If a gynecologist has diagnosed you with an ovarian cyst, do not be alarmed: as a rule, these formations are benign and do not pose a danger; surgery is not required. Often they do not need to be treated at all and disappear on their own within a few months. It is enough to periodically visit a gynecologist and undergo an ultrasound examination.
- What types of ovarian cysts are there?
- When is laparoscopy performed?
- When is laparoscopy not performed?
- Benefits of laparoscopy
- Preparation
- How is laparoscopy performed?
- Postoperative period
- Complications
- Is it possible to get pregnant after removing an ovarian cyst?
Sometimes ovarian cysts still have to be removed. Operations can be performed without an incision, through several punctures in the abdominal wall - laparoscopically. Euroonco employs expert-level gynecological surgeons who have extensive experience in performing such interventions. Come for a consultation with our specialist: he will tell you whether surgery is necessary in your case, and prescribe an examination that will help distinguish a benign neoplasm from a malignant one.
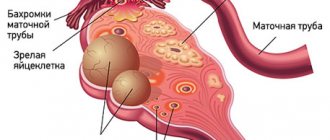
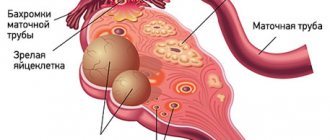
A cyst is not a specific disease. This term refers to any pathological cavity with fluid. The reasons for its formation are different. According to statistics, ovarian cysts are diagnosed in every tenth woman. They most often occur during puberty and menopause. Some girls have them from birth.
What types of ovarian cysts are there?
All ovarian cysts are divided into two large groups: functional , which occur in most cases, and pathological , which doctors have to deal with much less frequently.
Functional cysts are the result of disturbances during the menstrual cycle. Usually they do not cause complications and disappear on their own. They come in three types:
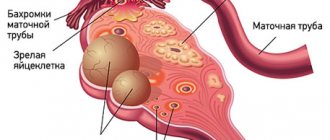
- Follicular . follicle matures in a woman’s ovaries . Normally, it should open and release the oocyte. If this does not happen and the follicle continues to grow, it turns into a cyst.
- Corpus luteum cysts . After the follicle releases the egg, it turns into a special gland - the corpus luteum . It produces the hormones estrogen and progesterone. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum atrophies. And if fluid accumulates in it, it turns into a cyst.
- Theca-luteal cysts often develop as a side effect of infertility treatment with hormonal drugs.
Pathological ovarian cysts are not associated with the menstrual cycle. They are always characterized by the appearance of “wrong” cells that should not be present normally. The most common types of pathological cysts:
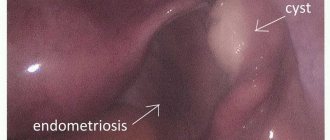
- Endometrioid . This is a form of endometriosis, a condition in which endometrial tissue (the lining of the uterus) gets into unusual places and grows there. In the ovaries, it can form cavities with fluid. They often appear as “chocolate” cysts filled with dark blood.
- Dermoid cysts , or teratomas , are a special type of benign tumors made from embryonic cells. There may be different tissues inside them, for example, skin, hair, nails. Dermoid cysts become malignant very rarely.
- Cystadenomas are benign neoplasms of epithelial cells. Usually they are filled with contents of a mucous or watery nature.
For more information about malignant cysts, please visit the ovarian cancer page on our website.
Questions
What to do if bloating occurs after laparoscopy?
As a rule, this condition does not require treatment and goes away on its own within 5-7 days. A small adjustment in nutrition, taking enzyme preparations and sorbents will help smooth out the discomfort.
I had surgery 7 years ago. Immediately after the operation, the belly increased above the navel. I asked the surgeon if it would pass, he replied that it would pass. However, 7 years have passed. Now I am 65 years old. gained weight. My stomach became like a ball from my chest to my navel.
To assess your condition, first of all, a personal examination is necessary, since with an online consultation, it is impossible to make an adequate conclusion based on the data provided. It is possible that the increase in abdominal volume is associated with a general increase in body weight.
When is laparoscopy performed?
If the ovarian cyst is small, does not cause symptoms and does not look cancerous, it can be left alone. No surgery needed. The gynecologist will prescribe periodic examinations and control ultrasounds. Moreover, postmenopausal women will have to do this more often, because they have a higher risk of malignant tumors.
Are there effective medications?
In some cases, hormonal contraceptives may be helpful. They help prevent the formation of new cysts in the ovaries, but do not affect the growth of existing ones. If a woman is bothered by pain, the doctor may prescribe drugs from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). But this is only symptomatic treatment. The only way to get rid of the formation is surgery.
If the cyst is “problematic,” then the doctor will definitely say that it needs to be removed. Indications for surgery:
- Large size of formation. In most cases, ovarian cysts have a diameter of 1–3 cm. Very rarely they reach 15–30 cm.
- Presence of symptoms: abdominal pain, pelvic pain, bloating, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, heavy periods, vaginal bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle. A large cyst can compress the intestines and bladder. This leads to problems with stool and urination.
- Suspicion of a malignant nature of the cyst - the risks are increased in postmenopausal women.
- Continued growth over 2–3 menstrual cycles.
- Pathological ovarian cyst.
What happens if the cyst is not removed?
If the doctor said that the cyst needs to be removed, then delaying the operation is primarily dangerous for postmenopausal women. They, as we have already mentioned, have a higher risk that the formation may turn out to be malignant. And with cancer, time is critical. The later treatment is started, the lower the chances that it will be successful and that remission will be achieved. The prognosis worsens and survival rate decreases.
At the Euroonko clinic you can receive treatment for ovarian cancer according to modern standards. Our doctors perform operations of any complexity; we have access to all the latest generation antitumor drugs registered in Russia. We work according to modern European, American, Israeli treatment protocols. For ovarian cancer complicated by peritoneal carcinomatosis, we use an innovative technique - hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC).
With benign ovarian cysts, serious complications can also occur, although they are rare. Large cysts may rupture. In this case, severe bleeding develops into the abdominal cavity, and severe abdominal pain occurs.
As the cyst grows, the risk of ovarian torsion increases. Due to compression of the blood vessels, it stops receiving blood supply, severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting occur. The result may be necrosis (death) of the ovary, and it will have to be removed urgently.
If you experience symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or a fever of more than 38 degrees, you should immediately seek medical help.
Other edema
After abdominoplasty, not only the area in which the correction was performed may swell, but also other areas of the body. This is a fairly rare situation, but sometimes this unpleasant side effect occurs. The dangers and risks depend on where exactly the swelling is located.
Swelling in the genital area is considered a type of normal condition. This area contains a lot of fatty tissue, which is loose and therefore absorbs and retains liquid well. The swelling in this area will go away on its own over time, you just need to be patient.
Swollen hands can be a concern when IVs are administered with various medications, causing the vein walls to become swollen and inflamed. This condition cannot be called dangerous; after stopping the IV drips, the phenomenon goes away on its own. But swelling of the legs, which occurs with varicose veins or a tendency to it, is a cause for concern if it lasts more than two weeks. In this case, it is recommended to consult with a specialist - a phlebologist or surgeon.
Preparation
Ovarian cysts are usually detected during an ultrasound examination. In order to better assess the size, location and internal structure of the neoplasm, the condition of the ovary, they usually resort to not only transabdominal (through the abdominal wall), but also transvaginal (using a special sensor inserted into the vagina) ultrasound.
In rare cases, usually when a malignant nature of the formation is suspected, computed tomography and diagnostic laparoscopy are prescribed. of cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) in the blood testifies in favor of cancer . But this analysis is unreliable, since a positive result can be obtained for uterine fibroids, endometriosis and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
Based on the examination results, the doctor advises the woman and explains which treatment tactics will be optimal in her case. If laparoscopic surgery is indicated, a date for hospitalization is set. You need to undergo a preoperative examination. It usually includes the following diagnostic methods:
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- General urine analysis.
- Blood test for hormone levels.
- Tests for infections.
- Cervical smears - cytological, flora.
- Blood clotting study.
- Determination of blood group AB0, Rh factor.
- Electrocardiography.
- X-ray of the lungs.
Laparoscopic removal of ovarian cysts is performed under general anesthesia - endotracheal anesthesia. The woman is hospitalized in the hospital the day before surgery. You can’t eat anything for 8 hours before surgery, and you can’t drink anything in the morning. Some time before anesthesia, premedication : the woman is given drugs that help her relax and calm down.
Disorders of the liver, pancreas and intestinal tract after cholecystectomy
Removal of the gallbladder rebuilds the processes of bile formation and bile excretion.
- There is an increase in bile production by the liver, which is the main cause of diarrhea after cholecystectomy. Taking choleretic drugs in these cases is undesirable!
- The most common area affected after gallbladder removal is the pancreas. In case of cholelithiasis, dysfunction of the sphincter apparatus of the biliary tract, impaired motor function of the gallbladder before surgery, chronic biliary pencreatitis is formed (pancreatitis, the cause of which is a violation of the bile secretion system).
- Sometimes there are lesions of the ductal system that disrupt the outflow of bile - narrowing, stones in the ducts, enlarged lymph nodes, inflammatory diseases in the sphincter-ductal system.
As a result, exacerbations of chronic pancreatitis after removal of the gallbladder occur quite often - from 5 to 90%. This scatter is explained by the fact that sufficient examination was not carried out before the operation to assess the condition of the pancreas, but in some cases there is an overdiagnosis of chronic pancreatitis.
In medical practice, it is noted that the longer gallstones exist in the gallbladder, the more often chronic pancreatitis occurs.
In the pancreas, the volume of enzyme secretion decreases, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency develops, and digestive processes are disrupted. Cholecystectomy, performed on time, helps to improve or normalize the parameters of the enzymatic function of the pancreas.
After removal of the gallbladder, the function of the duodenum is often disrupted, which is confirmed by the appearance of duodenogastric reflux, i.e., the reflux of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach, causing morphological changes in the outlet of the stomach and the formation of chronic reflux gastritis (gall).
After removal of the gallbladder, the function of the small intestine (absorption of food components) and the motor function of the large intestine (constipation, diarrhea) are impaired.
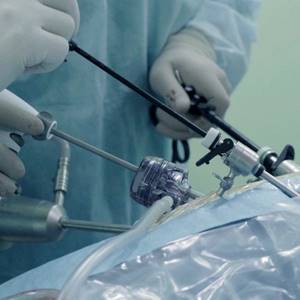
How is laparoscopy performed?
Laparoscopic intervention is performed through several punctures in the abdominal wall. Through one of them, in the navel area, a laparoscope - an instrument with a miniature video camera. It broadcasts an enlarged image onto the screen. For better visualization during surgery, the abdominal cavity is filled with gas.
Special laparoscopic instruments are inserted through additional punctures, and the cyst is removed with the help of them.
Depending on the specific situation, the scope of the operation varies:
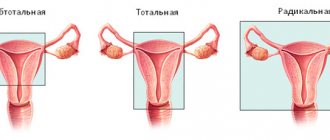
- Often it is possible to remove only the cyst, preserving the ovary.
- In some cases, it is necessary to remove the entire ovary - to perform an oophorectomy (oophorectomy) - while the second ovary can be saved. This has to be done if a malignant tumor is suspected, or if the cyst is in an “inconvenient” location, when it is difficult to remove it separately.
- In rare cases, both ovaries may have to be removed. This operation is performed only in extreme cases, especially in women of reproductive age, since menopause occurs after removal of both sex glands. The levels of female sex hormones decrease, and this can lead to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, hot flashes, etc.
Don't hesitate to ask your doctor questions before surgery. Ask what is the likelihood that during the operation you will have to remove both ovaries, what negative consequences this threatens, and how to cope with them.
Reasons for appearance
When performing correction in the abdominal area, the surgeon makes fairly large incisions and removes a large amount of tissue. During the intervention, various parts of the body are damaged - blood vessels, lymphatic channels, epithelium, connective tissues and more. In response to injury, the body begins to produce special substances that promote healing of damaged areas and restoration of normal physiology in the operated area.
These substances increase the permeability of the capillaries of the blood and lymph flow systems, due to which a certain amount of fluid from the vessels leaks into the soft tissues of the injured area. Thanks to this mechanics, damaged areas are nourished, tissue is restored and a new vascular network is formed. Abdominal swelling after abdominoplasty is a natural phenomenon in the postoperative period, part of the regeneration process, so you should not be afraid of it.
Complications
Laparoscopic operations are associated with a low risk of complications. As after any surgical intervention, in rare cases, infection and suppuration in the area of surgical sutures and bleeding are possible. If you are concerned about severe pain, vaginal bleeding, or increased body temperature, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Adhesions may occur after surgery. Very rarely, during surgery, damage to neighboring organs (intestines, bladder) is possible.
At the Euroonko clinic, operations are performed by experienced gynecological surgeons. Our operating room is equipped with modern equipment, multifunctional laparoscopic stands from leading manufacturers. This helps to minimize risks and perform the operation as safely as possible.
After removal, the cyst may recur, in the same ovary or on the other side. Only removal of both ovaries helps to completely eliminate relapse. But such an operation leads to menopause and undesirable consequences, so it is resorted to only in extreme cases.
Medicines and procedures
If abdominoplasty has left swelling so significant that it is difficult to reduce it using natural methods, various medications can come to the rescue. Usually, heparin ointment, Traumeel, Troxevasin and other similar ointments are prescribed to speed up resorption. It is important to note that under no circumstances should you self-prescribe medications. All medications must be approved by a doctor. In addition, the drugs cannot be mixed, therefore, if the surgeon has prescribed several ointments, they should be applied strictly according to the schedule.
You can also help your body with physiotherapy. This can be lymphatic drainage massage, phonophoresis, pressotherapy and much more. Procedures of this nature also affect the time it takes for swelling to subside after abdominoplasty, reducing the recovery period. But, as in the case of medications, you can resort to physical therapy only in consultation with your surgeon.
Massage is a good help against swelling.
Is it possible to get pregnant after removing an ovarian cyst?
You can get pregnant even with an ovarian cyst. Most often, they do not interfere with pregnancy, but they can make it difficult to conceive a child.
If during surgery only the cyst is removed or at least one ovary is left, the woman’s fertility is preserved. She may become pregnant in the future. Of course, you need to understand that reproductive function is affected not only by surgery. The ovarian reserve (the number of eggs in the ovaries - it constantly decreases with age) and concomitant diseases play a role.
Get a consultation with a doctor at the Euroonko clinic. Our doctor will tell you whether treatment is needed in your case, what type of surgery is indicated for you, and what is the likelihood that you will be able to conceive and carry a pregnancy in the future.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Playing sports during the recovery period
On the third day include:
- porridge with water;
- fermented milk products – kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt, low-fat cheeses;
- easily digestible fruits and berries without peel - apples, bananas, apricots, strawberries, melons and others;
- steamed vegetables - zucchini, peppers, carrots, eggplants, beets, tomatoes;
- seafood;
- boiled eggs;
- whole wheat bread;
- dietary meat and fish in the form of minced meat dishes.
By the end of the week, restrictions are reduced to a minimum. For a month, during the recovery period after laparoscopy, the following are excluded from the diet:
- Fatty, spicy, smoked food. The meat is baked, cooked in a double boiler or slow cooker. Soups are made without frying. Sausages, fatty fish, canned food, marinades, and pork are prohibited. Preference is given to chicken, rabbit, turkey, and veal.
- Products that cause gas formation. Exclude legumes (beans, peas, lentils), raw milk, baked goods (white bread, buns, any homemade pastries), and confectionery.
- Alcohol and carbonated drinks. It is allowed to drink weak tea, fruit drinks, compotes, and still mineral water. It is better to avoid juices, especially store-bought ones, as they contain citric acid and sugar. All alcoholic beverages are completely prohibited for a month. It is also advisable to avoid coffee after laparoscopy - starting from the second week, you can only drink weak coffee without cream.
Important! Doctors do not have a unanimous opinion about cigarettes. Some categorically prohibit smoking for 3–4 weeks, since nicotine and heavy metals slow down regeneration and provoke bleeding
Others believe that abruptly giving up a bad habit and the resulting withdrawal syndrome, on the contrary, can aggravate the patient’s condition.
Throughout the entire rehabilitation, especially in the first few days, meals should be fractional. You need to eat in small portions 6 – 7 times a day. It is necessary to monitor the regularity and consistency of stool.
Make up a balanced and nutritious diet. Food products must contain all the necessary vitamins, minerals, and elements. The exact diet is selected by the attending physician, taking into account the specific disease and individual characteristics of the patient.
Since complete rehabilitation lasts at least a month, it is necessary to limit physical activity. The following are prohibited:
- gymnastics, fitness, callanetics, yoga;
- training in the gym;
- swimming;
- dancing.
It is recommended to walk no longer than half an hour at a time
It is important that the patient avoids rough terrain - beams, ravines, etc. The road should be smooth, without ups and downs. A month and a half after laparoscopy, you can introduce physical exercises
You need to start playing sports gradually, increasing the load weekly. You should gradually introduce a simple set of exercises - turns, bends, leg swings. Then more difficult classes are included.
INDICATIONS FOR SURGICAL INTERVENTION
This modern operation has a number of advantages:
- detailed study and examination of organs,
- no obvious scars,
- minor blood loss,
- reducing the risk of infection and ingestion of foreign bodies,
- fast recovery.
Laparoscopy may be prescribed for:
- adhesions. This disease causes pelvic pain and female infertility. Often the method allows you to completely cleanse the pelvic organs,
- cysts of different shapes and sizes,
- complicated pregnancy,
- various tumors,
- endometriosis of any stage,
- hysterectomy,
- oncology of the genital organs.
Laparoscopy is considered one of the most gentle interventions. Dangerous complications are very rare, the frequency is one case per thousand. Negative consequences can be expressed in injuries to internal organs or disruptions in the cardiovascular system.