancies are minor, after a couple of weeks the expectant mother will need to undergo a repeat ultrasound. During this period of time the fetus will grow. For this reason, you should not ignore every planned study.
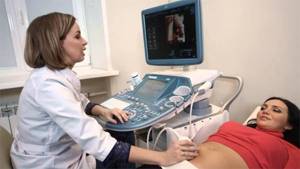
Research method
The second planned ultrasound during pregnancy does not require special preparation. The examination itself is done transabdominally with a conventional convex probe.
For the study, the woman is laid on her back; if necessary, laying on her left side is possible. If difficulties arise in diagnosis (the child is too active, his bladder is completely emptied), the study is stopped and continued after 20-30 minutes.
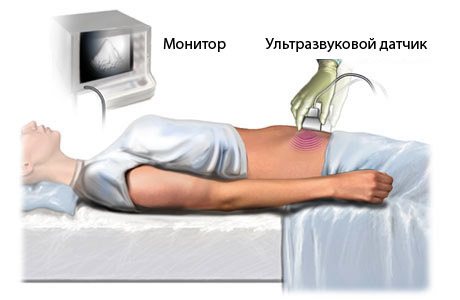
This type of examination is the most popular due to the absence of unpleasant sensations and fairly quick implementation (20-30 minutes)
Time frame for referral for repeat ultrasound examination
Many expectant parents are interested in at what stage is the second ultrasound done during pregnancy? As a rule, a repeat procedure is prescribed between 20 and 24 weeks. In addition to the fact that ultrasound makes it possible to most accurately examine the degree of fetal development, it also helps to determine:
- Exact gestational age;
- The correct structure of the internal systems and organs of the fetus;
- The amount of amniotic fluid;
- Possible developmental disorders;
- Existing risk regarding the likelihood of miscarriage;
- Gender of the unborn baby.
The timing of the re-test was not determined by chance. It is during this period that the process of formation of all systems and organs is completed, and the degree of their development is diagnosed. There is also the possibility of detecting anomalies that may subsequently not respond to treatment, as well as pathologies that provoke fetal fading, premature birth, and sudden death after birth.
If serious defects were discovered much later, serious negative consequences may arise. For example, a threat to the life of a pregnant woman, which could have been avoided if the repeat ultrasound procedure had been carried out on time. But it also happens that the doctor is not sure or has any doubts about the accuracy of the diagnosis after the second ultrasound procedure.
In this case, a week later it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound again. Subsequently, the results of the study will be compared. The specialist will assess the dynamics of the fetus’s condition.
Standard indicators for the second trimester
Fetometric parameters
This group of indicators includes a large number of fetal measurements, which are important in the diagnosis of defects and developmental anomalies.
Summary table of basic fetometric values.
| Fetometric indicators, cm | Gestation period, weeks | |||||
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | |
| Biparietal size | 3,58-5,19 | 3,91-5,58 | 4,22-5,91 | 4,47-6,29 | 4,81-6,59 | 5,11-6,81 |
| Fronto-occipital size | 4,79-7,02 | 5,32-6,44 | 5,61-7,92 | 6,11-8,34 | 6,49-8,72 | 6,91-9,04 |
| Average breast diameter | 3,12-4,89 | 3,55-5,32 | 3,81-5,64 | 4,02-6,06 | 4,31-6,34 | 4,62-6,65 |
| Average abdominal diameter | 3,51-5,35 | 3,88-5,61 | 4,11-6,04 | 4,34-6,41 | 4,67-6,71 | 5,03-7,13 |
| Femur length | 2,13-3,50 | 2,32-3,79 | 3,80-4,21 | 3,91-4,40 | 4,12-4,74 | 4,30-5,03 |
| Tibia length | 1,89-3,12 | 2,10-3,41 | 2,43-3,82 | 2,63-3,89 | 2,81-4,09 | 3,02-4,30 |
| Fibula length | 1,78-2,90 | 1,97-3,22 | 2,20-3,52 | 2,51-3,77 | 2,72-4,09 | 2,94-4,24 |
| Humerus length | 2,09-3,40 | 2,42-3,59 | 2,63-3,88 | 2,81-4,13 | 3,07-4,34 | 3,30-4,61 |
| Radius length | 1,72-3,11 | 1,91-3,20 | 2,08-3,39 | 2,30-3,63 | 2,49-3,78 | 2,69-4,02 |
| Ulna length | 1,81-3,10 | 2,03-3,30 | 2,22-3,63 | 2,41-3,78 | 2,61-3,89 | 2,81-4,10 |
| Head circumference | 14,4-18,2 | 15,6-19,4 | 16,8-20,6 | 18,0-21,8 | 19,1-22,9 | 20,2-24,1 |
| Abdominal circumference | 11,6-16,6 | 12,7-17,6 | 13,9-18,9 | 15,0-20,1 | 16,1-21,2 | 17,2-22,1 |
| Exhaust/coolant ratio | 1,05-1,23 | 1,04-1,25 | 1,06-1,23 | 1,05-1,22 | 1,05-1,23 | 1,01-1,20 |
| Distance between the outer edges of the eye sockets | 2,41-3,52 | 2,62-3,76 | 2,78-3,89 | 3,01-4,15 | 3,12-4,21 | 3,29-4,41 |
| Eye socket diameter | 0,71-1,11 | 0,79-1,21 | 0,83-1,25 | 0,91-1,35 | 0,92-1,36 | 1,01-1,41 |
| Interhemispheric size of the cerebellum | 1,61-2,02 | 1,81-2,20 | 1,93-2,31 | 2,02-2,63 | 2,11-2,69 | 2,31-2,89 |
Biparietal and fronto-occipital size, average diameters of the chest and abdomen are used to clarify the duration of pregnancy, determine the weight of the fetus, the correspondence of development to the gestational age, as well as to determine the symmetry and proportionality of development. Circumferences of the chest, head and abdomen are used to diagnose malformations and intrauterine growth retardation.
Measuring the length of the tubular bones of the limbs is carried out on both sides and is used to identify hypoplasia and aplasia of the limbs.
The interhemispheric size of the cerebellum is used in the diagnosis of brain abnormalities.
The distances between the edges of the orbits and the average diameter of the orbits are of an auxiliary nature and can be used in the diagnosis of defects of the facial skull.
Fetal anatomy
During the second ultrasound scan during pregnancy, the main task is to assess the structure of the internal organs and identify malformations that were not detected during the first ultrasound diagnosis.
Each specialist has his own principle of examination: from top to bottom, according to organ systems, haphazardly. The quality of the study does not depend on this; the main thing is that all organs are analyzed.
Brain and spine
Studying the structure of the brain using 2 ultrasounds usually begins in the axial plane, conducting a series of sequential sections. This allows us to study the structure of the lateral ventricles, cerebellum, optic thalamus, and interhemispheric fissure.
If pathologies are detected during this scan, then the study is carried out in other planes. At this stage, it is possible to identify the following defects:
- ventriculomegaly,
- hydrocephalus,
- hypoplasia of the corpus callosum,
- cerebellar abnormalities.
The standard study is complemented by a color Doppler study, which makes it possible not to miss developmental disorders of the vascular bed.
The spine is assessed along its entire length in two perpendicular planes. The evaluation criteria are structure, spinal curves, integrity of vertebral arches, muscle defects. This allows you to identify hernial protrusions (spina bifida).
When examining facial structures, it is important to evaluate the condition and size of the eye sockets, nasal bones, and the condition of the nasolabial triangle.
Respiratory system
Diagnosis consists of assessing the condition of the bronchi and lung tissue. During examination, important importance is given to the division of the bronchi, the echogenicity of the lung tissue and its homogeneity, as well as the correspondence of the size of the lungs to the period of pregnancy. The latter parameter is assessed based on measuring the chest circumference and calculating the ratio of the chest circumference to the abdominal circumference.
A formula for calculating lung volume has also been developed, but its use is limited due to the large error. Taking into account the fact that the main stage of maturation of lung tissue occurs in the third trimester, it is possible to identify only gross malformations during the periods discussed.
Heart
Prenatal diagnosis of heart defects is particularly difficult to diagnose. The standard protocol includes evaluation of only the 4-chamber section of the heart. If there are changes in this position, then detailed fetal echocardiography is recommended, which is a separate study.
Digestive system
The protocol deals with the stomach, intestines and liver as separate points. Diagnosis of pathology of the stomach and intestines does not cause difficulties due to the presence of anechoic contents, which allows one to evaluate the structures of organs and exclude atresia (closure of natural orifices) at any level.
When analyzing the structure of the liver, it is important to assess the condition of the liver vessels and the bile duct system.
Measurement of the organ is necessary only if hepatomegaly (pathologically large liver) is suspected. The main pathology is cysts, which are easily differentiated.
urinary system
Examination of the kidneys does not cause difficulties, since their location and appearance are typical. The bulk of the pathology is occupied by aplasia, hypoplasia and pyeloectasia.
The bladder is visualized due to the presence of anechoic urine in the lumen, and if it cannot be determined, the examination should be repeated after 10-25 minutes to exclude its aplasia.
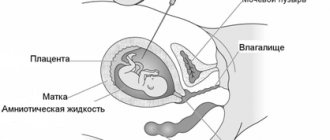
Assessment of the structures of the uterus and the state of the provisional system (umbilical cord, amniotic fluid, placenta) does not differ from screening ultrasounds at other times.
Ultrasound in the second trimester of pregnancy is of key importance in deciding on the further management of pregnancy, so the study should be carried out using expert equipment by high-class specialists.
Preparing for a repeat ultrasound
The repeated procedure takes place abdominally. Therefore, no special preparation is required. There is also no need to pre-fill your bladder. The waves used during manipulation pass through the amniotic fluid.
The diagnosis itself is carried out as follows. The patient lies down on the couch and exposes her stomach. A special gel is applied to the skin. The doctor uses a sensor to scan the surface of the abdomen in order to obtain information about the fetus and the condition of both its internal and maternal organs.
During the procedure, the doctor voices what he sees. If necessary, he can show an image of the head and limbs on the monitor. At the patient's request, video or photographic recording of the fetus is performed. During the examination, the doctor mainly pays attention to the parameters of the fetus, weight, length of arms and legs, number of fingers and toes. It is also mandatory to study the internal organs, first of all, their correspondence to the gestational age. In a fetus that is actively developing, the formation of the skeletal system occurs. Due to this, his outline already looks like a small person with a small amount of hair on his head.
Between 20 and 23 weeks, the grasping and sucking reflexes develop. It is noteworthy that at this time the nervous system has already developed so much that the fetus can feel touch.
The child, while inside, moves freely inside, can grab the umbilical cord, and sometimes sucks his finger. This can be seen upon examination. Also, during a repeat ultrasound, you can already hear the baby’s heart beating.
The results of the second procedure are documented in a separate conclusion - a protocol. It reflects the number of fetuses, its characteristics, the state of its internal organs and the mother’s. A repeat ultrasound should be performed only within a strictly designated period. Research at earlier stages often simply does not allow us to see possible pathologies and violations of norms, since the fetus is still quite small. And if the procedure is performed later, it is possible that time to correct a particular condition will be missed.
What kind of ultrasound is done during pregnancy?
Ultrasound during pregnancy is a universal, non-invasive and convenient research method. The procedure allows doctors to obtain reliable information about such parameters as:
- gestational age,
- fetal condition,
- its parameters,
- functioning of the umbilical cord, placenta and uterus.
The mechanism of the method is to analyze the differences in the reflection of sound waves from structures of different densities. During the examination, ultrasound with a frequency of 2 to 10 MHz is used.
Results of the second ultrasound
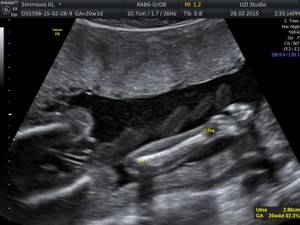
During the 2nd ultrasound, the following indicators are studied:
Fetometry or measurement of the main dimensions of the unborn child, which includes:
- biparietal size of the fetal head (BF);
- fronto-occipital size (FOR);
- head circumference;
- diameter (abdominal circumference);
- cephalic index (BPR/LZR) – assessment of head shape;
- the length of the paired tubular bones (femur, tibia, fibula, humerus, ulna and radius);
- ratio of BPR to DBC (femur length);
- OG (head circumference)/OB (abdominal circumference);
- DBK/OZH.
When should an ultrasound be performed for pregnant women?
To obtain more complete and comprehensive information, ultrasound is performed at certain stages of pregnancy, and such studies are called screenings. During the entire pregnancy period, any patient must undergo three ultrasound screenings:
I screening
11-14 weeks (ultrasound + biochemical screening for chromosomal pathologies)
II screening
18-22 weeks (ultrasound + Dopplerometry). You can already find out the gender of the baby!
III screening
30-34 weeks (ultrasound + Doppler ultrasound + cardiotocography)
Why is ultrasound used?
Ultrasound is one of the main diagnostic methods during pregnancy. With its help, a specialist can detect and prevent the development of pathologies, anticipate the emergence of various difficulties and choose the right tactics for managing pregnancy. For maximum benefit, it is necessary to undergo examinations at the right time as planned, and additionally if there are doctor’s recommendations. Ultrasound has the following advantages:
- Allows you to accurately determine the position and size of the fetus, the shape and size of the pelvic organs.
- The examination has no contraindications, it is completely safe and does not harm either the woman or the child.
- Diagnosis is painless.
- The study takes place in real time, the patient immediately receives a transcript of the data and an image of the fetus.
Table of normal ultrasound indicators at 17-25 weeks
| Term | BPR | LZR | DBK | DgRK | DP | OG | coolant | Stomach size | Heart rate | IAJ |
| 17–19 weeks | from 36 to 43 mm | from 32 to 70 mm | from 24 to 30 mm | from 11 to 31 mm | from 13 to 34 mm | from 112 to 174 mm | from 96 to 120 mm | from 12 to 20 mm | 110-180 beats/min | from 20 to 80mm |
| 20–22 weeks | from 47 to 53 mm | from 53 to 76 mm | from 33 to 39 mm | from 19 to 39 mm | from 24 to 39 mm | from 154 to 212 mm | from 138 to 162 mm | from 18 to 24 mm | 120-160 beats/min | from 20 to 80mm |
| 23–25 weeks | from 56 to 62 mm | from 77.5 to 86.5 mm | from 41 to 46 mm | from 22 to 44 mm | from 38 to 48 mm | from 211 to 251 mm | from 168 to 198 mm | from 24 to 28 mm | 120-160 beats/min | from 20 to 80mm |
Smaller sizes indicate VZRP, which can be symmetrical when all sizes lag behind the norm, but at the same time they are proportional and asymmetric when the coolant lags behind and the ratio of EG to coolant and DB to coolant is increased.
- VZRP comes in three degrees. With the first, the fetus lags in size by 2-3 weeks, with the second by 3-4 and with the third by 5 weeks.
- The lungs have three degrees of maturity - zero, first and second. By the end of the second trimester, the fetal lungs have the first degree.
- Low placentation is recorded when the placenta is attached 5.5 or more centimeters from the lower os of the uterus. The thickness of the placenta from 4.5 cm is an indicator of non-immune fetal hydrops, glucosuria, incompatibility of Rh blood of the mother and child, or the presence of infections. If the placenta is thinner than two centimeters, then it is diagnosed as premature ripening.
- AFI less than 20 mm is an indicator of oligohydramnios, more than 80 mm is an indicator of polyhydramnios.
- ICI is diagnosed if the size of the cervix is less than 32 mm in a pregnant woman for the first time and less than 20 mm in a pregnant woman again.
Almost all congenital and acquired pathologies are detected during the second screening ultrasound.
Online registration for second trimester ultrasound
At the clinic Dr. AkNer you can sign up for a 2nd trimester ultrasound at a time convenient for you. To do this, contact us at the contact number or fill out the online registration form, where you can indicate your details and desired appointment time. Please note the need to conduct research in a timely manner. This allows you to identify possible violations in a timely manner and take all necessary measures to eliminate them.
June 02, 2021
Ultrasound diagnostics doctor, candidate of medical sciences, Evseeva Ekaterina Leonidovna.