Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the most dangerous diseases in the world, the prevalence of which is growing every year. It ranks second in mortality of infectious origin after HIV/AIDS. Therefore, stopping the TB epidemic is a national task, and medical institutions, in particular the SANMEDEXPERT clinic, are doing everything possible to quickly and effectively identify a threatening infection in the early stages of the disease.
The causative agent of this disease, Mycobacterium - a group of 74 pathogenic aerobic bacteria - was discovered in 1882 by R. Koch. The disease can be found in both animals and people, for whom two types of Mycobacterium are most dangerous: tuberculosis, bovis. The threatening properties of these strains are their incredible adaptability, the ability to acquire new L-forms that are insensitive to antibiotics, and resistance to external factors. Thus, some pathogens can remain in the human body for years without showing themselves until a decrease in immunity gives the bacteria the “green light” to develop the disease.
Difficulties in diagnosis
Despite the development of antimicrobial therapy, diagnosing the disease, especially in its latent forms, is very difficult. By the time the first symptoms appear, the damage to lung tissue can already be significant, and treatment can be debilitating. Therefore, regular examination (even without detecting the first signs of the disease) and careful attention to your well-being will be the most competent and prudent approach on your part.
According to statistics, a third of the world's population has a latent form, but these people are not carriers of the infection and the probability of their disease is no more than 10%.
On the other hand, the activation of pathogenic strains of the Mycobacterium group means that a person, even without knowing it, is already infecting others. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, which means that the patient’s breathing, sneezing or coughing is deadly to others. Therefore, early diagnosis of tuberculosis in adults is of great importance from the point of view of the epidemiological situation. Due to the worsening incidence of tuberculosis and bronchial asthma in Moscow and the Moscow region, we offer you comprehensive early diagnosis.
Features and advantages of tuberculosis treatment at the Rassvet clinic
Contacting a phthisiatrician or other clinic specialists who diagnose and treat tuberculosis is necessary if there is a suspicion that an infection has developed. Rassvet also advises parents of children with abnormal skin tests - it is important for them to make sure that the test is false positive and check the health of all family members; and patients with chronic diseases - with certain treatment tactics, it is important for them to exclude the active tuberculosis process; and patients diagnosed with an active form of tuberculosis who need the selection of an adequate and effective treatment regimen or a second opinion on the diagnosis.
Dawn doctors are high-level professionals, the methods of diagnosis and treatment of diseases that they use are approved all over the world, their effectiveness has been tested and proven many times. Our TB specialists will quickly and accurately diagnose tuberculosis, select the optimal treatment tactics, develop an individual plan for the prevention of complications of the disease, and, if necessary, quickly involve colleagues from other specialties in your treatment.
Treatment of tuberculosis is a long and complex process, with a high risk of side effects, therefore, unfortunately, not all patients complete the course prescribed by the doctor. We will carefully support you on this difficult path, we will try to convince you of the importance of taking the necessary medications - in order to avoid treatment failure or the development of antibiotic resistance and an increased risk of complications.
Types of research
All surveys in this area are divided into three conventional categories:
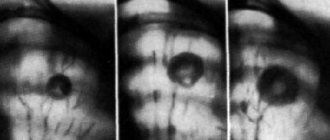
- mandatory diagnostics (chest X-ray, blood and urine tests, sputum culture to identify microflora);
- additional non-invasive examination methods (computed tomography, quantiferon test, ultrasound, sputum examination using polymerase chain reaction, detection of nonspecific microflora in sputum);
- invasive methods (lung biopsy, pleurobiopsy, bronchoscopy, pleural puncture, thoracoscopy, etc.).
Diagnosing tuberculosis in children is a responsible undertaking that can only be entrusted to competent specialists. SANMEDEXPERT Medical Center carries out all possible methods of identifying the disease at affordable prices.
Symptoms
- Severe cough for 3 weeks or longer;
- cough with blood in the sputum;
- pain when inhaling and coughing;
- labored breathing;
- poor appetite;
- weight loss;
- severe fatigue, weakness;
- increased sweating at night;
- chills;
- heat.
When tuberculosis develops outside the lungs, the clinical picture varies depending on which organ is affected. Tuberculosis of the spine is characterized by back pain; with tuberculosis of the kidneys, blood in the urine may be observed.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method
The PCR diagnostic method is widely used in medical practice and in our center due to its high sensitivity and information content. It allows you to examine material taken from a patient for the content of mycobacteria or sections of their DNA. The accuracy of testing makes it possible to detect even single pathogen cells (from 10 to 1000). Even in the case of a negative microbiological test result, PCR is capable of detecting infection and differentiating various forms of tuberculosis.
The material taken for analysis may be different (sputum from the lungs, biological sample of the urogenital tract, etc.). It depends on the indications and localization of mycobacteria in the body. No special preparation is required when taking samples. If you take this test in the SANMEDEXPERT laboratory, you will receive accurate results in the shortest possible time (up to 3 days).
Treatment of tuberculosis in adults and children
Treatment of latent tuberculosis is preventive; its goal is to prevent the activation and proliferation of mycobacteria. The drugs of choice here are isoniazid, rifapentine and rifampicin. Isoniazid monotherapy for 6-9 months is used less and less, short-term courses of treatment are preferred: a three-month course of isoniazid and rifapentine (once a week), a four-month course of rifampicin (daily), a three-month course of isoniazid and rifampicin (daily). They are effective, less toxic, and have higher treatment completion rates compared with long-term isoniazid monotherapy.
However, if short-term regimens are not available to the patient, treatment with isoniazid is prescribed for 6-9 months. It is effective, but comes with a higher risk of side effects. If the patient has been in contact with a patient with drug-resistant tuberculosis, an individual treatment regimen is selected.
When treating an active form of tuberculosis, a combination of antibacterial drugs is prescribed for a period of 6 to 12 months. The most common regimen is isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol. Important: failure to follow the doctor’s recommendations and refusal of the full course of treatment can cause the patient to develop drug-resistant tuberculosis. Multidrug resistance (MDR) in tuberculosis is very dangerous and is associated with fatal outcomes in patients. Treatment for MDR-TB can take from 20 to 30 months, and it must be understood that the patient's risk of side effects from the medications he takes increases many times over.
During treatment, the patient must periodically visit the doctor to monitor the condition. While on therapy, the patient should not have contact with other people for several weeks (with active TB).
Pregnant women with detected latent tuberculosis can postpone treatment and begin it 2-3 months after birth. However, women at high risk of progression to active infection should not delay therapy on the basis of pregnancy, even in the first trimester. For mother and fetus, refusal of treatment is more dangerous than the consequences of anti-tuberculosis therapy. Although the drugs used cross the placenta, their harmful effects on the fetus have not been proven. The concentration of drugs in breast milk is minimal, therefore, if we are talking about first-line drugs, breastfeeding is not a contraindication. Some anti-tuberculosis drugs (fluoroquinolones, streptomycin, kanamycin, amikacin, capreomycin) are contraindicated for pregnant women, so treatment specifics should be discussed with your doctor. The treatment of women with drug-resistant tuberculosis is especially discussed.
DNA analysis for the sensitivity of mycobacteria
Determining the presence of a pathogen is only half the task of diagnosis. Once pathogenic strains have been identified, the most important laboratory goal is susceptibility testing. “SANMEDEXPERT” in this case recommends express determination of sensitivity to antibiotics by studying the DNA of the pathogenic cell after exposure to anti-tuberculosis drugs. Mutations in the genome of mycobacteria make it possible to identify a group of effective substances and prescribe the most effective drug therapy to the patient. The duration of the study is also 2-3 days.
If the results of a diagnostic study confirm the fact of infection, then do not panic. Successful treatment is possible, this is confirmed by tens of thousands of patients who have coped with the disease. The difficulty is that the duration of the course can last for months, and the patient will need iron discipline to strictly follow all the doctors’ instructions, especially when there has been an improvement. Tuberculosis is an insidious disease that loves to return. Therefore, you need to get rid of mycobacteria immediately, during the first shock courses, without making any concessions.
At the SANMEDEXPERT clinic you will find the best TB specialists practicing modern methods of combating tuberculosis. You are provided with an accurate and prompt diagnosis and a well-designed course of treatment. The clinic cooperates with the Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University, all tests are carried out in the clinic.
A phthisiatrician gives an opinion for children and adults only on the basis of:
- Mantoux reactions
- Diaskintest reactions,
- CT,
- x-ray,
- fluorography,
- T-Spot.
On conducting mandatory medical examinations of employees of medical organizations
On December 29, 2015, the Chief State Sanitary Doctor for Moscow issued a decree according to which all employees of medical institutions must undergo a medical examination for tuberculosis.
Our clinic staff passed all the necessary tests. However, if the specialization of your institution does not require the availability of an appropriate diagnostic base, we invite you to undergo a tuberculosis test at SANMEDEXPERT. The reliability and efficiency of the result are guaranteed.
Remember that recently the incidence of tuberculosis among Moscow medical workers has approximately doubled. Take care of your health, as well as the health of your loved ones and patients - sign up for diagnostics today.
Groups and risk factors
Screening people at increased risk of tuberculosis is a priority for health systems around the world. Treating patients with diagnosed TB not only helps keep them healthy, but also helps control the spread of infection.
The risk group for tuberculosis includes:
- people with weakened immune systems - patients with HIV/AIDS, diabetes;
- patients undergoing chemotherapy, taking immunosuppressants and other medications to treat psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, after an organ transplant;
- elderly people, young children, people with malnutrition;
- using injecting drugs;
- in contact with a patient with tuberculosis;
- living in countries with a high prevalence of tuberculosis (Russia, Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, Latin America);
- doctors of certain specialties.
An increasing number of mycobacterial strains that are resistant to antibiotics remains a global health problem around the world. Resistance occurs when an antibacterial drug used to treat TB fails to kill all the bacteria it targets. Surviving bacteria become resistant not only to a specific type of antibiotic, but also to other drugs of this class.
Some strains of tuberculosis are resistant not only to first-line antibiotics (isoniazid, rifampicin), but also to fluoroquinolones, amikacin, capremiocin.
However, without effective treatment, tuberculosis can lead to the following complications: spinal tuberculosis, tuberculous arthritis, tuberculous meningitis, nephrotuberculosis, liver tuberculosis, cardiac tuberculosis (usually the outer connective membrane of the organ, pericardium).