X-ray: types, contraindications
X-ray examination was invented more than a hundred years ago as a method of non-invasive examination of internal organs.
Today, radiography is currently used to diagnose various pathologies in various fields of medicine.
Of course, the development of technology has given doctors the opportunity to use more advanced methods for diagnosing diseases, but even today radiography plays a significant role in clinical practice.
If you compare it with CT or MRI, then the statistics are in favor of this particular research method. The specific gravity of radiography is 15 times higher than that of MRI or CT.
The essence of the method
Radiography is a diagnostic method that is based on the use of X-rays. It must be understood that the radiation exposure of one procedure is not dangerous for humans, but it is necessary to limit the frequency of studies of this kind.
If we talk about classification, the following methods are distinguished:
- Overview – makes it possible to analyze any area of the body;
- Targeted - helps to collect information about the functioning of a specific organ and its structure.
The images obtained as a result of the procedure are called radiographs. The results of the procedure are important in terms of making a diagnosis.
Technology does not stand still, and now digital devices with a computer program are increasingly used. When using them, there is no need to make films by developing them. The picture is displayed on the monitor, but the pictures themselves are stored on electronic media.
AI for X-ray examination for COVID-19
The transition of radiography to digital imaging means that modern image analysis tools, previously used exclusively for more advanced techniques, can now be applied to radiography. The most advanced tool is artificial intelligence (AI).
A team of scientists from Canada has developed an open-source artificial intelligence algorithm called COVID-Net, which is designed to detect signs of the disease on chest X-rays. They claim that the convolutional neural network demonstrated almost 100% sensitivity and 83% accuracy in detecting COVID-19 in a small set of test data, but it is clear that more testing will be required in real-world conditions. They published their work on March 22 on arXiv.org.
As the novel coronavirus pandemic continues to spread, doctors on the front lines of the fight against it may turn to radiography more often.
“As the COVID-19 pandemic threatens to overwhelm healthcare systems around the world, chest x-ray can be considered as one tool for detecting COVID-19, but it is less sensitive than CT,” Wong and colleagues conclude in the journal Radiology.
Indications
Radiography is also used in oncology. The main purpose of its use is to obtain information about the state of a specific anatomical zone and deviations from anatomical norms.
We can say that the indications for conducting the study are the presence of a malignant neoplasm, the process of its treatment and follow-up.
Patients with cancer are advised to examine a number of anatomical areas:
- Areas of development of the primary tumor process;
- Areas of probable metastasis;
- Areas in which, based on clinical signs or patient complaints, there are likely to be metastases.
We will apply the method during treatment in such cases as:
- The need to select the optimal volume of surgical manipulation;
- In the postoperative period to monitor the condition of the lungs;
- In the postoperative period to control the installation of internal catheters or stents;
- To assess the dynamics of metastases in the lungs and bones during cyclic chemotherapy;
- For monitoring after completion of treatment in areas of probable relapse or metastases.
Clinical signs on x-rays
What features on an x-ray indicate COVID-19? Chest X-rays may show irregular or diffuse asymmetric opacities of lung tissue, similar to pneumonia but caused by other coronaviruses, according to a paper by Dr. Jonathan Rodriguez and colleagues published March 23 in the journal Clinical Radiology.
Meanwhile, researchers from the University of Washington in Seattle provided a list of the five most common signs of COVID-19 on X-rays. The most common finding was bilateral reticular nodular opacities, found in 52% of cases, followed by ground glass syndrome in 48% of cases. About 72 hours after patients arrived, these rates rose to 86% for reticular nodular opacities and 67% for ground glass opacities, they wrote in their study, published March 19 in JAMA.
Infection control and radiography
One of the advantages of X-raying patients with COVID-19 is its portability. Mobile X-ray systems should be used to evaluate patients suspected of having COVID-19, and a satellite X-ray center with mobile X-ray equipment dedicated to diagnostic imaging for COVID-19 could even be installed closer to intensive care units, reducing the risk of contracting the virus, writes Dr. Soheil Kuraki and colleagues in the April 2020 issue of the Journal of the American College of Radiology.
Meanwhile, Clinical Radiology authors also weighed in on infection control, highlighting the importance of using mobile X-ray systems. Systems must be installed to identify at-risk patients with suspected COVID-19, radiology personnel must be trained in disinfection procedures, and “clean” and “dirty” areas must be separated.
Mobile radiography has also been endorsed by an American College of Radiology (ACR) task force created to combat COVID-19, which recommended its use in outpatient settings because of the ease of disinfecting equipment surfaces, according to a March 11 guideline. The ACR statement recommends that diagnostic imaging centers provide ventilation in rooms with non-mobile x-ray systems or CT scanners—these rooms may need to be closed for ventilation for one hour between patient appointments, depending on the level of air circulation.
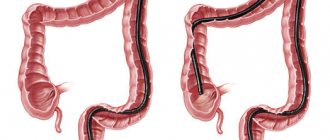
Types of research
We list the main types of research:
- Lung examination. Gives an idea of the presence and extent of changes in lung tissue.
- Heart study. Necessary for diagnosing diseases of the cardiovascular system, heart, imbalance of the pulmonary circulation.
- Spine examination. Using it you can indirectly determine the nature of osteochondrosis
- Examination of the stomach and duodenum. It is used to identify ulcers, perforations, foreign bodies, etc.
- Examination of the gallbladder. Important for assessing the condition of the bile ducts.
- Colon examination. Necessary for detecting polyps, tumors, foreign bodies, inflammatory foci.
- Abdominal examination. Necessary to clarify the diagnosis when complaining of severe abdominal pain.
- Study of bones and joints. It is used to diagnose fractures, subluxations and dislocations, ligament injuries, joint and bone diseases, etc.
- Dental examination. With its help, the doctor determines the size and location of teeth, abscesses, fractures of the jaw bones, malocclusion, etc.
- Metrosalpingographic study. Detects the presence of adhesions and anatomical changes in the uterus and fallopian tubes.
- Mammographic examination. Important for identifying tumor processes in the mammary gland.
Advantages and disadvantages of x-ray diagnostics
Radiography, in addition to reliable diagnostic information about the real state of the anatomical region under study, allows inexpensive and fairly rapid monitoring of the effectiveness of antitumor therapy. A few minutes are enough for the examination.
It is correct to take more than one direct photo - a “photo” from front to back, but also a side one, in order to have a complete understanding of the localization of the pathology inside the organ.
During the tumor process, layer-by-layer images are taken - tomograms, when the X-ray beam seems to cut the organ and surrounding tissues, forming a slice of any anatomical part at a certain distance from the skin. Several tomograms are taken in “steps” of several centimeters. Additional options increase the cost of the examination, which is still incomparable with the price of standard CT and MRI.
Not all organs are accessible to X-rays, for example, the pancreas is not visible at all, the intestines are noticeable only by their contents, additional contrast allows you to see many hidden internal organs.
Patients treat X-ray diagnostic procedures with ease because they do not hurt and there is no risk of infection. Each X-ray examination complements the total radiation exposure of the patient, but a cancer patient has to take many pictures and quite often, because without high-quality diagnostics it is impossible to either select the optimal treatment or evaluate its result. Nevertheless, from the point of view of the harm-to-benefit ratio, a cancer patient benefits from radiography more than he loses health due to radiation.
Radiography is inferior in image quality to CT and MRI, but there is not always a need to clarify “100%”; often the speed and accessibility of the examination is sufficient. Each method has been found to have an optimal place in the diagnostic and treatment process for an oncological patient.
Features of the event
Today, both large-sized and compact devices are used for research. The patient is in one room, the radiologist is in the adjacent one, from where he gives the necessary commands.
If the study is contrast, it is performed in the morning, usually on an empty stomach. A non-contrast study can be performed at any time.
The procedure is short, only a few minutes, except in cases where it is necessary to perform a series of photographs.
The position of the patient depends on which area needs to be examined.
Scintigraphy
To ensure accurate images, you need to remove metal jewelry; they can distort the results.
Radiography and fluoroscopy: principles of implementation
During an X-ray examination, rays are projected onto paper or film, and in modern devices - onto a film cassette or electronic matrix. Radiation is attenuated when passing through body tissues that have different structures, as a result of which the beam of rays is scattered and an image of varying degrees of intensity is formed on paper. This image is averaged; it represents the total shadow of all tissues through which radiation passes. A radiograph is a flat (two-dimensional) image of a three-dimensional object, so it is advisable to carry out radiography in two projections. Only in this case can the exact location of the lesion be determined.
During fluoroscopy, the image is projected onto a fluorescent screen, which is a cardboard sheet coated with a special fluorescent substance. Recently, devices that use X-ray television transmission have become widespread. During this test, the rays are sent to an X-ray image intensifier. The resulting image is displayed on the monitor screen. This image can be further processed and printed.
Preparing for X-rays
Modern digital devices require virtually no patient preparation. Diagnosis of the condition of the chest organs takes place “on the fly,” that is, it is possible at any time and only requires the removal of clothing and jewelry.
To study the state of the gastrointestinal tract, there is a need to empty the organs; when examining the esophagus, stomach, and gallbladder, you should not eat for several hours.
In case of oncological pathology of the colon, contrast is required, so the intestines are cleansed 2 hours before diagnosis. It is advisable to avoid foods that promote gas formation for a couple of days.
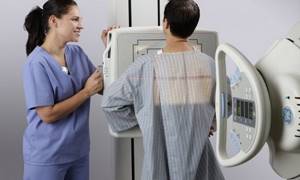
What does an abdominal x-ray show?
The X-ray diagnostic method is based on the fact that tissues of different densities absorb X-rays differently. Denser, for example, bone tissue transmits rays less well, so in the picture such tissue appears lighter. The method allows you to determine the location of organs, their integrity, the presence of foreign bodies and neoplasms.
An abdominal x-ray shows:
- how gas and liquid are distributed in the abdominal cavity, whether there is free fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- whether there are foreign bodies in the abdominal cavity (swallowed objects in the intestines, gallstones, kidney stones);
- whether there is damage to internal organs;
- whether there is intra-abdominal bleeding.
From the point of view of assessing the condition of specific organs, plain radiography of the abdominal cavity is not very informative, but it allows you to quickly determine whether the picture is pathological or not. If the wall of the stomach or intestines ruptures (perforation of an ulcer or destruction of the wall by a tumor), an x-ray will show gas escaping into the free abdominal cavity. Using an abdominal x-ray, you can diagnose intestinal obstruction and even determine the approximate location of the problem.
How are radiographic results interpreted?
Depending on the diagnostic task, radiography can be performed with an increase or decrease in the image, increased rigidity, several series and in several projections. Specialists know what to do and how to do it, they know all the capabilities of the equipment.
A blurry image is not only a waste of film and wasted time; blurriness requires re-examination and is associated with additional radiation exposure. For a better image, special filters are used, the capabilities and characteristics of which must be known to the X-ray room personnel and correlate them with the individual characteristics of the patient - his anthropometric data, weight and, ultimately, with the distance to the organ being studied.
Since complete immobility of the subject is impossible, the internal organs also move at their own rhythm, the image will be of high quality only with high power of the device and a short shutter speed.
A high-quality radiograph can be spoiled by incorrect interpretation. A standard for describing images has been developed, but the final result is related to the professionalism of the doctor, his experience and knowledge, observation and intuition, and of course, knowledge of clinical oncology. Our clinic has excellent equipment and staff, so X-ray reports are always of an expert level.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78