AST (aspartate aminotransferase, Ast) and ALT (alanine aminotransferase, Alt) are specific endogenous enzymes contained in the cells of human organs. They enter the blood only during pathological processes in cells. ALT and AST levels also increase during pregnancy, exercise, after taking certain medications, and liver disease.
The amount of AST and ALT in the blood is determined using a biochemical test. This is the most effective way to detect liver pathologies in the early stages. The fact is that at the very beginning, liver diseases are not accompanied by pain, because there are no nerve endings in the organ.
Pain in the right side that forces a person to see a doctor is most often caused by gallbladder pathology. Therefore, only regular biochemical blood tests will help detect liver disease in the early stages.
Normal levels of AST and ALT in the blood of women
Normal levels of AST and ALT in the blood of girls and women:
- AST - 0-31 units/l.;
- ALT - 0-35 units/l.
Normal values of AST and ALT in the blood of girls and women by age:
| Age | AST | ALT |
| newborns | 25-75 units/l.; | 48 units/l.; |
| 4-6 months | 15-60 units/l.; | 55 units/l.; |
| 3-6 years | 15-60 units/l.; | 32 units/l.; |
| 6-11 years | 15-60 units/l.; | 28 units/l.; |
| 11-18 years old | 15-60 units/l.; | 38 units/l.; |
| from 18 years old | Up to 31 units/l.; | Up to 35 units/l.; |
With age, the amount of AST and ALT in women decreases. Thus, the maximum level of ALT in the blood of a healthy woman over 50-55 years old is approximately 28 units/l. Closer to old age, its value varies from 5 units/l. up to 24 units/l.
Transferase levels in healthy girls and women can deviate from the norm by approximately 30%. This is a consequence of the following factors:
- stress, emotional outbursts/overloads;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- excess body weight;
- taking certain medications;
- sports stress, overwork, poor sleep;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages and drugs.
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is an enzyme that is found in all cells of the body, mainly in the liver and kidneys, less in the heart and muscles. Normally, ALT activity in the blood is very low. In cases of liver problems, the enzyme is released into the bloodstream, usually before characteristic symptoms such as jaundice appear. For this reason, ALT is often used as an indicator of liver damage.
Synonyms Russian
Serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase, serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase, SHPT.
English synonyms
Alanine aminotransferase, Serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, SGPT, Alanine transaminase, AST/ALT ratio.
Research method
UV kinetic test.
Units
U/L (unit per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous, capillary blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is an enzyme that is present primarily in liver and kidney cells and in noticeably smaller amounts in heart and muscle cells. In healthy people, activity in the blood is low, the ALT level is low. When liver tissue cells are damaged, ALT is released into the bloodstream, usually before characteristic symptoms such as jaundice appear. In this regard, the activity of this enzyme is used as an indicator of liver damage. Together with other tests that perform the same tasks, the ALT test is part of the so-called liver tests.
The liver is a vital organ that is located in the upper right side of the abdominal cavity. It is involved in many important functions of the body - in the processing of nutrients, the production of bile, the synthesis of proteins such as blood clotting factors, and also breaks down potentially toxic compounds into safe substances.
A number of diseases lead to damage to liver cells, which increases ALT activity.
Most often, an ALT test is prescribed to check whether the liver is damaged due to hepatitis and taking medications or other substances that are toxic to this organ. However, ALT does not always reflect only liver damage; the activity of this enzyme can also increase in diseases of other organs.
AST and ALT are considered the two most important indicators of liver damage, although ALT is more specific than AST. In some cases, AST is directly compared with ALT and their ratio (AST/ALT) is calculated. It can be used to identify causes of liver damage.
What is the research used for?
- To detect damage to liver tissue in viral and toxic hepatitis and other diseases. Typically, an ALT test is ordered together with an aspartate aminotransferase (AST) test.
- To monitor the effectiveness of treatment of liver diseases.
When is the study scheduled?
- For symptoms of liver disease: weakness, fatigue,
- loss of appetite,
- nausea, vomiting,
- abdominal pain and bloating,
- yellowing of the skin and eye whites,
- dark-colored urine, light-colored stool,
- itching.
- previous hepatitis or recent contact with hepatitis infection,
What do the results mean?
Reference values (ALT norm for men, women and children):
| Age, gender | Reference values | |
| 0 - 1 year | ||
| 1 – 4 years | ||
| 4 – 7 years | ||
| 7 – 13 years | ||
| 13 - 18 years old | ||
| > 18 years old | men | |
| women | ||
Normally, ALT activity in the blood is very low.
Causes of increased ALT activity:
- viral infections (excessively high ALT activity - more than 10 times higher than normal - is observed, for example, in acute hepatitis; in chronic hepatitis it is usually no more than 4 times higher than normal);
- taking medications or other substances that are toxic to the liver;
- diseases that slow blood flow to the liver (ischemia);
- bile duct obstruction, cirrhosis (usually as a result of chronic hepatitis or bile duct obstruction) and liver tumor (moderate increase in ALT).
In most liver diseases, ALT activity is higher than AST activity, so the AST/ALT ratio will be low. However, there are a few exceptions: alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis and muscle damage.
Important Notes
- Intramuscular injections, as well as intense physical activity, can increase ALT activity in the body.
- In some patients, liver damage and, as a result, an increase in ALT activity may be caused by taking dietary supplements. Therefore, it is necessary to inform your doctor not only about all medications you are taking, but also about nutritional supplements. In addition, frequent consumption of fast food can lead to a slight increase in ALT activity through liver damage; if nutrition is normalized, ALT activity returns to normal.
Also recommended
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Total alkaline phosphatase
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT)
- Serum albumin
Who orders the study?
General practitioner, internist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, hematologist, endocrinologist, surgeon.
Reasons for increased ALT
An increase in ALT levels may be due to:
- myositis;
- intrahepatic cholestasis;
- burns, severe intoxication, muscle injuries;
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- liver pathologies (hepatitis caused by viruses and alcohol, fatty hepatosis, cancer, cirrhosis);
- heart diseases (myocarditis and other pathologies that are accompanied by damage to myocardial cells);
- acute pancreatitis.
Also, the amount of ALT can be increased in cancer, progressive leukemia and obesity of III-IV degree. During a heart attack, this indicator practically does not change.
Major liver diseases
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammatory disease of the liver, most often of viral etiology. The most famous is Hepatitis A or Botkin's disease. It is also called jaundice.
Viral Hepatitis B and C almost always become chronic and lead to cirrhosis in 57% of cases and primary liver cancer in 78% of cases.
Alcoholic hepatitis stands apart . With regular alcohol intoxication, the liver develops processes of damage to hepatocytes and replacement of liver tissue with fatty or fibrous tissue with the development of fatty hepatosis and cirrhosis.
Rare forms of hepatitis include drug-induced hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, and bacterial hepatitis.
Hepatitis occurs as a manifestation of other infections: yellow fever, cytomegalovirus infection, rubella, mumps, Epstein-Barr virus infection, and various herpes infections.
Hepatoses
Unlike inflammatory liver diseases - hepatitis, hepatoses are degenerative-dystrophic diseases in which the functional activity of liver cells decreases, metabolism in hepatocytes is disrupted and liver tissue degenerates into fatty and/or fibrous.
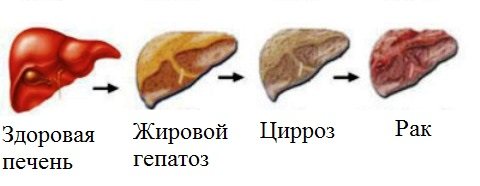
Hepatoses can develop independently or be a consequence of inflammatory or other liver diseases. In turn, non-inflammatory liver diseases are a prologue to the development of cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis of the liver
This is a chronic irreversible replacement of functionally active liver cells with rough fibrous tissue with the development of liver failure. In more than half of the cases, the cause of cirrhosis is chronic alcohol intoxication. In 25% of cases, cirrhosis develops after hepatitis B or C. When bile excretion is impaired, for example, with cholelithiasis, biliary cirrhosis occurs. The prognosis for cirrhosis is unfavorable.
Liver cancer
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a primary tumor of the liver. The greatest risk of developing liver cancer is observed with cirrhosis of the liver, viral hepatitis B and C, parasitic invasions of the liver, and alcohol abuse.
Metastasis to the liver is much more common when the primary tumor is located extrahepatically. Metastases are secondary foci of growth of any malignant tumor. They are formed when tumor cells penetrate the liver through the blood (hematogenous route) or lymphatic vessels (lymphogenous route). In tumors of the stomach, pancreas and mammary glands, large intestine, and lungs, liver metastases are detected in approximately half of the patients. In malignant tumors of the esophagus and melanoma, liver metastases are detected in a third of patients. In brain cancer, oral cavity cancer, prostate cancer, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, bladder cancer, and kidney cancer, metastases to the liver are extremely rare.
Parasitic liver diseases
Liver echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by the development of the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus in the liver. Other liver invasions: clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis, fascioliasis
Rare liver diseases
Liver hemangiomas are congenital or acquired abnormalities of the development of liver vessels. Non-parasitic liver cysts are a pathological cavity with a capsule filled with fluid.
Reasons for increased AST
Increased AST levels may be caused by:
- pancreatitis;
- poisoning (poisonous mushrooms, synthetic detergents, etc.);
- renal failure;
- cholestasis;
- pathologies (including cancer) of the liver and metastases in it;
- TELA;
- injuries, burns, muscle dystrophy;
- inflammations of an autoimmune and viral nature;
- heart diseases (angina pectoris, heart attack, myocarditis, rheumatic carditis, acute rheumatic carditis, cardiac surgery and angiography).
Heart disease is a common cause of increased AST levels after 45-60 years. Thus, as a result of a heart attack, the amount of AST increases by 2-20 times, while the ECG may not yet show signs of a heart attack.
If a high AST level persists on the 3rd day after a heart attack, the prognosis is poor. This may indicate both the growth of the infarct focus and the penetration of infection into other organs.
Liver tests. Diagnostic value in detecting liver diseases.
The insidiousness of liver diseases is that pain and other symptoms and signs appear in the later stages of the disease, when irreversible changes occur. Liver tests are an informative and cost-effective way to monitor the condition of the liver in both healthy and sick people. The cost of this analysis in Varna is 15 leva. It must be completed annually, and in the case of chronic liver disease or alcohol abuse - twice a year. Liver tests acquire the greatest diagnostic value in the early diagnosis of liver diseases with regular examinations and medical monitoring of the dynamics of laboratory parameters and clinical data.
Who needs AST and ALT diagnostics
If liver disease is suspected, experts recommend checking the concentration levels of ALT and AST. The following are symptoms that should promptly consult a doctor:
- high irritability, sleep disturbances;
- disruption of menstruation;
- frequent nausea and vomiting;
- itching (palms, soles of feet, back);
- pain or feeling of heaviness in the right side;
- blood clotting disorder;
- yellowish skin tone;
- frequent allergies.
A blood test for AST and ALT must be taken once a year for patients who are at risk, including:
- contacting people with viral hepatitis;
- alcoholics, drug addicts;
- working in hazardous industries;
- having a hereditary predisposition to diseases, which are indicated by high concentrations of AST and ALT.
Tests for AST and ALT are also required for donors before donating blood.
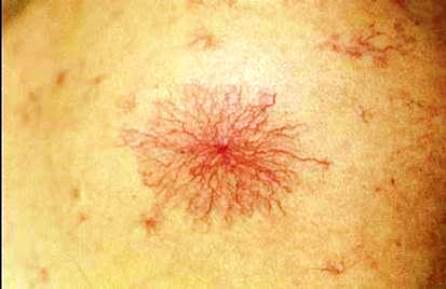
Symptoms and signs of liver pathology
- Discomfort and pain in the right hypochondrium
- Enlarged liver, sometimes enlarged spleen
- Bitterness in the mouth
- General weakness and fatigue
- Headache
- Symptoms of encephalopathy
- Increased sweating, edema, abdominal swelling (ascites)
- Yellow coloration (icterus) of the skin, mucous membranes, sclera
- Itchy skin, skin rashes
- Bleeding
- Digestive disorders, stool discoloration
- Dark foamy urine
- Spider veins
Rules for donating blood for AST and ALT analysis
One day before the test, you should refrain from physical activity and drinking alcohol, and try not to be nervous.
In the evening you can eat something light. Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach, and it is taken from a vein. The interval between the last meal and the test must be at least 14 hours. The patient is allowed to drink only water.
If you need to take the test during the day, you should fast for at least 4 hours before taking blood.