Advantages
- The test is highly accurate (95%) and excludes false positive results.
- The study is safe and can be used in different cases:
- The test has no side effects and does not involve the introduction of any drugs into the body.
- The method is not sensitive to the BLC vaccine and non-tuberculosis mycobacteria.
- The study has no contraindications.
- with a latent form of tuberculosis infection,
- both pulmonary and extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis,
— HIV-positive patients,
- if the patient receives Anti-TNF therapy,
- patients on renal dialysis and those who have undergone organ transplantation,
- children and adults without age restrictions,
- pregnant women,
- undernourished people,
- as a screening examination.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, antibodies
Antibodies to the causative agent of tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) are specific immunoglobulins produced by the immune system in response to infection with the causative agent of tuberculosis.
Synonyms Russian
Total antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, immunoglobulins of class G and M to the causative agent of tuberculosis (mycobacteria).
English synonyms
Anti-mycobacterium tuberculosis IgG, IgM, M. tuberculosis antibodies, IgG, IgM, MBT antibodies, total.
Research method
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
Do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood.
General information about the study
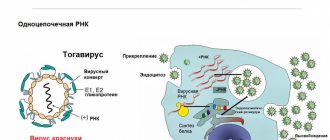
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by aerobic mycobacteria (M. tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. africanus, M. microti), common in soil, water and animals. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a species of mycobacterium that causes tuberculosis in humans in 92% of cases.
M. tuberculosis is transmitted by airborne droplets from patients with active tuberculosis. In 90% of people, after a primary infection, mycobacteria settle in the lower parts of the lungs and do not lead to the development of the disease, since an immune response is developed that does not allow an increase in the number of bacteria. However, if the immune system is severely weakened, tuberculosis bacilli begin to actively multiply and tuberculosis passes from a latent form to an active one. Possible damage to the lungs, bones, joints, genitourinary organs, lymphatic system, skin, eyes and nervous system.
Microscopic examination of sputum culture is still considered the gold standard for diagnosing tuberculosis. However, this method has both its advantages (high specificity) and disadvantages (low sensitivity, since a certain concentration of bacteria in the sample is required). The effectiveness of the method is lower for specific categories of people (HIV-infected people, people over 60 years of age and children who also have difficulty collecting sputum). In addition, this study takes a long time, since bacteria require 6-8 weeks to grow. Along with the bacteriological method, X-ray examination is widely used. Both methods are applicable only to pulmonary forms of tuberculosis. On the other hand, using the tuberculin test method it is almost impossible to differentiate latent and active forms of tuberculosis.
Differential screening diagnosis of active tuberculosis is possible by determining specific antibodies to M. tuberculosis by enzyme immunoassay.
At the active stage of tuberculosis, intensive production of IgG and IgM antibodies to specific antigens begins, which can be detected in the blood serum within a month from the beginning of activation of mycobacteria. High specificity of the test is achieved by using antigens specific to M. tuberculosis, which eliminates false-positive results in individuals vaccinated and infected with other mycobacteria. The sensitivity of this test system ranges from 61% (tuberculosis of the lymph nodes) to 100% (tuberculous exudative pleurisy) depending on the location of the infection; specificity – 95%.
What is the research used for?
- To detect active tuberculosis, especially extrapulmonary forms.
- To monitor the effectiveness of tuberculosis treatment.
- To identify infected individuals.
- To confirm the diagnosis (along with the use of additional diagnostic tests).
When is the study scheduled?
- When it is known that the patient has had long-term contact with tuberculosis patients or that his work involves constant contact with people at risk (homeless people, injection drug users, people in prison).
- For appropriate symptoms: weakness, fatigue, low-grade body temperature, night sweats, persistent cough for 2-3 weeks, chest pain (pulmonary tuberculosis), chronic pain in the back, joints, abdominal area with unknown etiology.
- For long-term unsuccessful treatment of chronic prostatitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis and inflammation of the endometrium (tuberculosis of the genitourinary organs).
- For anemia, leukocytosis.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
Result: negative.
Positivity rate: 0 - 0.79.
Negative result
- No active form of the disease.
Positive result
- Active form of tuberculosis of various localizations.
- Antibodies remaining after an illness.
- Tuber infection is the presence of mycobacteria in the body (if there are no clinical manifestations of the disease).
What can influence the result?
Effective treatment of tuberculosis is accompanied by a sharp increase in the number of antibodies, the level of which returns to normal after some time.
Important Notes
- This test is especially important when, with a negative result of X-ray examination, microscopy and the PCR method, there are symptoms of unknown origin, similar to manifestations of extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
- A positive result is not a sufficient basis for making a diagnosis of “active tuberculosis”, since this analysis must be accompanied by other diagnostic tests (bacterial culture microscopy, PCR) in accordance with the clinical picture and suspected sites of infection for a more in-depth examination.
- In the early stages of infection, the test may be negative because sufficient antibodies have not yet been produced. In such cases, if there are symptoms of infection, it is recommended to repeat the test after 2-7 weeks or perform other types of testing.
- The test is insensitive to BCG vaccination, since it involves antigens specific for M. Tuberculosis and uncharacteristic for M. Bovis.
- The possibility of false positive results from this analysis is excluded due to the lack of interference with other types of mycobacteria.
- The test is designed to detect only the active form of tuberculosis, regardless of its location.
- This study is suitable for patients with immunodeficiencies of various origins (HIV, oncology), since the test system can detect immunoglobulins of all three classes (G, M, A).
Also recommended
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis, DNA [real-time PCR]
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, DNA [real-time PCR]
Who orders the study?
Phthisiologist, infectious disease specialist, therapist, general practitioner.
Indications
It is preferable to take a T-SPOT blood test for tuberculosis in the following cases:
- Children who have been vaccinated with BCG and who have a false-positive Mantoux reaction.
- People for whom, for some reason, intradermal tests are difficult or contraindicated.
- If you have an allergic reaction to tuberculin, as well as other allergic and autoimmune diseases.
- If there is a possibility of extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
- As a screening examination for healthcare workers, military personnel, and people who travel a lot.
- Pregnant women.
- Patients with chronic diseases that reduce immunity (HIV, diabetes).
- Patients who are undergoing therapy that suppresses the immune system (chemotherapy, radiation, glucosteroid therapy, treatment with renal function replacement).
- Patients on kidney dialysis who are preparing for or have undergone an organ transplant.
Dear parents, please pay attention!
When taking a T-SPOT test for tuberculosis, the decision on additional examinations, admission to vaccination, admission to kindergarten or school is made by a TB doctor. There is no appointment with a TB doctor at the Medical Center. If the T-SPOT result is planned to be provided to a preschool or school institution, it is necessary to clarify in advance whether your institution will accept these results or will require a certificate from a TB doctor.
Detailed description of the study
Tuberculosis is a widespread infection that is one of the world's ten leading causes of death. In 2021, 10 million people fell ill with it, of which 1 million are children, for whom tuberculosis poses the greatest danger.
The causative agent of tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, is a microorganism that is spread by airborne droplets from tuberculosis patients. Typically, Mycobacterium tuberculosis affects the lungs, but can also affect joints, bones, eyes, skin and even the nervous system.
The danger of Mycobacterium tuberculosis also lies in the fact that they have many mechanisms that help them evade the immune response. Mycobacterial strains that are resistant to drugs and are difficult to treat are becoming more common.
Nevertheless, according to the World Health Organization, tuberculosis can and should be treated. Most cases of the disease are treatable, and the earlier the diagnosis is made, the more successful it is.
Common symptoms of active pulmonary tuberculosis include:
- Cough with sputum and sometimes blood;
- Weakness;
- Heat;
- Unexplained weight loss;
- Chest pain;
- Increased sweating at night.
Screening diagnostic methods are the Mantoux test and fluorography, or chest x-ray. These measures allow you to suspect tuberculosis in the early stages, but have low accuracy. A microscopic examination of sputum for the presence of mycobacteria is more informative. This method detects about half of actual cases of the disease and does not provide insight into drug resistance. For accurate diagnosis, molecular biological methods are required, one of which is the assessment of antibody titer (PCR testing is also informative).
Preparation
- When donating blood, you can drink plain water.
- For children under 7 years of age, an interval of at least 3 hours between blood donation and food intake is allowed.
- For children 7-15 years old, the interval between donating blood and eating should be at least 4-6 hours.
- For adolescents over 16 years of age and adults, blood must be donated on an empty stomach (8-12 hours of fasting).
- Taking medications while undergoing testing is in consultation with your doctor.
- To ensure that the results are informative, the analysis should be taken when there is no exacerbation of any disease.
Antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis quality.
Antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis qualitative
— identification of antibodies that are produced by the immune system in response to infection with the causative agent of tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis), for the purpose of early detection of tuberculosis infection.
Tuberculosis
is a widespread infectious disease in the world, the causative agent of which is the aerobic mycobacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The route of transmission of infection is airborne droplets and household contact.
The main source of infection is a sick person. In active pulmonary tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis may be present in the sputum. Only in 10% of cases does primary tuberculosis infection occur. In 90% of cases, mycobacteria settle in the lower parts of the lungs, and thanks to the development of an immune response, the disease does not develop. But it is worth noting that of these, only about 10% experience complete relief from the infection; in the rest, the immune system only manages to keep the infection in a latent form, in which bacteria do not multiply. When the immune system is weakened, dormant bacteria can induce reactivation and cause active tuberculosis.
Clinical picture of tuberculosis
The main symptoms of tuberculosis: general malaise, prolonged slight increase in body temperature to 37–37.5 ° C, headache, cough with sputum production for more than 3 weeks, chest pain, hemoptysis, sudden weight loss (5–10 or more kg), loss of appetite, increased fatigue.
Antibodies for tuberculosis
When infected, at the active stage of tuberculosis, lymphocytes produce immunoglobulins IgA, IgG and IgM - special proteins that neutralize bacteria, which can be detected in blood serum within a month from the beginning of activation of mycobacteria.
Analysis of the presence of antibodies to the causative agent of tuberculosis is not an independent diagnostic test. A positive test result does not allow one to distinguish between an active process and a latent infection; the interpretation of the analysis depends on the clinical picture. The test is recommended for use in combination with other examination methods, in the presence of clinical signs and symptoms of active disease, as well as in persons who are in close contact with patients with active tuberculosis. At an early stage of infection, the biomaterial may not contain immunoglobulins in sufficient quantity to determine a positive result.
If an infection is suspected and a negative result is obtained, it is necessary to conduct a dynamic study after 2–7 weeks, using other types of studies.
The use of the test is limited in immunosuppressed, immunodeficient individuals (including those with HIV infection), since their antibody level can be very low. With effective treatment, the concentration of antibodies in patients may increase, and the test result may be positive. It is advisable to evaluate the test results in conjunction with general information about the patient and the results of other types of research.
Indications:
- in combination with other types of research;
- for early diagnosis of tuberculosis infection.
Preparation
It is recommended to donate blood in the morning, between 8 and 11 am. Blood is drawn on an empty stomach, after 4–6 hours of fasting. It is allowed to drink water without gas and sugar. On the eve of the examination, food overload should be avoided.
Interpretation of results
The answer is given in a qualitative format: “positive”, “negative”, “doubtful”.
Reference values: negative.
Positively:
- infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis or other mycobacteria;
- false positive result (up to 10%) due to interference or relatively recent vaccination.
Negative:
- no infection;
- early stage of infection;
- low antibody titer in immunosuppressed and immunodeficient individuals;
- low antibody titer, false negative result in infected individuals (up to 15%).