BLD in a urine test is most often not a good thing. This parameter in the test results may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary area or in the kidneys. Naturally, if the parameter value exceeds the norm.
A person very often takes tests to diagnose the body, but has no idea what the medical terms on the test form say. What is BLD in urinalysis? What can red blood cells tell you about in urine, what danger do they pose to humans? Pathology or physiology?
What does urine analysis include?
During a urine test, physical parameters are assessed and the presence of sediment and organic matter is determined. Attention is also paid to transparency, smell, color. Optimal urine should be yellow, shades may vary. If it is brown or almost black, then there is a suspicion that hemolytic anemia is observed in the body, the development of malignant tumors or poisoning occurs. A red tint may indicate inflammatory processes, injuries, or renal infarction. Pink – about defects in hemoglobin production. The BLD CA norm in a urine test will be presented below.
If a person suffers from diabetes, then his urine is pale or colorless. A milky color occurs when there is a high concentration of phosphates, fats or pus. In addition, the shade may be affected by the foods consumed before analysis.
Normally, urine is clear, but due to salt deposits it gradually becomes cloudy. The smell, although specific, is not too strong. If the aroma of ammonia is felt, then there is reason to judge inflammation. The smell of apples is typical for diabetics. The urine smells sharp in those who eat sweet-smelling foods or take strong medications. It's quite normal. But what does BLD mean in a urine test?
Acidity should be 7.0. If the urine is slightly acidic, then this indicator is lower. Increased acidity is observed with kidney pathologies, stones, and fever.
A very significant indicator is density, which is denoted by the abbreviation SG. It reflects the concentration renal function. Optimal indicators range from 1003 to 1028, but small fluctuations are acceptable. In men, the specific gravity of urine is higher. If deviations are observed in one direction or another, this indicates pathological processes or diseases.
Let's look at how a BLD trace urine test is performed.
Provoking factors
The physiology that causes red blood cells includes the following:
- Mental as well as physical fatigue.
- Regular stressful situations.
- Staying in the mountains where there may be a lack of oxygen.
- Poisons and toxins that humans often have to deal with.

This is what BLD means in a urine test.
The human body has one peculiarity: it is able to adapt to all kinds of conditions, so in some situations the detection of red blood cells may be a completely normal indicator for an individual case. Pathologies that cause BLD include the following diseases:
- Presence of renal failure.
- Inflammatory processes in the genital area.
- Development of urolithiasis along with cystitis.
- Presence of cancer of the kidneys and gallbladder.
Urine analysis for organic substances
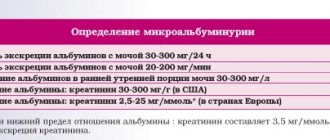
Protein scores are designated Pro. They should not exceed 0.03. In diabetics, MAU readings should be within the range of 4.25 mmol. From this result you can learn about the reversibility of kidney damage. Its level is monitored to monitor pathologies in order to begin treatment in a timely manner.
The glucose level is designated Glu. The best result is no sugar. If it is present, then we can talk about the presence of diabetes mellitus.
Bilirubin is designated as Bil. The ideal is its absence. If bilirubin is present, gallbladder or liver problems may occur. The explanation of BLD in urine analysis is presented below.

Urobilinogen (aka URO) is designated UBG and should be present in urine. This indicator is used to diagnose the condition of the blood, liver, the absence or presence of stones, and infections.
If there are ketone bodies in the urine, that is, Ket, then the patient may have diabetes mellitus. Such bodies appear after poisoning, stroke or anesthesia.
Ascorbic acid is designated Asc. The urine of a healthy person includes it in amounts of up to thirty milligrams. The BLD norm in urine analysis is of interest to many.
Using a microscope, urine is checked for leukocytes, designated as Leu; for men its indicators should be no higher than three, and for women – no more than five. If there are deviations, then we can judge about inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system.
Malignant tumors and inflammation present in the body will be reflected in the urine in the form of red blood cells, or Bld. In a urine analysis, based on their quantity, one can draw a conclusion about the progression of pathologies and the effectiveness of the therapeutic course. Red blood cells may appear in a woman's urine after she gives birth to a baby.
Urinalysis is a very good way to determine the condition of a person's body.
Basic Concepts
This indicator reports the number of red blood cells contained in the urine. When indicating “BLD” in the analysis, the norm for this value should be no more than three units for women. For men, this indicator should be within one unit. The value of red blood cells may be increased, which will indicate the development of hematuria in a person. Red blood cells increase in infectious diseases of the excretory canals, for example, with cystitis, hemorrhagic diathesis, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis.
Deciphering BLD in urine analysis should be carried out by professionals.
In addition, red blood cells in the analyzed urine may increase due to kidney injuries, as well as against the background of arterial hypertension, or after poisoning with toxic chemicals. Women's urine may contain blood that enters it during menstruation, which can also affect increased red blood cell counts. Normally, BLD is completely absent in the urine analysis of a healthy patient, or red blood cells can be detected through microscopic examination, but no more than two cells.
Types of red blood cells
In a healthy person, a normal indicator in urine sediment is either the absence of red blood cells, or their detection during microscopic analysis in an amount that does not exceed two cells in the preparation (that is, in all fields of view). An increased concentration of red blood cells is called hematuria. If the presence of blood in urine can be detected visually, that is, the urine has a red tint, then gross hematuria can be judged.
In this situation, during microscopy of urine sediment, the entire field of view will be covered with red blood cells, that is, the norm will be exceeded many times. If the number of red blood cells in urine is small, then it is impossible to notice blood with the naked eye, since the urine will have a normal color. Red blood cells are determined only through microscopic examination. In this case, we can talk about microhematuria. This is what BLD means in a urine test.
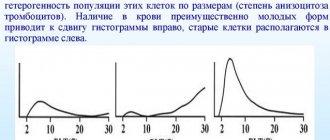
The appearance of red blood cells changes depending on the specific gravity and reaction of the urine. Red blood cells can be in the urine either unchanged (fresh) or changed (leached).
Unmodified red blood cells contain hemoglobin; their shape resembles greenish-yellowish discs. This species is found in alkaline, neutral and slightly acidic urine.
Changed red blood cells occur during long-term exposure to acidic urine. They do not contain hemoglobin; in appearance they resemble colorless rings. Such red blood cells are called leached. In addition, the changes are wrinkled red blood cells, which are found in urine with a high relative density, and with a low relative density their diameter increases. With prolonged standing of urine, red blood cells transform into an altered type. We have explained what BLD means in a urine test.
To determine the source of hematuria, the classification of red blood cells into unchanged and changed is not of great importance, since in the overwhelming majority of cases their transformation is influenced by the chemical and physical characteristics of urine. Leached red blood cells may indicate renal origin of hematuria when detected in freshly released urine.
The main property that may suggest a renal origin is the appearance of casts and protein in urine along with red blood cells. Most often, red blood cells appear in the urine due to various diseases of the urinary tract and kidneys. In some cases, hematuria begins after intense physical activity, but in such situations, red blood cells increase for a short period.
What to do if red blood cells are found in the urine
Blood in the urine is not an underlying condition. The doctor, having found out the cause, prescribes medications. If a tumor is found, surgical methods are used to remove it.
Important! You cannot independently treat serious diseases associated with the genitourinary system. The result may be deterioration of the body's condition or its death.
Immediate therapeutic measures
Immediate medical measures are taken in case of massive blood loss. The doctor must find the source of bleeding and stop it. Another case is an infectious disease that can cause sepsis (blood poisoning). Emergency treatment is carried out with broad-spectrum antibiotics through droppers. If antibiotics do not work within 3 days, they are changed to a drug from a different group.
If malignant neoplasms are detected that cause bleeding, emergency surgery is performed with excision of the tumor.
Diet for hematuria
If false hematuria is detected due to staining of urine with food, reduce the amount of food consumed. The dosage form is treated by changing drugs. The patient should not eat fatty, fried, salty, or spicy foods. Alcohol is excluded, it negatively affects kidney function.
Vegetables and fruits should predominate in a person's diet.
If edema and hypertension are observed, a person needs to reduce water intake. If the cause is an infection, drink more water.

Doctor's advice
The main advice that a doctor will give is that you cannot treat a disease of the genitourinary system on your own. A pediatrician or nephrologist prescribes medications depending on the cause of bldg in urine.
- Drugs that stop bleeding (Vikasol). Droppers are prescribed to replenish fluid loss.
- Injuries with massive bleeding caused by tumors or stones are treated surgically.
- If small stones are found in the ureter or urethra, antispasmodics and heat compresses are used to remove them. Large stones are removed surgically.
- The infection is treated with antibiotics. Before using them, a BAC test is carried out to test the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics.
- Physiological erythrocytosis of urine in pregnant women is not treated. This condition is associated with the growth of the uterus.
What does BLD indicate in a urine test?
So, BLD in the analysis are red blood cells, and their detection in urine is a negative symptom. If BLD is detected in the urine, then we can most likely talk about inflammatory processes occurring in the genitourinary area, or about pathological renal changes. If more than three units of red blood cells were found in the urine, then in medical terminology this situation is called hematuria, which has its own classification:
- microhematuria - in this case, the urine is of normal color, but red blood cells are detected in microscopic sediment;
- gross hematuria - with this type of disease, the urine becomes red or brown in color;
- renal - otherwise called renal, it allows you to detect kidney pathologies, heart attacks, injuries;
- extrarenal - its appearance is possible during inflammatory processes in the genitourinary area, and is a consequence of diseases such as urethritis, prostatitis and cystitis.
If red blood cells are detected in a urine test (BLD trace), the attending physician usually prescribes an additional examination for the patient. If the result of the secondary analysis is positive, there will be no doubt about the pathological transformations of the urinary tract and kidneys. The most common disease is hematuria, which is particularly common. The most dangerous form of all of the above is considered macrohematuria, which is accompanied by such pathologies as:
- malignant tumors of the renal pelvis;
- kidney cancer;
- malignant formations in the bladder and ureter;
- renal tuberculosis.
If a person is healthy, then there are no red blood cells in his urine. If they are detected in the urine, it is necessary to conduct repeated tests to refute or confirm the diagnosis.
Changed and unchanged red blood cells
Excessive presence of red blood cells is called hematuria. The presence of blood in this biological material is determined visually, since in this case the urine acquires a red tint. In such a situation they talk about macrohematuria. With macrohematuria, as part of a microscopic examination of the sediment, red blood cells will cover the entire field of view, that is, they will be many times higher than normal.
If there are a few red blood cells in the urine, then the blood will not be visible to the naked eye, since the biomaterial has a normal color. In this case, the BLD content in urine analysis is determined exclusively by a microscopic method. This phenomenon is called microhematuria.

Decoding BLD in urine analysis
A person comes to the clinic when something in his condition causes concern. The doctor should immediately write him a referral for tests. The most informative and common is a general urine test, which immediately reflects all the malfunctions in the body. However, an ignorant person is unlikely to be able to understand the terms.
Each indicator has its own standards, BLD in urine analysis is no exception, and if all of them are within these limits, then the patient does not need to worry, since there are no pathologies. But if any value is exceeded, we can talk about some kind of inflammation.
So, there should be no BLD in urine, and if the results are positive after repeated tests, you should sound the alarm and start treatment immediately.
Is it possible to have a false result from this test?
An increase in ubg, bld or any other indicator in a urine test is always a pathological symptom. But not in all cases the data from a general urine test can be considered reliable! Too many factors influence the result of such a diagnosis.
A false positive reaction can be caused by insufficient sterility of the urine collection container. In addition, during the collection of biomaterial, the relevant rules must be followed. To prevent foreign impurities from getting into the urine, you must wash yourself thoroughly before such a procedure. Failure of laboratory equipment can also affect the results of OAM.
That is why, if BLD is present in the urine, control testing is mandatory. Repeated analysis allows us to clarify the data of the first study.
It is possible to get false blood levels in the urine during a general examination for another reason. This discrepancy is caused by several physiological factors:
- altitude sickness;
- severe dehydration;
- eating too spicy and salty food the day before;
- negative effects on the body of toxins and toxic substances;
- period of menstruation in women;
- stress loads;
- hard labour.
If, even after re-diagnosis, bldg is detected again in the analysis, the patient should urgently visit a qualified specialist. Only a doctor can help establish the true cause of this disorder and eliminate it in a timely manner. Remember that the presence of blood cells in the discharge is also characteristic of cancer. It is advisable to identify and eliminate malignant tumors at the earliest stages of development.
Increased levels of bld in urine are too dangerous a clinical sign. That is why a specialist should treat such a disorder. Hematuria does not go away on its own, so do not ignore this pathological symptom and visit a doctor in time.
What is the reason for the increase in red blood cells?
If, after a general analysis of urine for red blood cells, a positive result was obtained, then this indicates a number of factors. In this case, pathological transformations in the genitourinary system and kidneys can be observed. In addition, the result may be false positive, which is determined by the physiological specifics of the human body.
Often, red blood cells are detected as a result of dehydration, a lack of fluid in the body. Water deficiency is caused by vomiting and stomach upset.
During physical activity, athletes lose large amounts of fluid, which can also cause BLD to appear in urine. After restoring the water balance in the body, red blood cells disappear.
The physiological factors that cause the appearance of BLD SA in urine analysis (we examined the norm) are:
- the temporary nature of the manifestation of red blood cells in urine, for example, after a person is in a hot workshop or in a hot bath, which causes overheating of the body;
- increased physical and mental stress;
- due to the increased content of glucocorticosteroids in the blood, which can often be associated with stress experienced by a person;
- when in mountainous areas where there is a lack of oxygen;
- poisons and toxins that people often encounter;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages, which causes the risk of vascular spasm, which causes the appearance of red blood cells in urine after drinking alcohol;

- a large number of spices in food.
In addition, urine may turn red not because it contains an excess amount of red blood cells, but because the concentration of hemoglobin in its composition is increased. When hemolysis develops, the red blood cells contained in the blood are destroyed, and this is typical for defects in urine filtration in the kidneys, and it all ends in acute renal failure.
It is worth noting that the human body is unique in the sense that it can adapt to the influence of various factors, and in a number of situations, the detected red blood cells can become a normal indicator for a particular person. Pathologies that cause BLD include the following diseases:
- kidney failure: ten cells;
- vulvitis, inflammation processes in the genital area, in the uterus: up to ten cells;
— cystitis, urolithiasis: 50 rbc/ul;
— diseases of the bladder and kidneys of an oncological nature: 250 rbc/u l. BLD trace-lysed in a urine test means traces of red blood cells. Normally they shouldn't be there.
If the red blood cells increase to two hundred and fifty cells, then this poses a serious danger to human life. The patient is urgently hospitalized, additional diagnostics are performed: biopsy, ultrasound, blood biochemistry, after which a therapeutic course is prescribed.
What else does BLD show in a general urine test?
The role of red blood cells (bld) in the human body
Red blood cells, passing through stages of development, combine with protein - hemoglobin. Together, they add oxygen, transporting it to its destination (organ, tissue). By giving away an oxygen molecule, they receive carbon dioxide in return. Its delivery is carried out to the lungs.
The next function is immune. On their surface, blds have receptors with which they bind antigen (foreign microorganism). Red blood cells carry it to the liver, where destruction occurs.
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which provides balance in the body, acting as a buffer.
Red blood cells take on certain types of amino acids, carrying them from the digestive system to tissues. Thus, they perform a trophic (nutritional) function.
Blds participate in acid-base and water-salt metabolism, maintaining their balance.
Renal type of red urine
In this case, urination simultaneously with blood is recorded in the patient against the background of such kidney pathologies as:
— autoimmune disease of the canals and glomeruli of the kidneys with acute or chronic glomerulonephritis;
- kidney cancer;
- urolithiasis disease;
- infection with pyelonephritis;
- hydronephrosis;
- a stab wound to the renal surface or a significant bruise - in such a situation, blood clots in the urine can take on the appearance of gross hematuria.

Hematuria
The most common disease, which occurs very often, is hematuria. Of all the above forms, macrohematuria is considered the most dangerous, which develops against the background of the following diseases:
- Presence of kidney cancer.
- Oncological diseases of the renal pelvis.
- Malignant neoplasms in the ureter and bladder.
- Presence of renal tuberculosis.
In a healthy person, the presence of red blood cells in urine should not be observed. And if they are detected in the urine, as has already been reported, it is necessary to take repeated tests in order to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis.
Postrenal type
To determine that the symptoms of hematuria in a patient are caused precisely by postrenal causes, it is necessary to conduct an examination, which may reveal inflammation in the urethra or bladder:
- due to damage to the mucous membrane of these organs by sand or stones;
- against the background of cystitis, both in women and men;
- for oncological neoplasms;
- during hard sexual intercourse, which damages the mucous membrane of the urethra;
- injuries to the urethra or bladder with simultaneous bleeding and vascular damage, which are accompanied by symptoms of gross hematuria.
Red blood cell norm
Normally, the color of urine should be from light yellow to yellow, and red blood cells in its sediment should not be detected. However, it should be remembered that its color may change under the influence of various dyes; for example, after eating beets, its tint may be pinkish. On general clinical test forms, blood in the urine is indicated by the abbreviations “KRO” or “BLD.” Normally, opposite these designations there is a “NEG” symbol, which means a negative result.
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Ask a question to an expert
, up to 3 red blood cells may appear in the field of view after heavy physical work, after prolonged strength exercises, or while standing for a long time. In this case, the patient is re-referred for a general analysis.
The determination of red blood cells in quantities exceeding the norm is recorded with the symbols “+”, “++”, “+++”, which means their number or numerical values.
Red blood cells in urine analysis in children
The norm for children in terms of the number of red blood cells should be no more than six in the field of vision for girls and four for boys. If their content is increased, this is called erythrocyturia. If the urine turns red due to too many red blood cells, then in this case we are talking about hematuria.
Since urine during its formation goes through a long path, starting in the kidneys and ending with the urethra, each of the sections along the way can become a source of red blood cells. What does BLD CA 25 ery/ul mean in a urine test? More on this below.
If significant defects in the formation of blood clots and the coagulation system are observed, then the red blood cells in urine are of extrarenal origin. They are detected in hemolytic anemia, low platelet count or impaired platelet activity, hemolytic-uremic syndrome and coagulopathies.
Renal red blood cells occur with glomerulonephritis, hereditary nephritis and IgA nephropathy.
If the calyces and pelvis are damaged due to vascular defects, carcinoma, kidney injuries, urolithiasis and cystic diseases, then the shape of the red blood cells during microscopy is unchanged, but their number is increased.
Since the movement of stones from the kidneys occurs along with the flow of urine, the urinary tract and its components are damaged: the bladder, ureters, urethra, as a result of which red blood cells appear in the urine.
With acute or chronic rhinitis, after catheterization of the bladder and with urethritis, red blood cells in the urine may also be increased. In a urine test, a BLD CA of 25 means that 25 red blood cells are detected per field of view.
Pathologies associated with the detection of red blood cells
If red blood cells are found in the urine, this is not a disease. It is necessary to look for the root cause that led to this condition. Most often, hematuria is a consequence of disorders in the urogenital tract. There are different causes of hematuria in children, women and men. Some of them are pathological (deviations from the norm), others are physiological (exist during the normal development of the body).
Hematuria in men
The urine of men may be yellow, but if red blood cells are found in it, it is necessary to take a repeat OAM and undergo additional tests. If the urine turns red, a serious illness has developed. There are the following causes of hematuria in men:
- bacterial infection of the urinary system: cystitis (in acute inflammatory processes of the bladder), pyelonephritis (purulent inflammation of the kidneys);
- kidney disease (glimerulonephritis, renal failure);
- diseases of other organs and systems (hemophilia, sickle cell anemia, arterial hypertension);
- the presence of stones that damage the mucous membrane with sharp edges;
- tumors benign or malignant;
- prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate);
- high sexual activity (microscopic hematuria in this case is more common in men than in women);
- high physical activity;
- damage in the area from the kidneys to the urethra;
- taking medications (blood thinners, antibiotics, hormones).
A change in the color of urine does not always indicate problems in the body. This happens for physiological reasons when a person consumes certain foods (blueberries, beets, blackberries) or artificial colors.
After detecting hematuria in men, the doctor conducts a survey and additional studies:
- Taking an anamnesis, studying family history.
- Digital rectal examination to determine or exclude prostatitis. During the examination, pain may occur, which indicates an enlarged prostate gland and possible hyperplasia (enlargement). If a nodule is palpable, the possible cause is cancer.
- Additionally, a full blood test, blood biochemistry, and ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys are performed. Cystoscopy uses a tube with a camera that is inserted into the urethra. The doctor examines the bladder for damage, stones, and tumors.
Hematuria in women
If a small number of red blood cells are found in a woman’s blood, this does not always indicate the presence of a pathological process. Hematuria can be caused by physiological processes:
- eating foods that cause red urine (beets);
- pregnancy (release of red blood cells into the urine due to compression of organs by the fetus);
- taking OAM during or immediately after the end of menstruation.
There are pathological causes:
- diseases causing mechanical damage (stones);
- infectious diseases of the urinary tract, in which bacteria damage the walls of blood vessels (pyelonephritis);
- inflammatory changes in the urethra (cystitis);
- taking medications (hormonal contraceptives, antibiotics) that cause blood stagnation and the release of blood clots;
- dysfunction of the genital organs, leading to disruption of the menstrual cycle.
Red blood cells in urine in pregnant women are a common occurrence. In the early stages, the cause is hormonal imbalance. In later stages, the fetus puts pressure on the mother’s internal organs, causing damage. During childbirth, damage occurs that causes postpartum hematuria.
What can red blood cells in a child’s urine indicate?
Changed red blood cells (due to impaired renal function) and unchanged ones (through the bladder, urethra) enter the child’s urine. In children, hematuria occurs in cases of serious illness. Therefore, parents should immediately contact a pediatrician or nephrologist to carry out drug treatment.
Possible reasons:
- intoxication of the body with dilation of the renal tubules (gastrointestinal infections, viruses, meningitis, sepsis);
- kidney pathologies (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, kidney tuberculosis);
- traumatic conditions (urolithiasis)"
- disorders in the urinary tract (cystitis, urethritis, phimosis in boys);
- temporary erythrocytosis (poor diet, consumption of food dyes and coloring foods);
- metabolic disorders;
- taking medications;
- anatomical anomalies (congenital disorders of organ formation) of the bladder, kidneys;
- prostatitis of early age.
With false hematuria (arising not due to erythrocytosis), pigments, rather than bld, are found in the TAM.
Increased red blood cells in urine in men
In some situations, men (especially older men) may need complex therapy for hematuria in the presence of prostate pathologies.
Blood under such circumstances means:
- A cancerous tumor in the prostate gland that can cause bleeding.
— Inflammatory processes in the prostate, as a result of which red blood cells mix with urine. BLD - trace intact - what is this in a urine test? This means there are no red blood cells in the urine, which is good.
Reasons for increasing the level
If, when interpreting urine tests, the bld value deviates upward, this always indicates the presence of health problems. The level of red blood components in the secreted fluid varies depending on the age or gender of the patient. For a man this figure is 0-2 red blood cells, for women it is 0-3. The norm of blood cells in a child’s urine is 0-1 cells, visible through a microscope lens.
The presence of blood in a urine test has its reasons. The following diseases can cause such a disorder:
- Kidney diseases of an infectious nature - glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular tract – hypertension.
- Urolithiasis - solid elements may have uneven or pointed edges that cut through the mucosa and cause bleeding in the lumen of the ureters and bladder.
- Poisoning by toxins and toxic chemicals.
- Damage to the walls of the urethra after catheterization and other medical interventions.
- Inflammatory processes in the urethra.
- Hemorrhagic diathesis.
What does the quantity 10 rbc/ul mean?
The determination of erythrocytes in urine in the amount of 10 cells per field of view can be observed in chronic renal failure, nephrotic syndrome, and pyelonephritis. Also, a small amount of them can be detected during inflammation of the reproductive system in women (endometritis, cervical erosion, vulvitis). You can also differentiate kidney disease from inflammatory diseases of the genital organs through a general clinical urine test, paying attention to the following criteria.
In chronic renal failure, leukocytes are also found in small quantities. The main sign indicating chronic renal failure is a decrease in urine density (“SG” on the form) to 1.010. Traces of mucus and single cylinders are also found.
Nephrotic syndrome is indicated by a protein content of up to 40 g/l, up to 20 leukocytes and a large number of cylinders.
Pyelonephritis is characterized by a large number of leukocytes up to 100, a low protein content - up to 2 g/l, and the presence of casts, bacteria and mucus.
This number of red blood cells in the urine test form is also indicated by the “+” symbol.