RBC is an abbreviation for red blood cells in blood tests. The main functions of this formed element of blood are transport, protective and regulatory.
Red blood cells are the formed elements of blood; in blood tests they are abbreviated as RBC.
The formation of red blood cells (erythropoiesis) in adults occurs in the red bone marrow of flat bones. It contains so-called pluripotent stem cells - the common precursors of all blood cells. After passing through several stages of differentiation and maturation, anucleate red blood cells leave the bone marrow in the form of so-called reticulocytes (young red blood cells).
Mature red blood cells circulate in the blood for an average of 100–120 days, after which they are phagocytosed by the cells of the reticuloendothelial system of the bone marrow (in the presence of pathology, also the spleen and liver). When the life of erythrocytes is shortened and after blood loss, the rate of erythropoiesis can increase several times. The lifespan of red blood cells in men is slightly longer than in women.
Basic functions of red blood cells
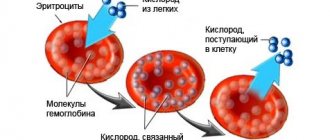
The transport function of erythrocytes is that they transport O2 and CO2, hormones, amino acids, cholesterol, fats, polypeptides, carbohydrates, proteins, enzymes, various biologically active compounds (prostaglandins, leukotrienes, etc.), trace elements, etc.
The transport function is provided by a special protein included in the RBC - hemoglobin. It has the ability to form compounds with oxygen and carbon dioxide.
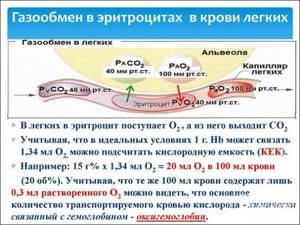
Hemoglobin performs the transport function of blood
Red blood cells play a significant role in specific and nonspecific immunity and are involved in vascular-platelet hemostasis, blood coagulation and fibrinolysis (meaning that red blood cells perform a protective function).
The regulatory function of RBC is determined by the hemoglobin contained in the cells. Red blood cells regulate blood pH, water metabolism and the ionic composition of plasma.
Role of RBC in the body
The main and most obvious functions relate to tissue respiration. Red blood cells are structured quite specifically when compared with other structures, formed elements.
They do not have a core, are flat in shape, and are characterized by a large surface area. Inside the cell you can find hemoglobin, which actively binds gas particles.
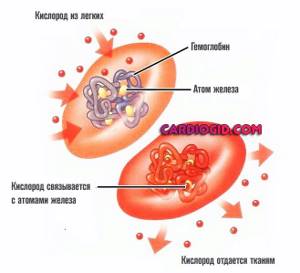
From here, their key purpose becomes clear:
- Oxygen transfer. In the lungs, the red blood cell is filled with O2 and transports it to all tissues. Releases the substance, thereby ensuring normal breathing.
- Movement of carbon dioxide. This is a waste product that needs to be eliminated. Cells do this too. They carry the harmful substance back to the lungs, where it is released and leaves the body with exhalation.
Despite the above, these are not the only functions of red blood cells. There are others, less obvious.
They can be represented in a small list:
- Regulation of electrolytic balance. Indirectly. Thanks to the active work of cells, the blood is in a state of stability. Its acid-base balance remains the same and does not change. This is a guarantee of life. The very possibility of the existence of an organism.
- Ridding the body of toxic substances. In addition to binding gases, the cell can bind to a harmful compound and naturally eliminate it from the body.
- Ensuring clotting. The main role here belongs to platelets. But red cells also help the normal process.
- Activation of the immune system. Another indirect task that is solved in the course of the main activity. Thus, the defensive forces are constantly in combat readiness. This helps prevent infectious processes. On the other hand, it prevents the development of oncological conditions, cancer or benign tumors.
It is red blood cells that are partly involved in the synthesis of new cells. By supporting bone marrow activity and stimulating its activity.
There is also a laboratory, artificial task. Its essence is to study possible disorders of the body.
An increase or decrease in the concentration of red blood cells is a nonspecific indicator. But you can start from it and make a diagnosis after a comprehensive diagnosis.
Determining the number of red blood cells in a blood test
A separate blood test to calculate the number of RBCs is not prescribed. The value of the indicator is usually determined as part of a general blood test.
Reasons for conducting a study to determine the number of red blood cells:
- preventive and clinical observation, including before surgical interventions;
- control of drug treatment in patients with chronic anemia or bleeding;
- examination of pregnant women;
- diagnosis of anemia, polycythemia and other diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- examination of patients with infectious and somatic diseases (prescribed simultaneously with a biochemical blood test).
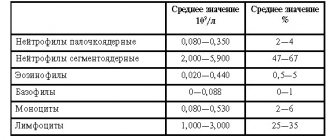
In the result forms, all parameters are indicated by abbreviations of English terms:
- RBC (red blood cells) - erythrocytes, or red blood cells;
- WBC (white blood cells) - leukocytes, or white blood cells;
- HGB (hemoglobin) – level of hemoglobin in whole blood;
- HCT (hematocrit) – hematocrit (an index representing the percentage ratio of the volume of blood cells to the volume of blood plasma);
- PLT (platelets) – platelets;
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) – ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
The transport function is provided by a special protein included in the RBC - hemoglobin. It has the ability to form compounds with oxygen and carbon dioxide.
If RBC is elevated in the blood test, an additional in-depth study - a comprehensive clinical blood test - may be prescribed. It includes the determination of erythrocyte indices:
- MCV – average volume of one red blood cell;
- MCH – average content of hemoglobin in one red blood cell;
- MCHC – hemoglobin concentration in the erythrocyte (not in the total blood volume);
- RDW-CV – erythrocyte distribution width, that is, the presence and concentration of red cells in the blood that differ significantly in size from the norm.
What to do to normalize the indicator
RBC in a blood test is a test that will help determine the appropriate treatment method if there are deviations from the norm. You can normalize the indicators with the help of medications and folk remedies; you can find out which one will be suitable from your attending hematologist.
Medicinal and traditional methods of increasing RBC levels
To increase the number of red blood cells, the following drugs are recommended:
- Contains divalent ferum sulfate (Tardiferon, Ferretab, Aktiferin, Feroplex, Fero-Folgamma, Sorbifer Durules and Gino-Tardiferon).

- Contains trivalent ferum sulfate for adults (Biofer, Ferrum lek, Ferlatum Fol, Maltofer, Ferlatum and Fenyuls).
- Contains folic acid and vitamin B9, which increases the concentration of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood (Biofer, Ferretab, Maltofer Fol and Gyno-Tardiferon).
- With cyanogen cobalamin, vitamin B12 and ascorbic acid, which saturate the blood with red blood cells and hemoglobin (Ferro-Folgamma, Sorbifer Durules and Actiferrin).
- Preparations for injection and internal administration, due to which hemoglobin and oxygen in the blood increase (Venofer, Cosmofer and Argeferr).
There are also traditional methods for raising red blood cells; they are suitable for those who are allergic or intolerant to medications.
The best folk remedies are:
- A decoction of rose hips and wild rosemary. Rosehip and wild rosemary contain a large amount of vitamins and enzymes that help improve blood circulation and increase red blood cells. To prepare, you need to add 100 g of rose hips and wild rosemary, then boil and let sit for 10-15 minutes. It is recommended to drink the decoction 2-3 times a day, on an empty stomach before eating.

- Hawthorn decoction. Hawthorn infusion improves heart function and blood circulation; consuming it has a chance to increase hemoglobin and red blood cells. To prepare, you need to brew 150-200 g of hawthorn, then let it brew for 5-10 minutes. Hawthorn can be drunk by adults and children, if there is no allergic reaction or individual intolerance to the body.
- Radish salad and radishes. Radishes and radishes contain high amounts of iron and vitamin B9, which increase red blood cell counts. To prepare, you need to chop or blend 1-2 radishes and radishes, then add sugar or salt to taste. Eating salad is not recommended for those who have gastritis or stomach ulcers.
- Apple and quince salad. Quince and apples are the main sources of iron that will help improve your RBC levels. To prepare, you need to peel and chop 2-3 apples and 1-2 quinces, then add sugar to taste. You can also add carrots, pears and radishes to taste if you are not allergic.
- Walnuts with honey. Walnuts contain vitamins and enzymes that help increase RBC. You need to consume them with honey 1-2 times a day, unless there is an excess of iodine and thyroid diseases.
Before choosing medications yourself, you need to consult a hematologist and nutritionist. It is also necessary to see an allergist and undergo tests that will determine whether you are allergic to medications and pills.
Drugs and folk remedies to lower RBC
To lower red blood cells and hemoglobin concentration in the blood, hematologists prescribe the following medications:
- Acetylsalicylic acid, which helps thin the blood, making it less saturated with oxygen and hemoglobin (Aspirin, Aspeter, Plocard, Aspecard and Acekor).
- Dipyridamole, which helps to constrict blood vessels and thin the blood with an increased level of red blood cells (Curantil, Aklotin, Agenox and Acekor cardio).
- Clopidogrel, which reduces oxygen in hemoglobin, causing red blood cell counts to decrease (Atherocard, Platogril, Lopigrol and Trental).
When the concentration of red blood cells is high, leeches are also used; this method is called hirudotherapy.
To lower red blood cells and hemoglobin, experts recommend the following folk remedies:
- Tincture of dandelions and horsetail. Dandelion and horsetail leaves help lower red blood cell counts while improving the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. To prepare, you will need 20-50 g of dandelion stem and 50-100 g of horsetail leaves, then boil. After preparation, you need to let the broth brew for 10-15 minutes, then drink 2-3 times a day after meals.
- Chamomile and calendula decoction. To prepare the decoction, you need to pour boiling water over 100 g of chamomile and 100 g of calendula, then let it brew for 10-15 minutes. Chamomile and calendula help thin the blood and constrict blood vessels, which can help get rid of excess RBC and hemoglobin in the blood.

- Lemon juice. Lemon contains a large amount of acetylsalicylic acid, which thins the blood and makes it less saturated. To prepare, just squeeze 1-2 lemons into a glass of water, then add sugar or honey to taste. It is recommended to drink juice 2-3 times a day after meals.
- Dill decoction. Dill improves the functioning of the liver, kidneys and blood, thereby reducing the concentration of red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood. To prepare the decoction, you need to boil 50 g of dill, then let it brew for 10-15 minutes. Dill decoction can be drunk by adults and children if there are no allergic reactions or other contraindications.
- Banana and apricot salad. To prepare the salad, you need to finely chop or blend 1-2 bananas and 2-3 apricots, then add sugar, dried apricots or raisins to taste. The salad will help improve the functioning of the intestines, heart and blood circulation, thereby reducing the levels of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood.
- Black sweet tea. If there is an excess of hemoglobin and red blood cells, it is recommended to drink black tea with sugar 2-3 times a day, which helps reduce levels. It is advisable to drink sweet black tea in its pure form, without flavoring additives that negatively affect the functioning of the intestines and stomach in general.
RBC in a blood test is an examination that will help determine whether the indicators are elevated or decreased. Based on this, treatment can be determined. It is also worth reviewing your diet and adding foods that, based on test results, will increase or decrease RBC levels in the blood.
Normal RBC in children
The formation of red blood cells in the embryo occurs in the yolk sac, in the fetus - in the liver and spleen. In newborns, the RBC value in the blood test is high, which is due to the movement of blood from the placenta into the bloodstream during birth and significant loss of water later. In subsequent months, the body grows, but the formation of new red blood cells does not occur, which causes a decrease in the number of red blood cells by the third month of life.
In childhood, the number of red blood cells gradually changes. The normal level of red blood cells in the blood of children:
- up to 1 year: 3.3–4.9 x 1012/l;
- 1–6 years: 3.5–4.5 x 1012/l;
- 6–12 years: 3.5–4.7 x 1012/l;
- 12–16 years: 3.6–5.1 x 1012/l.
Reasons for the decline
A decrease in the number of RBCs is due to bone marrow dysfunction or cell death.
If we talk about specific disorders:
- Hemolytic anemia. Hereditary form of the pathological process. As the name suggests, in this condition, blood cells break down. Red cells destroy themselves. Significantly ahead of schedule. The body quickly becomes exhausted and is unable to ensure the maturation of replacement cells.

- Lack of vitamins. Deficiency of certain substances can also have a similar effect. True, this condition is easy to correct. It is enough to normalize your diet or eliminate factors that impede the absorption of beneficial compounds.
- Bone marrow pathologies. Like cancer, congenital underdevelopment. Often these are genetic abnormalities that cannot be cured radically.
- Irradiation. Exposure to radiation has a negative effect. It inhibits the functioning of the bone marrow. Results may be unpredictable. In the early stages, at least, the number of red blood cells decreases.
- Hormonal imbalances. A temporary phenomenon that provokes a drop in the RBC level. It is important to restore the concentration of compounds.
- Parasitic lesions. Helminthiases. We need to eliminate the worms, then everything will return to normal.
- Nutritional factor. Perhaps the culprit is improper, insufficient nutrition. The goal is to enrich the diet with healthy foods.
If there are few red blood cells, anemia develops. This condition is preventable.
Interpretation of a blood test for RBC: the norm in men and women
Normally, the number of red blood cells in men is 4–5 x 1012/l. In the absence of pathologies of the hematopoietic system, this indicator, as a rule, does not change. In women, the number of red blood cells is lower, usually the value does not exceed 4.5 x 1012/l.

Red blood cell count may decrease during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the number of red blood cells can decrease to 3–3.5 x 1012/l, which does not mean pathology and is considered normal. Also in women, physiological fluctuations depend on the phase of the menstrual cycle. After 45 years, a gradual decline in ovarian function begins, the process is accompanied by changes in blood composition. When deciphering a blood test for RBC, the norm for women of this age is considered to be 3.6–5.1 x 1012/L. With the onset of menopause, the activity of physiological processes decreases, but the number of red blood cells does not change significantly.
Decoding answers
The results are deciphered by a laboratory assistant, after which the hematologist makes a conclusion and determines the norm of indicators in accordance with age and gender.
The interpretation of the answers will depend on whether the indicators are low or high, which indicates illness or hormonal imbalance.
Reasons for deviation of the content of red blood cells in the blood from the norm
If the number of red blood cells exceeds the norm, this phenomenon is called erythrocytosis, if the number is lower - erythropenia, or anemia.

Erythrocytosis is observed with increased physical activity
Causes of absolute erythrocytosis (increased production of red blood cells):
- erythremia (malignant disease of the bone marrow);
- conditions associated with hypoxia (due to lung diseases, heart disease, the presence of abnormal hemoglobins, increased physical activity, stay at high altitudes, obesity);
- pathologies associated with increased production of erythropoietin (in patients with kidney parenchyma cancer, hydronephrosis and polycystic kidney disease, liver parenchyma cancer, benign familial erythrocytosis);
- conditions associated with an excess of androgens or adrenocorticosteroids in the body (with pheochromocytoma, Cushing's syndrome, hyperaldosteronism).
Also in the blood test there may be increased RBC values with relative erythrocytosis. A change in the number of red blood cells can be observed in the following cases:
- dehydration due to excessive vomiting, diarrhea;
- polyuria;
- diabetes;
- conditions after burns;
- emotional stress;
- smoking and alcoholism;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- arterial hypertension.
Mixed erythrocytosis is noted due to blood thickening and placental transfusion (physiological erythrocytosis of newborns).
When the life of erythrocytes is shortened and after blood loss, the rate of erythropoiesis can increase several times.
A decrease in the RBC value in a blood test is observed in the following cases:
- bleeding in acute or chronic course;
- iron, B12 or folate deficiency anemia;
- chronic kidney disease (decreased erythropoietin synthesis);
- hypothyroidism;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hemolysis;
- aplastic anemia;
- oncological diseases of the bone marrow or metastases of other tumors to the bone marrow;
- chronic infections;
- systemic connective tissue diseases;
- pregnancy.
Reasons for the increase
The growth of RBC in the blood in 80% of cases indicates pathological processes. Which ones and how heavy are another question. Possible factors for violation include:
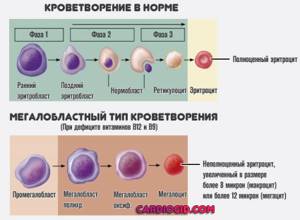
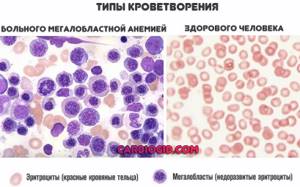
Megaloblastic anemia
It develops if the body has little vitamin B12. Or when the substance is not absorbed enough. For example, during inflammation of the digestive tract, metabolic disorders.
The disease leads to changes in the hematopoietic pattern. Inferior cells emerge into the channel. But they are registered by hardware analyzers, which is why false results are obtained.
The condition is accompanied by several typical symptoms:
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Feeling of fog in the head.
- Dyspnea.
- Exercise intolerance.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Pressure surges.
- Cardiac disorders.
Here are just some of the signs of the disorder.
Treatment is carried out by hematology specialists. The goal is to compensate for the vitamin deficiency. If necessary, correct the pathological process that interferes with the absorption of the substance.
Artificial substitutes are used, and inflammation therapy is also carried out. Read more about the megaloblastic form of anemia in this article.
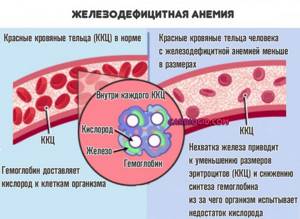
Iron-deficiency anemia
Another type of disorder. In this case, there is not enough iron. Unlike the megaloblastic form, this one is not as aggressive and develops rather slowly.
A full clinic unfolds over several weeks, or even months.
Among the manifestations of the pathological process:
- Feeling weak.
- Heart disorders.
- Drowsiness.
- Brittle hair and nails.
- Dry and dull skin.
- Pallor.
- Tendency to distort taste preferences.
- Dyspnea.
- Impaired memory and cognitive functions in general.
The patient needs to be treated. The task falls on the shoulders of the hematologist. Load doses of iron are prescribed and the drug is administered according to a strictly verified scheme.
If the reason is insufficient absorption of the substance, treatment of the underlying pathological process is required. This is the only way to bring the situation back to normal. Everything takes up to several weeks.
Read more about the causes and treatment of iron deficiency anemia here.
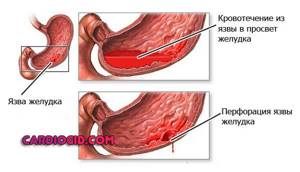
Blood loss
Massive or scanty. Doesn't matter. The point is that the body tries to compensate for the violation on its own. After all, formed cells leave the body mechanically and fall out of active activity.
The intensification of bone marrow function is temporary. Therefore, as soon as the condition returns to normal, the number of red blood cells will also restore itself.
Whether the patient needs to be treated is decided by the doctor in each specific case. The same applies to the treatment regimen.
In case of heavy blood loss, a transfusion of red blood cells, plasma or whole liquid connective tissue is prescribed. In this case, it is necessary to observe that there is no conflict or rejection of the substance. This is the main task for the first few days after the procedure.
If the blood loss is not so great, they look for the cause of the disorder. These may be erosive ulcers, inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract, gynecological problems and other disorders.
The question remains with the specialist. After a thorough diagnosis, the cause is eliminated. From now on, everything should return to normal.
Therapy is the prerogative of the hematologist. Also, if necessary, third party specialists are involved.
Pathologies of the cardiovascular system
Diseases of cardiac structures. Multiple in nature. Here are just the most common options:
- Hypertension. Persistent increase in blood pressure.
- IHD. Cardiac ischemia.
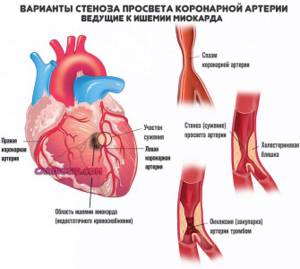
- Coronary insufficiency. When the myocardium does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients.
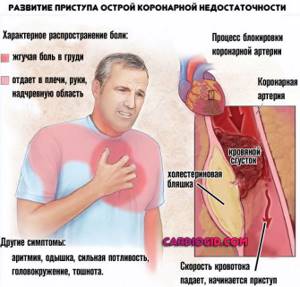
- Previous heart attack. As an acute, urgent condition.
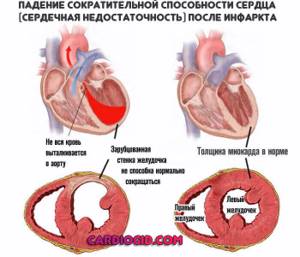
All diseases of the cardiovascular system, one way or another, are united in the hypoxic factor. There is not enough oxygen. Is the body trying to compensate for the pathological condition through increased production of red blood cells? which causes an increase in RBC in the blood.
For a while this is enough, then everything starts all over again. As soon as decompensation of the condition occurs.
Treatment is specific, depending on the diagnosis. In any case, a cardiologist should work with the patient.
Antihypertensive drugs, cardiac glycosides, and organic nitrates are prescribed.
It is important that the means clearly correspond to the situation. Otherwise it will only get worse.
RBC values will return to normal as soon as the primary pathological process is eliminated. This may take up to several months or a little less.
Hypoxia
Often, RBC in a blood test deviates from the norm upward as a result of the ischemic process. It has already been said about it. A special case of a violation is coronary insufficiency and a heart attack. But there are also situations that are not so pronounced.
For example, among them:
- Encephalopathy. A chronic complex process in which the brain is insufficiently supplied with blood.
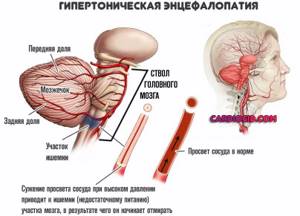
- Transient ischemic attacks. Acute nutritional disturbances of cerebral structures without signs of critical condition.
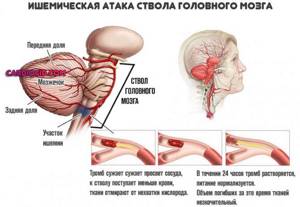
- Stroke. Intense disorder of trophism of nerve tissues of the brain. Urgent help is required, otherwise the patient may die.
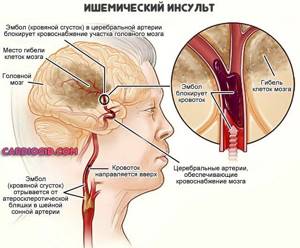
- Weakening of trophism against the background of thrombosis and vascular inflammation.
The point is one thing. These disorders cause poor nutrition and breathing. The body tries to compensate for the deficiency. If the disorder is long-standing, there is no point in it. The process will continue to progress.
Treatment is the task of a specialized specialist. If the heart suffers, a cardiologist works. The brain is a neurologist. You may need the help of a vascular surgeon.
Therapy is multifaceted. Depends on the pathological process. Cerebrovascular drugs are prescribed. If the problem is excess cholesterol - fibrates, statins. And further down the list.
Lung pathologies
Disorders of the respiratory system. If you understand how gas exchange occurs, it becomes clear what's what.
The fact is that red blood cells are filled with oxygen upon contact with the lungs. Carbon dioxide is removed in exactly the same way. Therefore, any deviations in the functioning of the respiratory structures lead to the same outcome.
The degree of disturbance depends on how pronounced the primary pathological process is.
Possible diagnoses include:
- Pneumonia.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Respiratory failure.
- Tracheitis, laryngitis. Even if indirectly, they affect the activity of the lungs.
And so on. If the pathology is neglected, it will be difficult to cope. It is necessary to begin correction from the very start of the disease.
Therapy falls on the shoulders of the pulmonologist. Several types of drugs are used:
- Bronchodilators. To expand the lumen of the respiratory tract and restore normal gas exchange.
- Antibiotics. To eliminate the infectious process.
- Stimulators of antibody production. So-called antiviral agents.
The list is far from complete. Glucocorticoids are also used. After correction of the underlying condition, red blood cells return to normal.
Bad habits
Smoking is especially harmful. The problem is not so much nicotine, cadmium compounds, antimony and arsenic. They are contained in cigarettes and any tobacco products and really harm the body.
It's a matter of hot smoke. It burns the walls of the respiratory tract and causes thermal damage. More mucus is produced, a slow but sure degeneration of tissues, the epithelium of the inner lining of the bronchi and lungs, occurs.
The result will not take long to arrive. Chronic inflammation at an early stage leads to an increase in the content of red blood cells, RBC increases.
Then, if you don’t do anything and don’t give up cigarettes, lung cancer is likely to develop. This condition will lead to an even more rapid increase in the number of red cells.
There can be only one treatment here - quit smoking as quickly as possible. It's difficult to cope on your own. If this is the case, you should consult a psychotherapist.
Smoking drugs: marijuana, hashish, nasvay and other chemical rubbish has an equally negative effect and even more so. Complications develop many times faster and are much more dangerous.
Malignant oncology
Simply put, cancer. It doesn’t really matter what localization it is. In any case, when the process is sufficiently developed, bleeding begins.
Unnoticeable at first. But red blood cells leave the body and lose their functional properties. Then more and more pronounced. The body compensates for the lack of cells by producing new ones.
Cancer has specific focal symptoms. But there are some general signs of a violation:
- Increase in body temperature.
- Pathological thinness. Due to the gluttony of cells and the need for abundant nutrition. There is simply nothing left for all other systems.
- Weakness.
The treatment strategy is standard. With some reservations and amendments for a specific clinical case.
- The tumor is removed. As much as possible. Ideally, if you can eliminate it completely.
- Radiation treatment involves exposing tissue to radiation.
- Chemotherapy. To kill remaining cells and prevent relapse.
The prognosis is determined by the oncologist who is caring for the patient. It is better to address the question to him.
Bone marrow disorders
As a rule, acquired forms of the pathological process. These are so-called myeloproliferative diseases. When cells are produced in excess.
RBC in the blood test is increased due to the fact that the brain substance synthesizes them too quickly - the rate of maturation also increases. True and false forms of violation are possible.
- In the first case, the red blood cells are complete. These are ordinary red blood cells.
- In the second, the cells are immature. Defective forms, although registered by analyzers, still cannot perform the functions assigned to them.
Bone marrow disorders are often congenital. Genetically determined types of pathology cannot be treated. All that remains is to fight the symptoms.
In all other cases, etiotropic methods are used.
The basis is cytostatics. They slow down the production of formed cells and suppress bone marrow activity. This is a temporary but absolutely necessary measure.
As a supplement, glucocorticoids are prescribed. True, not always. Hematologists provide treatment.