Just a few decades ago, surgical treatment of diseases of the reproductive system could permanently deprive a woman of the opportunity to become pregnant in the future. Developments in modern medicine make it possible to reduce surgical intervention in the treatment of gynecological diseases to a minimum - laparoscopy is used instead of abdominal surgery. Pregnancy after laparoscopy is as likely to occur as in healthy women, and in some cases the chances of success are even increased.
Pregnancy after ovarian laparoscopy
This type of surgery is usually performed in cases of treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, endometriosis and removal of ovarian cysts. After the operation, the ovaries restore their function within just a few days.
Due to the fact that the operation is quite complex, pregnancy after ovarian laparoscopy should be planned under the supervision of the attending physician. There is a high probability that if conception is successful in the first months after surgery, a woman may require hormonal maintenance therapy.
— Why is laparoscopy becoming more and more popular in the West and in Russia?
“This technique has high diagnostic capabilities, allows you to immediately proceed to surgical correction of the identified pathology and, in most cases, avoid large and traumatic open surgery, reduces the time patients stay in the hospital, reduces the cost of treatment, reduces the percentage of formation of postoperative adhesions, and is easily tolerated by patients. Laparoscopy has changed the face of classical surgery, allowing the doctor to effectively solve diagnostic and therapeutic problems without leaving traditional marks on the patient’s body.
Pregnancy after laparoscopy of uterine fibroids
Laparoscopy is an extremely effective method for treating uterine fibroids, as well as various malformations of the uterus. However, this type of operation is not performed in the following cases:
- low location of myomatous nodes;
- strong enlargement of nodes;
- presence of a large number of nodes;
- enlargement of the uterus to a size exceeding the size of the fetus at 11-12 weeks of pregnancy.
You can plan to conceive after laparoscopy of uterine fibroids no earlier than 3-4 weeks.
Carrying out
Laparoscopy is performed in stages:
- Anesthesia is administered. The anesthesiologist consults the patient in advance, determines the tendency to allergic reactions, and selects the dosage of the anesthetic.
- 2-4 thin incisions are made in the suprapubic and umbilical zones to insert instruments and a micro-video camera through them. The abdominal area is pre-filled with carbon dioxide to “move it aside” (pneumoperitoneum), expanding the surgical area to improve visualization.
- Using manipulators, the doctor controls the instruments while monitoring the process on the screen.
- After eliminating the problem, a detailed examination of the operated organ and the entire space around it, the laparoscope is removed. The punctures are sutured or only treated with an antiseptic and a sterile bandage is applied without stitches.
The entire operating process is displayed on the monitor and controlled by a computer system. This almost eliminates errors during laparoscopy, which takes no more than an hour. There is no blood loss or it is minimal - up to 15 ml. After a few hours, if you feel normal, you can leave the hospital. With the help of laparoscopy, you can remove uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, cut adhesions, restore the patency of the oviducts, perform an audit of the reproductive organs - everything that will help lead to a healthy pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy and laparoscopy
Unfortunately, 10-15% of women experience a pathology such as ectopic pregnancy. After laparoscopy in this situation, the patient’s fertility is preserved due to the preservation of the fallopian tube during the operation. In this case, the doctor removes the fertilized egg from it.
The earlier an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed, the lower the risk of complications.
After laparoscopy, the doctor individually determines the time when a woman can begin planning a pregnancy.
Recommendations from the MAMA Reproduction Clinic
Our task is to do everything possible to ensure that you have healthy children and that you, their parents, are happy. Our doctors are engaged in scientific activities, which allows the MAMA Reproduction Clinic to offer its patients unique opportunities. All you need to do to benefit from our years of experience is call and make an appointment.
You can discuss the required scope of examination with the Clinic doctor at your initial appointment.
Take the first step - make an appointment!
or call 8 800 550-05-33
free phone in Russia
Laparoscopy as a method of combating infertility
This type of surgery is currently one of the most effective ways to combat infertility. Pregnancy in patients after the procedure is observed within a year in 85% of cases. Laparoscopy allows you to determine the exact cause of infertility in a woman, and in some cases, during the operation, eliminate it.
Using laparoscopy:
- adhesions in the fallopian tubes are separated;
- normal ovarian activity is regulated;
- neoplasms of benign and malignant nature are removed;
- ovulation is restored.
After eliminating the causes of infertility using a treatment method such as laparoscopy, intrauterine pregnancy can be expected in the near future.
In most cases, pregnancy occurs within one calendar year after laparoscopy. You can start trying to conceive as early as 4-6 weeks after surgery. According to statistics, in 20% of women pregnancy occurs immediately, in 20% over the next 3-5 months, in 30% of patients attempts to conceive become successful within 6-8 months. The remaining 15% of women prepare for pregnancy within a year.
There are still 15% of patients who do not become pregnant within a year. In cases where laparoscopy was performed to eliminate adhesions in the fallopian tubes, repeating the procedure may lead to successful conception.
Preparation
Before laparoscopy, the patient undergoes a medical examination, her anamnesis and medical record are studied, and basic tests are taken:
- blood, urine;
- coagulogram;
- biochemistry;
- RV, HIV, hepatitis;
- FLG, ECG;
- ultrasonography (transvaginal or abdominal);
- colposcopy;
- cervical smears for oncocytology and microflora.
If based on the results there are suspicions of other diseases, then an additional examination is prescribed. This may be a polymerase chain reaction (PCR), MRI, or biopsy. If PCR shows an infection, then laparoscopy is postponed until recovery, since acute or chronic inflammation from the acute stage is a temporary limitation to the procedure. If magnetic resonance imaging reveals metastases or a primary cancer site of a different location (not in the reproductive area), then a completely different approach is chosen for treatment. Pregnancy can occur after successful elimination of non-metastatic cancer or a benign tumor. Biopsy material from the suspicious area is taken during the laparoscopy itself.
You need to prepare as for any intervention: do not eat foods that increase gas formation, and cleanse your intestines with an enema the day before. The timing of the planned implementation is 7-10 days before the expected ovulation.
You have questions?
You can contact the leading specialists of the AltraVita clinic
Laparoscopy during pregnancy
Laparoscopy is the most favorable method of surgical intervention during pregnancy. The risks of complications threatening the health of the mother and fetus are minimal. As a rule, if the need arises, surgery is performed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, but surgical intervention at any other stage cannot be ruled out.
Laparoscopy during pregnancy is performed for the following indications:
- necrosis of myomatous node;
- cancer;
- benign ovarian tumors;
- appendicitis;
- torsion of the uterine appendages.
- What is laparoscopy?
— Laparoscopy
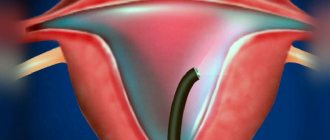
I is an examination of the abdominal cavity through an opening in the abdominal wall using the optical system of a laparoscope. There are three types of laparoscopy. Diagnostic - visual examination of the abdominal organs using an additional manipulator (usually proceeds to the surgical stage). Operative - almost the entire scope of gynecological operations is performed, including hysterectomy. Control - carried out to monitor the effectiveness of previously performed surgical treatment. According to the time of implementation, laparoscopy is divided into planned and emergency. Laparoscopy can be either a stand-alone operation or combined with hysteroscopy or vaginal surgeries.
Is it possible to get pregnant
The issue of being able to get pregnant and bear a child is extremely important for many women. The chances of pregnancy depend on the extent of resection that was performed during surgery. If the fallopian tube was removed on only one side, then pregnancy is possible naturally. In the case where the removal of the affected part of the organ was bilateral, pregnancy cannot occur naturally.
However, this does not mean that a woman will never be able to give birth to a child. Most tubal removal surgeries do not involve the uterus or ovaries. IVF techniques allow a woman to become pregnant. A woman's egg is collected by aspiration from the ovary. A man, the future father of a baby, donates sperm. The role of the fallopian tube is taken on by a fertility doctor. In the laboratory, special conditions are created for the fertilization of an egg outside the body. The embryo then grows and develops for several days. This period corresponds to the journey of the zygote through the fallopian tube to the uterus. On the 4-5th day, embryos are implanted into the uterus, where implantation of the embryo and its subsequent development occur naturally.
Back to list of articles
How is the operation performed?
First, the artery is punctured. A probe is inserted into the incision and moved through the vessel under X-ray control. The catheter is clearly visible on the monitor screen. To identify the vascular pattern, a contrast agent is injected into the lumen of the artery. With the blood flow it moves to smaller vessels. After this, special embolic particles are introduced. They are the ones who clog the lumen of blood vessels. The arteries supplying nutrition to the organ are not affected. Thanks to this, you can save it.
Currently, there are a number of irrefutable statistical data and scientific research results on the impact of this procedure on the likelihood of conceiving a child and the successful development of pregnancy. These data indicate that the possibility of conceiving a child is higher after uterine artery embolization compared to other methods of surgical treatment.
The pregnancy rate after embolization is high. It is significantly higher than the rates obtained from studies of women who underwent the procedure through myomectomy. Even large fibroids are removed fairly quickly.
Important! Pregnancy may not occur for a number of other reasons. Various gynecological problems (hormonal disorders, incompatibility with a partner, chronic infectious diseases, etc.) become obstacles to conception.
That is why before planning a pregnancy you should definitely undergo a full examination.
Possible complications
If conception occurs with endometriosis, there are dangerous periods during which the risk of complications is high. First of all, these are the first two months when the placenta is formed - there is a risk of spontaneous abortion. At week 20, there is a risk of fetal development faltering; after week 24, bleeding may occur due to placental abruption. A rather serious complication is bleeding, which can be caused by ruptures of the vessels of the uterus, ovaries, or bleeding of the endometriotic zones. Premature birth is also possible.
Is pregnancy possible with one fallopian tube?
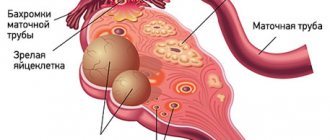
If the condition of the second fallopian tube is suitable for conception, then pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy with removal of the tube is possible. Fertilization of an egg by a sperm occurs in the lumen of the fallopian tube, so if a woman has only one tube, but it is passable, then the chances of becoming pregnant are quite high.
Ovulation in a healthy woman occurs alternately in the right and then in the left ovary, respectively, and conception can occur in both the right and left fallopian tube. If the egg matures in the ovary on the right for one month, but the right tube is removed, then fertilization will not occur. However, next month, when ovulation in the left ovary and the left fallopian tube is patent, conception naturally and pregnancy with one tube can occur.
When is laparoscopy performed?
If the ovarian cyst is small, does not cause symptoms and does not look cancerous, it can be left alone. No surgery needed. The gynecologist will prescribe periodic examinations and control ultrasounds. Moreover, postmenopausal women will have to do this more often, because they have a higher risk of malignant tumors.
Are there effective medications?
In some cases, hormonal contraceptives may be helpful. They help prevent the formation of new cysts in the ovaries, but do not affect the growth of existing ones. If a woman is bothered by pain, the doctor may prescribe drugs from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). But this is only symptomatic treatment. The only way to get rid of the formation is surgery.
If the cyst is “problematic,” then the doctor will definitely say that it needs to be removed. Indications for surgery:
- Large size of formation. In most cases, ovarian cysts have a diameter of 1–3 cm. Very rarely they reach 15–30 cm.
- Presence of symptoms: abdominal pain, pelvic pain, bloating, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, heavy periods, vaginal bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle. A large cyst can compress the intestines and bladder. This leads to problems with stool and urination.
- Suspicion of a malignant nature of the cyst - the risks are increased in postmenopausal women.
- Continued growth over 2–3 menstrual cycles.
- Pathological ovarian cyst.
What happens if the cyst is not removed?
If the doctor said that the cyst needs to be removed, then delaying the operation is primarily dangerous for postmenopausal women. They, as we have already mentioned, have a higher risk that the formation may turn out to be malignant. And with cancer, time is critical. The later treatment is started, the lower the chances that it will be successful and that remission will be achieved. The prognosis worsens and survival rate decreases.
At the Euroonko clinic you can receive treatment for ovarian cancer according to modern standards. Our doctors perform operations of any complexity; we have access to all the latest generation antitumor drugs registered in Russia. We work according to modern European, American, Israeli treatment protocols. For ovarian cancer complicated by peritoneal carcinomatosis, we use an innovative technique - hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC).
With benign ovarian cysts, serious complications can also occur, although they are rare. Large cysts may rupture. In this case, severe bleeding develops into the abdominal cavity, and severe abdominal pain occurs.
As the cyst grows, the risk of ovarian torsion increases. Due to compression of the blood vessels, it stops receiving blood supply, severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting occur. The result may be necrosis (death) of the ovary, and it will have to be removed urgently.
If you experience symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or a fever of more than 38 degrees, you should immediately seek medical help.
My approach to treating endometriosis
Due to the fact that it is not always possible to determine the depth of tissue damage by endometriosis, I prefer radical removal of lesions within healthy tissue rather than cauterization. Unlike other methods, the use of this technique allows the diagnosis to be confirmed histologically.
- The operation itself is performed through several small incisions.
- Endometrioid lesions can affect other pelvic organs, all of which must be removed. My many years of experience in performing gynecological, urological, and proctological operations make it possible to perform the intervention efficiently and safely for the patient.
- Thanks to the use of modern equipment, all manipulations are carried out with maximum precision, so the risk of damage to nearby structures (ureters, bladder, intestines, etc.) is eliminated.
- Use of atraumatic instruments, LigaSure electrothermal tissue ligation device, absorbable suture material, ultrasonic scissors, anti-adhesion barriers, etc. — makes it possible to operate quickly and efficiently.
- If the patient has other pelvic diseases that require surgical treatment, there is the possibility of performing simultaneous operations: getting rid of several pathologies at once during one anesthesia.
For patients treated in our clinic, after radical excision of endometrioid lesions, I recommend abstaining from conception for 1 to 8 months, depending on the clinical situation. However, when planning pregnancy with endometriosis, it is also important to take into account the peculiarities of the course of the disease. If hormonal therapy, possibly a second operation, is necessary, preparation for conception is longer and may require from several months to a year.
Risks
A benign tumor is dangerous because it can provoke uterine tone.
Important! As the gestation period increases, the walls of the organ stretch. This leads to disruption of the blood supply to the tumor. As a result, the formation may become inflamed. This will lead to severe pain. An increase in uterine tone is also inevitable.
In addition, situations are dangerous when the fertilized egg, after fertilization, attaches to the location of the formation. In this case, there is a risk of improper development of the placenta. This pathology can cause frozen pregnancy, spontaneous abortion, and fetoplacental insufficiency.
Important! Even an experienced gynecologist will not give a forecast regarding the “behavior” of fibroids after conception, during pregnancy. Some formations may decrease, others may increase.
What if the fibroid is removed?
Removal surgery may be performed during pregnancy. But it is very important to correctly assess all risks. It is believed that there is no threat to the woman’s health during such an operation. However, there is a possibility of miscarriage. No doctor can predict how the situation will develop. Even an experienced professional will not determine all the risks and their degree.
That is why intervention can and should be carried out before planning a pregnancy. If the operation is successful, then conceiving a child is possible about a year after it. Several specialists will monitor your pregnancy.
What technique increases the chances of becoming a mother?
Arterial embolization (EMA)
This vascular operation is used to block the uterine arteries.
The technique was first used in 1979. Then it was used to stop uterine bleeding. The method began to be used in the 90s of the last century.
The essence of the method
Embolization of the uterine arteries is based on mechanical blockage of the lumen of the vessels that supply blood to the uterus.
Important! The arteries feeding the formation have a diameter of 0.5 mm. This is slightly larger than the diameter of the remaining myometrial vessels.
Special particles are injected into the area of the arteries that provide blood supply to the fibroids. There is a decrease in blood flow, and the amount of oxygen and nutrients is reduced. Against this background, there is a decrease in education.
Request a call back Get a free consultation