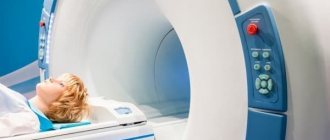
MRI scanner The phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) underlies one of the most modern and informative diagnostic techniques, used in therapy, surgery, obstetrics and gynecology. The disadvantages of MRI are the presence of contraindications, the impressive time required for the procedure, and the high cost of the equipment. However, there are many more benefits. Among them are the versatility, accuracy, information content and safety of the method. With MRI, it is incorrect to say what radiation dose falls on the patient: there is no radiation load here. The procedure is based on the effect of a magnetic field on tissue. The method can be used during pregnancy. Let's take a closer look: does MRI irradiate (when examining the spine and other structures) or not?
Is MRI safe?
The main advantage of MRI, in addition to its high informativeness for diagnosis, is the absence of ionizing radiation .
The MRI method is based on the electromagnetic characteristics of hydrogen atoms, which quantitatively predominate over other particles in human tissue. A constant high-power magnetic field is maintained inside the tomograph; radio signals with a frequency close to the vibration frequency of hydrogen pass through it. Due to resonance, the radio wave is amplified, which is recorded in a special matrix and converted by a computer into an image.
Since different tissues of the human body contain different amounts of hydrogen, the outgoing signals from different organs and tissues differ significantly, which makes it possible to obtain fairly accurate images.
There is no medical evidence that this procedure is harmful to health or causes any complications. Among the millions of people who have undergone magnetic resonance imaging, there have been no cases of ill health or harm to the body after the examination.
The only inconvenience for the patient when conducting magnetic resonance imaging is the duration of the study. An MRI scan can take anywhere from 15 minutes to 1 hour. During this period, the patient should lie still . The examination itself is an absolutely painless procedure ; the effect of magnetic waves does not cause any discomfort to the patient.
What parts of the spine are examined on MRI?
When examining the spine, MRI makes it possible to study the condition of not only all bone parts (from the cervical to the coccyx), but also other important structures:
- intervertebral discs;
- spinal cord and its membranes;
- vessels and nerves;
- ligaments;
- cartilage tissue;
- intervertebral joints;
- adjacent muscles and fiber.
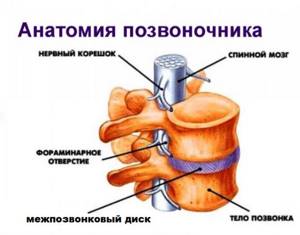
The structure of the spine using the example of a separate segment
Magnetic resonance imaging accurately determines the location of herniated protrusions of intervertebral discs, their size, the degree of degenerative changes, and impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. With its help, adhesions in the epidural tissue are differentiated from inflammatory ones, as well as from tumor and vascular neoplasms.
Spinal sections:
- cervical;
- chest;
- lumbar;
- sacral;
- coccyx.
All departments can be studied in detail during magnetic resonance scanning.
How often can an MRI be done?
MRI is prescribed for various pathologies of the substance and blood vessels of the brain, paranasal sinuses, diseases of the spine and spinal cord, joints, abdominal and pelvic organs. This study is carried out as necessary. As a rule, an initial MRI allows you to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. A repeat MRI examination is prescribed to clarify the condition of an organ or system after surgery, to monitor the treatment process, and for a more refined diagnosis using a contrast agent.
Since electromagnetic waves do not cause radiation exposure to the human body, unlike X-ray examinations, MRI can be done as often as required for diagnosis and effective treatment. Thanks to the constant improvement of computer technology, the MRI procedure has become absolutely safe for the public, and at the same time the most informative for the doctor.
Indications for MRI
Conventionally, the entire human body is divided into regions. Each area has specific indications for examination. There are also indications for diagnosing individual organs, several adjacent areas or the entire human body.
You can get a referral from your doctor for an MRI of the brain in the following cases::
- neoplasms of the brain, calvarial bones, meninges;
- abnormalities of brain development;
- suspicion of an aneurysm;
- stroke;
- various head injuries, especially in cases where there is suspicion of the formation of an intracranial hematoma;
- various diseases of the eyes and inner ear;
- detecting changes in the brain in patients with dementia and multiple sclerosis;
- monitoring the persistence of remission in oncology.
MRI of the pituitary gland is indicated in the following cases:
- metabolic disorder, which leads to rapid increase in body weight (obesity);
- menstrual irregularities in women;
- disruption of the functioning of other endocrine glands of the body, for which the pituitary gland is the coordinating organ (acromegaly, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, etc.);
- visual impairment and oculomotor disorders of unknown origin;
- headache.
MR imaging of the eye orbits is used for:
- the presence of a foreign body inside the eyeball or in the retrobulbar space;
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasms in the orbital area;
- various degenerative diseases, such as optic nerve atrophy;
- hemorrhage in the eye;
- inflammatory processes affecting the structures of the eyeball, extraocular muscles, optic nerve, lacrimal glands, fatty tissue of the orbit;
- changes in the orbit that may be a consequence of injury;
- pathologies of the retina (dystrophy, suspected retinal detachment or thrombosis of the vessels supplying it);
- impairment or loss of vision, the causes of which are unknown;
- the appearance of a number of eye symptoms, the causes of which are not clear, for example, exophthalmos (bulging eyes), pain in the eyes, etc.
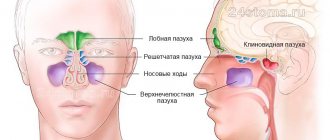
MRI of the sinuses will be indicated in the following cases:
- frequent headaches, the cause of which is not established;
- toothache or pain in the cheekbone area, when dentists do not find any pathology of the teeth and gums;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract with frequent relapses and complications in the ears;
- congestion in the ears, the cause of which cannot be identified by other means;
- suspicion of a cerebrospinal fluid fistula (a small hole through which the cranial cavity is connected to the nasal cavity and through which cerebrospinal fluid constantly flows);
- allergic rhinitis, fungal sinusitis;
- suspicion of a tumor in the sinuses;
- determination of the stage and prevalence of malignant neoplasm;
- differential diagnosis of hemorrhage in the nasal sinus (hemosinusitis) and purulent sinusitis.
MRI of the chest cavity and mediastinum is performed in the following cases:
- oncological search: suspicion of the presence of a malignant tumor, determination of its location, stage of development of the process, presence of metastases;
- confirmation of the presence of a tumor in the chest, which was suspected by other research methods, differential diagnosis of a tumor, tuberculosis, inflammation and other pathological processes;
- assessment of the condition of the heart muscle after myocardial injury (area of damage, condition of the scar, etc.);
- heart defects;
- blood clots in the cavities of the heart;
- pathology of the thoracic aorta (wall dissection, narrowing, aneurysm);
- exudative pericarditis;
- study of heart function, clarification of its size in various diseases (cardiomyopathy, heart defects, angina pectoris);
- emphysema, pneumonia.
Indications for examination of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space:
- the presence of congenital structural features of internal organs from minor anomalies to gross defects;
- injuries to internal organs, suspicion of the presence of foreign bodies, with the exception of metal ones;
- formation of adhesions, scars, infiltrates, abscesses after surgery on the abdominal organs;
- oncological search - detection of a tumor or its metastases in the thickness of the organs or soft tissues of the abdominal cavity;
- determining the nature of the pathological process in a particular organ (liver cirrhosis or fatty hepatosis, portal hypertension, pancreatitis, obstructive jaundice, etc.).
Reasons for ordering an MRI of the adrenal glands include::
- decreased or increased blood pressure;
- deepening of the voice in women, excess hair growth on the face and body;
- an increase in the size of the mammary glands in men;
- a sharp increase in body weight for no apparent reason;
- decreased muscle strength, muscle weakness.
Indications for MRI of the pelvic organs, common for men and women:
- difficulties in diagnosing the disease based on previous studies (ultrasound, x-ray, colonoscopy, etc.);
- the presence of contradictions between the nature and severity of the clinical picture of the disease and the data of the examination methods used;
- oncological diseases, assessment of the nature of the neoplasm (benign, malignant), its size, vascular growth, involvement of nearby organs in the process;
- injuries to bones, soft tissues and pelvic organs;
- the presence of chronic pain in the pelvic area and sacrum;
- infertility, the causes of which are not clear;
- congenital features of the development of the genitourinary system;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- suspicion of diseases of the rectum, bladder;
- postoperative monitoring of the condition of the pelvic organs.
Indications for MRI of the pelvic organs in women are:
- suspicion of acute surgical pathology of the reproductive system, such as cyst rupture or ovarian apoplexy;
- endometriosis, a common adhesive process in the pelvic organs;
- vaginal bleeding, the causes of which are unknown;
- control of fetal position in the third trimester of pregnancy.
MRI of the spine is prescribed in the following cases:
- spinal injuries, both acute and chronic;
- the presence of chronic pain in the spine, the cause of which is not clear;
- abnormalities of the spine;
- herniated intervertebral discs;
- tuberculous spondylitis (inflammation of the vertebrae);
- tumors of the spine and surrounding soft tissues, metastases of tumors to the spine from other organs;
- malformations (vascular anomalies), circulatory disorders in the spinal cord;
- osteomyelitis;
- preparation for surgery on the spine or spinal cord;
- monitoring the condition of the spine and spinal cord after treatment during the period of remission.
Contraindications for MRI
In some cases, MRI can cause some harm to health, and therefore doctors do not prescribe this research method to the patient. Common reasons for refusing magnetic tomography include:
- The first trimester of pregnancy (absolute contraindication), the second and third trimesters - for health reasons, strictly individually;
- The presence in the patient’s body of various metal implants for medical purposes (pacemakers, hemostatic clips applied to the vessels of the brain, wires in the bones, orthopedic structures, artificial joints, etc.);
- Fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia);
In addition, there are a number of absolute and relative contraindications to MRI.
Who is prohibited from performing MRI?
It is prohibited to examine patients with magnetic resonance if:
- there are metal objects in the body (implanted hearing aids, prostheses, plates, pins, staples, clips, knitting needles, rods);
- there are post-traumatic foreign “non-medical” objects in the body (bullets, fragments, metal shavings);
- an implanted pacemaker has been installed (except for MRI-compatible ones);
- there are non-ferromagnetic prosthetic heart valves installed less than 6 months ago;
- had vascular stenting surgery less than 1 month ago;
- a non-monoblock artificial lens was implanted (has wire legs).
Why can't MRI be done on patients with implanted metal objects? It should be understood that a magnetic field can cause displacement of ferromagnetic materials located in soft tissues, for example, prosthetic heart valves, clips on blood vessels, or metal fragments in the patient’s body. Metal products installed in bone formations (vertebrae, jaws, long bones) do not move under the influence of the tomograph magnet, since they are rigidly fixed in solid structures.
If you place a person with metal objects in his body under a tomograph coil, the magnetic field it creates can heat them up. It is difficult to predict how the product will behave inside the patient’s body. To avoid dangerous consequences after the procedure, patients with metal objects in the body should avoid MRI examinations.
MRI is not performed on patients who require constant connection to life support devices (artificial ventilation, round-the-clock monitoring, hemodialysis).
MRI for a child
For young children, MRI examinations are performed according to strict clinical indications in specialized clinics, usually using anesthesia. If it becomes necessary to have an MRI performed on an older child, parents should explain to him that the examination does not cause pain. The only inconvenience can be the loud sound of the tomograph (earplugs are required) and the duration of the examination procedure, during which it is necessary to lie still.
If diagnosing a disease in a child is possible without magnetic resonance imaging, then pediatricians try not to prescribe the study due to the inconvenience that is difficult for the baby to bear. If the study is still necessary, and the child is unable to remain motionless, sedatives and anesthetics are used. An MRI of a child under anesthesia is possible strictly after consultation with an anesthesiologist .