A pregnant woman's body must adapt to carrying a baby and the upcoming birth. The main burden, of course, falls on the female pelvis. Ultrasound of the symphysis is the only accurate method for identifying pathology - symphysitis, in which the symphysis pubis is stretched more than normal. Examinations are carried out during pregnancy and after childbirth.
Ultrasound of the pelvis - 1000 rubles. Consultation with a specialized doctor based on the results of ultrasound and tests - 500 rubles. (optional).
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
The pubic symphysis: where it is located, why the symphysis diverges
The content of the article
The bones of the female pelvis are a ring that includes the sacrum, coccyx and a group of symmetrical paired bones - the ischium, pubis, and pelvis. The pubic bones are located in the central lower abdomen. They are connected to each other by the pubic symphysis, which is called the symphysis pubis.
During pregnancy, the structures of the symphysis soften and the ligaments weaken. This is necessary for the normal passage of the child through the birth canal. Softening of the symphysis occurs under the influence of the hormone relaxin, produced in pregnant women in the ovaries and placenta. Disruption of this process is called symphysitis.
Physical therapy
The following devices can be used as part of DLS therapy:
- Crutches with elbow support.
- Pelvic support devices: Lumbopelvic brace (the brace should be positioned strictly cephalad to the greater trochanter of the femur. The study does not recommend the use of a lumbopelvic brace as monotherapy because lumbar stability must be achieved through proper motor control and coordination ).
- Prescription pain relievers (use NSAIDs during pregnancy with caution).
- Social services.
Birth planning
- Women with DLS should give birth in an upright position with their legs slightly apart.
- The gap between the pubic bones should never exceed the maximum, so patients are advised to wear special tapes on both legs.
- During childbirth, you should not rest your feet on the midwife's thighs, use footrests, or use surgical forceps, as they can further stretch the ligaments.
- During labor and childbirth, the legs should be minimally apart.
Prevention
- Informing the patient: about her illness, as well as about the connection of the disease with the required and permissible load;
- about the need for rest;
- to reduce fear;
- to motivate the patient to actively participate in the treatment process;
- tips for everyday life (do household chores while sitting if possible, sleep with a pillow between your legs, keep your legs bent to get in/out of bed).
- The patient should avoid activities that place excessive stress on the pelvis (squats, intense exercise, prolonged standing, lifting and carrying heavy objects, stepping over things, twisting movements, vacuuming, and stretching exercises).
Exercises for hips
Aerobic exercise
- Moderate-intensity vigorous walking, defined as 64 - 76% of maximum heart rate, or 3 times a week for 25 minutes.
- Stretching exercises for the following muscles: hamstrings, inner and lateral thighs, quadriceps and back muscles. We should do it 3 times a week, 2 times a day. The duration of each exercise is from 10 to 20 seconds.
Strengthening exercises
Read about lower back pain and pelvic floor muscle incompetence here.
- The patients performed the following exercises: bending the torso forward, “cat”, diagonal twists, bending the upper body, raising the legs from the knee-elbow position (with parallel performance of Kegel exercises and control of pelvic tilt).
- The exercises are performed 3 times a week (2 sets of 3-5 repetitions on each side).
- The duration of each exercise is from 3 to 10 seconds.
- Pelvic muscle exercises [evidence level 1a]. (Exercises for instability of the lumbar spine)
- In early pregnancy: to reduce the risk of developing symphysis pubis dysfunction:
- Deep Abdominal Exercises: To increase core stability and prevent women from developing pelvic or back pain during pregnancy.
- You should start with a small number of repetitions, gradually increasing the time of muscle contraction.
- Particular attention should be paid to the transverse abdominis muscle, an important muscle whose contraction synergistically activates the pelvic diaphragm.
Stabilization exercises
Causes and signs of symphysitis in pregnant women
The causes of symphysitis are not yet fully known. Scientists are constantly adding to the list of factors that contribute to excessive divergence of the pelvic bones during pregnancy. In particular, it has been established that the following conditions can cause disturbances in the structures of the symphysis:
- Lack of calcium
- the main element of bone tissue; - Excessive production of relaxin
due to hormonal disorders. - Heredity
- many diseases of the musculoskeletal system are inherited. - Lack of collagen
- this protein forms the basis of ligaments and cartilage.
Adverse factors that increase predisposition to symphysitis
- complications from previous births;
- large fruit (from 4 kg);
- insufficient physical activity before pregnancy;
- congenital pelvic pathologies;
- post-term pregnancy;
- numerous births.
Since there are many causes of pathology, ultrasound of the symphysis is recommended for all pregnant women.
Decoding the results
After performing an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis, the doctor compares the data obtained with established standards and draws a conclusion about the condition of the pubic symphysis. There are general norms; there are no gradations by week.
The most important thing is the condition of the symphysis pubis before childbirth, the distance between the bones, and the presence of an inflammatory process that determine the woman’s management tactics.
Signs of normality and pathology on ultrasound of the pubic symphysis:
- During pregnancy, bone divergence by a distance of up to 5 mm is considered normal, this is physiological;
- an increase in the gap from 6 to 9 mm indicates the 1st degree of symphysitis;
- 2nd degree is characterized by a discrepancy of 10-19 mm;
- if the bones of the symphysis have diverged by 20 mm or more, this is the 3rd degree of symphysitis;
- the presence of inflammation, tissue swelling, softening or separation of bones is a sign of the disease.
The pain syndrome does not always correspond to the degree of the disease; much depends on the pain threshold of a particular woman. When the bones diverge by 6–7 mm, some cannot walk, while others with a gap width of 12 mm give birth.
Basic recommendations for detecting signs of symphysitis during ultrasound of the symphysis pubis:
- wearing a bandage or bandaging the pelvis;
- decreased physical activity - lie more, walk less;
- when standing or sitting, distribute weight on both legs;
- do not sit cross-legged;
- do not stay in one position for more than an hour;
- correction of body weight;
- Use the elevator to get to the floor;
- a course of vitamins B, C, PP, etc.;
- a course of minerals containing calcium, phosphorus, etc.;
- performing a set of exercises prescribed by a doctor, the purpose of which is to reduce the load on the pubic symphysis, which reduces pain.
With the 1st degree of symphysitis, natural delivery is possible if the baby is not large, the pelvis is not narrow, and the birth canal is well passable. After the baby is born, the woman continues to take medications and wear a bandage.
A woman with stage 2 disease often has a natural birth. If there are complications, for example, an inflammatory process or a large child, a caesarean section is used.
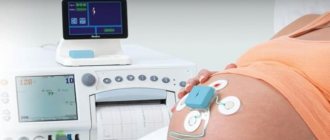
During the pushing period and the birth process itself, the child’s condition is assessed using CTG. Based on the number of heartbeats, the doctor makes a conclusion about the well-being of the baby in the womb. This is important because there is a possibility of hypoxia.
3rd degree poses a danger to the health and life of a woman. Rupture of the symphysis pubis during childbirth is a severe traumatic situation that always requires treatment and a long period of rehabilitation. In rare cases, when the bones diverge by 30–50 mm, surgical treatment may be used to connect the pelvic bones. Symphysitis of the 3rd degree is an indication for a cesarean section.
After delivery, ultrasound of the symphysis pubis is performed several times.
This is necessary to assess the dynamics of reduction of the resulting gap. The pain syndrome may persist for several more weeks.
Signs of pathologies of the symphysis pubis: when is it necessary to do an ultrasound of the symphysis?
The first symptom of symphysitis is pain in the pubic symphysis (pubic region). Due to excessive stretching of the joint, inflammation begins. The pain is especially felt when walking quickly and when climbing stairs. The disease corresponds to the end of the second - beginning of the third trimester. It is not uncommon for symphysis to develop after childbirth.
At the first symptoms of stretching and inflammation of the symphysis, you need to do an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis and undergo treatment. Ultrasound diagnostics is the most informative and only safe method of examining pregnant women at any stage.
You need to make an appointment for an ultrasound if you notice:
- Acute pain in the pubic area during movement and exertion. The pain can radiate (give) to the perineum, legs, and lower back.
- Unpleasant sensations and pain when climbing stairs, when the load falls on one side.
- Pain in the pubic region when lying down or bending over;
- The bosom looks swollen.
- Visual change in gait - it resembles the movement of a duck - small steps.
- clicking sound when palpating (inspecting) the pubis.
It should be understood that symphysitis in the first stages occurs without pain. A dangerous moment is the second trimester of pregnancy during the period of active fetal growth and increased load on the pelvis.
Epidemiology/Etiology
There are several theories about the origin of symphysis pubis dysfunction:
Aslan et al. They say that the etiology of the disease is unknown. During pregnancy, the load on the pelvis changes, ligaments and muscles weaken. This leads to spinopelvic instability, which manifests itself as DLS.
In early pregnancy, the corpus luteum produces large amounts of the hormone relaxin and progesterone. From the 12th week, this function is taken over by the placenta and the decidua of the uterus. Relaxin breaks down collagen in the sacroiliac joints, causing tissue softening. Progesterone has a similar effect. However, there is no correlation between relaxin levels and the degree of symphysis pubis dysfunction. A Norwegian study found that genetic predisposition to DLS may be caused by defects in relaxin secretion. It may seem that relaxation of the ligamentous apparatus directly indicates the presence of a hormonal basis for the disease. However, there is not enough data to support this theory.
The influence of stress and cortisol levels on pelvic pain.
Other factors leading to DLS include physically exhausting work during pregnancy, as well as pathological fatigue, poor posture and lack of exercise. Excess weight, multiple pregnancies, older pregnancies, a history of difficult labor, and shoulder dystocia may also play a role.
Effective adaptation of joints to a given load requires adequate joint compression and coordinated efforts of muscles and ligaments. This is the key to effective joint reactions to changing conditions. During pregnancy, ligaments and muscles become weaker and cannot perform their functions as they did before. As a result, the pelvic tilt changes, which leads to spinopelvic instability, most often manifested in dysfunction of the pubic symphysis.
In short, the causes of this instability are hormonal (influence of the hormone relaxin), metabolic (calcium metabolism), biomechanical (stress during pregnancy and exercise), underdeveloped muscles, body composition (weight), anatomical and genetic variations.
- The pelvic floor is made up of three layers of muscles. The superficial layer innervated by the pudendal nerve includes the bulbocavernosus muscle, the ischiocavernosus muscle, the superficial transverse perineal muscle, and the external rectal sphincter.
- The deep layer is the urogenital diaphragm, which is also innervated by the pudendal nerve. These include the urethral sphincter, constrictor bladder muscle, urethrovaginal sphincter and deep transverse perineal muscle.
- The pelvic diaphragm is made up of the following muscles: the levator ani muscle (pubococcygeus muscle, also known as pubo-prostatic, pubovaginal, pubo-anal, puborectal, iliococcygeus), coccygeus muscle, piriformis muscle and obturator internus muscle. These muscles are innervated by the sacral roots of the spinal cord (S3-S5).
The function of the pelvic floor muscles is to support the organs lying on it. The sphincters (anal and urinary) allow conscious control of the bowel and bladder. Thanks to this, we can consciously control the excretion of feces or fatus, as well as urine.
When contracted, the pelvic floor muscles are able to lift the internal organs and compress the openings of the sphincters of the vagina, anus and urethra. When the pelvic floor muscles relax, urine may leak and feces may be released uncontrollably. Pregnancy changes the functioning of these muscles, as well as their function.
Risk group
The gynecologist will also prescribe an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis in cases where the pregnant patient is at risk:
- with a diagnosis of kyphoscoliosis;
- with a narrow pelvis;
- if the fetus is larger than normal:
- if there are changes in the hip joints associated with injuries;
- with incorrect presentation of the fetus;
- during multiple pregnancy;
- for pathologies in previous pregnancies - ruptures of the pubic ligaments, prolonged convergence of the pelvic bones, childbirth using forceps and other methods of obstetrics.
What is revealed
Ultrasound examination makes it possible to determine the degree of stretching of the symphysis:
- first – 7-9 mm;
- the second – up to 20 mm;
- the third – more than 20 mm.
If dilation exceeds 10 mm, depending on the woman’s condition and the size of the fetus, the obstetrician-gynecologist may decide to deliver by cesarean section. Natural childbirth with severe deformation of the symphysis pubis is fraught with rupture of the pubis, requiring a long period of rehabilitation during the most critical period for a young mother.
What does an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis show?
A sonologist (usually a gynecologist) evaluates the condition of the semphyseal complex, which includes the pubic bones, ligaments and soft tissues located directly above the joint.
Ultrasound effectively detects a number of pathological changes:
- softening of bones and ligaments;
- sprain;
- rupture of ligaments and tissues;
- expansion of the bones of the pubis;
- volume of inflammation.
Thanks to Doppler, the doctor also detects excess fluid in the tissues, causing swelling.
How is an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis performed?
The technique does not require special training. Ultrasound is performed using the usual method - safely and without pain.
A pregnant woman lies down on a special couch. The doctor applies the gel to the pubic area and surrounding tissue. Next comes the standard examination procedure with a highly sensitive sensor. The examination may take up to 15 minutes.
If a woman is at risk or has abnormalities, the examination is carried out multiple times, the last time just before giving birth. Ultrasound of the symphysis can be combined with other types of examination, for example, it is useful to immediately perform a screening ultrasound of the fetus.
Preparation
No special preparatory measures are required. The procedure is not at all dangerous for either the woman or the baby. On average, such a study lasts about 15 minutes. The procedure does not imply any restrictions either before or after. It is important to note that the sensor is in contact with the body for no more than five to seven minutes (as already mentioned, during pregnancy, exposure to ultrasonic waves should be minimal).
If symphysitis was detected during an ultrasound, the doctor will give the patient recommendations in accordance with the complexity of the case. For some women, it will be enough to limit themselves in physical activity, perform simple exercises and wear a bandage. Other patients may require bed rest and even hospitalization.
Natural birth and caesarean section for symphysitis
The results of an ultrasound scan of the symphysis should be taken with you to the maternity hospital and the receiving obstetrician-gynecologist should be immediately notified of the presence of pathology.
Natural childbirth with symphysitis is allowed if 3 conditions are met:
- Pathology does not go beyond the first degree.
- The fetus is of normal weight.
- The patient's pelvis has normal parameters (not narrow).
In other cases, a caesarean section is recommended, although exceptions may be made. For example, natural childbirth may be recommended based on the experience of previous pregnancies, in case of intolerance to anesthesia required for cesarean section, small size of the fetus, etc. But in these cases, you need to understand that the risk of complications after childbirth, in particular rupture of the womb, exceeds 50%.
A rupture of the womb, of course, can be treated, but this condition will not allow you to fully engage with the baby, since it will not be possible to stand up for a long time and put stress on the legs and pelvic bones.
If an ultrasound showed a sprain of the pubic ligaments, divergence of the pubic bones, or inflammation in the symphysis pubis, you will have to rearrange your daily routine and perform a number of procedures.
The doctor will prescribe:
- restriction of movement - in case of significant pathology, bed rest must be observed until childbirth;
- wide bandaging of the pelvic area with special bandages or wearing a pelvic bandage;
- a diet that limits carbohydrates, which contribute to weight gain, and includes foods rich in calcium;
- vitamins, calcium gluconate or dietary supplements containing easily digestible calcium;
- special gymnastics for pregnant women (physical therapy), with minimal stress on the body.
For mild disorders, exercise limitation, calcium diet, and exercise therapy are prescribed.
Drug treatment
During pregnancy:
- Paracetamol.
- Codeine-based drugs.
- Epidural using morphine/bupivacaine/fentanyl for 24-72 hours to break the cycle of pain and muscle spasm.
After childbirth:
- NSAIDs.
- Epidural using morphine/bupivacaine/fentanyl for 24-72 hours to break the cycle of pain and muscle spasm.
Other:
- If it is impossible to relieve the pain, go to the hospital.
- Injections of cortisol, chymotrypsin and lidocaine directly into the symphysis area.
Carefully monitor the effectiveness of measures taken and their side effects.
Where to do an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis in St. Petersburg, prices
The modern and very cozy Diana clinic in St. Petersburg invites pregnant women and those who have already given birth to undergo an ultrasound of the symphysis in our medical center. The examination is carried out using a new expert-class ultrasound machine with a Doppler sensor. Here you can undergo all pregnancy screenings, have an ultrasound scan in 3D and 4D formats, and take any tests without waiting in line.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter