How is an ultrasound of the stomach done?
In medical clinics, there are two ways to perform an ultrasound examination of the stomach - transabdominal and endoscopic forms. Both methods have their pros and cons.
Transabdominal ultrasound of the stomach
With transabdominal ultrasound of the stomach, scanning is carried out through the wall of the abdominal cavity. This fairly simple, non-invasive examination method is most often used for primary screening of gastrointestinal tract diseases. It has no contraindications. The doctor evaluates the anatomy of the stomach in a standard transabdominal manner on an empty stomach in a position where the patient lies either on his back or on his side. At the beginning of the procedure, the subject is asked to lie down on a couch covered with a disposable sheet. The ultrasound doctor, after lubricating the sensor and the area of study with gel, systematically moves it along the abdominal wall, receiving tissue scans on his monitor.
Endoscopic ultrasound of the stomach
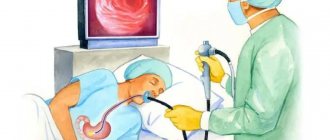
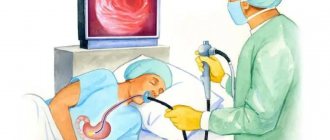
The endoscopic ultrasound method of the stomach is considered one of the most informative ways to examine the stomach. EndoUS is a method of endoscopic diagnostics, during which intraluminal ultrasound scanning of the walls of the studied organ of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as adjacent anatomical structures and tissues, is performed. During the examination, a flexible probe with a camera on the end is placed directly into the stomach through the mouth. To do this, the patient is asked to lie on his side; a mouthpiece is placed in the mouth opening, which must be clamped with the teeth. The mouthpiece provides protection against damage to the flexible part of the sensor. In order for the sensor to pass more easily into the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to perform swallowing movements. This form of ultrasound diagnostics is usually performed under local anesthesia, as the procedure can be unpleasant.
Ultrasound of internal organs for children at the Markushka clinic
An ultrasound of the child’s internal organs is done in order to fully assess their structure, condition and functional characteristics. The harmlessness and information content of ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to effectively use this technique for examination, starting from a very early age. Thus, an ultrasound of the internal organs of a newborn is often performed as part of the first screening aimed at identifying possible congenital pathologies. In infancy, an ultrasound scan of the child’s lungs
, if he has breathing problems and an ultrasound of the thymus gland - in children it shows the state of immunity.
If the baby has problems with bowel movements, frequent regurgitation, and little weight gain, the doctor may also recommend a separate ultrasound of the newborn’s stomach
to determine the cause of these problems. Ultrasound of the stomach in older children is often necessary as a preventive or diagnostic measure, since problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, unfortunately, are not uncommon in our time, which is due to poor ecology and poor nutrition. To be more informative, the examination is carried out comprehensively, that is, in addition to ultrasound of the stomach, the child undergoes ultrasound diagnostics of the intestines, esophagus, pancreas and liver. It is worth remembering that the norms of liver ultrasound in children, as, in general, the norms regarding other organs, have their own characteristics and are very different from adults, so the examination results should be interpreted only by a doctor.
It is important to take into account that in order to increase the information content of the ultrasound, children must strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions regarding diet, which will allow them to correctly determine the size and location of the pancreas, liver and other organs. This is especially important when preparing for an ultrasound of the esophagus in a child.
, and examination of the intestines. Many parents are concerned about the question when prescribing an ultrasound of the intestines for a child: “How is this procedure done?” In most cases, the transabdominal method is used, which does not distinguish ultrasound of the child’s intestines from other ultrasound examinations. Only rarely is the endorectal method used with the insertion of a sensor into the rectum. But even if the study is scheduled to be conducted in this particular way, you should not worry. The sensor used is small in size, and the procedure causes minimal discomfort.
In addition to an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, it is worth doing an ultrasound of the inguinal hernia
if there is a suspicion that the child has it. In this case, a timely examination will allow you to take conservative measures in time or solve the problem promptly.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs of a child
may also sometimes be prescribed. Boys are referred to it in the absence of one of the testicles in the scrotum, as well as in cases of severe dropsy, to decide whether the operation is advisable. Girls are examined to exclude malformations of the uterus and ovaries. In addition, a pelvic ultrasound is performed on a child to determine the sex in the presence of a genetic pathology. Much more often, doctors use a diagnostic method such as pelvic ultrasound in adolescents in order to be able to observe the process of development of the internal genital organs.
Ultrasound of the stomach with water-siphon test
Ultrasound of the stomach with a water-siphon test is a type of transabdominal ultrasound. It is carried out to study the function of gastric emptying. This procedure takes place in two stages. The first results are taken in the morning on an empty stomach. The patient is in a standing or sitting position, then the doctor applies the gel to the abdomen and begins scanning, moving the sensor sequentially in different directions across the abdominal area. After the first reading, the patient must drink a glass of tea without sugar through a straw, and after 5 minutes the test is repeated. Afterwards, the doctor compares the results and calculates the time it took for the gastric sphincter to return to its original position. For a healthy person, emptying time takes 25 minutes. Due to decreased gastric motility, neuropathy of various etiologies, or other diseases, fluid may remain in the stomach for more than 40 minutes. This study helps identify pyloric stenosis or reflux due to sphincter insufficiency.
| Ultrasound service | Price according to Price, rub | Promotion price, rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, stomach) | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of one organ (liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, bladder, adrenal glands) | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys | 1700 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the bladder | 2000 rub. | |
| Kidney ultrasound | 800 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland) | 2400 rub. | 1999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidney + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + pelvic ultrasound with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
| Comprehensive body diagnostics (MRI of the thoracic spine, MRI of the lumbar spine, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist, consultation with a therapist) | 11700 rub. | 7000 rub. |
What is endoscopic ultrasound?
To examine the abdominal and pelvic organs, one of the traditional diagnostic methods is most often used - transabdominal ultrasound.
, which is carried out through the anterior abdominal wall.
Endoscopic ultrasound is a hybrid technology - a combination of ultrasound and endoscopy. If with conventional ultrasound recognition is performed through the skin, then endoUS is performed by inserting a special ultrasound endoscope into the esophagus and directed to the organ that needs to be examined.
«At the Northern Clinic, this procedure will be performed using a specialized echoendoscope manufactured by Pentax and a Hitachi ultrasound scanner. This equipment has an innovative elastography function to evaluate tissue density, which allows the recognition of benign and malignant tumors. The echoendoscope is equipped with a high frequency sensor, which allows you to get a clearer image and see the smallest details; we will notice changes that are simply inaccessible to conventional ultrasound examination
", explains Denis Borisovich.
“Another undeniable plus is that only this method allows you to visualize the walls of the hollow organs of the digestive tract, to examine what is in the deep layers of the walls of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum”
Is the stomach visible on an ultrasound?
What will an endoscopic ultrasound of the stomach show?
On endosonography, the stomach is visible very well. Using this examination, the diagnostician will be able to evaluate the inner layer of the stomach, detect inflammation of the mucous tissue and hyperemia. An endoscopic ultrasound scan will be more accurate than a non-invasive form of diagnosis because the sonologist sees tissue pathologies up close. During the scan, the doctor does a complete analysis:
- esophagus;
- stomach and its walls;
- vascular system.
EUS helps:
- evaluate the layers of the stomach walls;
- register metastases;
- detect malignant tumors;
- determine the location of neuroendocrine tumors.
Using endosonography, the volume of the organ and the condition of the folds are measured, the presence of erosion and polyps is checked, enlarged lymph nodes are visualized, the type of cyst is determined, and an ulcer is detected. By prescribing this type of diagnosis, the doctor has every chance of detecting oncological pathology in the early stages. In case of stomach cancer, the doctor will be able to determine the depth of the tumor, its composition, size, location, nature of the tumor and make a timely decision on resection. Endoscopic ultrasound is an invasive examination method. Therefore, the procedure allows for a biopsy and therapeutic manipulations, for example, to select material for morphological examination using a puncture, and to drain abscesses in the stomach.
What will a transabdominal ultrasound of the stomach show?
During a transabdominal ultrasound of the stomach, the shape, size of the organ, thickness and uniformity of the walls, and signs of congenital anomalies of the stomach are studied. The doctor will pay special attention to echogenicity, which will be different for neoplasms of the wall lining. During transabdominal ultrasound, some features of the body negatively affect the course of the study - these are excess weight and flatulence. Unfortunately, such an ultrasound scan can be uninformative for overweight people, since the fat layer of the abdominal cavity is too large for the ultrasound signal to penetrate through it. In addition, some types of tumors cannot be seen with a regular scan through the abdomen. New methods of abdominal ultrasound using echo contrast agents or Doppler sonography give doctors greater diagnostic capabilities. For example, Doppler ultrasound helps diagnose the vascular system of the gastrointestinal tract in real time. All modern ultrasound methods have the option of visualizing the “picture” not only on the monitor, but also printing it or recording the entire procedure in digital format. This allows specialists to re-examine ultrasound data and compare the results of different scans, studying the dynamics of the disease. All types of gastric ultrasound have their own unique diagnostic advantages. When identifying pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, ultrasound scanning is most often prescribed in combination with other types of hardware examinations - MRI of the abdominal cavity or CT of the gastrointestinal tract, laboratory tests. The decision on the correct combination of diagnostic methods is made by the attending physician, based on the primary diagnosis and the purpose of the scan.
In what cases is endosonography used?
Ultrasound endoscopes come in two types: radial
and
linear
(convex). The radial one allows you to obtain a detailed image of the walls of hollow organs and structures located next to them, and with the help of a linear echoendoscope you can perform a fine-needle aspiration (suction) biopsy to collect material for morphological examination. The main indication for the use of endoscopic ultrasound is the staging of tumor diseases of the upper digestive tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum). During the study, the depth of tumor invasion into the organ wall is determined, and the condition of regional lymph nodes and distant metastases is assessed.
The use of echoendoscopes also makes it possible to diagnose submucosal formations of the upper digestive tract, determine whether a formation is benign or malignant, and identify the layer from which it comes. All this is fundamentally important for determining further treatment tactics.
In addition, EUS helps to diagnose diseases of the pancreaticobiliary zone, identify tumor lesions of the pancreas, major duodenal papilla and bile ducts. Using an echoendoscope, it is possible not only to determine the nature of cystic and other neoplasia of the pancreas, but also to perform a fine-needle aspiration biopsy for morphological examination and confirmation of the diagnosis. “ A linear echoendoscope allows for a number of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures: puncture of affected lymph nodes, puncture of bile ducts and pancreatic cysts, drainage operations. Even small pancreatic cysts can be successfully drained under the guidance of endosonography, which allows you to select the most suitable point for puncture, where there are no large vessels and there is the tightest contact of the cyst wall with the organ wall. All this reduces the risk of complications."
, notes Denis Borisovich.
“The Northern Clinic also uses contrast ultrasound examinations, which make it possible to obtain images of blood vessels in tumors, which increases the accuracy of diagnosis.” D.B. Degterev
Preparing for an ultrasound of the stomach
Transabdominal ultrasound of the stomach requires preparation, which begins several days before the appointment date of the procedure. This is important to obtain the most reliable information during the study. Preparation includes a number of simple steps:
- It is required 2-3 days before diagnosis to exclude from food foods that increase gas formation, for example: bakery and confectionery products, cabbage, legumes, carbonated drinks.
- It is necessary to undergo the study on an empty stomach (drinking is also excluded). The last meal should be 8-9 hours before the procedure. The exception will be patients with diabetes or stomach ulcers. They are allowed light food - some crackers, unsweetened tea.
- Avoid smoking 3 hours before the ultrasound scan.
- If the patient has increased gas formation, it is recommended to drink Mezim, Espumisan or Festal. This will help get rid of flatulence.
- Empty your bowels. Laxatives should only be used by patients with difficulty bowel movements and constipation.
Contraindications
Transabdominal ultrasound screening has no specific contraindications. It can be done on any patient, including small children and pregnant women. This examination can be combined with any form of diagnostics and carried out on the same day.
It is sometimes difficult to perform ultrasound diagnostics on patients with skin lesions in the abdominal area. If there are scars in the scanning area, it will be difficult for the doctor to ensure that the sensor fits tightly to the skin. Because of this, the sensitivity of the ultrasound signal will decrease and the scan results may be less informative.
It is not advisable to conduct an ultrasound examination if there are infectious skin lesions on the patient’s body. Movement of the sensor can cause discomfort in the patient and transfer infection to healthy areas.
EUS has a number of more serious limitations. It will be difficult to do it if the patient has:
- anatomical changes that prevent the use of an echoendoscope (esophageal diverticula);
- stenosis of the upper esophagus;
- postoperative deformation of the bulb.
Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Therapist with 25 years of experience