Since 1972, medicine began to use a new highly effective method for diagnosing human internal organs, based on X-ray radiation - computed tomography.
The principle of operation is that a rotating X-ray tube with built-in sensors takes many images and then sends them to a computer. The program processes incoming images and makes visual sections of body parts, displaying them on the monitor.
This diagnostic technique does not force the patient to undress, does not cause pain or claustrophobia. The scanning duration takes about 1 minute. If it is performed with contrast enhancement, then the procedure is repeated several times.
What does a CT scan of the skull bones show?
Upon completion of the diagnosis, the radiologist analyzes the images obtained on the computer screen and makes a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the bone tissue, internal organs, blood vessels and head. Also, x-ray examination allows you to detect pathological changes that develop in the initial stages of the disease.
When a computed tomography scan of the skull and at the same time the brain is performed, an analysis of the condition of bone tissue, blood vessels and soft tissues is performed.
A CT scan of the skull bones shows the presence of traumatic brain injuries. The scan also allows you to see:
- injuries of bones and soft tissues;
- presence of foreign bodies;
- development of disturbances in smell and vision;
- development of abnormalities in the head area;
- results of the operation (it also becomes possible to control the recovery stage).
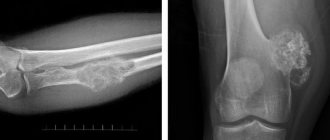
Using a tomograph, fibrous dysplasia, cancer of the bone tissue of the skull and myelin disease are detected. The study of bone tissue is carried out on the basis of 3D images (thin sections up to 2 mm) and the construction of their reconstructions.
How is an MRI of the mandibular joint performed?
There is nothing scary in the procedure itself. The only inconvenience is the need to lie motionless in the magnetic capsule until the end of the procedure.
The patient is placed on the retractable table of the device, which slides inside the tomograph. After this, the scanning procedure begins, the scanning data is sent to the computer and undergoes the necessary processing.
After diagnosis, the radiologist examines the resulting image. The conclusion along with the photograph will be given to you either on the same day or the next.
- Why do you need an MRI?
- What diseases can MRI detect?
- MRI of the head for children.
- MRI of cerebral vessels.
- Features of MRI of the head in the presence of dental implants.
- What to choose for a head examination - MRI or EEG.
CT scan of the temporal bones: what does it show?
Using a CT scan of the temporal bones, doctors are able to obtain a picture of the pyramid of the temporal bones, see damage to the mastoid process, the condition of the auditory canal, and changes in the structure of the inner and middle ear.
The question of what a CT scan of the temporal bones shows can be answered by giving a list of indications for the procedure. It is prescribed for:
- identifying otitis media;
- detection of damage due to injuries;
- the presence of abscesses in the temporal region;
- the presence of mastoiditis;
- detection of hearing impairment and otosclerosis;
- detection of tumors;
- examination before surgery;
- examination to find the causes of purulent discharge from the auricle.
CT scan for otitis
Bacterial inflammation of the middle ear leads to damage to the mucous membranes, accumulation of pus inside the cells of the mastoid process, and the tympanic cavity. Long-term persistence of chronic inflammation leads to the release of pus to the outside, the appearance of a perforation in the eardrum. Pathology creates dangerous complications:
- Hearing loss;
- Infiltration of the inner ear;
- Spread of pus through the circulatory system;
- Destruction of the walls of the mastoid process;
- Destruction of internal cavities;
- Thrombosis of the sigmoid sinus;
- Abscess development;
- Epidural hematoma;
- Empyema;
- Involvement of the auditory ossicles in the inflammatory process with hearing loss.
The conclusion of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging often ends with the diagnosis of “mastoiditis”. Misinterpretation arises from the detection of aseptic fluid inside the mastoid cells, which occurs after simple exudative otitis. Mastoiditis can be correctly diagnosed only after detection of inflammatory lesions of the bone septa.
CT scan of the pelvic bones: what does it show?
By performing a CT scan of the pelvis, the doctor receives clear images of the ischium, iliac and pubic bones. At the same time, laying them out into thin visual sections makes it possible to establish compactions in the bone and soft fibers.
Thus, we can identify a list of factors that answer the question of what a CT scan of the pelvic bones shows:
- the presence of damage to the pelvis and its soft fibers;
- the presence of development of abnormal phenomena and dysplasia in the pelvic area;
- tumor development;
- presence of Crohn's disease and myelin disease;
- presence of a foreign body;
- identification of pathologies in the hip joints.
In addition, this manipulation is carried out when the operation is planned.
Benefits and Risks
- Computed tomography (MSCT) of the temporal bones allows high-quality visualization of not only bone tissue, but also soft tissue, and the quality of the image of bone tissue is better than on MRI.
- The procedure is absolutely painless and takes on average 10 minutes.
- The procedure does not require special preparation and only when conducting a study with contrast, it is recommended to conduct the study on an empty stomach.
- The dose of ionizing radiation during the study is quite low, but, nevertheless, it is not recommended to conduct multiple studies, since a certain risk of harmful effects on humans in such cases is much higher. However, the diagnostic value of this method of studying the temporal bones is much higher than the risks. The image quality of soft tissues on MRI is higher and, therefore, if more detailed visualization of the soft tissue structures of this area is necessary, an MRI study is recommended.
CT scan of facial bones: what does it show?
Many citizens who do not have a medical education are interested in the question of what a CT scan of the facial bones shows.
This manipulation allows the doctor to assess:
- the integrity of the bones that form the face;
- condition of the eye sockets, nose, paranasal sinuses;
- the actual condition of the soft tissues of the patient’s face.
A doctor may prescribe a CT scan for a patient if:
- there have been facial injuries (especially if bone displacement is visible to the naked eye);
- there is inflammation of the facial tissues;
- there is a tone of facial muscles;
- oncological processes take place.
This manipulation is also recommended when it is not possible to perform an MRI for certain reasons. The examination helps to understand whether the jaw bones are in place. In addition, this manipulation also helps to detect tumors within the cartilage tissue. The convenience of CT is that you can suspect the disease at an early stage and begin to treat it.
Oncology is clearly visible on CT images; the doctor can always examine the contours of the tumor. The doctor can also determine the extent of tumor growth in the area of the skull, nose and orbital area. In some cases, there is a need to introduce a special substance that will help produce contrast. Contrast is administered to the patient intravenously.
How does the procedure work?
- The patient turns off all electromagnetic devices.
- Removes clothing and jewelry with metal fittings.
- Lies down on the pull-out couch.
- It is secured with wide straps. Stillness is one of the main conditions for obtaining high-quality images. Fixation will help the patient maintain this state throughout the entire process.
- The couch slides into the tomograph tunnel.
- During the examination, the device makes characteristic sounds. To reduce the noise effect, you can use earplugs.
- The scan takes 5-15 minutes without contrast. If contrast is required, the examination period will last 30-40 minutes.
- At the end, the radiologist examines the result. Writes a conclusion.
- It is worth considering that the diagnostician is not involved in making a diagnosis and prescribing therapy. This is done by a specialist doctor. Therefore, the photographs and examination report must be transferred to him.
CT scan of the pyramids of the temporal bones: what does it show?
This manipulation allows us to identify pathological changes and identify abnormalities in bone structure (if they occur). To understand what a CT scan of the temporal bone pyramids shows, the patient needs to come to see a doctor. No preparation is required for the diagnostic procedure.
During the procedure, the patient receives a minimal amount of radiation, so an ENT or maxillofacial surgeon can refer for diagnosis in many cases. Tomography is prescribed if:
- the patient complains of problems with hearing and vision;
- dizziness occurs;
- pain occurs in the temples;
- suffers from chronic otitis media;
- discharge from the ear is observed;
- a foreign object has entered the ear and cannot be removed independently;
- There were injuries to the temporal lobes.
If the doctor suspects the development of a tumor process in his patient, a CT scan will also be prescribed.
The procedure is also carried out in the case of destruction of the temporal bones (or in the case of indirect signs of it).
This procedure is also carried out during the preoperative period. In the post-implantation period, a diagnostic study is carried out in order to see how well the foreign body has taken root. Diagnostics allows you to assess the speed of healing.
The temporal bone, also called the pyramid, is examined if there are complaints of poor hearing quality. The pyramid is studied during diagnosis because it contains important blood vessels, the inner and middle ear. When studying this area, the medical staff usually uses a contrast agent.
The study reveals:
- abscess;
- otitis acute or chronic;
- progression of the infectious process;
- otosclerosis, as well as mastoiditis;
- the presence of an oncological process;
- fractures of the pyramid bones;
- cracks in the bones;
- soft tissue injuries;
- severe hemorrhages;
- presence of neuromas.
If a contrast agent is used, the tomography takes about 30 minutes. Without the use of contrast, diagnosis is faster. Decoding the results obtained from the procedure takes less than an hour.
The procedure is not particularly difficult. The patient lies down on a medical table, which slides into a special area. Then the tomograph is turned on, rotating within the study area. The patient will hear a slight noise. At a certain point, the specialist will ask the patient to hold his breath. The person must follow all commands that come from the medical staff.
For a hyperactive child, the procedure can be carried out provided that the baby is put into a state of medicated sleep.
Contraindications
There are few contraindications for the examination; these include only the presence in the body of implants, metal plates, pins, a pacemaker, a neurostimulator and similar foreign objects containing metal.
Also, MRI of the auditory nerve (as well as other types of tomography) may not be allowed for people whose nervous system is damaged and they do not control their movements, patients whose weight exceeds 120 kg.
For pregnant women and nursing mothers, the procedure is performed only in cases where the need for diagnosis outweighs the possibility of side effects.
Patients with allergies to contrast agents and patients with renal failure are first sent for a biochemical blood test so as not to harm the body. Based on the results of the LHC, a decision is made on the possibility of conducting an examination.
Children and people suffering from claustrophobia are pre-administered sedatives, since you need to lie absolutely still while the tomograph is operating.
Why do doctors often prescribe the CT procedure to their patients?
This manipulation attracts doctors for four reasons:
- safe (it does not imply any harm to the patient’s health);
- may involve the introduction of a contrast agent, which will help to obtain clear outlines of the organ being examined and thereby obtain an accurate result;
- takes very little time;
- offered at a low price.
Before the procedure, the doctor will ask the patient to remove earrings and piercings. No special preparation is needed if the procedure is performed without contrast. If a contrast agent is administered, the patient will be asked to fast 7 hours before the procedure.
Preparation
The procedure lasts approximately 10 minutes. The X-ray tube of the tomograph rotates around the area being examined. The patient needs to remain still so that the doctor performing the test can get clear images. The patient will hear absolutely everything the doctor tells him. If necessary, a contrast agent is injected.
No special preparation is required for the procedure (no different from standard preparation). Before performing the procedure, study the contraindications.
Where can I get a bone CT scan?
Today there are many organizations that offer bone CT scans. The free piter-mrt service is ready to help with choosing a clinical diagnostic center. Here is a list of clinics where computed tomography of bone tissue is performed.
The proposed list of organizations includes:
- all centers in the locality of interest (only those centers that offer a diagnostic procedure are reflected in the list);
- address of the organization indicating the nearest metro station;
- the company's phone number, which you can call at any time to make an appointment;
- organization rating (the rating is displayed as the number of positive and negative reviews from patients of the clinic).
Thanks to a convenient list of companies, a citizen will be able to choose the most suitable organization based on price and proximity to home or work.
Otosclerosis on CT
An inherited genetic disease, otosclerosis occurs due to metabolic disorders. The exact cause of the disease could not be determined. Morphological changes in pathology are accompanied by the proliferation of bone tissue with filling of the mastoid cells. Resorption is caused by the activity of bone cells - osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Places of destruction are filled with connective tissue fibers. Sclerosis of the inner ear leads to hearing loss (conductive). In young people, the nosology is characterized by the formation of a sclerotic focus near the anterior edge of the vestibule. A novice radiologist does not always detect changes. The process is bilateral, therefore it is accepted as the anatomical norm.